The role of the gallbladder in the body
The gallbladder is an organ of the digestive system, normally not exceeding 6–12 cm in length and 4–5 cm in width. It is a kind of reservoir for concentrated bile, regularly produced by liver cells - hepatocytes.
In addition to collecting and temporarily storing the secretion produced, the gallbladder performs absorption, concentration and contractile functions. In other words, what happens in it:
- absorption of water contained in hepatic bile,
- accumulation of bile acids,
- their uniform release after eating.
In the latter case, the smooth muscles of the organ contract and the bladder bile stored in it is sent in measured portions to the duodenum. Once in the intestines, it performs a number of functions:
- rebuilds digestion from gastric to intestinal, neutralizing the enzyme of gastric juice;
- mixes fats;
- activates lipase – a fat-splitting catalyst;
- ensures the absorption of fat-soluble vitamins, calcium salts and amino acids;
- enhances the work of microscopic glands of the mucous membrane, responsible for the production of protective mucus;
- prevents the development of pathogenic microflora;
- stimulates parietal digestion with the participation of enzymes produced by the glands of the intestinal wall, and the motor activity of the small intestine.
However, it should be taken into account that for good digestion two prerequisites are necessary: normal contractile function of the gallbladder and stability of the quantitative and qualitative ratio of bile components.
Up to contents
Sample menu and delicious dishes
- Cereal porridge is best for breakfast It can be eaten with blackcurrant jam or any other jam. You can use tea with milk as a drink.
- For second breakfast, you can eat vegetable or fruit puree. As a drink, jelly or compote would be an ideal option. For lunch, it is better to prepare vegetable borscht, to which you can add low-fat sour cream. It’s a good idea to add buckwheat porridge with chicken to your diet as a second dish.
- For an afternoon snack , you can use cottage cheese dessert with banana and drink dried fruit compote.
- For dinner , you can cook lean fish, make a salad of fresh vegetables with olive oil and make a drink from chicory.
- At night you can eat yogurt with oat bran, but they need to be soaked in it in advance.
Cooking "delicious treats"
You may find the following dishes useful, which are not harmful to your health, but still have excellent taste:
| Squash with buckwheat and chicken | Buckwheat must be cooked before this. The minced meat is mixed with chopped onions and carrots and filled with peeled squash. You need to cut off the caps first. They are used to cover stuffed squash. Prepared vegetables should be baked in the oven for at least one hour. |
| Stuffed pike | The pike is thoroughly cleaned of scales and all entrails are removed. The onion should be stewed a little in water until half-cooked and then turned through a meat grinder. The same should be done with fish fillets and bread soaked in water. Then add protein, salt and chopped parsley to the minced meat. The pike is filled with minced meat and wrapped in gauze. You need to cook the fish in water for about 1.5 hours. |
What gallbladder diseases may cause stool retention?
The main reason for the development of so-called biliary constipation is insufficient flow of bile into the intestines. It is caused by a violation of the motor function of the gallbladder and, as a consequence, a change in the biochemical properties of bile.
There are several diseases of the biliary system that can provoke stool retention:
- biliary dyskinesia . Functional disorder associated with disruption of the activity of the hepatic and vesical sphincters (muscle rings) and a disorder of the contractile function of the organ;
- inflection of the gallbladder. This is a congenital or acquired pathology due to deformation of the organ in various parts;
- cholecystitis. An inflammatory disease that develops as a result of infection of the gallbladder with Escherichia coli, coccal microflora, Proteus, Giardia or hepatitis virus;
- cholelithiasis. Multifactorial pathology that occurs due to an imbalance in the ratio of bile components (decreased secretion of bile acids and increased production of cholesterol or bilirubin);
- postcholecystectomy syndrome. It is a consequence of removal of the gallbladder and restructuring of the biliary system.
Up to contents
Features of constipation in various gallbladder diseases
Stool retention, which occurs as a result of impaired intestinal motor function, in various diseases of the gallbladder may be accompanied by not entirely uniform clinical symptoms.
