The pancreas is one of the most important organs involved in digestion, metabolic processes and the production of hormones. It has a complex structure and consists of different tissues. The pancreas is located deep in the abdominal cavity behind the stomach. Therefore, the pathological processes occurring in it can only be diagnosed using instrumental methods. The doctor does not always immediately discover that the patient has an enlarged pancreas. After all, the symptoms of such a condition may not be clearly expressed, and upon palpation it is impossible to determine this pathology.
Functions of the pancreas
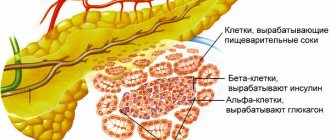
First you need to understand what role the pancreas plays in the human body. Unlike many other organs, it performs the functions of both external and internal secretion:
Exocrine secretion produces pancreatic enzymes that are necessary for the process of digesting food. In addition, it neutralizes the acidic environment of the gastric chyme, thereby preparing it for movement into the duodenum.
Internal secretion - inside the gland there are groups of cells that do not have excretory ducts. They secrete hormones that regulate carbohydrate metabolism directly into the systemic circulation.
Damage to the pancreas, as well as all its diseases, are considered very dangerous and require an urgent and correct treatment regimen.
Causes of reactive pancreatitis
The main cause of reactive pancreatitis is premature activation of enzymes produced by the pancreas. Normally, enzymes are activated only after they enter the intestines. But if the pancreatic duct is narrowed, for example, due to chronic diseases or alcohol abuse, stagnation of pancreatic juice occurs. As digestive enzymes accumulate, they begin to have a destructive effect on pancreatic tissue, which leads to severe inflammation and release of breakdown products into the blood.
The most common causes of reactive pancreatitis:1
- exacerbation of chronic pathologies: peptic ulcer, viral hepatitis, cholelithiasis;
- consumption of fatty, fried foods, alcohol;
- intestinal infections;
- food and industrial poisoning;
- endoscopic interventions on the biliary organs;
- abdominal injuries.
To determine the nature of damage to the pancreas and surrounding tissues, specialists may prescribe a comprehensive examination, which includes:1
- blood, urine and stool tests;
- ultrasound diagnostics of the digestive tract;
- X-ray examination;
- MRI, CT of the digestive system;
- endoscopic diagnosis.
In complex clinical cases, to clarify the diagnosis and choose the correct medical tactics, laparoscopy may be required - a microsurgery in which small (0.5-1.5 cm) incisions are made in the abdominal cavity to access the pancreas.
The main causes of gland enlargement
When a person has an enlarged pancreas, this is not considered a disease. In most cases, this may be a congenital trait that is harmless from a health point of view. To find out the exact diagnosis of the disease, you need to see a doctor and perform the appropriate studies and tests. Pancreatic enlargement can be divided into 2 types:
- Total, when the gland increases evenly over the entire surface.
- Local, when one part or area of the surface suffers. For example, when (the head of the pancreas is enlarged).
Reasons for complete enlargement of the gland:
- hereditary anomaly;
- toxic effects due to alcoholic beverages or the effect on the body of certain medications;
- damage to nearby internal organs.
Local enlargement of the pancreas:
- when cysts form;
- purulent contents;
- pancreatitis.
And this is an inexhaustible list of reasons for the development of this disease. Only the attending physician can identify the real cause by diagnosing the whole organism.
First aid when identifying signs of disease
You must begin fasting for at least 24 hours. Be sure to drink a lot of mineral water with a high content of alkalis. To relieve pain, apply ice on the left side just above the navel. Only a doctor prescribes tablets. But to relieve spasm and severe pain, you can drink Papaverine or No-shpa and immediately call a doctor at home. If the pain is acute, seek emergency help. Other medications should not be taken unless prescribed by a specialist.
It is important to know that pain appears for a reason; it warns of possible tissue necrosis. Signs of cancer can also begin with severe pain. This may result in complete removal of the organ.
The function of the pancreas is extremely important. If pain occurs in the corresponding place, you should immediately consult a doctor, since a malfunction of this organ can lead to irreversible changes in the body.
Reasons for local increase
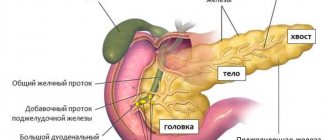
The structure of the pancreas is divided into three conventional parts: head (beginning), body (middle) and tail (end). Depending on the location of the pathological process, doctors may suspect different diseases.
An increase in a separate part of the secretory organ may indicate the presence of the following conditions:
- Pseudocyst.
- Abscess.
- Benign tumor.
- Malignant formation.
- Presence of stones.
