Sigmoidoscopy is a diagnostic method that most of us have not heard of. Meanwhile, this research method is widely used to diagnose diseases of the genitourinary area, rectum and sigmoid colon. Most often, the diagnostic procedure is prescribed by a proctologist.
Together with our experts, we found out how sigmoidoscopy is performed and to whom it is prescribed. We also learned about the nuances of preparing for sigmoidoscopy - diet, medications and cleansing procedures.
What is sigmoidoscopy
Sigmoidoscopy is an examination of the rectum and sigmoid colon. The procedure is performed using a special device - a rectoscope. This is a tube or tube with a diameter of 1.8–2 cm and a length of approximately 35 cm with a light, camera, magnifying lens and an air supply system. Tubes are made from a variety of materials, but nowadays they usually use disposable plastic ones.
A proctoscope is inserted into the patient’s anus to examine the condition of the intestinal mucosa to a depth of approximately 30 cm. During the examination, the image from the camera is transmitted to the monitor; the equipment also allows you to enlarge the picture and make a recording.
Sigmoidoscopy can be combined with other diagnostic and therapeutic procedures. During the procedure, you can remove the foreign body, cauterize the bleeding vessel, remove the polyp and take tissue for a biopsy. In this case, a proctoscope with operating equipment is used.
Device structure
Patients often do not know what rectoscopy is and how it is done, imagining a painful and even dangerous procedure. In fact, the study rarely gives complications, and it is carried out using a rectoscope (sigmoidoscope). The instrument is a tube made of metal, which has flower growers, various tubes and a lighting system.
Due to the design features of the device, preparation for rectoscopy is carried out not only for the patient, but also for the rectoscope itself. It is carefully treated with disinfectants so as not to pose the slightest danger to the person being examined.
The following procedures can be performed using a rectoscope:
- Visual assessment of the condition of the distal parts of the intestine (i.e., diagnosis);
- Tissue biopsy from suspicious areas;
- Pulling out foreign objects;
- Elimination of polyps and other similar formations;
- Electrocoagulation;
- Stopping bleeding using coagulation.
In some cases, a simple diagnosis ends with therapeutic measures, which is very convenient for both the patient and the doctor. The ability to simultaneously examine the intestines and perform some therapeutic procedures can reduce risk and trauma for the patient, as well as save the doctor’s time.
Indications for sigmoidoscopy
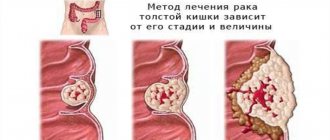
With the help of endoscopic examination of the rectum and sigmoid colon, inflammatory processes, developmental anomalies, foreign bodies, injuries, hemorrhoids, benign and malignant neoplasms are identified. The procedure is prescribed to patients who have been diagnosed or suspected of having diseases such as:
- BPH;
- internal hemorrhoids;
- polyps of the rectum and sigmoid colon;
- ulcerative colitis;
- anal fissures, fistulas and abscesses;
- malignant tumors of the rectum and sigmoid colon.
To the point
Intestinal irrigoscopy: what to prepare for and why this procedure is needed
As a rule, these pathologies are accompanied by characteristic symptoms: pain during bowel movements, bleeding from the rectum, chronic constipation. But it also happens that the disease is asymptomatic. In this case, the doctor may prescribe a preventive examination if the patient is at risk (age over 45 years, cancer of the rectum and sigmoid colon in close relatives).
Sigmoidoscopy is often performed before surgery. For example, in patients diagnosed with rectal cancer, a study is used to determine the location of the tumor in order to select the optimal surgical tactics.
Contraindications
An absolute contraindication is the patient's serious condition:
- severe general condition of the patient;
- cicatricial narrowing of the rectum
- cardiovascular or respiratory failure;
- lack of consciousness due to stroke or traumatic brain injury.
Relative contraindications:
- massive intestinal bleeding;
- acute inflammatory processes of the anus and rectum;
- exacerbation of hemorrhoids with node thrombosis;
- acute fissure of the anal area and/or rectum.
Preparation for sigmoidoscopy
An endoscopic examination can only be performed if there is no food, gases or feces in the intestines. Therefore, in preparation for sigmoidoscopy, they follow a diet, take laxatives and do cleansing procedures.
Diet with menu
During preparation for sigmoidoscopy, they switch to a low-slag diet. 2-3 days before the procedure, you need to avoid foods that cause gas formation. These are legumes, rye bread, fresh fruits, cabbage, beets, greens, alcohol, kvass, juices and carbonated drinks.