Constipation due to biliary dyskinesia
With a decrease in the tone of the gallbladder and a decrease in the contractile activity of the sphincters, spastic constipation may develop. It is characterized by difficult excretion of hard, fragmented (so-called sheep) feces. Patients may complain of bloating, flatulence, and periodic cramping abdominal pain caused by spasm of the muscles of the internal organs. Due to the prolonged retention of feces in the intestines, putrefaction processes intensify and intoxication of the body develops. It is manifested by weakness, increased fatigue and a general decrease in performance.
With increased contractile function of the gallbladder and accelerated excretion of bile, atonic constipation may develop and a feeling of incomplete bowel emptying may occur. In this situation, dense feces of large diameter cause pain during defecation, can injure the mucous membrane and lead to the formation of anal fissures.
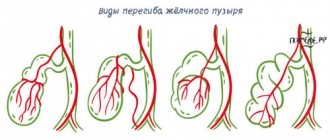
Constipation due to bending of the gallbladder
When the gallbladder is deformed due to insufficient bile flow or its complete cessation, the digestion and absorption of fats is impaired. As a result, feces take on the appearance of hard, dry lumps. Due to problems with defecation, blood streaks are often found in the stool. This condition is also characterized by patient complaints of nausea, a bitter taste in the mouth and abdominal pain of varying intensity.
Constipation with cholecystitis
With infectious inflammation of the gallbladder, stool may be absent for up to 3-4 days. The pathological condition is often accompanied by gas formation and clinical symptoms similar to the manifestations of constipation when the organ is bent.
Constipation due to cholelithiasis
Stool retention in cholelithiasis, which occurs as a result of a decrease in intestinal contractile activity, is of a reflex nature. In this situation, spastic constipation may develop.
Constipation after cholecystectomy
Problems with bowel movements are one of the main consequences of gallbladder removal. Developing due to a violation of the outflow of bile into the intestines, a decrease in the activity of digestive enzymes and insufficient digestion of fats, constipation after cholecystectomy occurs of the atonic type. The stool may contain undigested pieces of food, mucus and streaks of blood.
Up to contents
Treatment of gallbladder inflection
Gallbladder: schematic representation of organ placement
Treatment is prescribed individually and only by the attending physician. Self-medication is not recommended. Before this, it is necessary to undergo diagnostics, identify the causes of the bend in the gallbladder, specify the location of the bend, only after an ultrasound and tests the doctor will prescribe treatment:
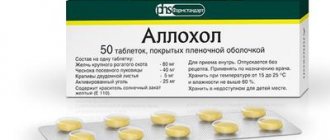
- Choleretic drugs. If the gallbladder is bent, choleretic drugs are prescribed to improve the flow of bile into the intestinal lumen. Similar drugs include Hofitol, Allohol. A drug called Aristochol contains medicinal herbs and acts in several directions at once: improves intestinal function, increases the flow of bile and relieves spasms.
- Painkillers and antispasmodics. For pain, the doctor prescribes painkillers and antispasmodics, such as Drotaverine, No-Shpa, Baralgin. For nausea and vomiting, intramuscular injections are possible.
- Antibiotics. The doctor may prescribe antibiotics for cholecystitis, if the gallbladder is bent due to an infection that provokes inflammation of the gallbladder mucosa. Ampiox is often prescribed.
- Physical procedures. Physiotherapy is most often aimed at warming up: ozokerite therapy, paraffin therapy.
- Breathing exercises. The abdominal type of breathing is useful, when with each inhalation the diaphragm and abdominal organs develop. This will help avoid bile stagnation.
- Vitamin therapy. Vitamins will help strengthen the general condition of the body, increase immunity, which is especially important when there is an excess caused by infection.
- Traditional medicine. Choleretic herbs include milk thistle, tansy, and immortelle. Tansy decoction also has an analgesic effect. It is also recommended to take a decoction of rose hips, valerian, chamomile with mint, and hop cones. For gallbladder diseases, it is sometimes recommended to eat mustard, horseradish and garlic with other foods. However, you need to be careful with this, since such products are contraindicated for other diseases of the digestive system.
