October 7, 2019
A bitter taste in the mouth that constantly occurs is a reason to be wary and go to a doctor for examination. An unpleasant phenomenon does not always indicate that a serious disease has developed in the body, but the percentage of cases where the causes of its occurrence are completely harmless is very small. The editors of the UltraSmile.ru portal advise you to read the article in order to have useful information on this topic and to rule out possible pathologies in time.
There can be many causes of bitterness in the mouth
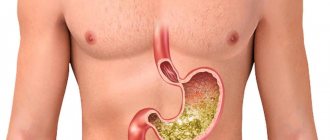
Gallbladder and liver diseases
If the taste of bitterness in your mouth has become your constant companion, then the first thing to rule out is stagnation of bile, which occurs due to pathologies of the gallbladder and liver. Bile is produced in the liver, then it enters the gallbladder, where it is stored until food enters the stomach. This beneficial liquid helps the stomach digest food. As soon as you eat, bile enters the duodenum - this is a natural phenomenon. With pathologies of the gallbladder and liver, the fluid does not come out completely or stagnates, a lot of it is formed, and a bitter taste appears in the mouth.
In case of pathologies, our internal organs try to get rid of bile and can even arrange an “emergency discharge” of it, causing some of the liquid to enter the esophagus and even the oral cavity.
In case of liver disease, it can cause bitterness
What does bitterness in the mouth mean? The phenomenon may indicate the development of cholelithiasis, cholecystitis, hepatitis, cirrhosis, cancer, dyskinesia (impaired motility of the gallbladder). Unpleasant sensations in the mouth appear most often in the morning, as soon as you wake up, and also after playing sports. They may be accompanied by tingling and discomfort in the right hypochondrium, belching, dry mucous membranes, and indigestion. The bitter taste may alternate with a metallic or “iron” taste.
Anatomy of taste
Taste arises from the interaction of food and taste receptors, which are located on the neuroepithelial cells of the oral cavity. Taste buds are a group of receptors; they are localized on the pharynx and larynx, tongue, and palate. On the surface of the tongue, the bulbs are located inside the taste buds, which are divided into groove-shaped, mushroom-shaped and leaf-shaped.
Taste receptors are nerve cells, but they do not have axons. Information is transmitted to the nerve fibers of the bulbs. The cell bodies of neurons are located in the ganglia of VII, IX, X pairs of cranial nerves. The signal then passes to the nucleus of the brain stem, then to the gustatory cortex and certain areas of the cerebral cortex. Taste sensations are transmitted through the petrosal nerve and the chorda tympani. The glossopharyngeal nerve innervates most of the papillae. The vagus nerve is responsible for sensation in the pharynx and larynx through the laryngeal nerve.
There are five basic tastes: sour, sweet, umami, salty and bitter. Each of them is necessary for a person to meet the needs of the body. The perception of taste is also influenced by the appearance of food and its consistency. Attitudes towards dishes largely depend on individual preferences, as well as cultural and hereditary factors.
Dental diseases
A bitter taste in the mouth sometimes has quite obvious reasons for its occurrence, both in women and men. It can be caused by pathogenic bacteria that multiply due to poor hygiene, inflammation of the gums, the development of gingivitis and periodontitis, caries, pulpitis, and periodontitis. Then in almost all cases it will be accompanied by the appearance of bad breath, and there may also be signs of inflammation of the mucous membrane: bleeding and swelling of the gums.
Inflammation and bleeding of the gums causes this problem.
Galvanic syndrome
Do you have a bitter taste in your mouth and are wondering what it means? Perhaps the problem lies in the fact that you have dentures made of dissimilar metals installed in your mouth.
Read the article on the topic: electric current in the mouth. Find out what to do to recover quickly!
The problem needs to be solved, because if everything is left as is, the disease will progress, general health may worsen, and nervous disorders may begin.
