The article was checked by gastroenterologist E.G. Melnikova. , is for general informational purposes only and does not replace specialist advice. For recommendations on diagnosis and treatment, consultation with a doctor is necessary.
At the Clinical Hospital on Yauza, you can identify the causes of a prolonged cough, achieve its relief or completely stop it. With us you can undergo all the necessary examinations (laboratory, endoscopic, radiation diagnostics - ultrasound, X-ray, CT and MRI) and consultations with specialists, including a gastroenterologist (if the cough is associated with gastrointestinal pathology).
Although gastroenterological diseases are not often the cause of cough, they must be excluded during the diagnostic process. Often the cough that accompanies diseases of the gastrointestinal tract is long-term and debilitating. However, purely symptomatic therapy does not bring relief. Establishing or confirming a rare cause of cough is quite difficult and requires time and effort from both patients and doctors.
Causes of cough in diseases of the digestive system
- Diseases of the esophagus and stomach (gastroesophageal disease);
- foreign bodies in the esophagus;
- infections (viral - enterovirus, adenovirus);
- parasitic infestations (worms);
- intestinal dysbiosis.
At the medical center on Yauza, you can undergo all the necessary examinations and consultations with any specialists quickly and without delay - the experience of doctors and modern diagnostic capabilities speed up obtaining results and increase the accuracy of diagnosis.
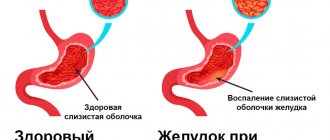
Esophagitis symptoms and treatment
The clinical picture of GERD is polymorphic and often depends on the nature of the underlying gastrointestinal pathology. However, it is quite specific and is represented by esophageal (esophageal) and extraesophageal (extraesophageal) symptoms.
Esophageal symptoms include complaints such as heartburn, belching, regurgitation, bitterness in the mouth, “wet spot” symptom, dysphagia, odynophagia (pain in the sternum while eating). The last two complaints are quite rare in childhood and, as a rule, indicate significant motor and/or structural disorders of the esophagus. It should be noted that the severity of clinical signs of the disease in children does not always correlate with the intensity of reflux and the quality of the refluxate.
Extraesophageal symptoms of GERD are also very diverse. Currently, the following extraesophageal “systemic” manifestations of this disease are distinguished: 1) bronchopulmonary (cough, shortness of breath, difficulty breathing, asthma attacks), 2) otorhinolaryngological (hoarseness and loss of voice, recurrent pain in the throat and/or ears), 3) cardiological (heart pain, rhythm disturbances), 4) dental [3,4,8].
that GER - associated bronchopulmonary disorders are in first place on this list. They are the most studied, better known to practitioners and have acquired a certain evidence base in recent years.
The history of studying the relationship between the pathology of the esophagus and the bronchopulmonary tree begins from the end
19th century. Thus, back in 1892, W. Osler noted the need to avoid excessive eating and was the first to describe attacks of suffocation associated with aspiration of gastric contents. In 1934, G. Bray pointed out the connection between the digestive tract and bronchial asthma (BA). Further study of this problem was continued by the works of Mendelson (1946) and Frieland (1966). They also introduced the term “reflux-induced BA” [1].
In subsequent years, Mansfield and Stein identified decreased airway patency associated with heartburn. Serious pediatric studies on this topic were first conducted in the 60–70s of the last century, and by now there is sufficient factual material. A peculiar reflection of this experience was the classification of BA edited by I.M. Vorontsova (1996), in which “gastroesophageal reflux asthma” is highlighted as a separate item.
GER - associated respiratory disorders are traditionally divided into 2 groups: “upper” (apnea, stridor, laryngitis) and “lower” (bronchial obstruction syndrome, bronchial asthma). The symptoms inherent in these conditions are characterized in the English literature by a special term - RARS (reflux-associated respiratory syndrome).
The connection between the esophagus and the bronchial tree is explained by their common origin from the primary digestive tube and common innervation by branches of the vagus nerve [9].
GER can cause respiratory diseases in two ways: 1) direct, with the development of mechanical occlusion of the lumen of the tracheobronchial tree by aspiration material and 2) indirect (neural) with the development of discrinia, edema and bronchospasm [3,5].
