Causes of the disease and classification of stomach pain
Stomach pain has certain causes.
Among the most common reasons are the following:
- damage/disorder of the digestive organs;
- stimulation of receptors in the area of ulcerative lesions;
- excessive release of hydrochloric acid;
- convulsive contractions that form in the area of the ulcer.
The symptom of pain can occur with varying strength, frequency and intensity of action.
According to experts, such pain is graded into:
- pulsating (can be caused by convulsive contractions of smooth muscle);
- burning (the main indications for its appearance are a high content of hydrochloric acid);
- pulling (appears a short time after eating);
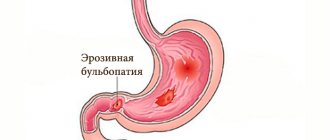
- sucking (arise due to erosive changes).
Symptoms
Pain syndrome in the intestines is distinguished by duration, intensity and nature.
Severe, sharp pain can occur when ulcerative lesions of the gastrointestinal tract appear. The person is unable to perform any activities due to severe pain.
The nature of the pain syndrome is pulsating, aching, burning, baking, shooting.
Unpleasant sensitivity in this area after sleep can occur in conjunction with other indicators.
The sick person feels nauseous, is haunted by heartburn and has a bitter taste in the mouth. He may also be worried about increased gas production, stool disturbances, decreased appetite, and general malaise.
Hunger pain in the stomach is observed 6-8 hours after eating food. These pains may appear in the morning. They disappear spontaneously after a person eats.
It is very difficult to diagnose pathology by symptoms alone. To accurately establish the diagnosis, additional examination methods are performed.
The main symptoms indicating hunger pains and the time of their appearance
It is generally accepted that pain in the stomach occurs in a state preceding the onset of illness. The appearance of a gag reflex, lack of appetite, heartburn are the main symptoms indicating pain in the stomach.
These symptoms can be observed at any time of the day or night, it all depends on the lifestyle a particular person led. If the patient feels stomach pain 5-6 hours after eating food, then this is quite normal. Obviously, stomach pain is a common occurrence for a hungry person, but if the pain persists after satiety, this already indicates that the pathology is progressing.
Stomach pain at night also indicates the presence of ulcerative formations.
Be that as it may, a patient experiencing painful sensations in the stomach area is indicated for a special procedure, fibrogastroduodenoscopy. After it is carried out, the attending physician is likely to diagnose the exact form of the disease. A malignant tumor is another reason why a person may experience stomach pain. As is the case with the fibrogastroduodenoscopy procedure, the presence of a malignant tumor in the stomach can be determined using a special method - a biopsy.
The presence of a pain symptom may also be accompanied by disruptions of the hormonal system. As a result, hormones responsible for satiety of the body and the appearance of hunger begin to be produced in excessive quantities, resulting in pain in the stomach, a gag reflex and heartburn.
Stomach pain can be partially alleviated by consuming purified water or baked milk. A forced gag reflex can also help reduce attacks of pain.
Stomach ache
As you know, pain in the abdominal cavity can be caused by diseases of the organs that are located in it. Unlike, for example, a heart attack, in this case the pain does not require urgent measures, although here the correct diagnosis is no less important. If your life after your first heart attack will never be the same again, then if a surgeon removes your gallbladder or inflamed appendix, he will thereby destroy the disease itself. And men who experience abdominal pain are usually very afraid of appendicitis and ulcers. Although they might be better off worrying about their gallstones or diverticula, as ulcers and appendicitis are not that common these days.
Also, unlike pain that occurs in the chest, acute abdominal pain almost never requires an immediate response; even with a perforated ulcer, a short delay of a couple of hours is not at all fatal. However, if it is a couple of days late, patients usually either die or doctors are sued. But fortunately, abdominal pain in many cases are symptoms of completely minor disorders. And in order to better understand them, you can use the following tips.
First of all, you need to determine exactly where it hurts. Thus, the navel serves as the border between the lower and upper sections of your digestive tract (even though the large intestine runs higher, serious pain is usually localized there at the bottom). And the small intestine, folded into loops, is located in the center of your abdomen behind the navel. He is usually extremely rarely exposed to serious illnesses. The most common sources of your abdominal pain may include:
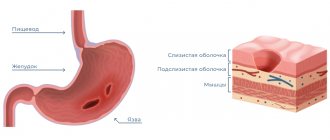
- The duodenum is the first section of the small intestine, about 25 cm long. Food enters it directly from the stomach and here ulcers usually occur more often than in the stomach, but in the duodenum the pain cannot be distinguished from gastric pain.
- Stomach - located above the horizontal line that passes through the navel under the arch of the ribs of the chest (the so-called epigastric region). Even at school they explained to us that the stomach digests and mixes food, and its main function is its storage and accumulation. However, a person without a stomach can also digest food normally, but if it is consumed in large quantities, unpleasant sensations may appear.
- The liver is the largest organ located in the abdominal cavity. The liver is located in its upper right part. It should be noted that quite rarely liver diseases are a source of acute abdominal pain.