Galvanosis can occur from different metals
Gastrointestinal diseases
What does bitterness in the mouth mean? There is a very high probability that the culprit is diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, which are accompanied by such a phenomenon as reflux. For example, gastritis, pancreatitis, ulcers, colitis, enteritis. Reflux is the release of acid from the stomach into the esophagus and larynx. To get rid of acid, our salivary glands begin to secrete alkaline saliva, which extinguishes this acid. This saliva has a very bitter taste and is accompanied by heartburn. With such pathologies, the tongue acquires an unhealthy yellowish tint.
With gastrointestinal disease, a yellow coating appears on the tongue and an unpleasant taste
Symptoms
Let us consider in more detail the characteristics of the symptom of the disorder depending on the cause that provoked it. A sweet and sour taste in the mouth appears after consuming large amounts of sugar, lactose-containing foods and coffee. Other causes of the symptom include:
- sudden cessation of smoking;
- liver pathologies;
- dental diseases (caries, periodontitis, gingivitis);
- poisoning by toxic substances at work;
- uncontrolled use of certain types of drugs;
- diabetes.
A bitter-sour taste in the mouth is most often associated with dietary errors. It can also appear due to bad habits such as smoking or drinking alcohol.
List of other factors causing discomfort:
- taking antibiotics, allergy medications, NSAIDs, medications for seizures;
- problematic outflow of bile from the body;
- gallbladder diseases;
- liver dysfunction;
- duodenal ulcer;
- gastritis;
- initial stages of diabetes;
- hormonal imbalance (during pregnancy, puberty or menopause);
- chronic anemia.
When taking medications, acid in the mouth will not appear immediately. This requires a long course of drug treatment.
A sour-salty taste occurs with the development of sialodenitis. The problem is associated with inflammation of the salivary glands. It develops independently or as a complication of a prolonged runny nose and other otolaryngological pathologies.
Other causes of symptoms include:
- abuse of carbonated drinks or coffee;
- dehydration of the body;
- uncontrolled consumption of alcoholic beverages;
- damage to the sinuses;
- poor nutrition.
Intestinal parasites
A bitter taste in the mouth may indicate extremely unpleasant reasons. For example, the fact that parasites (giardia or helminths, pinworms and roundworms) have appeared in the body and are actively living. Parasites literally stick to the inner lining of the small intestine, which causes its reflex contraction, as well as tissue damage. As a result, indigestion occurs and gastrointestinal pathologies occur.
Parasites can also cause this symptom
Nowadays, it is not so easy to catch these parasites, but small children who put everything they can and cannot put into their mouths still quite often become victims of parasites, and adults can also become infected from them. Often helminthic infestations are called the “dirty hands” disease.
Which doctor should I contact?
If there is a disturbance in the sense of taste, then first of all you need to consult a general practitioner, that is, a therapist, since the causes may include a wide variety of abnormalities of tissues, organs and organ systems. If a child has problems with taste, you need to show him to the pediatrician. The therapist can prescribe a consultation with an endocrinologist, neurologist, dentist, hematologist and psychiatrist.
The specialist will need information from the patient, such as how long the disorder has been present, which tastes differ and which do not, whether the disorder is permanent or occurs from time to time. Testing to determine flavor combinations may be required.
Neuropsychiatric disorders
If there is a bitter taste in the mouth, on the tongue and on the lips, then here's what it can mean: the person has developed severe depression1, chronic stress or schizophrenia.
Surprisingly, even ordinary stress or nervous overstrain can contribute to the appearance of bitterness, and our physiology is to blame for everything: in the process of a nervous breakdown, all organs become tense (this occurs due to the release of adrenaline and norepinephrine into the blood), the tone of the gallbladder is disturbed, and muscle spasms occur. .
Stress can contribute to bad taste
Thyroid pathologies
When bitterness in the mouth has become a symptom that accompanies you constantly, what does it mean? The reason may again lie in the reflux of bile into the esophagus, but in this case, such a phenomenon is provoked not by pathologies of the liver and gallbladder, but by disturbances in the functioning of the endocrine system and hormonal imbalance. For example, this serves as one of the symptoms of diseases such as hypothyroidism and hyperthyroidism, diabetes mellitus. With diabetes, in addition to bitterness, a person may experience dry mucous membranes, but sweating, on the contrary, increases - these are signs of increased blood sugar levels. Also, with all of the above pathologies, the taste of iodine may periodically appear.