- Duodenitis with inflammation of the intestinal papilla.
Local enlargement of the middle part of the organ is much less common than the head or tail.
Symptoms of enlargement
Very often the pathology does not manifest itself for a long time. But there are times when even a small deviation from normal parameters quickly makes itself felt. If a person has at least one symptom indicating a change in the size of the pancreas, one should immediately consult a doctor.
The doctor prescribes specific studies that will accurately determine the condition of the gland. You can suspect the presence of a pathology in the functioning of an organ by the presence of the following characteristic signs:
- There is pain in the upper abdomen. The intensity of pain may increase or decrease. Most often, patients who have dilated pancreas describe discomfort and pain, like a slight burning sensation in the abdominal cavity. In addition, some patients say that pain with an enlarged gland manifests itself in severe attacks. Pain that occurs in the peritoneal area can migrate to the left arm and to the lumbar region.
- Discomfort that appears in the stomach area may accompany an increase in body temperature to a level of 38-39 degrees. Most often, an increase in temperature is associated with the development of an inflammatory process in the tissues of the organ.
- The patient develops a feeling of nausea, which can be aggravated by vomiting and digestive disorders, manifested by diarrhea. When a malfunction occurs, a bitter taste is felt in the oral cavity.
The appearance of bitterness may indicate the influence of the increased volume of the pancreas on the normal functioning of the liver.
Methods for diagnosing the disease
Most often, patients with abdominal pain and digestive disorders turn to a therapist. His task is to find out why such symptoms appeared. It is impossible to make an accurate diagnosis based solely on external manifestations and examination of the patient, so an examination is prescribed. If a pancreatic dysfunction is suspected, ultrasound is most often prescribed. It is with the help of this examination that an increase in the size of an organ or its parts can be detected.
Additionally, an MRI may be prescribed. Sometimes, as a result of such an examination, diffuse enlargement of the gland is detected. This means that the organ is enlarged evenly over its entire surface, and there are no tumors or cysts. Blood tests are also important to make an accurate diagnosis. They help determine the content of necessary enzymes and hormones. Such a comprehensive examination allows you to timely identify the presence of serious pathologies and prevent complications.
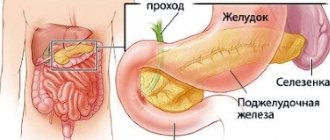
Characteristics of the gland
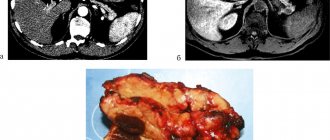
The pancreas is located behind the stomach at the level of the last two thoracic vertebrae, near the gallbladder. By palpation it is impossible to determine the size and change in either an adult or a child. This can only be done using scintigraphy, MRI or ultrasound. The specialists who conduct them do not have the right to write their diagnosis in the conclusion, but are only required to describe what they saw on the screen indicating the dimensions. Only a gastroenterologist can make a final diagnosis.
Very often, pancreatitis becomes the root cause of pain. This is inflammation of the pancreas.
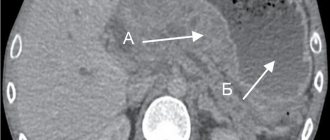
An ultrasound will immediately reveal a change in the size of the organ or a partial increase in a certain area of it - the tail or head. However, you should know that local enlargement is more dangerous, in contrast to general changes in the organ. In most cases, ultrasound examination reveals an increase in the size of the head of the pancreas. Normal head sizes are 18-26 mm, tail sizes are 16-20 mm (depending on the age of the person). This is considered the basis for diagnosing chronic pancreatitis in the acute stage. A fairly common disease that responds well to treatment.
When the disease worsens, changes are not immediately noticeable. More than 6 hours should pass between the attack of pain and the ultrasound.
It is important to draw the doctor’s attention to a partial increase in the size of the gland in a patient who has not previously complained of pain characteristic of pancreatitis. This may be evidence of the onset of cancer development. It is with oncology that local enlargement of the head or tail of the pancreas is characteristic. With pancreatitis, in addition to the general enlargement of the organ, the contours and echostructure also change.
If studies have revealed an increase in the size of the gland or its individual parts, the patient needs a more thorough examination and additional tests to make an accurate diagnosis and exclude cancer.
Treatment
Treatment of the pancreas is always complex. It includes:
- Special diet.
- Prescribing drugs that suppress the activity of the pancreas.
- Taking enzymes that compensate for insufficiency of pancreatic function.
If conservative treatment is ineffective, surgical intervention is resorted to.
