Early symptoms of bowel cancer
There are no clear signs and symptoms of bowel cancer. Whatever manifestations you have, based on them it is impossible to say with certainty that this is intestinal cancer. Symptoms do not even always allow one to suspect this disease. They are nonspecific and occur in hundreds of other diseases. This is one of the reasons why the disease is not detected on time and is often diagnosed only at a late stage.
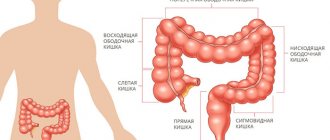
Signs and symptoms of bowel cancer depend on many factors:
- Localization of the tumor (right or left part of the colon, sigmoid colon, etc.)
- Histological tumor type
- Nature of growth (endophytic - into the wall of the organ or exophytic - into the lumen of the organ)
Let's talk about the first signs of intestinal cancer that you can detect on your own. If they are detected, you must consult a doctor for tests and an in-depth examination.
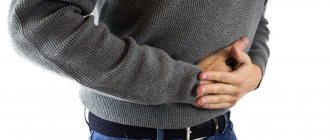
Abdominal pain
Abdominal pain is the most common symptom found in gastroenterology. It is also the least specific. Chronic pain may be the first sign of colon cancer, especially if the tumor is located on the right side of the colon (ascending colon). The severity of pain may vary. Sometimes the pain is weak and aching. Then the person does not seek medical help, trying to overcome these primary signs of intestinal cancer with the help of various drugs. He thinks about gastritis, peptic ulcers, food infections - about anything, but not about a tumor.
In other cases, the pain is sharp, paroxysmal. A person may even be hospitalized in a hospital. In this case, the chance that the doctor will detect an intestinal tumor is quite high. After all, the incessant high-intensity pain syndrome will force the gastroenterologist to conduct a full diagnosis.
Upper dyspepsia
Intestinal discomfort syndrome develops, which includes a whole group of different symptoms. This includes the phenomena of upper and lower dyspepsia. Upper dyspepsia is nausea, vomiting, heaviness in the epigastrium, belching, and lack of appetite. These first signs of intestinal cancer are most typical for the location of the tumor in the transverse colon. It is in close anatomical proximity to the small intestine and stomach, squeezing them.
Lower dyspepsia
Lower dyspeptic syndrome or intestinal disorders include:
- Flatulence
- Constipation
- Diarrhea
- Rumbling
Most often, such symptoms of intestinal cancer in the early stages appear in the case of a left-sided tumor. That is, when it is located in the descending part of the colon.
The frequency of development of intestinal obstruction with this localization of the oncological process is explained by the fact that feces first pass through the right half of the intestine, and then through the left. Here they already have a fairly dense consistency. Therefore, the passage of feces past is significantly more difficult. Symptoms of bowel cancer in the early stages are caused by partial intestinal obstruction, but in later stages it can become complete. In this case, the person does not have bowel movements, experiences severe pain and ends up in a surgical hospital, where the tumor will be discovered.
Impurities in feces
Sometimes the first symptoms of bowel cancer are the presence of impurities in the stool. A person discovers blood, mucus, and pus in feces. This symptom is characteristic not only of intestinal cancer. There are dozens of other diseases that are also accompanied by impurities in stool. Moreover, many of them are much more common than intestinal cancer, the symptoms and signs of which can be disguised as hemorrhoids, anal fissures, inflammatory processes of the distal intestines (proctitis, sigmoiditis). The more distal (closer to the anus) the tumor is, the more likely it is that the presence of impurities in the stool will be the first detected symptom of bowel cancer at an early stage of the disease. Especially often, bleeding from the anus is detected with neoplasms of cancer of the rectum or sigmoid colon.
Intoxication syndrome
General intoxication syndrome is manifested by weakness, malaise, muscle pain, headache, fever, and progressive loss of body weight. Due to constant blood loss, anemia develops. The result is pale skin, shortness of breath, and increased heart rate.
Such symptoms are most typical for neoplasms of the right half of the intestine. After all, here, in the ascending part of the colon, there are many villi, through which nutrients enter the blood. As a result, tumor decay products penetrate into the systemic bloodstream and symptoms of intoxication develop.