Improper functioning of the thyroid gland can cause pathology
Treatment and preventive measures
Since a sour taste in the mouth is only a symptom, after identifying the causative disease, the doctor will prescribe appropriate treatment and tell you what to do to improve its effectiveness. It is important to pay due attention to the quality of oral hygiene, if necessary, carry out its sanitation, undergo professional teeth cleaning, and improve gum health.
How to remove the sour taste caused by gastrointestinal diseases? In addition to drug therapy prescribed by your doctor, you should follow these recommendations:
- do not overeat at night;
- Take warm food in small portions 5-6 times a day;
- drink enough clean water;
- limit consumption or completely avoid smoked, salty, fatty foods and alcohol, which have a bad effect on the digestion process and liver function;
- consume less red meat, strong coffee and tea, carbonated drinks and other foods with sour or bitter taste;
- introduce plant foods, cereals, eggs, dairy products, fish into the diet;
- to refuse from bad habits.
It is important to analyze the drugs that are used. A diet is also recommended for pregnant women. Expectant mothers should not take a horizontal position or engage in active physical exercise after eating. Hiking in the fresh air is shown.
Causes of bitter taste not associated with serious illnesses
- consumption of low-quality and stale food: a bitter taste in the mouth often appears due to the consumption of expired or specific food products. For example, pine nuts are rich in healthy fats, but if they are stored for too long, the fats in them begin to oxidize and become bitter.
- overeating at night: especially if the food was fatty and “heavy”. A similar phenomenon is also caused by products that provoke increased gas formation in the intestines (cabbage, beans, baked goods),
- love for carbonated drinks: champagne, mineral water with gas,
- drinking alcohol,
- decreased activity of taste buds: this problem is most often encountered by older people, whose hormonal levels change with age and some receptors become insensitive. A problem also arises for people who smoke, because... with constant exposure to smoke on the mucous membrane, dystrophy of the taste buds occurs,
- taking medications and herbal decoctions: choleretic, as well as antifungal and antihistamines can have this effect,
- pregnancy: the taste of bitterness in the mouth and the reasons for its appearance in women are often associated precisely with bearing a child. The symptom is typical for the second half of pregnancy, since it is during this period that the growing and developing child begins to put pressure on the internal organs and displace them, which increases the likelihood of bile reflux into the esophagus,
- hormonal changes in the body: for example, in women at the onset of menopause,
- a lack or excess of vitamins in the body: for example, a lack of zinc or an excess of B12 contributes to the appearance of a bitter taste.
Pregnancy often causes nausea and bitterness in the mouth
How is diagnostics carried out?
Only an accurate diagnosis is the key to successful treatment. For this purpose, you may have to visit several specialists: a therapist, a dentist, a gastroenterologist, an endocrinologist, and a gynecologist. The child must first be shown to a pediatrician.
Each of the listed reasons has its own method of diagnosis and elimination. In addition to collecting anamnesis and visual examination of the mouth, neck and head, doctors may prescribe the following studies:
- blood and urine tests;
- Ultrasound;
- FGDS;
- X-ray with HF;
- CT or MRI.
Various tests are also carried out to evaluate taste sensations.
The “character” of bitterness will tell you about the problem
If you have a bitter taste in your mouth and are thinking about what it all means, then see the table below.
| Symptom | Possible pathology |
| Bitterness appears in the morning | It is necessary to check the liver and gallbladder |
| The taste accompanies constantly | Gallstone disease, cholecystitis, gastrointestinal oncology, hormonal imbalance, thyroid problems, mental disorders |
| An unpleasant symptom appears after you have eaten | Pathologies of the gastrointestinal tract and duodenum, consumption of poor quality food |
| The taste is present situationally, for a short time | Taking medication, taking antibiotics, smoking, allergies, stress |
| Bitterness + bad breath | Dental diseases (gingivitis, stomatitis, periodontitis and periodontal disease), gastrointestinal problems. |
| Bitter taste combined with heartburn | Gastroesophageal reflux disease |
However, we advise you not to engage in self-diagnosis, but to go to see a doctor who can definitely confirm or refute the diagnosis based on blood tests, examination and ultrasound. To begin with, it is better to visit a gastroenterologist; you also need to see a dentist who will rule out diseases of the oral cavity.
