Increased acidity of gastric juice causes a lot of discomfort to a person. This pathology is accompanied by constant heartburn, painful sensations in the epigastric region and other manifestations. Hypersecretion of hydrochloric acid is common during pregnancy. Treatment during pregnancy is complicated by the fact that most medications are contraindicated during this period.
Treatment should not be delayed, since increased acidity leads to various complications. How to deal with this phenomenon correctly so as not to harm your health and the health of your unborn child?
Newspaper "News of Medicine and Pharmacy" Gastroenterology (348) 2010 (thematic issue)
During pregnancy, a woman's stomach is especially vulnerable. Pregnancy is often accompanied by increased acid production, although it is possible that it may decrease. It is known that with increased stomach acidity, an increase in appetite is characteristic. However, it is not recommended to load the stomach with high acidity during pregnancy. During pregnancy, the stomach produces more hydrochloric acid not so much to increase appetite, but to increase the bactericidal properties of its contents.
An unpleasant feeling of slight heat or burning in the pit of the stomach, sour belching - all these symptoms are combined into one term “heartburn”. During pregnancy, heartburn is caused by hormonal and physical changes in a woman's body. It is observed in approximately 50% of women during pregnancy at any stage, but more often in the second and third trimesters, and is provoked by the consumption of abundant fatty, fried and spicy foods. Its occurrence is due to the reflux of acidic (much less often alkaline) gastric contents into the lower esophagus and its irritating effect. As is known, in pregnant women the tone of the lower esophageal sphincter is significantly weakened, which is the result of the action of progesterone, and an enlarged uterus by the 25th week contributes to an increase in intra-abdominal pressure, which prevents complete closure of the sphincter. Progesterone also reduces contractions of the esophagus and intestines, slowing digestion. The feeling of heartburn is accompanied by a feeling of melancholy and depressed mood.
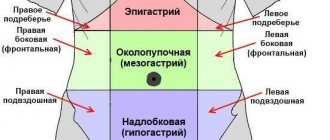
Another symptom typical of stomach pathology is pain. The nature of pain in stomach diseases may indicate not only the disease, but also the presence of complications. Thus, the occurrence of burning pain in patients with gastritis or peptic ulcer may indicate the addition of solarium. Pregnant women with chronic gastritis with reduced gastric secretion usually experience a feeling of heaviness and fullness in the epigastric region. This feeling also appears with pyloric stenosis. In pregnant women with chronic gastritis with preserved secretion, the pain is often dull and aching. The intensity of pain in stomach diseases can vary. With chronic gastritis, pain in the epigastrium is usually low-intensity, and with gastric ulcer, and especially with duodenal ulcer, the pain is usually severe. With a perforated ulcer, the pain intensity is so high that pain shock is possible.
According to a number of authors, chronic duodenitis occurs in pregnant women much more often than is diagnosed, is observed in the first trimester of pregnancy or 4-5 weeks before birth and is characterized by cyclical exacerbations (spring - autumn). The clinical picture is dominated by pain; night and hunger pains are typical; eating reduces them. The goal of drug treatment for chronic duodenitis in pregnant women is to achieve remission of the disease. In the uncomplicated course of chronic gastritis or duodenitis, the patient’s condition is not significantly disturbed, and the disease does not have a noticeable effect on the course of pregnancy and its outcome. When vomiting during pregnancy occurs, treatment of gastritis or duodenitis should be combined with treatment of early toxicosis.
The literature describes isolated information about the course of pregnancy against the background of Ménétrier's disease. Analysis of literature data does not allow us to draw conclusions about the etiology of the disease, although the role of cytomegalovirus is assumed. Along with the complaints characteristic of chronic gastritis, pregnant women experience lethargy and possible swelling of the lower extremities. It was noted that in the second half of pregnancy the disease is severe, but it is not a contraindication for pregnancy. During pregnancy, the diagnosis is established on the basis of gastroscopy, in which the gastric mucosa is pale gray, swollen, easily vulnerable, eroded, with the presence of hemorrhages. Treatment is symptomatic, since, according to most researchers, gastrectomy outside pregnancy is indicated.