The appearance of such symptoms should be a reason to immediately consult a doctor for diagnosis.
Select a clinic and treatment
Briefly about the manifestations of symptoms in various cancers
For colon cancer
As colon carcinoma develops, it affects intestinal function. Symptoms include discomfort, bloating and alternating constipation with loose stools.
Among the dangerous complications is intestinal obstruction, this occurs due to the tumor blocking its lumen, first partially, then completely.
Patients with carcinoma rarely pay attention to abnormal bowel movements, thinking that this is a common symptom of the disease. But stool retention, difficulty in passing gas, a bloated abdomen and increasing pain indicate that intestinal obstruction is increasing.
If there is no stool for three days, intestinal gases do not pass away, your health worsens, you need to see a doctor immediately.
To completely block the lumen, intoxication, acute pain, and vomiting are added to the indicated symptoms. There is very, very little time to save a person.
For rectal cancer
Carcinoma reveals itself by such a sign as uneven stool. That is, constipation is replaced by diarrhea and vice versa. In this case, it seems to the person that the act of evacuation is incomplete.
Obstruction is rare, but constipation can be caused by muscle dyssynergia that becomes part of the tumor, as well as metastasis to the lymph nodes.
Clinical forms of bowel cancer
Based on which symptoms of intestinal cancer appear first, the disease is divided into several clinical forms.
Toxic-anemic form
Signs of intestinal cancer that dominate in the case of the toxic-anemic form of the disease are intoxication and anemic syndrome. Such patients often experience neither abdominal pain nor dyspeptic symptoms. They don't even contact a gastroenterologist.
Patients can be treated by infectious disease specialists for a long time for unknown infections, because the pathology is accompanied by elevated body temperature and symptoms of general intoxication. Sometimes they are observed for a long time by a hematologist for iron deficiency hypochromic anemia. Since the manifestation of intestinal cancer is disguised as other diseases, it is usually diagnosed late, when the tumor has already reached a large size and spread to other organs.
Enterocolitic form
In colon cancer, symptoms often resemble inflammatory diseases. Patients are diagnosed with colitis or enterocolitis. Their disease is expressed by intestinal disorders. Even the presence of impurities in the stool and elevated body temperature are often not sufficient grounds to suspect that these are symptoms of bowel cancer. The patient is often diagnosed with dysentery and treated with antibacterial drugs.
Dyspeptic form
In the dyspeptic form, the disease manifests itself as gastrointestinal discomfort. Phenomena of upper dyspepsia occur. Often such patients are diagnosed with cholecystitis, gastritis or gastric ulcer. However, examination of the upper digestive tract does not yield any results. After all, the signs of colon cancer are caused by compression from the outside when the tumor reaches a noticeable size.
Obstructive form
Symptoms associated with intestinal obstruction most often develop when the tumor is located in the left colon. It mechanically blocks the movement of feces. At the initial stage of the disease, a person suffers from constipation. Subsequently, complete intestinal obstruction occurs.
Pseudoinflammatory form
At an early stage, it is most difficult to diagnose pseudoinflammatory bowel cancer. It imitates, depending on the location of the tumor, pyelonephritis, appendicitis, peritonitis. Such symptoms of intestinal cancer in women can cause a visit to a gynecologist with suspected adnexitis, salpingoophoritis, or pelvioperitonitis.
In the pseudoinflammatory form of the disease, abdominal pain, elevated body temperature, and symptoms of peritoneal irritation appear. Leukocytosis is detected in the blood - a laboratory sign indicating an inflammatory disease.
Often, such symptoms of colon cancer appear against the background of a real purulent inflammatory process, which develops as a complication of cancer. Purulent inflammation can develop as a paracolitis. It is caused by tumor disintegration and tissue rejection due to bacterial infection.
Tumor form
With bowel cancer, symptoms are sometimes not detected at all. The patient does not complain about anything. And then the first clinical sign that is detected during an objective examination is a palpable formation in the abdomen. This form of the disease is also called atypical. Because a palpable tumor, as the first symptom of intestinal cancer, is very rare.
Stages of stomach cancer
The following stages of adenocarcinoma of the stomach or esophagus are distinguished:
- Stage I. At this stage, the tumor is limited to the mucous membrane that lines the inside of the esophagus or stomach.