Hemorrhoids in women
When women are most susceptible to developing hemorrhoids: talking to doctors
On a diet before sigmoidoscopy you can eat:
- dietary meat;
- fermented milk products;
- porridges other than pearl barley, oatmeal and millet;
- weak broths.
There is no dinner on the eve of the examination, only tea is allowed. On the day of the procedure, you must refuse food.
Drugs
Bowel cleansing drugs are used as an alternative to enemas. To prepare for sigmoidoscopy, specialized medications are used, such as Moviprep, Picoprep, Phosphoflit. Forlax,. The most effective are drugs based on macrogol, a substance that retains water in the intestinal lumen and thereby increases osmotic pressure and peristalsis. Drugs from this group include Fortrans and Moviprep.
show more
Enema
To cleanse the intestines, you can use ready-made microenemas, for example, Microlax and Enema-Clean. These are saline solutions for rectal administration that have a laxative effect. Microclysters are given several hours before the procedure.
show more
You can use the classic method - give an enema using an Esmarch mug. In this case, 1.5 liters of water at a temperature of about 36˚C is injected into the rectum. Purification is carried out until the rinsing waters become clean. The procedure is performed the day before the examination and again the next day, no later than 4 hours before the procedure.
Approximate diet
3 days before the procedure:
- Breakfast: 200 ml tea, oatmeal, 1 piece of toast.
- Second breakfast: 250 ml low-fat fermented baked milk.
- Lunch: chicken broth, 2 steamed meatballs, cucumber salad.
- Afternoon snack: cottage cheese casserole and compote.
- Dinner: biscuits and 250 ml of low-fat kefir.
In 2 days:
- Breakfast: hibiscus, buckwheat, 1 slice of white bread.
- Second breakfast: 250 ml of dairy products.
- Lunch: steamed sea fish, rice porridge and juice.
- Afternoon snack: low-fat yogurt.
- Dinner: tea and semolina porridge.
For 1 day:
- Breakfast: 1 soft-boiled egg, toast and fruit compote.
- Lunch: green tea, broth and low-calorie cookies.
Due to the fact that therapeutic nutrition is designed solely for cleansing the body, it is recommended to reduce physical activity. The diet will help stabilize intestinal activity and reduce the formation of gases.
How is sigmoidoscopy performed?
Before the procedure, the patient removes all clothing from the lower part of the body, puts on disposable underwear and stands on a special couch in a knee-chest position or lies on his side. Then the doctor performs an external examination and palpation of the anal canal to identify eczema, external hemorrhoids, polyps, and rectal prolapse. After this, a tube is inserted into the anus, which has been previously lubricated with petroleum jelly or a special gel. The device is inserted gradually using rotational movements, up to the distal sigmoid colon (to a depth of approximately 30 cm from the anus).
During the examination, air is pumped through the tube so that the folds of the mucous membrane straighten out and all the areas being examined become visible. After all manipulations are completed, the sigmoidoscope is carefully removed. On average, the procedure takes from 10 to 30 minutes, depending on the anatomy of the intestine and the complexity of diagnosis.
Hemorrhoids in men
The main methods of treating hemorrhoids in men used today
Types of rectoscopy:
Anoscopy
During anoscopy, a small hose called an anoscope is used for diagnosis. Thanks to it, it is possible to inspect the area of the last 5 cm of the anal canal. The examination can be carried out at any time; special bowel cleansing is not required.
Proctoscopy
To study the condition of the rectum, proctoscopy is performed. Using a proctoscope, consisting of a hose 8-15 cm long and a magnifying optical system, the proctologist can see the anus and the area of the lower intestine. Before proctoscopy, you need to drink a laxative or do an enema to cleanse the intestines.
Sigmoidoscopy
Sigmoidoscopy allows you to examine the sigmoid intestine, collect material for a biopsy and detect colon cancer at an early stage. For this study, a light, long and flexible hose is used - a sigmoidoscope. Before the examination, you should follow a diet consisting of broth and liquid for 1-2 days.
1 Preparing the device for rectoscopy
2 Preparing the device for rectoscopy
3 Preparing the device for rectoscopy
Popular questions and answers
Sigmoidoscopy can be prescribed to people of all ages as part of a preventive examination and if a specific disease of the rectum and sigmoid colon is suspected. Therefore, it would be a good idea to find out how painful this procedure is and what complications it can cause. Our experts answer readers’ questions: surgeon, coloproctologist Tatyana Gavrilova and candidate of medical sciences, surgeon of the highest category Maksud Magomedov .
