In children, processes of formation and development of organs occur in the body inside the womb and after birth. The baby's gastrointestinal tract is no exception. Its operation fails in some situations.
Constipation in children is common. To get rid of the problem, pediatricians often prescribe suppositories. This type of medicine is easy to use. How do they work, what are rectal suppositories made of? Which of them are safe for newborns and for which age groups are they suitable?
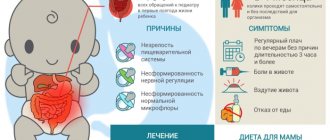
Diseases and risk factors
Constipation in children can be caused by a number of diseases that directly or indirectly affect the digestive process.
Hirschsprung's disease
This disease is characterized by a congenital defect in the nerve endings of the colon. These nerve endings are necessary to regulate the contractile function of the intestines, due to which feces are transported. Due to the lack of nerve endings, the intestinal walls do not contract, thereby causing stagnation and accumulation of contents.
Celiac disease
Celiac disease, or celiac disease, is a chronic digestive and immune disorder that damages the small intestine. The disease occurs due to eating foods containing gluten. Gluten is a protein found primarily in flour products such as pasta, cookies, and bread.
This disease occurs due to genetic characteristics of a person, which lead to the inability of the intestines to absorb gluten and disrupt the process of formation of feces.
Spina bifida
A congenital spinal malformation, a type of neural tube defect, often combined with defects in the development of the spinal cord. The defect is an incomplete closure of the neural tube in an incompletely formed spinal cord, which leads to paralysis of the lower extremities, bowel and bladder dysfunction.
Hypothyroidism
Hypothyroidism or underactive thyroid gland. The thyroid gland is an organ that produces a large number of hormones that control the functioning of the body. If the gland does not produce enough hormones, a person experiences a number of symptoms, which include constipation.
Constipation can also be caused by other diseases that affect the digestion process in one way or another. These include various tumors pressing on the intestines, injuries to the brain and spinal cord, and diabetes.
A number of medications can also cause indigestion:
- Anticonvulsants;
- Preparations containing aluminum and calcium - antacids;
- A number of painkillers;
- Some antidepressants;
- Antispasmodics.
Sources:
- Guidelines. Program for optimizing feeding of children in the first year of life in the Russian Federation. — Moscow, 2022 — https://akev.info/images/documents/Programma2019.pdf
- Bogdanova N.M. Functional constipation in young children: causes of development, diagnostic criteria and management tactics // MS. 2018. No. 17.
- Zakharova I. N., Sugyan N. G., Maykova I. D., Berezhnaya I. V., Kolobashkina I. M. Constipation in children: to help the pediatrician. Issues of modern pediatrics. 2015; 14(3):380–386. doi: 10.15690/vsp.v14i3.1374)
- Mazankova Lyudmila Nikolaevna, Rybalchenko Oksana Vladimirovna, Kornienko Elena Aleksandrovna, Perlovskaya Svetlana Gennadievna Probiotics in pediatrics: pros and cons from the perspective of evidence-based medicine // Ros Vestn Perinatol and Pediat. 2016. https://cyberleninka.ru/article/n/probiotiki-v-pediatrii-za-i-protiv-s-pozitsii-dokazatelnoy-meditsiny
- Tyazheva Alena Aleksandrovna, Pechkurov Dmitry Vladimirovich, Koltsova Nadezhda Serafimovna Prebiotics in the nutrition of young children // Ros Vestn Perinatol and Pediat. 2022.