The main goal of therapy is to eliminate the main cause that led to the pathological process in the pancreas. In parallel with this, symptomatic treatment is prescribed to alleviate the patient’s condition. Any medications, including painkillers, should only be prescribed by a doctor.
Groups of drugs that can be prescribed:
- Enzymes (Creon, Pancreatin).
- Antispasmodics (No-shpa, Spazmalgon, Meverin, Duspatalin).
- Antacids (Almagel, Maalox).
- Antibiotics (Clarithromycin, Amoxicillin).
- Blocking the enzymatic function of the organ (Omez, Ranitidine, Famotidine).
You can relieve the condition yourself with the help of still mineral water. The liquid helps remove excess pancreatic juice and also removes toxins from the entire body. After relief of the acute condition, the doctor will prescribe maintenance therapy and give a list of medications that the patient will take on his own. To monitor the condition of the pancreas, it is recommended to undergo examination by a gastroenterologist, even in the absence of complaints.
Treatment of inflammation of the tail and head of the pancreas
A gastroenterologist can recommend additional consultations with an infectious disease specialist, surgeon, or oncologist. Before visiting a doctor, you must adhere to several rules. Do not heat the abdominal area or drink alcohol. It is necessary to remove everything fried, fatty, smoked and spicy from your diet.
The main methods of treatment are properly organized dietary nutrition, physiotherapy and the use of special medications.
And only in rare cases is surgery required. A more detailed description of the course of treatment depends on the individual case, the course of the disease and the diagnosis.
Power control
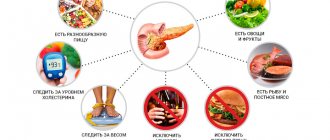
In order for treatment to be effective, it is necessary to identify the reason why the gland could increase in size. In any case, prescribing a diet is the first point in treatment. Most often, the diet consists of protein foods with a limited amount of fats and carbohydrates. The patient should forget about such products as:
- alcohol;
- dairy products with a high percentage of fat;
- broth and soups prepared with it;
- vegetables and fruits that have not undergone heat treatment;
- sweets and baked goods.
Products that are allowed:
- poultry, fish;
- fermented milk products;
- dietary bread;
- any cereals and pasta;
- steamed vegetables;
- weak tea;
- baked fruits.
When the pancreas greatly increases in size, a proper diet may not have any effect. For example, in cases of the development of cystic formations, only surgical intervention can help. This also applies to pancreatitis, which cannot be cured with diet alone.
When choosing products for cooking, you can rely on the following table:
| Forbidden | Allowed |
| Sweet products, creams | Natural sweets, dried bread, jam, honey, crackers, marshmallows |
| Fried, smoked, spicy | Chicken, lean fish |
| Legumes, all mushrooms | Low-fat lactic acid products |
| Sorrel, onion, garlic, radish | Porridge cooked in water |
| Carbonated drinks, alcohol | Dried fruit compote, jelly, sweet tea |
Below is a menu with which you can provide yourself with a complete and varied diet:
| Breakfast | Snack | Dinner | Afternoon snack | Dinner |
| Semolina porridge with apple and green tea; rice porridge with orange; oatmeal and jelly; rice porridge with crackers; barley porridge with honey | Pumpkin puree; baked apple; cottage cheese with honey and tea; steam cutlet and rosehip infusion; grated apple with cottage cheese and biscuits | Vegetable broth with boiled meat, crackers; carrot soup with other vegetables and meatballs, compote; vegetable puree soup, meatballs; low-fat steamed fish, mashed potatoes; rabbit cutlets, stew | Low-fat cottage cheese with fruit; low-fat yogurt with crackers, honey and apple; steam omelette; cottage cheese casserole; baked apple | Beef cutlet, compote; potato casserole with minced meat, jelly; baked fish with vegetables; mashed potatoes, steamed fish; vegetable casserole, boiled chicken |
At the end of the acute period, the patient can eat quite varied, the main thing is a gentle cooking regime.
Dangerous consequences of pathology
What to do if the pancreas is enlarged? Look for the cause of inflammation, and at the same time change your lifestyle and diet. Sometimes an enlargement of the pancreas in a child occurs during therapy with antibiotics and metronidazolam, as a side effect of the drugs. The doctor’s response when treating pancreatitis without symptoms is to observe and study the dynamics of the pathology. Treatment is necessary to avoid the development of complications.
Acute inflammation is fraught with diabetes mellitus, peritonitis, the appearance of cysts, and damage to neighboring structures. Chronic pancreatitis provokes enzymatic deficiency, disrupts the flow of bile, and increases the risk of stone formation. Complications relate to cell changes - cancer, ascites, chronic pain. The disease is becoming younger and is detected before the age of 5 years.