How is sigmoidoscopy different from colonoscopy?
Colonoscopy also refers to endoscopic research methods, but allows you to examine the entire large intestine, and sigmoidoscopy – only part of it. The inspection equipment also differs. For colonoscopy, a colonoscope is used - a long probe with a camera. Unlike sigmoidoscopy, colonoscopy is done under general anesthesia—the patient is put into a medicated sleep for 10–15 minutes. During sigmoidoscopy, anesthesia is performed only if an operating device is used.
Will it hurt during a sigmoidoscopy?
According to patient reviews, sigmoidoscopy is a painless, although not very aesthetic, procedure. Unpleasant sensations may occur when air is pumped into the intestines through the device. All other manipulations do not cause discomfort. Many reviews of sigmoidoscopy say that waiting for the procedure caused more negative emotions than the examination itself.
What should be done after sigmoidoscopy?
After the examination, patients lead a normal lifestyle. There is no need to follow a diet or take any medications.
What complications may arise?
The likelihood of complications during and after the procedure is minimal.
Theoretically, damage to the rectal wall is possible, but this happens in exceptional cases. A sign of injury to the mucous membrane is bleeding from the anus. In this case, you should immediately consult a doctor. Sigmoidoscopy is considered a safe method of examination and is suitable even for infants. During the examination, there is no radiation exposure to the body, so the procedure can be repeated as many times as necessary for diagnosis and monitoring of therapy. Sources:
- Rectoromanography. Standardization of the procedure. Recommendations. Central Clinical Hospital No. 6 of Yekaterinburg https://endoexpert.ru/vse-dlya-raboty/sop-rektoromanografiya/
- Preparation for endoscopic examination of the intestine. https://medexpert.website/download/podgotovka2.pdf
- Journal "Current issues of endoscopy". Methodological recommendations for preparing patients for endoscopic examinations. https://clck.ru/ajsmW
What information does this diagnostic method provide?
Professional interpretation of the results of rectoscopy is carried out by comparing the data obtained during the examination with standard indicators. When a neoplasm or inflammatory process is identified, the doctor describes their nature, size, and location. The results of the examination are given to the patient on the day of the examination. He should contact his doctor about them.
Simferopol Women's Health Clinic “Femina” offers a wide range of instrumental diagnostic tests. We employ experienced specialists. The clinic is equipped with modern medical diagnostic equipment. Make an appointment by phone or online via online registration.
Sigmoidoscopy (rectoscopy)
Sigmoidoscopy (rectoscopy) is a method of endoscopic examination of the rectum and distal sigmoid colon by examining their internal surface using a sigmoidoscope inserted through the anus.
Sigmoidoscopy is the most common, accurate and reliable method for examining the rectum and lower sigmoid colon. In the practice of a coloproctologist, sigmoidoscopy is a mandatory component of every proctological examination. This study allows you to visually assess the internal surface of the rectum and distal third of the sigmoid colon to a level of 20-35 cm from the anus.
Rectoscopy, performed for preventive purposes, is becoming increasingly widespread. As a preventive measure for the early diagnosis of malignant neoplasms of the rectum, people over 40 years of age are recommended to undergo sigmoidoscopy once a year.
With skillful use of a rectoscope, this procedure is painless or slightly painful and does not require preliminary anesthesia.
Contraindications
There are practically no contraindications to examining the intestine through a sigmoidoscope. However, in some conditions and diseases (profuse bleeding from the intestine, narrowing of its lumen of a congenital or acquired nature, acute inflammatory diseases of the anal canal and abdominal cavity, acute anal fissure), the study is postponed for some time (for example, during a course of conservative therapy) or is performed with great caution when placing the patient in gentle positions or after anesthesia.
Sigmoidoscopy technique
To undergo the examination, you will need to remove all clothing from the waist down, including underwear, and then be assisted on a couch on all fours.
Sigmoidoscopy is performed only after direct digital examination of the rectum. Sigmoidoscopy with rigid tubes is usually performed in the knee-elbow position of the patient. This position is very convenient for examination: the anterior abdominal wall seems to sag a little, which makes it easier to pass the tube from the rectum to the sigmoid colon.
