Causes of nausea, diarrhea, headache
Nausea, diarrhea, and headache are a characteristic set of signs of disturbances in the functioning of the stomach and intestines. Among the causes are infectious and non-contagious diseases that affect the digestive processes and cause intoxication of the body.
Food poisoning
One of the most common causes of nausea, diarrhea, headache and weakness is poisoning. Toxins enter the body with food, penetrate the bloodstream and spread through cells and tissues. Unpleasant symptoms are a protective reaction of the body, an attempt to cleanse the blood of toxins and toxic compounds.
Symptoms of poisoning appear within several hours after consuming low-quality products. These include:
- nausea followed by vomiting;
- diarrhea, disruption of the digestive tract;
- pallor of the skin and mucous membranes;
- general weakness, lethargy;
- Possible increased temperature and rapid heartbeat.
Poisoning with poisonous mushrooms poses a great danger to health. The most commonly reported poisoning is toadstool. This mushroom contains poisonous compounds that quickly spread through the blood, affecting cells and tissues. If medical care is not provided in a timely manner, brain damage and disruption of the nervous system, including death, may occur. First aid consists of gastric lavage to urgently remove toxins from the body; intravenous drips of electrolyte solutions will also be required.
Nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, headache are characteristic symptoms of alcohol poisoning. The reason may be the use of low-quality drinks or excess dosage. Compounds that are formed during the breakdown of ethyl alcohol are poisonous to humans. They can cause acute intoxication, which is accompanied by nausea, diarrhea, fever, and headache. Symptoms usually subside within 1–2 days, but severe poisoning may require longer treatment.
Infectious diseases of the stomach and intestines
Viral and bacterial diseases that affect the mucous membrane of the gastrointestinal tract are a dangerous cause of nausea, headache, diarrhea and other symptoms. They are dangerous at any age, but in children they occur in a more acute form and can cause an increase in temperature to critical levels and other complications. Infection occurs through consumption of contaminated water, poorly purified foods (especially vegetables and fruits), raw meat and eggs. Treatment is selected individually, depending on the type of pathogen and the stage of the disease.
- Salmonellosis is a bacterial disease that manifests itself as nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and acute headache. You can become infected through contaminated water, infected chicken eggs and meat. These products are especially dangerous in their raw form. Treatment is long and takes place in an infectious diseases hospital.
- Rotavirus infection (intestinal flu) is a disease that is transmitted through household contact, therefore it spreads quickly and poses a great danger. Symptoms are pronounced: high fever, nausea and vomiting, digestive tract dysfunction. During treatment, the patient needs to reduce all contacts with others, so treatment is carried out in a hospital.
- Toxic infections are a group of diseases caused by pathogenic bacteria. The deterioration of health is provoked by the products of their metabolism, which poison the body and are strong toxins. This group includes clostridiosis, staphylococcosis, botulism and other dangerous diseases. They occur in a more severe form in children, but in adults they can also cause dangerous complications and a protracted course.
Treatment of a bacterial infection of the gastrointestinal tract is with antibiotics. They destroy pathogens and promote their elimination from the body, but do not eliminate the consequences of long-term intoxication. During the recovery period, doctors recommend following a diet and taking probiotics to normalize the balance of microflora.
When should you see a doctor?
If diarrhea, vomiting, nausea and other health problems do not go away within 24 hours, then you should forget about self-treatment. This is especially true in a situation where a person’s body temperature rises and blood appears in the stool or vomit. In such a situation, you need to call an ambulance or go to the hospital yourself.
Emergency medical care is required in the following situations:
- Diarrhea and vomiting do not stop longer than 1-2 days.
- Body temperature rises to high levels.
- Blood and mucus are visible in the stool and vomit.
- The person is in severe pain.
- Symptoms of dehydration appear: the mouth becomes dry, you are constantly thirsty, weakness and dizziness increase.
- Vomiting and diarrhea develop in a child or in a pregnant woman.
- Several people in one family fell ill at once.
To establish a diagnosis, the doctor will prescribe the following tests to the patient:
- Donating blood and urine for general analysis.
- Analysis of feces for helminth eggs.
- BAK stool culture.
- Coprogram.
- Ionogram.
- Renal function tests.
Instrumental diagnostics comes down to the implementation of the following techniques: irrigoscopy, colonoscopy, sigmoidoscopy, ultrasound. Only based on the results of a comprehensive diagnosis will it be possible to detect the exact cause of the ailment and prescribe treatment.
Parasite infestations
Helminths are parasitic organisms that can enter the human body from the outside and then feed at its expense. There are a huge number of types of helminths. They vary in shape and size and can reach up to several meters in length. Parasites most often inhabit the human intestines and feed on digested food. Some varieties are found in the liver and bile ducts, lungs, heart, as well as in blood vessels and other organs.
When the first symptoms appear, it is necessary to undergo tests to determine the type of helminths and begin treatment. These include:
- constant nausea, vomiting;
- diarrhea that alternates with constipation;
- sudden weight loss without changing your diet;
- pain in the stomach and head.
Treatment of helminthiasis takes place in several stages. Initially, the patient is prescribed a gentle diet, and at the same time tests are carried out to determine the type of parasite. The main stage is taking specific anthelmintic drugs, the action of which is aimed at a specific pathogen. After a repeat analysis confirms the complete absence of worms, it is necessary to restore the mucous membrane of the digestive tract and normal microflora. To achieve this, the patient continues to follow a diet and takes enveloping agents.