Diagnosis of gastroenterological cough
In case of prolonged and persistent cough, including those arising in connection with gastrointestinal diseases, a complete and thorough examination of the entire body is required to exclude other causes. Our center has all the capabilities to make an accurate diagnosis: laboratory (clinical, biochemical and immunological tests for examining blood, urine and feces), endoscopic, ultrasound, X-ray methods, CT and MRI.
In case of parasitic infection and dysbiosis, cough is associated with the involvement of the immune system in the pathological process - in the clinic you can undergo various allergic and immunological tests, stool examination for worms and bacteria, and culture of material on special media.
For gastroesophageal disease and foreign bodies of the esophagus, endoscopic diagnosis, computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging are often necessary. Our center has a modern endoscopic installation for conducting and video recording examination of the walls of the esophagus, stomach, duodenum, colon, and rectum. If necessary, a tissue biopsy is taken during the examination.
The condition of the chest organs will be shown in detail by an X-ray examination using a digital system, CT and MRI.
Also, when diagnosing diseases of the small and large intestine, a virtual colonoscopy may be required - the most accurate and complete CT examination of the intestine.
For quick removal
To quickly eliminate heartburn, you can use one of the following methods:
- Soda. Anyone who suffers from such a problem knows that ordinary soda will help to quickly cope with it. Doctors categorically do not recommend this method, since the expected harm outweighs the benefits of using the medicine. During a chemical reaction, soda, combining with hydrochloric acid, irritates the mucous membranes of organs. That is why this medicine must be used carefully. To minimize the harm of the mixture, you need to add soda to a glass of water, mix well and add a little honey (if you are not allergic). In this way, the walls of organs can be protected from destruction.
- Honey. A solution with honey will help quickly eliminate the problem. To prepare the medicine, you need to dissolve 20 g of a natural product in 200 ml of warm water. You need to drink the solution slowly. This will stop your throat from scratching and the discomfort in the esophagus will disappear.
- Chalk. Regular white chalk is effective. To use this method, you need to crush the chalk to a powder. If heartburn occurs, you need to eat a tablespoon of the product with plenty of water.
Home methods can be used as one-time remedies when pharmaceuticals are not available, which are more effective and safe. Such drugs include Maalox, Gaviscon, etc. If you have frequent heartburn with sore throat and sore throat when swallowing food, or weakness, you should definitely visit a gastroenterologist to diagnose the root of the problem.
Return to contents
Treatment of chronic cough
Our clinic’s specialists work in accordance with international and domestic standards in the field of medicine. Treatment of cough is aimed, first of all, at eliminating the cause that causes it, that is, treating the underlying disease.
Symptomatic therapy is traditional - the use of bronchodilators and mucolytic (sputum-thinning) pharmacological agents that facilitate breathing.
Come to the Clinical Hospital on Yauza - they will help you cope with any type of cough.
You can see prices for services
Non-traditional treatment for reflux
System of endoscopic signs of GER in children (according to G. Tytgat as modified by V.F. Privorotsky et al., 2002)
Morphological changes
0 degree. There are no signs of damage to the esophageal mucosa.
I degree. Moderate focal erythema and (or) friability of the mucous membrane of the abdominal esophagus.
II degree. The same + total hyperemia of the abdominal esophagus with focal fibrinous plaque and the possible appearance of single superficial erosions, often linear in shape, located at the tops of the folds of the mucosa.
III degree. The same + spread of inflammation to the thoracic esophagus. Multiple (sometimes merging) erosions located in a circular pattern. Increased contact vulnerability of the mucous membrane is possible.
IV degree. Esophageal ulcer, Barrett's syndrome, esophageal stenosis.
Motor disorders
A. Moderately expressed motor disturbances in the area of the LES (raising of the Z-line up to 1 cm), short-term provoked subtotal (along one of the walls) prolapse to a height of 1–2 cm, decreased tone of the LES.
B. Clear endoscopic signs of NKJ, total or subtotal provoked prolapse to a height of more than 3 cm with possible partial fixation in the esophagus.
B. The same + pronounced spontaneous or provoked prolapse above the crura of the diaphragm with possible partial fixation.