- Stage II. The cancer at this stage has spread deeper, growing into the deeper muscle layer of the esophagus or stomach wall. Cancer can also spread to the lymph nodes located near the stomach; these are regional metastases.
- Stage III. At this stage, the cancer may have spread through all layers of the esophagus or stomach and spread to adjacent structures. Or it may be a smaller tumor that has spread more widely to the lymph nodes.
- Stage IV. It indicates that the cancer has spread to distant parts of the body and there are distant metastases.
Clinical diagnosis of colon cancer and risk groups
Since intestinal cancer manifests itself with symptoms characteristic of many other diseases, the doctor does not refer every patient who comes to him with abdominal pain for a biopsy. And even if blood is detected in the stool, the doctor would rather think about an inflammatory process than a tumor, because intestinal inflammation is much more common than malignant neoplasms.
To understand which symptoms of colon cancer require targeted diagnosis, all patients who complain are divided into risk groups based on oncological pathology. A high risk group means that the probability of detecting colon cancer during the diagnostic process reaches 70-80%.
Here are the main criteria by which a person can be classified as a high-risk group for cancer:
- Bleeding from the rectum, which is accompanied by increased frequency of stools, an increase in the number of false urges for at least 6 weeks in a row, regardless of the patient’s age
- Increased frequency of bowel movements and false urge to defecate for 6 weeks in a row without bleeding in patients over 60 years of age
- Chronic bleeding from the rectum in the absence of other clinical signs, provided the patient is over 60 years old
- The presence of a palpable (determined by touch through the abdominal wall) tumor-like formation in the abdominal cavity, regardless of age
- During digital rectal examination, a mass is palpated in the rectum
- The presence of unexplained anemia with a hemoglobin level in men less than 110 g/l, in women less than 100 g/l in menopause
All these symptoms of bowel cancer are quite common. They cause the doctor to be wary of cancer. The patient is shown an examination aimed at detecting a tumor and determining its histological type.
There is also a low risk group. Here are the signs of intestinal cancer that are a reason to include patients in this group for their subsequent examination:
- Long-term treatment of chronic intestinal diseases, frequent exacerbations, low effectiveness of conservative treatment used
- Bleeding from the rectum due to the appearance of anal symptoms
- Bleeding from the rectum in combination with anal fissures or rectal prolapse
- Constipation or diarrhea for at least 6 consecutive weeks
- Abdominal pain
Get diagnosed in Germany
Risk factors
Family history
It has been proven that colon cancer is inherited. According to the National Health Service, approximately 20% of people with this diagnosis have immediate (parents, siblings) or other close relatives (grandparents, uncles, aunts) who have had colorectal cancer.
Nutrition
It is well known that a diet high in red meat or meat products increases the likelihood of developing this disease. For this reason, it is advisable to adhere to a balanced diet with a very small amount of unhealthy fats and high amounts of dietary fiber.
Smoking
It is known that smokers are much more likely to develop cancer and heart disease.
Alcohol
A large study (EPIC) showed a link between alcohol and intestinal cancer. However, even small amounts of alcohol can increase this likelihood. The following fact was also revealed: when drinking two standard doses of alcohol daily, the risk increases to 8%.
Obesity
Women and men who are overweight have a higher risk of colorectal cancer than people of normal weight.
Physical inactivity
People who do not pay enough attention to adequate sports activities increase the likelihood of this cancer.
Diagnoses of the gastrointestinal tract and hereditary diseases
Some diseases of the gastrointestinal tract are considered basic for the development of colorectal cancer, for example, Crohn's disease, as well as such inherited pathologies as FAP (familial adenomatous polyposis), HNPCC (hereditary non-polyposis colorectal cancer), etc.
Racial and ethnic predisposition
African Americans have the highest predisposition to developing colorectal cancer of any racial group in the United States, as do Jews of Eastern European descent.
Diabetes mellitus type II
Patients with this diagnosis are prone to developing colorectal cancer. Such people also have other risk factors, such as being overweight.
Night shifts
One study found that people who worked night shifts at least 3 times a month for 15 years were more likely to develop bowel cancer.