Peptic ulcer disease in pregnant women is quite common, but the exact incidence is difficult to estimate, since diagnosing peptic ulcer disease during pregnancy is difficult. The chance of encountering this disease in pregnant women has increased significantly, although in the vast majority of cases pregnancy softens the clinical course of peptic ulcer disease. The reason for the favorable course of peptic ulcer disease in pregnant women has not been fully studied. Some researchers believe that this is the result of altered secretory (decreased production of hydrochloric acid and increased mucus production) and motor functions of the stomach in the direction of reducing it and increasing blood supply. It has been established that during pregnancy, in 40% of cases, remission of gastric and duodenal ulcers occurs due to the high level of progesterone in the body, which stimulates the production of mucus, which is a protective mechanism of the gastric mucosa. Perhaps the overproduction of sex hormones, namely estrogens, plays a role. It has been established that estrogens perform a protective function, increase the intensity of regenerative processes, and improve blood supply to the gastroduodenal area. For most women, the disease does not affect the process of bearing and giving birth to a child. However, exacerbation of peptic ulcer disease during pregnancy, although unlikely, is still possible (in 10% of cases). Most pregnant women associate it with excessive anxiety, fear of the upcoming birth and its outcome, probably because pregnancy itself is stressful for a woman. The main symptoms of a peptic ulcer are: pain in the epigastric region (under the stomach), belching of air, food, nausea, sometimes vomiting, constipation, flatulence, weight loss. Peptic ulcer disease is dangerous due to its complications, one of which is gastrointestinal bleeding, which sharply increases the risk of fetal death. Massive bleeding during pregnancy is an indication for emergency surgery.
Stomach cancer is quite rare in pregnant women. The authors note that for stomach cancer in pregnant women, the first symptoms appear at 15–16 weeks of pregnancy. Pain in the epigastric region, lack of appetite, nausea, vomiting are noted, melena is possible, but the symptoms are unclear and the clinical picture is blurred. The diagnosis is established on the basis of fibrogastroscopy with biopsy. Treatment is only surgical, since conservative treatment is not effective. According to most authors, the prognosis for the mother and fetus is unfavorable.
Gastric resection is one of the most common operations for gastric disease. It is known that pregnant women with a resected stomach are more likely to develop digestive system disorders, which is explained by the depletion of compensatory capabilities in this category of women. However, the issue of the influence of pregnancy on the health of women with a resected stomach and on the course of pregnancy itself in this category of women has not yet been sufficiently studied and is poorly covered in the literature.
Pregnancy imposes significant restrictions on the choice of diagnostic methods and on determining treatment tactics. X-ray examination of the stomach is not recommended for pregnant women, therefore the only diagnostic method for stomach pathology is esophagogastroduodenoscopy, although its implementation can be difficult.
Since therapy aimed at destroying Helicobacter pylori is not carried out during pregnancy, diagnosis of this infection is carried out after childbirth (a breath test is performed if necessary). Antacids are recommended for use during exacerbations of peptic ulcer disease in pregnant women. Antacids containing aluminum, calcium, or magnesium are considered safe and effective in treating heartburn during pregnancy. However, magnesium-containing antacids should be avoided during the third trimester of pregnancy because they may trigger preterm labor. In addition, antacids containing sodium bicarbonate should be avoided to avoid the occurrence of metabolic alkalosis. In addition, it is possible to prescribe enveloping and astringent agents of plant origin - decoctions of chamomile, St. John's wort.
H2-blockers of histamine receptors are also undesirable for pregnant women. However, it has been established that ranitidine is the only histamine H2 receptor antagonist that has been well studied during pregnancy. In a double-blind, placebo-controlled study, JD Larson et al. (1997) proved that ranitidine, taken several times a day by pregnant patients with heartburn (if antacids are ineffective), reduced its severity. No adverse effects on the fetus have been reported. A study on the safety of ranitidine by JE Richter (2003) showed that pregnant women who took it from the first trimester throughout pregnancy gave birth to healthy children. Taking proton pump inhibitors for acid-dependent conditions by pregnant women is undesirable and is possible only if antacids are ineffective. More recently (May 2010), new evidence has emerged showing an increased risk of hip, wrist and spine fractures with long-term or high-dose use of proton pump inhibitors, as well as a more than doubling of the risk of having a baby with heart defects. Only when the threat to the mother's health outweighs the potential risk to the fetus is it possible to prescribe short-term courses of proton pump inhibitors. Recently, evidence has emerged that lansoprazole and pantoprazole are priority representatives of this class of drugs, since their relative safety in pregnant women has been studied. Due to the fact that the range of medications for acid-dependent gastric conditions during pregnancy is limited, dietary measures play an important role. In addition, it is recommended to limit physical activity, semi-bed rest, split meals, and strict adherence to diet No. 1 during the period of exacerbation of the disease.