- Constipation in young children Candidate of Medical Sciences, Associate Professor E.A. Baranaeva Belarusian State Medical University. — https://www.bsmu.by/files/febac709afcce952f683debd9ead10d0/
- Zakharova I.N. Functional constipation in children // “RMZh” No. 15 of 07/08/2009 p. 988 - https://www.rmj.ru/articles/pediatriya/Funkcionalynye_zapory_u_detey/
- Diet therapy for functional digestive disorders in young children. Guidelines for healthcare workers. — https://praesens.ru/files/2020/nutricia/FINAL_Monograph%20Nutrition%20First.pdf
- S.I. Erdes, B.O. Matsukatova, A.S. Antishin, Episodic and chronic constipation in children: a step-by-step approach to therapy within the framework of the IV Rome criteria https://con-med.ru/upload/iblock/6c1/ Mikrolax.pdf
- Functional constipation in children of different age groups | Dumova N.B., Kruchina M.K. | “RMJ” No. 15 dated June 28, 2012 https://www.rmj.ru/articles/gastroenterologiya/Funkcionalynyy_zapor_u_detey_raznyh_vozrastnyh_grupp/?print_page=Y#ixzz71T1bFe2T
- Instructions for use of the drug MICROLAX® // Registration number N011146/01 // RF GRLS. – URL: https://grls.rosminzdrav.ru/Grls_View_v2.aspx?routingGuid=f052fb31-5426-4bc1-958f-9fce793aa43f&t=(access date: 08/31/2021)
Signs of the disease
Source: t.tomsickova / Depositphotos
Clinical manifestations of constipation are varied. They become most pronounced with prolonged constipation and are:
- Bowel movements less than 2 times a week;
- The stool comes out heavily, its substance is dry, hard, consisting of many pieces;
- Defecation is accompanied by pain;
- The child may feel that some of the contents have not come out;
- Abdominal pain and bloating;
- Traces of liquid stool on underwear.
You should immediately seek medical help if you have the following symptoms:
- Bleeding from the anus;
- Blood in the stool;
- Weight loss;
- Vomit.
If older children can talk about a problem with the intestines, then parents may not even be aware of the problem of a very young child.
Important: symptoms of constipation in an infant:
- Problems with sleep, the child often wakes up and cries.
- When changing the diaper and washing the baby, he behaves restlessly, fidgets, and begins to cry. This is associated with pain during bowel movements.
- The baby poops less frequently than usual and his or her stools are hard or pellet-like.
Chronic constipation is characterized by skin changes. It becomes pale, acquires an earthy tint, and loses elasticity. Becomes dry and flaky. There is a coated tongue and bad breath.
Mother's diet
Source: Alexander Dummer: Pexels
Breastfeeding mothers often wonder how their diet affects the quality of their breast milk and how choosing foods for it can affect the baby's digestive system. However, most women do not need to restrict their diet while breastfeeding and should aim for a nutritious and varied diet.
In some cases, infants may seem to avoid feeding after the mother has taken certain foods. In this case, a woman can simply eliminate this food from her diet and return to it after stopping breastfeeding.
Important: Special recommendations include avoiding caffeine while breastfeeding. Caffeine is easily transmitted to the baby through milk. It reduces the amount of iron in milk, which can lead to iron deficiency anemia. It is recommended that a nursing mother consume no more than 400 milligrams of caffeine per day. The most caffeine is found in coffee and chocolate, and the least in tea.
A healthy diet while breastfeeding is essentially the same as a nutritious diet without breastfeeding. The main difference is that breastfeeding people need 450 to 500 extra calories per day. But if you want to lose weight after pregnancy, you can do without them, having first discussed this with your doctor.
A healthy diet for a pregnant woman includes:
- Fruits, especially rich in potassium and vitamin A (melon, banana, apricot, mango, oranges). Helps reduce the risk of constipation in both the child and the mother;
- Vegetables containing vitamin A and potassium (spinach, carrots, tomatoes, red peppers);
- Grain products, especially brown rice and whole grain bread;
- Protein-containing foods such as beans, peas, nuts, meat, fish, mussels.
Important: A nursing mother needs to drink a lot of water, especially in the first weeks after birth. Lack of fluid negatively affects milk production. A sufficient amount of water ensures the efficient functioning of the digestive system, helps food to be absorbed, which means breast milk will be well-balanced in nutrients. The higher the conditional quality of milk, the lower the likelihood of constipation in a child, since balanced milk improves peristalsis and fecal removal.
Eat to live
To avoid problems, mother must eat properly.
For a child to grow, he must be fed.
In order to avoid problems with nutrition, a breastfeeding mother must eat properly, and then there will be no problems.
