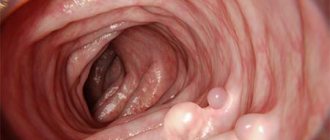
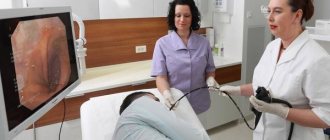
Diseases of the large intestine occur in people of all ages. Modern research methods, including irrigoscopy, help make an accurate diagnosis. However, most patients have not heard of this procedure or do not know why and how it is performed.
We talked to our experts about how intestinal irrigoscopy is performed and why it is prescribed. We also learned how to prepare for the procedure, what diet to follow and what medications to take.
What is intestinal irrigoscopy
Irrigoscopy is an x-ray examination of the large intestine, which helps diagnose diseases and developmental abnormalities. The procedure is performed using an X-ray contrast agent based on barium sulfate or sodium amidotrizoate. It is administered using an enema, after which X-rays (irrigograms) are taken.
A radiopaque mixture fills the intestine and helps visualize all areas of the mucous membrane. Thanks to this, the doctor can assess the location, thickness and structure of the intestinal walls, see the narrowing and expansion of the lumen, foreign bodies and neoplasms. If necessary, double contrast is used: after bowel movement, it is filled with air and a series of photographs is taken again.
The X-ray contrast mixture does not dissolve, but is excreted unchanged from the body for several days after the procedure.
Indications for intestinal irrigoscopy
An X-ray examination of the large intestine is prescribed by a doctor to identify or exclude problems characteristic of this part of the gastrointestinal tract. Previously, the patient is prescribed other examinations: blood and urine tests, ultrasound of the abdominal cavity. Based on the examination results, the doctor decides to perform intestinal irrigoscopy.
Good to know
How to reduce the risk of developing hemorrhoids during pregnancy?
X-ray examination is indicated for patients who have previously been diagnosed with the following conditions:
- polyps and other neoplasms;
- Crohn's disease;
- diverticulosis;
- dolichosigma;
- intestinal obstruction;
- ulcerative and ischemic colitis;
- presence of foreign bodies;
- Hirpschrung's disease.
Patients with these diseases usually complain of standard symptoms: stool problems, flatulence, pain and heaviness in the abdomen, painful sensations during bowel movements, and the appearance of blood in the stool. However, the doctor will not prescribe an x-ray based on symptoms alone, but will refer the patient for a preliminary examination. X-rays are most often used to clarify the diagnosis and assess the need for surgical intervention.
Contraindications to intestinal irrigoscopy
Intestinal irrigoscopy has contraindications, like most medical procedures. X-ray examination is not prescribed for pregnant women, people with allergies to contrast agents and patients after recent surgery.
X-rays are contraindicated in people with severe cardiovascular disease, progressive ulcerative colitis and toxic megacolon.
To the point
How to treat hemorrhoids in men: pills, diet or surgery
Indications
The irrigoscopy method is used to diagnose the following diseases:
- Fistulas;
- Tumors in the large intestine;
- Megacolon;
- Spikes;
- Scarring;
- Diverticula;
- Inflammation in the colon (chronicle).
Irrigoscopy is prescribed when:
- The functioning of the intestines (large) is impaired;
- There are difficulties with defecation;
- There are abdominal pains, but the causes are unclear;
- An inflammatory process in the intestinal area is suspected;
- There are substances of a different color in the feces;
- There are recurrent formations;
- They want to assess the consistency of anastomoses in the intestines.
Preparation for intestinal irrigoscopy
Proper preparation for intestinal irrigoscopy greatly influences the outcome of the procedure. X-ray examination will be useless if there are feces and food debris in the lumen of the large intestine. Therefore, before intestinal irrigoscopy, they follow a diet and perform cleansing procedures.
Diet
The diet before intestinal irrigoscopy should be low-slag. Allowed are weak broths, low-fat fermented milk products except cottage cheese, white fish and dietary meats: chicken breast, rabbit and turkey. Avoid foods that cause gas from your diet:
- fresh vegetables - cabbage, legumes, beets;
- greenery;
- fresh fruits - bananas, apples, apricots, oranges;
- Rye bread;
- oatmeal, pearl barley and millet porridge.
You need to eat in small portions, and steam or boil foods. It is recommended to drink up to 2 liters of liquid - fruit drinks, compotes, plain water and weak tea. Lunch on the eve of the procedure should be light; dinner and breakfast should be avoided.