Previous cancer treatment
Some research shows that men who have undergone chemotherapy for testicular or prostate cancer have a higher risk of bowel cancer, which is believed to be due to an undesirable effect of the treatment.
Symptoms of colon and stomach cancer
During the diagnostic process, the doctor is required to distinguish between different diseases that have similar clinical signs. A good oncologist or gastroenterologist always knows what signs of intestinal cancer distinguish it from stomach cancer.
Both diseases are accompanied with varying frequency by:
- Abdominal pain
- Discharge of blood from the anus
- Upper dyspepsia (belching, discomfort, etc.);
- Loss of body weight and general intoxication syndrome
- Signs of anemia (pale skin, shortness of breath, tachycardia)
But some symptoms of stomach and intestinal cancer are significantly different. They enable the doctor to suspect the main localization of the pathological process.
Here are the main differences:
- Vomiting blood . With stomach cancer, blood pours directly into its cavity, so it can come out with vomit. This does not happen with colon cancer. Vomiting is very rare. And even if it is present, there are no blood impurities in the vomit.
- Pain . Regardless of the stage of bowel cancer, symptoms are mainly localized in the lower or middle abdomen. Accordingly, the pain is localized below the navel or on the side, in the right or left iliac region. With stomach cancer, pain occurs above the navel, usually on the left. Although it is difficult to judge unambiguously the origin of the oncological process by the localization of the pain syndrome. After all, pain in the upper abdomen can also be observed with cancer of the transverse colon. But in any case, the location of the pain helps, in combination with other clinical signs, to suggest where exactly the tumor may be located.
- Blood in stool . Symptoms of stomach and intestinal cancer include impurities in the stool. However, blood looks significantly different depending on whether it is mixed with hydrochloric acid. The more distal (closer to the anus) the source of bleeding (tumor) is located, the more scarlet the blood will be. If the bleeding comes from the stomach, the blood will be black.
- Fast stomach filling . Early satiety, a feeling of a full stomach, and vomiting after eating are characteristic of stomach cancer. The tumor takes up a lot of space and reduces the volume of the organ.
Knowing what symptoms differ between intestinal and stomach cancer, the doctor can correctly plan the scope of necessary diagnostic tests. For example, if stomach cancer is suspected, he will prescribe an FGDS, and if there are symptoms of intestinal cancer, he will perform an irrigoscopy or colonoscopy.
Treatment methods
To treat the symptom, dietary changes and the consumption of significant amounts of fluid are necessary.
Balanced physical activity, which is recommended by a specialist, plays an important role.
The prescription of laxatives and enemas is indicated exclusively by a doctor.
Among the methods of treating symptoms in cancer:
- Surgical manipulation;
- Chemotherapy;
- Radiation therapy;
- Immunotherapy;
- Targeted therapy.
A little about the last two methods. Immunotherapy is designed to enhance the immune defense properties. If this happens, the body has the ability to find and destroy cancer cells itself.
Targeted therapy is innovative. Using this method, it is possible to specifically target cancer cells without affecting healthy ones.
Symptoms of colorectal and intestinal cancer
According to the international classification, symptoms of intestinal and rectal cancer indicate one disease called colorectal cancer. Translated from Latin, “colon” means “colon”, and “rectum” means rectum. In fact, the rectum is part of the intestines. However, differential diagnosis is still necessary. It is important for the doctor to know the exact location of the pathology in order to plan the optimal treatment strategy. Despite many common symptoms (constipation, intestinal obstruction, anemia, bleeding), some signs of colon and rectal cancer are radically different.
For rectal cancer:
- The leading symptom is rectal bleeding
- Feeling anal symptoms (itching, foreign body sensation)
- The tumor is palpable during digital rectal examination
- The pain is localized in the anus, not the abdomen
At the same time, a number of symptoms uncharacteristic of rectal cancer may appear in the presence of cancer in the colon. These include rapid weight loss, severe intoxication syndrome, and upper dyspepsia.
Prevention and diagnostic methods for colon cancer
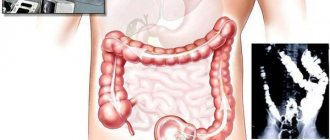
Colon cancer is preventable. The most important step in preventing colon cancer is screening. Any abnormal screening test result should be followed by a colonoscopy. Some doctors prefer to begin their investigations by performing a colonoscopy as a screening test.