If you are not breastfeeding naturally, consult your doctor and choose the right formula appropriate for your age.
Give food on time, in compliance with the feeding schedule, and monitor the activity of the digestive system.
Listen to see if the tummy is grumbling, if excess gases are being released, and if bowel movements occur on time and the required number of times. If they are not there in due time, try to find the cause and eliminate it.
Age norms
A breastfed newborn baby can have bowel movements as many times as he is fed. If a child has stool 1-2 times a day or less during the first 3 months of life, you should consult a doctor. For bottle-fed children under one year of age, constipation is considered to be the absence of independent bowel movements during the day.
A common cause of constipation in breastfed infants is disturbances in feeding and nutrient absorption.
If there is quantitative underfeeding or good absorption of the mother's breast milk, the volume of feces in the child is not sufficient to arouse the urge to defecate. In such cases, retention of stool for 2-3 days is not considered true constipation.
Important: Constipation in infants who are breastfed and complementary foods is caused by a lack of foods containing plant fiber. Excess fat in food aggravates constipation and promotes even greater hardening of stool.
In addition to reducing the frequency of bowel movements with constipation, children may experience a decrease in appetite and abdominal pain. With chronic constipation, the volume of stool increases.
When you can't do without medical help...
Unfortunately, not in all cases you can cope with constipation on your own. If defecation disorders are accompanied by severe pain in the tummy, the baby refuses to eat, his stomach is very swollen, and blood is found in the stool, immediately go to the doctor . He may prescribe laxatives, which are still best not to get carried away with (as well as enemas). If the cause of constipation is dysbacteriosis, then the pediatrician will prescribe drugs to restore the microflora (for example, Biocomplexes Normoflorins). After examining the child, the doctor may refer you to other specialists, for example, an endocrinologist or urologist. The causes of constipation often have an emotional and psychological component (perhaps something scared the baby, he was stressed). In this case, you will need the help of a neurologist.
Causes and types
Source: freepik - ru.freepik.com
Constipation in a child can be one of the manifestations of diseases not directly related to the pathology of the gastrointestinal tract (such as rickets, hypothyroidism). However, in the vast majority of cases, constipation is caused by problems with the intestines themselves.
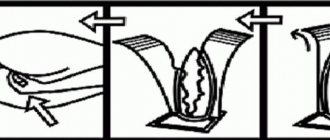
During digestion, the intestinal walls contract in waves, pushing the contents towards the outlet - this phenomenon is called peristalsis or intestinal motility. There are two main options for intestinal motility disorders:
If the child’s stool is very rare, accompanied by bloating, and the volume of feces during bowel movements is large (as in an adult), we can assume that this is the so-called atonic constipation. Constipation associated with insufficient contractile activity of the intestines is called atonic. In this case, the child may not have the urge to defecate for a long time.
Compulsory measures (long-term potty training) usually only aggravate the situation and reinforce the child’s negative attitude towards what is happening.
Thick stools consisting of hard, smooth pellets (the so-called “sheep feces”), abdominal pain, and sometimes pain during defecation usually indicate spastic constipation. Spastic constipation in children occurs due to spasms (increased contractile activity) of the intestines.
In some cases, stool is released in the form of a ribbon or a thin stream. In such a situation, the child should be consulted with a surgeon to exclude organic pathology of the rectum (narrowing, neoplasm).
Constipation after introducing complementary foods
The baby is growing, improving his skills, and it’s time to introduce him to new foods. These circumstances, on the one hand, help to establish peristalsis, and on the other, increase the risk of constipation.
By six months, the baby is already trying to control bowel movements, because he has realized that unpleasant sensations appear after it - itching, burning and other discomfort in the areas where feces fall. In order not to experience discomfort, the child tries to restrain the urge. At first he fails to do this, because the rectum has already learned to work - to reflexively contract and push out waste. And after a couple of months everything works out, the baby wins and starts on the path leading to chronic constipation. To take the child beyond this vicious circle, the mother must minimize the duration of contact of the baby’s skin with feces and expand his diet by introducing complementary foods.