The assembled sigmoidoscope, after checking the operation of the lighting system and lubricating the tube with Vaseline or a special gel, is inserted into the anus along the longitudinal axis of the anal canal to a depth of no more than 4-5 cm. Then the obturator is removed, and all further sigmoidoscopy is performed only under visual control. The tube is passed so that its edge does not rest against the intestinal wall, but follows strictly along the intestinal lumen, while air is constantly pumped into the intestine.
When performing sigmoidoscopy, attention is paid to the color, shine, moisture, elasticity and relief of the mucous membrane, the nature of its folding, features of the vascular pattern, the presence of pathological changes, as well as to evaluate the tone and motor function of the examined sections.
When performing sigmoidoscopy, attention is paid to the color, shine, moisture, elasticity and relief of the mucous membrane, the nature of its folding, features of the vascular pattern, the presence of pathological changes, as well as to evaluate the tone and motor function of the examined sections.
Complications
Sigmoidoscopy is a safe procedure. Complications (perforation of the intestinal wall, etc.) with methodically correctly performed rectoscopy are extremely rare. In case of perforation of the rectum, emergency surgery is indicated.
Preparation for sigmoidoscopy
Option #1
An important condition for performing sigmoidoscopy is thorough cleansing of the colon from contents. On the eve of rectoscopy, the patient is prescribed a low-slag diet during the day, and only tea in the evening. The study is carried out on an empty stomach.
To prepare the intestine for examination, it is cleaned using enemas (1.5-2 liters of plain water at body temperature). It is advisable to do the first enema the evening before the examination; approximately 3-4 hours before the examination, 2 more enemas are given with a 45-minute break.
An Esmarch mug is used to perform a cleansing enema. It can be bought at almost any pharmacy
An Esmarch mug is a reservoir (glass, enamel or rubber) with a capacity of 1.5-2 liters. At the bottom of the mug there is a nipple onto which a thick-walled rubber tube is placed. For a rubber reservoir, the tube is its direct continuation. The length of the tube is about 1.5 m, the diameter is 1 cm. The tube ends with a removable tip (glass, plastic) 8-10 cm long. The tip must be intact, with smooth edges. It is preferable to use plastic tips, since a glass tip with a chipped edge can seriously injure the intestine. After use, the tip is washed well with soap under running warm water and boiled. Next to the tip on the tube there is a tap that regulates the flow of fluid into the intestines. If there is no tap, it can be replaced with a clothespin, clamp, etc.
For enemas, use only water from a proven source (one that is safe to drink). For children, it is better to use only boiled water. The water temperature is about 37-38 degrees. Colder water significantly increases intestinal motility and causes unpleasant pain. Using water with a temperature of more than 40 degrees for an enema is dangerous to health.
One way to perform an enema is as follows. Lie on the bed close to the edge on your left side with your legs bent and pulled towards your stomach. Place an oilcloth (plastic film) under your buttocks, and lower the free edge of it into a bucket in case you cannot hold water. Pour 1-1.5 liters of water at room temperature into Esmarch's mug, lift it up to a height of 1-1.5 m and lower the tip down to release a small amount of water and along with it air from the tube. Fill the tube (drain some liquid from the tube), then, without lowering the mug, close the valve on the rubber tube. Check if the tip is broken, lubricate it with Vaseline (soap, vegetable oil) and, spreading the buttocks, insert the tip into the anus with light rotational movements. The first 3-4 cm, insert the tip towards the navel, then another 5-8 cm - parallel to the tailbone. If there are obstacles and the tube rests against the intestinal wall or hard feces, remove it 1-2 cm and open the tap. Pressurized water will enter the large intestine. Almost immediately there will be a feeling of “fullness” in the intestines and an urge to stool. At these moments, you need to reduce the flow rate of liquid from the mug by closing the tap on the tube or squeezing it. Gentle circular stroking of the abdomen will help reduce discomfort.
If the tip is clogged with feces, it should be removed, cleaned and reinserted. If your rectum is filled with stool, try flushing it out with a stream of water. Esmarch's mug does not need to be completely emptied. Leaving a little water at the bottom to prevent air from entering the intestines, close the valve that regulates the flow of liquid and remove the tip. Place a pre-prepared pad (cloth, repeatedly folded toilet paper, etc.) on the perineum, which must be pressed between the legs.
Option No. 2
Preparation for colonoscopy with the drug “Fortrans” (France). The drug "Fortrans" is intended for preparing the gastrointestinal tract for diagnostic studies (including colonoscopy and irrigoscopy) as well as for surgical interventions on the intestines.