Histological examination of biopsy specimens of the esophagus and (or) stomach, as well as x-ray examinations of the upper gastrointestinal tract are carried out according to standard methods and are described in the relevant manuals.
The “gold standard” for determining pathological GER is daily pH monitoring, which allows not only to record the fact of reflux, but also to determine its nature (physiological or pathological). The study is carried out using Gastroscan-24 (Russia) or Sinectics-medical AB (Sweden) devices. To date, there are no uniform standards that allow us to definitely establish the connection between GER and bronchial obstruction. To document this fact, equipment is needed that allows one to simultaneously assess respiratory function and register GER. Therefore, various indices are currently being developed to judge the presence of such a relationship [9].
The principle of the acid perfusion test (Bernstein test) is to assess the child’s subjective sensations during artificial acidification of the lower third of the esophagus with a 0.1% solution of hydrochloric acid (or pure lemon juice, the pH of which is known). The test is assessed as positive in cases where the child experiences chest pain or heartburn in the first 3 minutes of the test.
The basic method for studying the functional state of the lungs is spirometry (study of external respiration function). The study is carried out using a computer spirograph, in which air flow is measured using flow meters, and the volume is calculated by integrated flow.
Bronchoprovocation tests allow us to determine the reactivity of the tracheobronchial tree. Tests with methacholine and histamine are carried out only during remission. These irritants directly affect the bronchi, which have smooth muscle fibers. This leads to a reduction in the latter, stimulation of cholinergic activity and an increase in vascular permeability. In low concentrations, these drugs do not have side effects and do not cause long-term broncho-obstructive reactions.
Pulse oscillometry allows you to determine the components of total respiratory resistance (friction and reactance in a certain frequency range).
In the above diagnostic algorithm there is no mention of scintigraphy of the esophagus (to confirm the fact of reflux) and lungs (to ascertain aspiration of gastric contents into the lungs) using food labeled with a technetium isotope. The limited data available in the literature indicate the low sensitivity of this method [3,6,8,9].
One of the key questions of the “relationship” of GER and BA is the following: does GER play the role of the only triggering point of the bronchial obstruction mechanism or does it act as an integral part of some combined mechanism?
In the latter case, there may be a triple component of the triggering of bronchial obstruction: atopy, infectious dependence and GER. What place does each factor occupy on this kind of “pedestal of honor”? This is a question, the answer to which would significantly facilitate the development of adequate treatment programs and allow us to avoid the formation of forms of AD that are torpid to the basic treatment.
Unfortunately, there is no exact answer to this question yet, and we have to come to terms with the fact that in real life we have only two situations that allow us to associate GER with bronchial obstruction syndrome or BA: 1) “pure” GER-dependent variant; 2) a variant in which GER plays a certain negative role in the genesis of AD along with other factors.
CF, unlike AD, is not a model of a “classical” GER-dependent disease, and the relationship between GER and CF is less clear. However, the disorders that occur with CF, such as increased intra-abdominal pressure during coughing, slower gastric emptying, impaired motor function, increased production of hydrochloric acid, are “fertile ground” for the occurrence of GER and the development of GERD.
HOW TO GET RID OF HEARTBURN
Effective treatment of heartburn in the throat involves addressing the immediate cause of its occurrence. Additionally, symptomatic therapy is prescribed, the essence of which is to eliminate characteristic symptoms.
In most cases, heartburn can be relieved quickly and effectively. For this purpose, several groups of drugs are used, the most popular of which are proton pump inhibitors and antacids. They are characterized by a high degree of safety and effectiveness4. The group of antacids includes the drug Rennie®️. It contains calcium carbonate and magnesium hydroxycarbonate. They quickly neutralize excess hydrochloric acid and effectively fight heartburn. The positive effect occurs in less than a minute after the tablet is dissolved. Rennie®️ has several flavors - cooling, mint (without sugar), orange. The drug can be taken by adults and children over 12 years of age. The maximum daily dose is 11 tablets. The minimum interval between doses is 2 hours5.