Proteins, fats and carbohydrates included in foods are absorbed in the small intestine, but do not reach the large intestine, where feces are formed. The same cannot be said about fiber. While the baby drinks breast milk or formula, this component of the dish is unfamiliar to him. Even if a nursing woman herself eats a lot of plant foods, the baby gets nothing. Fiber, as already noted, is not absorbed in the intestines, does not enter the blood, which means it is not in breast milk. For the first time, the baby receives fiber with complementary foods, trying his first 25 grams of pureed zucchini, carrots and other vegetables. Plant fibers literally attract all waste, resulting in the formation of feces, which help the intestines master proper peristalsis. In this section of the gastrointestinal tract, in the intestines, there are many muscles, they must learn to consistently contract - tense and relax - in order to squeeze waste out.
The next new product should be introduced a month after the previous one. The new product will likely cause more frequent and loose stools at first. If it is not green and does not foam, there is no need to run to the doctor and ask to prescribe fixatives. Be patient, after a while the innovation will be mastered and bear fruit. Instead of liquid and shapeless yellow-white feces, you will see formed brown feces.
Treatment of constipation in children
Should I get an enema for constipation? It is not worth resorting to enemas often, since this suppresses the natural urge to defecate and disrupts the normal formation of the reflex. However, occasionally for constipation in children, you can use this remedy, following all the necessary recommendations. You can learn how to properly give an enema to a child from this video:
The volume of an enema for constipation in a newborn child up to 1 month is 30 ml, for a child 1-3 months - 30-40 ml (the smallest enema, not completely filled), for a child 3-6 months - 90 ml, 6-12 months - 120-180 ml. It is important to remember that the water in the enema should not be warm, but at room temperature (22-24 degrees). Toxic substances accumulated in the intestines quickly dissolve in warm water and are subsequently easily absorbed into the bloodstream.
If it seems that the intestines have not been completely cleansed, you should not rush: usually after the first portion, provoked by an enema, there is independent stool. Large-volume enemas should be performed by a doctor, as serious complications can occur.
What to do if your child is constipated?
- For any constipation in children, it is important that the child receives enough fluid - with water or clear, low-fat broth.
- For atonic constipation, massage of the anterior abdominal wall in a clockwise direction, laying on the stomach, and mild tactile irritation of the anus helps well.
- For spastic constipation, it is possible to use baby suppositories with glycerin. You should not introduce any foreign substances (soap, baby oil, etc.) into the rectum.
Treatment of constipation (especially chronic) in children is impossible without adherence to the regimen. It is advisable to teach your child to go and poop at the same time every day. To stimulate bowel movements, you can give your child a drink of cold water or fruit (for example, apple) juice in an age-appropriate dose. These activities must be carried out at the same time every day.
List of suppositories for constipation
Suppositories with a laxative effect are prescribed to babies from the first days of life. To get rid of childhood constipation, such remedies are chosen for several reasons:
- the effect of the medicine facilitates the easy process of removing food processing products, toxins from the child’s body,
- reduction of possible pain during the process of passing feces.
Rectal suppositories for newborns and children of other ages have several varieties and can be used in different situations.
Laxative suppositories
Regardless of the type of drug, there are several rules for their safe use:
- It is necessary to use a special position when inserting the suppository. There are two ways: when the child lies on his back with his legs pulled up to his chest or on his side with his legs slightly bent,
- To facilitate insertion of the suppository, it is recommended to treat the anus with a sufficient amount of moisturizer. For children, it is safe to use Vaseline oil or baby cream,
- The suppository is carefully inserted into the anus, then the buttocks are slightly squeezed and fixed in this position for some time,
- The procedure should be a one-time procedure and should not be used regularly.
- before administering the drug, it is necessary to treat the baby’s anus area with soap and water, the procedure is carried out with clean hands,
- the baby should lie on his side, then he needs to carefully insert the suppository into the anus,
- ask the baby to remain in a lying position for at least 20 minutes.
Only a doctor, having assessed the child’s condition, can prescribe a rectal drug, a regimen for its use and safe dosages. Self-treatment with folk remedies is unacceptable.
