Published: 01/16/2018 Updated: 04/27/2021
An abundance of fatty foods and alcohol does not have the best effect on the functioning of the pancreas. But our well-being depends on how functionally stable it is.
In order not to provoke a pancreatic attack, it is important to remember the factors that negatively affect the condition of the pancreas. And if pain develops, immediately undergo an examination to diagnose pancreatitis.
Diagnosis of pancreatitis
Diagnosis of pancreatitis should begin with determining the main parameters of inflammation in the pancreas. To do this, you need to donate blood, urine and feces to CITILAB:
- 21-20-007 - Alpha amylase. The pancreatic enzyme increases in the blood during acute pancreatitis and necrosis of the pancreas.
- 21-20-009 - Lipase. The amount of enzyme that breaks down fats also increases sharply during the inflammatory process.
- 84-84-005 - Pancreatic elastase in feces. A decrease in the level of this enzyme indicates gland dysfunction.
Urine tests are necessary because the level of enzymes during inflammation increases in the urine an order of magnitude higher than in the blood:
- 21-85-007 - Alpha amylase in urine.
- 21-85-008 — Pancreatic alpha-amylase in urine.
In case of chronic pancreatitis, in order to reduce the likelihood of exacerbation, it is necessary to follow a special diet: give up alcohol, fatty foods, sweets and fast food, and also quit smoking.
Be healthy!
Total amylase in daily urine
Amylase is one of several enzymes that are produced in the pancreas and are part of pancreatic juice.
Synonyms Russian
Urine diastasis, urine amylase.
English synonyms
Urine Amy, Urine Alpha-amylase, Urine AML, Urine diastase, Urine amylase.
Research method
Kinetic colorimetric method.
Units
Units/day (unit per day).
What biomaterial can be used for research?
Daily urine.
How to properly prepare for research?
- Do not drink alcohol for 24 hours before the test, and do not drink diuretics for 2 days.
- Eliminate spicy, salty foods and foods that change the color of urine (for example, beets, carrots) from the diet 12 hours before the test.
- Avoid physical and emotional stress during the collection of daily urine (during the day).
General information about the study
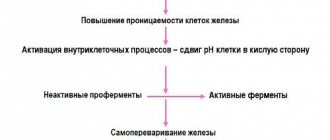
Amylase is one of several enzymes that are produced in the pancreas and are part of pancreatic juice. Lipase breaks down fats, proteases break down proteins, and amylase breaks down carbohydrates. From the pancreas, pancreatic juice containing amylase passes through the pancreatic duct into the duodenum, where it helps digest food. The amylase molecule is so small that it can pass through the kidney barrier and then be excreted in the urine.
Normally, only a small amount of amylase circulates in the bloodstream (due to the renewal of salivary and pancreatic cells) and enters the urine. When damage to the pancreas occurs, as in pancreatitis, or if the pancreatic duct is blocked by a stone or tumor, amylase begins to enter the bloodstream in large quantities and then into the urine.
This enzyme is also secreted by the salivary glands, the ducts of which open into the oral cavity. Therefore, its activity in urine may increase with pathology of the salivary glands.
Small amounts of amylase are produced in the ovaries, intestines, bronchi and skeletal muscles.
What is the research used for?
- For the diagnosis of acute or chronic pancreatitis, as well as for identifying other diseases involving the pancreas in the pathological process. As a rule, urine amylase activity corresponds to blood amylase activity, but rises and falls with a delay of 6-10 hours in comparison. After acute pancreatitis, urine amylase activity may remain elevated for up to 7-10 days, in contrast to blood amylase, which usually returns to normal after 2-4 days.
- To monitor treatment for cancer affecting the pancreas.
- To determine the efficiency of the kidneys (compare the activity of amylase in the blood and urine).
When is the study scheduled?
- For symptoms of pancreatic pathology: intense pain in the abdomen and back (“girdling pain”),
- temperature rise,
- loss of appetite,
- vomiting.
What do the results mean?
Reference values: 1 - 408 U/day.
Reasons for increased amylase activity in urine
- Acute pancreatitis. In this disease, amylase activity can exceed the upper reference value by 6-10 times. Typically, its activity in urine increases 6-8 hours after damage to the pancreas and can remain at a high level for up to 2 weeks. However, in some patients with acute pancreatitis, amylase may increase slightly or even remain normal. In general, its activity does not reflect the severity of damage to the pancreas in this disease.
- Chronic pancreatitis. With it, the activity of urine amylase is initially moderately increased, but then it can decrease and return to normal as the damage to the pancreas worsens.
- Trauma to the pancreas.
- Pancreas cancer.
- Blockage (stone, scar) of the pancreatic duct.
- Acute appendicitis, peritonitis.
- Perforation (perforation) of a stomach ulcer.
- Decompensation of diabetes mellitus – diabetic ketoacidosis.
- Impaired drainage in the salivary glands or salivary ducts, such as with mumps (mumps).
- Surgery on the abdominal organs.
- Acute cholecystitis is inflammation of the gallbladder.
- Intestinal obstruction.
- Aborted tubal pregnancy.
- Ruptured aortic aneurysm.
Reasons for decreased amylase activity in urine
- Pancreatic insufficiency, when its function decreases.
- Chronic renal failure.
- Severe hepatitis.
- Cystic fibrosis (cystic fibrosis) of the pancreas is a severe hereditary disease associated with damage to the exocrine glands (lungs, gastrointestinal tract).
- Removal of the pancreas.
- Macroamylasemia is a rare benign condition where amylase binds to large proteins in the serum and therefore cannot pass through the glomeruli.