Notice
: Undefined variable: post_id in
/home/c/ch75405/public_html/wp-content/themes/UltraSmile/single-item.php
on line
45 Notice
: Undefined variable: full in
/home/c/ch75405/public_html/wp-content /themes/UltraSmile/single-item.php
on line
46
Rate this article:
( 16 ratings, average: 4.56 out of 5)
prevention
- Smulevich A.B. ‹‹Depression in general medicine: A guide for doctors››. Section VII. Diagnosis and differential diagnosis. Recognizing depression.
Why does a sour taste appear?
The digestive system has a complex structure. The presence of any aggressive factors and internal changes in various organs negatively affects its functioning, as evidenced by the appearance of a sour taste. The main causative factors for the appearance of an unpleasant symptom:
- Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD). When food enters the stomach, it does not return to the esophagus thanks to a special valve. It does not work properly in patients with GERD. Because of this, food enters the esophagus, which explains why a sour or bitter taste appears.
- Insufficient oral hygiene and dental diseases: caries, gingivitis, periodontitis, stomatitis and other infections caused by fungi.
- Taking certain medications. There are drugs that, in addition to their main action, affect taste buds in the brain or tongue. This includes antibiotics, drugs prescribed as part of chemotherapy for the treatment of neurological, cardiovascular diseases, and certain psychological conditions (depression, anxiety, insomnia).
- Bad habits. An unpleasant aftertaste may be caused by smoking and chewing tobacco for a long time.
- Dry mouth. Insufficient saliva production is accompanied by incorrect perception of taste. The disorder worsens with anxiety or stress.
- Lack of zinc in the body. It is observed when there is insufficient intake of this element into the body, its poor absorption, for example, when taking certain medications.
- Pregnancy and other conditions of the female body. Hormonal changes in expectant mothers cause a sour taste. This also happens due to the pressure of the uterus on the stomach. At the same time, heartburn appears. An undesirable symptom is also observed in women during menopause, which is explained by changes in hormone levels. By the way, hormonal disorders in men are also sometimes accompanied by the appearance of a sour taste.
- Radiation therapy, which affects the head and neck area. This can damage saliva tissue, causing an unpleasant taste.
- A number of diseases (gastric ulcer, disorders of the liver and its ducts, gastroduodenitis, pancreatitis, diaphragmatic hernia, chronic anemia, helminthic infestation).
There are many more reasons that provoke an unpleasant symptom. These are neurological disorders, operations or head injuries, poisoning with heavy metals and highly toxic substances.
Comments
I am diagnosed with gallbladder dyskinesia. I take the medications prescribed by the doctor, they always helped well, but recently they stopped helping, the bitterness appeared again and plus there was added pain in the right side. What to do?
Aly (10/27/2019 at 09:10 pm) Reply to comment
- First of all, you need to contact your doctor so that he can evaluate the changes, adjust your medication intake and, if necessary, refer you to other specialists. A surgeon may be needed to rule out appendicitis and other abdominal diseases that require surgery. You should not self-medicate.
Editorial staff of the portal UltraSmile.ru (02.11.2019 at 09:19) Reply to comment
Write your comment Cancel reply
Types of taste disorders
There are three main types of taste disorders:
1. Hypergeusia – increased taste sensations of a pathological nature. Patients complain of increased taste sensations. The most likely causes for the pathology are damage to cortical neurons and hypersensitization.
2. Hypogeusia and ageusia - a decrease in the intensity of taste sensations up to complete absence. The causes are various disorders and damage to the structures of the taste analyzer, for example, burns, neuritis, encephalitis and hemorrhages in the brain.
3. Dysgeusia is a pathological perversion of taste and inclinations to food. Pathology may be manifested by a desire to consume expired products or substances that pose a danger to health and life.
With lesions of the central nervous structures, false taste sensations are sometimes observed when sweets seem salty, for example. This pathology is called parageusia.