- The gallbladder is a small sac located on the lower right side of the chest. So oily bile continuously flows into the gallbladder from the liver, where it accumulates and concentrates. And after eating food, the gallbladder delivers it to the duodenum in order to improve the absorption of food fats. Gallbladder pain can occur for completely different reasons. The most common cause is stones formed from hardened bile. This is due to the appearance of cholesterol in bile, which precipitates first at high concentrations, as well as when bile is dehydrated. However, the stones are completely harmless as long as they lie motionless in the gallbladder. And problems can begin when they move, blocking the bile duct, which leads to the small intestine. And the pain that can occur when the stone is pushed through the duct can last up to several hours.
- Colon. Most often, pain occurs somewhere in the left lower abdomen (cramps, diverticulitis, diarrhea, constipation), and sometimes even in the right lower abdomen (appendicitis). However, the most serious diseases in the colon can rarely cause pain above the navel. But we must not forget about the pain in the left upper abdomen, which occurs with the syndrome of accumulation of gases in the splenic flexure. Also, the colon on the right under the liver has another 90° turn, but with a much smoother radius, and therefore pain from gas is not so often noted here.
- The pancreas is located in the abdominal cavity quite deep behind the duodenum and stomach. It produces a certain secretion, which contains many enzymes, which then enters the small intestine through a separate duct. With inflammation of the pancreas (pancreatitis), pain usually occurs in the epigastric region, which can be felt on the left.
After you determine the nature of your pain (aching pain, burning, gas pain), try very hard to somehow abstract yourself from it. Some textbooks describe the pain of an ulcer as a burning sensation, and the pain from a blocked duct with a stone as colic, which increases to a maximum and immediately subsides. And pain from gases is usually compared there to a certain movement of a large ball through the insides. All these descriptions may sometimes not correspond to your sensations, since the nerves that transmit pain signals from internal organs, unlike the nerve endings of the skin, are too primitive. Sometimes your life depends on many subtle sensations, but the signals inside the body can only serve as a rough warning. A burn to the stomach with acid can cause either aching, dull, gnawing, sharp pain, or cause no pain at all.
When exactly do you feel pain?
The pain that woke you up in the middle of the night deserves special attention. Usually, pain at night in the stomach area can signal an ulcer, since after midnight the stomach is usually empty, and the secretion of acid increases after about 2 hours. Such pain sometimes appears with almost any dysfunction of the stomach, as well as with various indigestion and dyspepsia.
You might want to think about connecting your pain to your food. Often with ulcers, "hunger pains" are felt because the food neutralizes the acid, but these usually go away immediately after eating, but not always. And pain from gases usually occurs after eating 1-2 hours, but not because food releases them when they enter the stomach, but precisely because when food is digested, the intestines contract intensively, thereby compressing the gases already present there .
Symptoms associated with pain
Sometimes infections can be accompanied by fever. Also, with gastric catarrh, diverticula, and appendicitis, the temperature may rise. However, this is not observed with gallstones, gases, or ulcers. But the absence, presence, or even a slight rise in temperature cannot accurately indicate the seriousness of the violation.
Vomiting can begin when the outlet of the stomach is blocked, and even with a chronic ulcer. And blocking the outlet of the stomach sometimes requires surgical intervention. Vomiting is often accompanied by severe pain due to gallstones or exacerbation of an ulcer, but generally vomiting is not a specific signal about some kind of problem in your digestive tract. The same applies to diarrhea.
Risk level
A small hernia (diverticulum) often occurs in the colon in people of middle age and older, since after prolonged consumption of food that is poor in coarse fibers, its walls weaken, the weakest parts of the colon sag, thereby protruding outward into sacs called diverticula. Typically, in older people, you can find dozens of diverticula, which do not bother them at all, until they start to bleed a little or rupture the wall of the colon. A rupture (perforation), as a rule, provokes a very painful infection (diverticulitis), which is usually treated with antibiotics, a liquid diet, but sometimes this disorder may require surgical intervention.
If you constantly ate coarse fiber foods in large quantities and did not suffer from constipation, then your colon experienced little stress, and your risk of diverticulitis is quite small.
It is worth noting that appendicitis is dangerous at any age, but usually this disease is typical for people in adolescence or early adulthood. And pain in the lower right part of the abdomen, which is accompanied by nausea, low fever, and a general painful condition, can usually indicate appendicitis.
Also, severe pain in the same area, while general health is normal, is usually associated with intestinal irritation and gases.
Gallstones are twice as common in women as in men.
How severe is your pain?
Most often, moderate pain may indicate a not very serious illness. And excruciating pain also may not necessarily be a symptom of a disease that threatens your life, since it can even accompany simple gastroenteritis (stomach catarrh), but you should still pay attention to it.
Do not self-medicate.
Seek medical help promptly.
Useful video
Many patients at an appointment with a gastrologist admit that their stomach hurts in the morning. Such pains are different; they may differ in symptoms and causes. They have one thing in common: this pain doesn’t just appear.
You wake up and after a couple of minutes you feel discomfort in your stomach. The pain is accompanied by bloating, a burning sensation in the upper chest, and mild nausea. And it makes you feel nauseous until you take some action. And this immediately spoils your mood, the day is not going well. What happens to the body? Let's figure it out.