Glycerin suppositories
By the name of the group of suppositories “glycerin suppositories,” one can determine that the main active ingredient of such products is glycerin. It is this that provides maximum lubrication of the internal surfaces of the small patient’s rectum. Additional components are added to the preparations: sodium carbonate (soda) and stearic acid. Excipients stimulate the work of the rectal muscles, liquefy hard feces and promote their comfortable removal from the body.
The result of using the product for most children comes quickly - within 20 minutes. There are cases when, after using a glycerin-based suppository, the process of bowel movement does not occur. It is prohibited to immediately administer an additional dose of the drug to children; the procedure can be repeated after 12 hours.
Read also: The mechanism of action of "Lioton" for hemorrhoids, composition, analogues, price, reviews
A newborn child in the first 3 months of life should not receive a laxative of this type in a course exceeding 3 days.
Glycerin suppositories
The list of laxatives of this type contains several medicines that have names - “Glycerin”, “Glycelax”. In the pharmacy chain, such drugs are presented in different dosages - for children and for adults.
Candles with sea buckthorn oil
Laxative rectal suppositories with sea buckthorn have properties that allow them to be used to solve the problem of childhood constipation. To rid the intestines of feces, pediatricians recommend using this type of suppository in a dosage: for infants, a quarter of a regular suppository is enough, then the dose can be increased depending on the age of the baby.
The oil has lubricating, wound-healing, and antiseptic properties. Therefore, prolonged childhood constipation, which may be accompanied by redness and even injury to the anal area, is the main indication for the use of such a drug. Before starting treatment, you need to do an allergy test - natural sea buckthorn oil can cause allergic reactions.
The treatment rules contain several recommendations:
The maximum duration of treatment should not exceed 10 days. If the desired effect is not achieved, medical advice is required.
Rectal preparation with sea buckthorn
Oil-based medicines for rectal use are named after the main active ingredient – sea buckthorn oil.
Traditional methods of treatment
In addition to standard treatments, there are alternative ways to combat constipation.
Abdominal massage
In addition to relieving symptoms and treating constipation, abdominal massage has a strengthening effect on the abdominal muscles and relieves pain from infant colic.
Source: oksun70 / Depositphotos
The essence of the massage is light and gentle stroking of the child’s abdomen, smoothly transitioning to pinpoint pressure with the pad of the index finger from the navel to the periphery. The massage also ends with a smooth transition to stroking. The procedure is performed an hour before and after meals.
Treatment with medicinal plants
Many plants have a laxative effect and can be used as an auxiliary element in complex treatment. These plants include:
- anise;
- zhoster laxative;
- dandelion officinalis;
- horse sorrel;
- big plantain.
Plants are taken in the form of decoctions, infusions and teas. It is recommended to take breaks between courses of treatment for 2-3 weeks. This is necessary to avoid getting used to the fees and reducing their effectiveness.
It is not recommended to use medicinal laxatives without a doctor’s prescription: they can lead to increased gas formation and cause discomfort in the child.
Acupuncture
Acupuncture is an element of traditional Chinese medicine. The essence of the method is to insert thin needles into different parts of the body. To treat constipation, needles are inserted into the area of the large intestine. This procedure helps to relax the intestinal walls and facilitate bowel movements.
Insufficient knowledge of the effectiveness of acupuncture prevents it from becoming a standard method in the treatment of constipation. The method may be accompanied by pain and bleeding.
Important: Acupuncture should only be performed by a qualified professional. And it is worth remembering that any trend from alternative medicine cannot replace real, evidence-based treatment.
Candles during pregnancy
Suppositories for constipation for pregnant women are selected individually in each trimester, together with a specialist.
The main condition is a gentle effect on the intestines, since while the fetus is in the uterus, stress on the abdominal wall is excluded. The use of oral laxatives that stimulate intestinal filling with fluid is not recommended. Preference should be given to suppositories.
Suppositories that can be used to treat constipation during pregnancy: [9]
- Microlax.
- Sea buckthorn candles.
- RectActive.
- Dulcolax.
- Guttalax express.
- Glycerin suppositories.
- Bisacodyl.