Drugs
Preparation for irrigoscopy includes taking laxatives, which speed up the cleansing of the large intestine. The medicine and dosage regimen are prescribed by the doctor. Fortrans, Duphalac, Endofalk, and Picoprel are often used as laxatives.
2–3 days before the procedure, you should stop taking medications that increase or decrease intestinal motility. These drugs include papaverine, no-spa, drotaverine, metoclopramide, halidor.
Enema
A cleansing enema is done in the evening and in the morning. During the procedure, 2–2.5 liters of liquid are gradually introduced into the intestines. Enemas are repeated until the water becomes clear without any admixture of feces. The cleansing procedure is not indicated for everyone; for example, it is not performed by patients with gastrointestinal bleeding and ulcerative colitis.
Features of the study
To examine the intestines, two types of high-contrast water-soluble substances are used:
- the first contains barium sulfate (this is the main substance), tannin (for better adhesion of the substance in the digestive tube), sodium citrate, gelatin or cellulose (to increase the viscosity of the drug);
- the second type of contrast is sodium amidotrizoate (Verografin or Urografin). This is a rather expensive drug, it is used only in certain cases - in newborns with suspected various gastrointestinal anomalies or at any age with suspected perforation of the intestinal wall.
The medicine is introduced into the intestines through the rectum using a contrast enema. For one study, approximately half a liter of solution is needed. In some cases, air is also injected into the anus (as a low-contrast agent) for better visualization of the organ. Air helps determine the thickness of the organ wall and mucosal folds.
Double contrast is a method for a more detailed study of the condition of the mucosa. This method is preferable for identifying local tumor relapses or relapses in the area of postoperative anastomosis. It is not used for intestinal obstruction, in weakened patients, with severe intestinal diverticulosis (prevents the search for tumors) or with a long colon.
The most common technical difficulties during irrigoscopy:
- Poor preparation and residual stool in the intestine, making visualization difficult.
- Patient incontinence of contrast agent.
- Insufficient filling of the right intestine with contrast.
- Perforation of a pathologically altered rectum when filled with contrast.
Particular care should be taken when prescribing contrast examinations to patients, because in most cases it is impossible to predict the body's reaction. The patient may experience allergic reactions and anaphylactic shock.
It is also very important that the radiologist who conducted the study deciphers the study.
Where is intestinal irrigoscopy performed?
This is a non-invasive procedure that is done in x-ray rooms in hospitals and outpatient clinics. X-ray examinations are performed in clinics, hospitals and diagnostic centers.
By the way
How to deal with intestinal obstruction in adults
Fully or partially limited products
The diet of a slag-free diet provides for the complete exclusion of fatty meats and meat products (canned food, smoked sausages, bacon, ham), marinades, smoked meats, animal fats, all raw vegetables and root vegetables (radishes, cabbage, garlic, carrots, turnips, beets, onions), garden greens, coarse porridges (oatmeal, pearl barley, millet), fatty varieties of white and red fish, mushrooms, legumes (lentils, peas, beans, beans), which cause increased gas formation in the intestines, rye bread, fruits (grapes, pear, peach, bananas , tangerines, apple), dried fruits and all types of nuts and berries.
Whole milk and dairy products - cream, sour cream (with the exception of fermented milk) are excluded from the diet. It is not allowed to consume chocolate, any pastries and sweets, coffee, juices with pulp and nectars, confectionery products (cakes, cakes, cookies), sweets, carbonated drinks, seasonings. Drinking alcohol-containing and sweet carbonated drinks is strictly prohibited.