1. S. A. Baranov, Yu. O. Shulpekova, V. M. Nechaev / MODERN CONCEPTS ABOUT THE PATHOGENESIS OF HEARTBURN / Siberian Medical Journal. 2018;33(3) https://cardiotomsk.elpub.ru/ 2. I. V. Maev, A. A. Samsonov, N. G. Andreev/ SYMPTOM OF HEARTBURN: HUMAN DISCOMFORT OR A SERIOUS PROBLEM?/ PHARMATEKA No. 10 — 2011 https://lib.medvestnik.ru/ 3. I. A. Sholomitskaya, N. V. Kapralov/ HEARTBURN: A MODERN VIEW AT THE PROBLEM/ Belarusian State Medical University https://www.bsmu.by/ 4. G. D. Fadeenko / Heartburn: causes and effective treatment / GASTROENTEROLOGY • DOCTOR'S CONSPECT No. 17 (270) 2011 https://health-ua.com/ Instructions for medical use of the drug Rennie®️
L.RU.MKT.CC.01.2021.3592
Consequences of heartburn
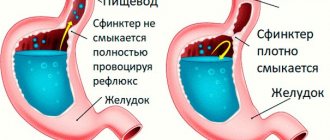
Of course, heartburn occurs periodically in healthy people. For example, during pregnancy, when an enlarged uterus puts pressure on the stomach. Constant heartburn with a frequency of more than 2 times a week gives rise to the diagnosis of gastroesophageal reflux disease, or GERD for short.
Symptoms of chronic reflux:
- Sour, bitter belching, hiccups.
- Early satiety, vomiting after eating.
- Discomfort, bloating.
- Your throat may hurt and you may feel a burning sensation when swallowing.
- Sore throat, cough, choking.
The consequences of neglected GERD are very disastrous. Stable exposure of the esophagus to HCl causes inflammation or esophagitis. As a rule, heartburn is a characteristic sign of increased acidity of gastric juice. Hyperacidity creates favorable conditions for the growth and reproduction of the Helicobacter microbe. A high degree of contamination of the gastric mucosa by Helicobacter pylori is a leading factor in the development of gastric and duodenal ulcers.
Esophageal stricture
If esophagitis continues for too long, the resulting scar tissue can narrow the esophagus. This stricture can lead to difficulty passing and swallowing food, which can become stuck at the level of scar tissue, causing pain.
Large pieces of food may become stuck and this situation may require endoscopic intervention to remove them. The stricture may cause frequent choking when eating. Because of this, patients often refuse to eat and lose a lot of weight.
Stricture is treated by widening or stretching the esophagus (bougienage or dilatation). These treatment procedures can have multiple effects on the stricture. But taking stomach acid blockers (proton pump inhibitors, PPIs, or H2 blockers) may prevent scarring in the esophagus from returning in the future.
Causes of burning in the chest
The list of “causative agents” of the problem is quite long: from irritating foods to serious diseases.
Heartburn after eating
Heartburn often occurs after eating fatty foods.
Excessive production of hydrochloric acid occurs as a result of eating certain foods. These include:
- smoked meats;
- marinades;
- fatty, spicy, fried foods.
The causative agents can be foods with high acidity. These include some fruits (especially citrus fruits). Heartburn after tomatoes and dishes prepared with them is due to excessive formation of gastric juice.
Errors in nutrition are the most common cause of this phenomenon.
Heartburn with bloating
Sometimes heartburn is accompanied by bloating
The combination of such phenomena indicates disturbances in the healthy intestinal microflora. The presence of pathogens in the gastrointestinal tract is rapidly increasing. During their life, gas is produced.
The main location of the latter is the intestines, but penetration into the duodenum and stomach is also common. The result is a combination of such phenomena as:
- flatulence;
- burning in the chest;
- constant belching;
- specific smell of acetone from the mouth;
- stool disorders, nausea, discomfort in the abdominal area (manifest in later stages).
The danger lies in the high probability of intoxication of the body with waste products of bacteria, prolonged stool disorder, and disturbances in the process of food digestion. The result is a suppression of the immune system, a change in the color of the skin.
Heartburn during pregnancy
Heartburn is common during pregnancy
Women carrying a child are well familiar with the phenomenon in question. Reflux (the release of “sour” food from the stomach into the esophagus) is observed at different times.