Colonoscopy is a detailed examination of the intestinal lumen and walls of the colon. During a colonoscopy, it is possible to detect and remove polyps of the colon and rectum. There is anecdotal evidence that diet has a significant effect in preventing the development of colorectal cancer. It is generally accepted that high fiber and low fat are dietary measures that can prevent the development of colorectal cancer.
Finally, pay attention to your gut health and function. Any changes in bowel habits, such as constipation, diarrhea, or traces of blood in the stool should be discussed with a coloproctologist.
Clinics and cost of treatment for colon cancer
When choosing a clinic for the treatment of intestinal cancer, you should focus on its technical capabilities and the experience of its doctors. The clinic should use modern diagnostic equipment for accurate cancer staging, and all types of operations and drug treatment should be carried out here.
The following clinics specialize in the treatment of intestinal cancer:
- University Hospital Dusseldorf, Department of Gastroenterology, Hepatology and Infectology
- University Hospital of the University of Munich. Ludwig Maximilian, Department of Gastroenterology and Hepatology
- University Hospital Ulm, Department of Gastroenterology and Hepatology
- University Clinic named after. Goethe Frankfurt am Main, Department of Gastroenterology, Hepatology, Pulmonology, Allergology, Endocrinology and Diabetology
- University Hospital Würzburg, Department of Gastroenterology, Hematology, Oncology, Hepatology, Infectology, Rheumatology and Clinical Immunology
The cost of treatment for colon cancer directly depends on the therapeutic technique. Average prices for medical procedures are presented in the table below:
| Procedure | average cost | |
| 1 | Laparoscopic resection of intestinal tumor | €18 900 |
| 2 | Bowel tumor resection using the da Vinci robot | €28 450 |
| 3 | Cytoreductive surgery and hyperthermic intraperitoneal chemotherapy (HIPEC) for colon cancer | €51 500 |
| 4 | Treatment of colon cancer with chemotherapy | €7 030 |
| 5 | Treatment of colon cancer using embolization or chemoembolization | €31 625 |
| 6 | Rehabilitation after completion of the main course of treatment | €1,196 per day |
The treatment program can be adjusted based on the results of the examination. In this case, its value changes.
Select a clinic and treatment
Treatment survival statistics
The prognosis for bowel cancer depends on a number of factors, so it is impossible to predict the success of therapy with certainty. Unfortunately, 80% of patients with colorectal cancer are diagnosed with advanced stage disease. About 40% of cases are inoperable. There is no cure for them, and the only thing patients can count on is relief of symptoms and slowing down the progression of the disease.
What about the other 60% of patients? If the disease is diagnosed at stage I, the 5-year survival rate reaches 90%. This does not mean that the patient will live only 5 years. On the contrary, it means that the disease is under control and the risk of cancer recurrence after 5 years is low.
If colorectal cancer is detected at the last stage, when metastases have already appeared in other organs and their removal is impossible, the 5-year survival rate is only 7%. If metastases are surgically removed - 25-35%. The average survival rate of patients with colorectal cancer is 40%.
IMPORTANT:
Most often, cancer metastases affect the liver through the blood and lymphatic vessels, less often the lungs, ovaries, adrenal glands, brain and bones.
Organization of treatment abroad
]Booking Health[/anchor] has been organizing medical tourism in many countries around the world for many years. We have direct contracts with most major clinics in Germany.
Therefore, every patient can receive quality medical services:
- Without intermediaries
- At a reduced price
- Without the need to purchase insurance for foreign patients, the cost of which reaches 50% or more of the cost of the treatment program
- Without the risk that the price will increase during the treatment process
Each Booking Health client receives insurance. It is valid for 48 months and covers any unexpected medical expenses up to 200 thousand euros.
]Booking Health[/anchor] takes care of all organizational issues. We will choose a clinic for you, negotiate with its administration, speed up the start of treatment, prepare documents for you, and translate medical documentation. We will book a hotel for you, meet you in Germany and take you to the clinic by car. You will be able to completely focus on your own health, getting rid of unnecessary worries about organizing treatment abroad.