The required degree of cleansing of the large intestine is achieved:
- no cleansing enemas
- without additional laxative intake
- without long-term adherence to a slag-free diet
- without outside help
- without abdominal pain and excessive gas formation
The drug solution has a fruity taste. This type of preparation is ideal for patients with diseases of the liver, gallbladder and pancreas.
The action of the drug is based on the combination of a high molecular weight polymer with an isotonic solution of electrolytes, which prevent the absorption of water from the stomach and intestines. The solution promotes accelerated bowel emptying. The presence in the solution of electrolytes corresponding to the osmotic pressure of physiological solution replenishes the intestinal secretion of potassium, sodium, chlorine bicarbonate, and therefore there are no changes in the composition of body fluids.
There are two possible types of preparation with Fortrans:
A. One-stage preparation with Fortrans.
The day before (the day before the test), exclude vegetables, fruits, potatoes, berries, mushrooms, and greens from your diet. On the day of colonoscopy, you can only drink sweet tea and boiled water.
On the day of colonoscopy, depending on your weight (up to 50 kg - 2 sachets, 50–80 kg - 3 sachets, over 80 kg - 4 sachets), the drug is diluted in water boiled at room temperature at the rate of 1 sachet per 1 liter of water, the required amount of solution Drink on the day of colonoscopy from 5-6 to 10 am in fractional portions (a glass every 15-20 minutes). The solution can be washed down with boiled water. The stool begins to pass 1.0-1.5 hours after starting to take the drug and stops 2-3 hours after taking the last dose of the drug.
On the day of the test, before the colonoscopy, you can drink a cup of sweet tea. Colonoscopy may be performed no earlier than 4 hours after the last dose of the drug.
B. Two-stage preparation with the drug “Fortrans”.
Preparation is carried out both on the eve of the colonoscopy and on the day of the study. On the eve of the colonoscopy, breakfast is allowed until 12 noon (semolina, yogurt, scrambled eggs, tea). After 12.00 clear broth, tea, and boiled water are allowed.
On the eve of the colonoscopy, depending on your weight (up to 50 kg - 1 sachet, 50-80 kg - 2 sachets, over 80 kg - 3 sachets), the drug is dissolved in water boiled at room temperature at the rate of 1 sachet per 1 liter of water. The required amount of solution is drunk from 17 to 20-21 hours in fractional portions (a glass every 15-20 minutes). The solution can be washed down with boiled water. The stool begins to pass 1.0-1.5 hours after starting to take the drug and stops 1-3 hours after taking the last dose of the drug.
On the day of colonoscopy, from 7 to 9 a.m., drink another 1 liter of solution at the rate of 1 sachet per 1 liter of water. After taking the last dose of the drug, stool stops after 1-2 hours. The solution can be washed down with boiled water. Colonoscopy may be performed no earlier than 4 hours after the last dose of the drug.
During the days of preparation for a colonoscopy, you can take the medications you need, with the exception of iron supplements and activated carbon.
Emergency colonoscopy in patients with intestinal obstruction and bleeding can be performed without preparation. It is effective when using special endoscopes with a wide biopsy channel and active irrigation of the optics.
Sigmoidoscopy in children
Indications for sigmoidoscopy in children include bleeding from the lower parts of the digestive tract of varying intensity and frequency, a symptom of incomplete bowel movement, prolapse of tumor-like formations, hemorrhoids, and intestinal walls. Using sigmoidoscopy, it is possible to recognize nonspecific ulcerative colitis, acute and chronic proctosigmoiditis, developmental anomalies of the distal colon, tumors and other pathological processes.
Contraindications include diffuse peritonitis, severe inflammatory changes in the anal and perianal area, and a significant degree of narrowing of the anus. Preparation for the study includes a cleansing enema the evening before the study and in the morning 11/2-2 hours before the study. In case of intended endoscopic interventions, the same preparation is indicated as for colonoscopy.
The sigmoidoscopy technique in children of the older age group does not differ compared to adult patients. For young children, sigmoidoscopy is performed under general anesthesia, in the supine position. Pay attention to the condition of the mucous membrane - its color, the nature of the surface, shine, vascular pattern, the presence of overlaps, the severity of haustration.
To perform sigmoidoscopy in children, special children's rectoscopes with replaceable tubes of different diameters and a set of instruments for endoscopic interventions are used.
← previous article archive of articles next article →