Vaginal acidity test
Test strips for determining vaginal pH
There are special test strips for determining vaginal pH, which help identify the level of acidity at home, without contacting a gynecologist. They are freely available, sold in most pharmacies and available without a prescription.
Test strips for determining vaginal acidity are small pieces of special gray-green paper. To check the pH yourself, you need to open the test package immediately before taking the measurement, since prolonged exposure to air can affect the accuracy of the test strip. Next, you need to apply the strip to the vaginal wall for a few seconds (the exact time is usually indicated by the manufacturer on the packaging), then remove it and compare it with the color scale included in the test kit. When exposed to an acidic environment, the color of the strip changes, and this helps determine changes in the acidity of the vagina. If the result does not correspond to any of the given shades of the verification scale, you need to select the closest color.
Vaginal pH, video
Vaginal ph. Source – Yulia Oliynyk
The doctor decides how to reduce acidity in the vagina for faster and more successful conception. At the same time, he prescribes a series of tests aimed at examining both partners. Home methods of reducing vaginal acidity (for example, using soda douching) can harm women's health.
To protect yourself from possible pH imbalances, it is important to select suitable intimate hygiene products that do not negatively affect acidity levels. To do this, we recommend that you familiarize yourself with the washing gels for intimate hygiene “Ginocomfort”. Thanks to their balanced composition, these products maintain the physiological level of acidity and at the same time have a delicate cleansing effect.
If you already have an imbalance in your pH level, you can reduce its manifestations with the help of the intimate moisturizing gel "Gynocomfort".
It was developed by specialists from the pharmaceutical company VERTEX, has undergone clinical trials and has a package of necessary documents and quality certificates. Testing of the gel, carried out at the Department of Dermatovenereology with the clinic of St. Petersburg State Medical University, showed its good tolerability by women, the absence of side effects and allergic reactions. The product helps to cope with vaginal dryness, itching and burning - common symptoms of both increased and decreased acidity of the vagina. Sources:
- STATE AND REGULATION OF NORMAL MICROBIOCENOSIS OF THE VAGINA. Orlova V.S., Naberezhnev Yu.I. // Scientific bulletins of Belgorod State University. Series: Medicine. Pharmacy. – 2011. – No. 22 (117). – pp. 15-21.
- HORMONAL STATUS AND VAGINAL MICROBIOCENOSIS. Dobrokhotova Yu.E., Zatikyan N.G. // Obstetrics, gynecology and reproduction. – 2008. – No. 2. – P. 7-9.
- Anaerobic microflora of the female reproductive tract. Valyshev A.V., Elagina N.N., Bukharin O.V. // Microbiol. - 2001. - No. 4, pp. 78-84.
- Bacterial vaginosis - modern concepts, complex treatment. Tikhomirov A.L., Oleinik Ch.G., Sarsania S.I. // Guidelines. – M. – 2005. – P. 5–7, 11–18.
- Microecology of the vagina. Microbiocenosis in normal conditions, in pathological conditions and methods for its correction. Kafarskaya L.I., Efimov B.A., Pokrovskaya M.S. // Lecture. – M. – 2005. – P. 1-5.
- https://www.researchgate.net/publication/11817901_Origins_of_vaginal_acidity_high_DL_lactate_ratio_i…
- https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/322537.php
- https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fmicb.2016.01936/full
- https://www.pubfacts.com/detail/16859053/Association-of-bacterial-vaginosis-trichomonas-vaginalis-an…
How to increase vaginal acidity and why might this be necessary?
From a medical point of view, it is more correct to talk not about increasing the pH level of the vagina, but about its restoration and normalization. To do this, you need to make an appointment with a gynecologist, who will select the appropriate therapy. The main thing in such cases is not to self-medicate, as this can further aggravate the situation.
Treatment of low and high vaginal acidity usually includes correction of local immunity, combating pathogenic flora and normalizing the lactobacilli population.
How to reduce acidity in the vagina for conception?
Increased vaginal acidity
Increased vaginal pH levels do not create the most favorable environment for sperm. This unique protective mechanism ensures that only the fastest, healthiest and strongest sperm can reach the egg for fertilization. In some cases, this interferes with conception.