Other reasons
Nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, headache and fever are nonspecific signs of a number of diseases and conditions. They can be detected with the following violations:
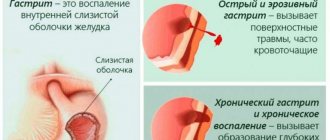
- inflammatory diseases of the stomach and intestines (gastritis, enteritis, colitis), as well as peptic ulcers;
- traumatic brain injuries, blows and bruises to the head;
- stressful situations, nervous tension;
- acute attacks of migraine;
- surges in blood pressure.
When the first symptoms appear in children, you should immediately consult a doctor. Nausea, diarrhea, headaches are signs that may indicate acute and chronic diseases of the digestive tract. With timely treatment, their further development can be prevented and the condition can be maintained with a special diet and medications.
How to help if a child has diarrhea and vomiting?
The worst thing with diarrhea is dehydration.
The biggest threat to a baby’s life caused by diarrhea and vomiting is severe dehydration, and with this comes destabilization in the body as a whole. The organs stop functioning properly, and a few days after the onset of such an illness, this can even be fatal for the baby. This is why you need to prevent dehydration as soon as possible.
The first step is to ensure the flow of water into the digestive organs, this will ensure the normal functioning of all organs. Many parents make the grave mistake of noticing that their child has diarrhea and vomiting. They leave it without special attention and do not take any action, hoping that everything will go away on its own; this is completely wrong.
You need to address dehydration in the first hours. You need to replenish lost fluid with the help of special solutions. They can be purchased at the nearest pharmacy, and for those babies who are still breastfed, they need to be applied to the mother’s breast more often.
Examination methods
Timely diagnosis is the first step to successful treatment of diseases that are accompanied by nausea, diarrhea, and headache. At the first stage, it is necessary to differentiate infectious diseases and isolate the patient in a hospital if necessary. Next, additional methods are prescribed, thanks to which you can determine the exact cause of poor health. These include:
- bacterial seeding of biological material for accurate determination of pathogens of infectious diseases;
- Ultrasound of the stomach and intestines is the main method for detecting inflammatory processes in these organs;
- endoscopic examination of the mucous membrane of the gastrointestinal tract;
- CT and MRI of the brain are prescribed if various disorders of the central nervous system are suspected.
At the Clinical Brain Institute, the diagnostic scheme is selected individually. It will include only those techniques that are necessary to understand the overall picture of the disease.
Bacteria or viruses
Bacteria and viruses are a common cause of diarrhea.
These 2 factors provoke disruption of intestinal motility, food is not fully digested. The body urgently needs to rid itself of the potential source of infection - diarrhea occurs. Diarrhea itself is not dangerous and goes away on its own without treatment. But when fever, nausea, and vomiting occur, this is a reason to seek medical help. The causes of this pathology:
- Food poisoning
- Acute intestinal infections, including rotavirus
- Hepatitis of various etiologies
- Inflammation of the appendix
These diseases require urgent medical care at a hospital. Only stomach flu - or rotavirus in adults - can be treated at home.
Treatment of headache, diarrhea and nausea
Treatment of nausea, diarrhea, and headache will differ depending on the stage of the disease and its causative agent, as well as the age of the patient and other factors. In most cases, the regimen includes taking various medications to relieve the symptoms of the disease and eliminate its cause.
- Antibiotics are the first method of treatment for bacterial diseases of the gastrointestinal tract. They can be taken in the form of tablets or injections. More often, broad-spectrum antibiotics are prescribed, which act simultaneously on a large number of bacteria. After the course of treatment, it is recommended to take probiotics to restore normal microflora of the stomach and intestines.
- Other drugs - the course of treatment involves taking symptomatic drugs. To improve your well-being, you may need medications that help with vomiting and nausea. Painkillers, anti-nausea medications, and enveloping agents may also be effective.
- Diet is a must for nausea and diarrhea. On the first day, the doctor may prescribe a fasting diet; only mineral water is allowed. Next, add light foods that are easily digestible. Fatty foods and sweets, fried and salty foods are contraindicated. A gentle diet must be observed not only during illness, but also in everyday life.
- Surgery is only necessary in rare cases. So, surgery may be necessary for Crohn's disease to remove the inflamed area of the intestine.
At the Clinical Brain Institute, you can undergo a complete examination for headaches that are accompanied by nausea and diarrhea. Qualified doctors, modern equipment, and the opportunity to receive comprehensive treatment in a hospital setting are our main advantages.
Medicines and precautions for diarrhea and vomiting in a baby
An increase in temperature is an alarming symptom
When starting to treat childhood diarrhea, it is important to always remember that even a medicine such as Loperamide must be used with extreme caution, as intestinal obstruction may occur. If diarrhea is caused by an infection in the intestines, taking medications against diarrhea can slow down the body's ridding of toxins, and this can lead to a general deterioration in the condition of the child, who has not yet had time to recover from the illness.
If a child has blood when excreting feces, and the body temperature is elevated, even if not greatly, medications for diarrhea are generally contraindicated. After all, on the one hand, diarrhea removes all harmful substances and toxins, but, on the other hand, the body at the same time loses a lot of fluid, which needs to be constantly replenished. Thus, the intestines will be completely cleansed and there will be no harm to health. But this should happen under the strict supervision of a pediatrician.