Diagnostics
To find out the true cause of constipation, the patient is prescribed a diagnostic examination. This may include:
- clinical and biochemical blood and urine tests;
- coprogram (stool analysis);
- Ultrasound of the abdominal organs;
- cholecystography (x-ray of the gallbladder);
- colonoscopy (endoscopic examination of the large intestine);
- duodenal intubation (examination of the contents of the duodenum).
Up to contents
How long should food restrictions be observed?
In case of exacerbation of the clinical manifestations of this pathology, it is advisable to use only a milk-curd diet. At this time, grapes, apples, dried fruit compote, practically not sweet, are allowed. Diet table No. 5 according to Pevzner will subsequently help normalize the functioning of the gallbladder when the main symptoms subside. This diet will need to be followed at all times.
You can print out the following reminder and stick it on your refrigerator to help you remember which treats to avoid and which foods are welcome:
Features of the treatment of constipation in diseases of the gallbladder
Treatment of constipation that develops against the background of the above-mentioned diseases requires an individual comprehensive approach, which may include the following measures:
- nutrition correction (compliance with therapeutic diet No. 5 and 5a);
- organizing an optimal drinking regime (you should drink about 1.5–2 liters of clean water per day);
- increase in physical and motor activity;
- therapeutic exercises;
- massage;
- physiotherapeutic procedures (electrical stimulation of the intestine - exposure to electric current, during which the intestine contracts, simulating natural urges);
- drug therapy. May include taking laxatives, as well as drugs that enhance the formation of bile (choleretics) and stimulate the contractile function of the gallbladder (cholekinetics).
Up to contents
Cooking and eating
Dishes are prepared boiled, baked, food is salted normally. The food should be warm. Diet: at least 4 times a day, preferably 5-6 times.
Allowed
Bread: day-old or dried wheat, rye and other types of bread, shortbread cookies
Soups: various soups from vegetables, cereals, pasta with vegetable broth or milk, fruit soups Meat and poultry dishes: products from lean beef, poultry, boiled or baked after boiling, in pieces or chopped. Milk sausages
Fish dishes: various low-fat varieties of fish (cod, pike perch, navaga, pike, carp, silver hake) boiled or steamed
Vegetables: various types of vegetables and herbs, sour sauerkraut, canned green peas, ripe tomatoes
Dishes made from flour, cereals, legumes and pasta: crumbly semi-viscous porridges, puddings, casseroles, dishes made from oatmeal and buckwheat porridge are especially recommended
Eggs: no more than one per day, added to dishes, egg white omelet
Fruits, berries, sweet dishes: various fruits and berries except very sour ones, canned fruits, compotes, jelly, lemon (with tea), sugar, jam, honey
Milk, dairy products: milk with tea, condensed, dry, low-fat cottage cheese, small amounts of sour cream, mild cheeses (Dutch, etc.). Cottage cheese and cottage cheese products are especially recommended Fats: butter, vegetable oil (up to 50 g per day)
Appetizers: soaked herring, pressed caviar, salads and vinaigrettes, jellied fish
Drinks: tea and weak coffee with milk, non-acidic fruit and berry juices, tomato juice, rose hip decoction
Must be excluded
All alcoholic drinks, fresh baked goods, pastry products (cakes, pancakes, pancakes, fried pies, etc.), soups with meat, fish, mushroom broths, fatty varieties of beef, lamb, pork, goose, duck, fatty varieties of fish (stellate sturgeon, sturgeon, beluga, catfish), mushrooms, spinach, sorrel, radish, radish, green onions, pickled vegetables, canned food, smoked meats, caviar, ice cream, products with cream, chocolate, legumes, mustard, pepper, horseradish, black coffee, cocoa, cold drinks, cooking fats, lard, cranberries, sour fruits and berries, hard-boiled and fried eggs.
Download and print:
Diet No. 5
Make an appointment Do not self-medicate. Contact our specialists who will correctly diagnose and prescribe treatment.