What can influence the result?
- Urine amylase activity is increased in pregnant women.
- Captopril, corticosteroids, oral contraceptives, furosemide, ibuprofen, and narcotic analgesics can increase amylase activity.
Important Notes
Amylase activity in children is low in the first two months of life; it rises to adult levels only by the end of the first year.
Also recommended
- Serum total amylase
- Milase pancreatic
- Lipase
Who orders the study?
General practitioner, therapist, gastroenterologist, surgeon.
What is amylase, what is this enzyme needed for?
Metabolism in the body is the basis of its functioning. A large number of different substances are involved in this process. In particular, we are talking about enzymes and acids. Their constant exposure helps to provide humans with useful substances and minerals.
As the body works, substances are formed that need to be removed from the body. This occurs through the release of feces, urine and sweat.
If you conduct a urine test, then knowing its composition will help you learn a lot about the processes occurring in the body and its condition. In particular, this will tell us about the inflammatory processes occurring in humans, despite the fact that at the moment their external signs may not appear.
Amylase is one of the enzymes that is produced by the pancreas and along with saliva. It serves to break down carbohydrates that enter the body with food. It is excreted from the body along with urine. Based on the chemical composition and amylase content in urine, conclusions can be drawn about the condition of the pancreas.
This enzyme can be of two types:
- S amylase. It is produced by the body along with saliva. The enzyme thus obtained constitutes approximately 60% of its total supply.
- P amylase also has another name: pancreatic amylase, which is produced by the pancreas. Its share in the body is about 40%.
As soon as the process of eating begins, when it enters the oral cavity, the process of breaking down into elements useful for the body begins: proteins, carbohydrates, fats, and so on. When food enters the stomach, hydrochloric acid partially suppresses the action of those enzymes contained in saliva, but those produced by the pancreas enter there. The breakdown of carbohydrates ends when food enters the duodenum.
General information
The enzyme is a component of pancreatic juice and is responsible for the breakdown of carbohydrates. The concentration of the enzyme in the blood is normally low. Pancreatic juice enters the duodenum and is involved in the process of food digestion. The presence of the enzyme in the blood is normally explained by the renewal of the cells in which it is contained. The release of amylase into the blood in large quantities is most often caused by a blockage of the pancreatic duct (for example, a tumor or stones) or significant damage to the pancreas.
This test is of high importance in the diagnosis of pancreatitis
and a number of other diseases in which the pancreas is involved in the pathological process. It is often prescribed in conjunction with a blood test for lipase (an enzyme that is responsible for the breakdown of fats). Also, the test results are used to monitor the condition of patients with cancer that affects the pancreas; assessing the results of surgical intervention.
4.Treatment
Not so frequent cases of conditionally normal darkening of urine under the influence of controlled situational factors (and restoration of color in a natural way) are discussed above. As for pathological causes, then, of course, therapeutic prescriptions will be determined by the entire complex of diagnostic data and individual anamnestic information. It is unrealistic to identify all possible schemes or at least directions of treatment in this case.
However, again and again we draw attention to the fact that the timeliness of seeing a doctor is not just important - this factor can have a critical, life-saving significance.
Decoding the results
The norm of total amylase is 28-100 U/l. The pancreatic enzyme concentration is interpreted in relation to the total amount of amylase. The most common cause of elevated readings is pancreatitis. In acute illness, values can exceed the norm by 6-10 or more times. It remains high for 3-5 days. If the readings are several times higher than normal, the pain is most likely caused by damage to the pancreas. It must be taken into account that in some patients with acute pancreatitis, enzyme activity remains within normal limits or increases slightly. The severity of the disease cannot be judged from the results of this test. For example, if most of the cells that produce the enzyme die, its activity remains within normal limits. With a chronic disease, the indicators first increase and then gradually decrease. Most often, chronic disease develops in alcoholics. An increase in the amount of the enzyme can be explained by other reasons (for example, pancreatic malignancy, peritonitis, pregnancy).
A decrease in the amount of the enzyme is observed in patients with high cholesterol, severe hepatitis, decreased pancreatic functionality, and cystic fibrosis. To obtain an interpretation of the results and further recommendations, you should consult a doctor. In many cases, if indicators are violated, the patient requires immediate medical attention. Self-medication is unacceptable, as it can cause irreversible pathological changes in the body.
3. Symptoms and diagnosis
Having noticed intense darkening of urine, you should first of all inspect your own well-being and analyze what situational factors this phenomenon may be associated with. If such factors are found and there are no other disturbances, it is usually enough to restore the water balance and/or normalize the diet so that the urine acquires a natural color within one to two days.
If dark urine is accompanied by disturbances in well-being or signs of any dysfunction, you should consult a doctor immediately: wait-and-see tactics in such cases can pose a very real risk to health and life. At an appointment with a urologist, gynecologist, andrologist, nephrologist (depending on which specialist intuitively seems most logical in a particular situation), you will need to answer a number of questions, and you need to be prepared for this: the urine has just darkened or become cloudy; the shade changed to brown, red, dark orange; whether there is an unusual smell; are there any impurities of blood, pus, mucus, and if so, how much and what kind (flakes, threads, foam, clots, etc.); whether the frequency and volume of urination has changed; what is the nature and localization of painful sensations; what is the chronology and dynamics of the development of disorders, etc.
Based on the results of a clinical interview, external examination and palpation examination, laboratory tests will be prescribed (needless to say, the first on the list will be a urine test) and instrumental diagnostics (ultrasound, CT, MRI, urocystoscopy, one or another radiographic technique).
About our clinic Chistye Prudy metro station Medintercom page!