Table of prohibited products
| Proteins, g | Fats, g | Carbohydrates, g | Calories, kcal | |
Vegetables and greens | ||||
| beans | 6,0 | 0,1 | 8,5 | 57 |
| peas | 6,0 | 0,0 | 9,0 | 60 |
| Brussels sprouts | 4,8 | 0,0 | 8,0 | 43 |
| cauliflower | 2,5 | 0,3 | 5,4 | 30 |
| bulb onions | 1,4 | 0,0 | 10,4 | 41 |
| carrot | 1,3 | 0,1 | 6,9 | 32 |
| radish | 1,2 | 0,1 | 3,4 | 19 |
| white radish | 1,4 | 0,0 | 4,1 | 21 |
| turnip | 1,5 | 0,1 | 6,2 | 30 |
| beans | 7,8 | 0,5 | 21,5 | 123 |
| horseradish | 3,2 | 0,4 | 10,5 | 56 |
| garlic | 6,5 | 0,5 | 29,9 | 143 |
Fruits | ||||
| oranges | 0,9 | 0,2 | 8,1 | 36 |
| bananas | 1,5 | 0,2 | 21,8 | 95 |
| cherry | 0,8 | 0,5 | 11,3 | 52 |
| grapefruit | 0,7 | 0,2 | 6,5 | 29 |
| lemons | 0,9 | 0,1 | 3,0 | 16 |
| apples | 0,4 | 0,4 | 9,8 | 47 |
Berries | ||||
| grape | 0,6 | 0,2 | 16,8 | 65 |
Mushrooms | ||||
| mushrooms | 3,5 | 2,0 | 2,5 | 30 |
Nuts and dried fruits | ||||
| nuts | 15,0 | 40,0 | 20,0 | 500 |
| dried fruits | 2,3 | 0,6 | 68,2 | 286 |
| raisin | 2,9 | 0,6 | 66,0 | 264 |
Snacks | ||||
| potato chips | 5,5 | 30,0 | 53,0 | 520 |
| salted popcorn | 7,3 | 13,5 | 62,7 | 407 |
Cereals and porridges | ||||
| porridge with milk | 3,3 | 2,9 | 17,4 | 105 |
| oat bran | 8,0 | 4,0 | 10,0 | 110 |
| pearl barley porridge | 3,1 | 0,4 | 22,2 | 109 |
| millet porridge | 4,7 | 1,1 | 26,1 | 135 |
| boiled brown rice | 2,6 | 0,9 | 22,8 | 110 |
| barley porridge | 11,5 | 2,0 | 65,8 | 310 |
| rye bran | 11,2 | 3,2 | 32,0 | 221 |
Flour and pasta | ||||
| pancakes | 6,1 | 12,3 | 26,0 | 233 |
| vareniki | 7,6 | 2,3 | 18,7 | 155 |
| dumplings | 11,9 | 12,4 | 29,0 | 275 |
Bakery products | ||||
| loaf with wheat bran | 9,2 | 2,8 | 51,4 | 273 |
| buns | 7,9 | 9,4 | 55,5 | 339 |
| rye-wheat bread | 8,1 | 3,4 | 42,2 | 222 |
Confectionery | ||||
| candies | 4,3 | 19,8 | 67,5 | 453 |
| cake | 3,8 | 22,6 | 47,0 | 397 |
| halva | 11,6 | 29,7 | 54,0 | 523 |
Cakes | ||||
| cake | 4,4 | 23,4 | 45,2 | 407 |
Chocolate | ||||
| chocolate | 5,4 | 35,3 | 56,5 | 544 |
Raw materials and seasonings | ||||
| seasonings | 7,0 | 1,9 | 26,0 | 149 |
| mayonnaise | 2,4 | 67,0 | 3,9 | 627 |
Dairy | ||||
| milk | 3,2 | 3,6 | 4,8 | 64 |
| condensed milk | 7,2 | 8,5 | 56,0 | 320 |
Meat products | ||||
| pork | 16,0 | 21,6 | 0,0 | 259 |
| salo | 2,4 | 89,0 | 0,0 | 797 |
Sausages | ||||
| smoked sausage | 28,2 | 27,5 | 0,0 | 360 |
Bird | ||||
| duck | 16,5 | 61,2 | 0,0 | 346 |
| goose | 16,1 | 33,3 | 0,0 | 364 |
Fish and seafood | ||||
| pink salmon | 20,5 | 6,5 | 0,0 | 142 |
| Red caviar | 32,0 | 15,0 | 0,0 | 263 |
| salmon | 19,8 | 6,3 | 0,0 | 142 |
| seaweed | 0,8 | 5,1 | 0,0 | 49 |
| fish balyk | 20,4 | 12,5 | 0,0 | 194 |
| herring | 16,3 | 10,7 | — | 161 |
| salmon | 21,6 | 6,0 | — | 140 |
Oils and fats | ||||
| animal fat | 0,0 | 99,7 | 0,0 | 897 |
| cooking fat | 0,0 | 99,7 | 0,0 | 897 |
Alcoholic drinks | ||||
| dry white wine | 0,1 | 0,0 | 0,6 | 66 |
| red dessert wine | 0,5 | 0,0 | 20,0 | 172 |
| whiskey | 0,0 | 0,0 | 0,4 | 235 |
| vodka | 0,0 | 0,0 | 0,1 | 235 |
| cognac | 0,0 | 0,0 | 0,1 | 239 |
| liquor | 0,3 | 1,1 | 17,2 | 242 |
| beer | 0,3 | 0,0 | 4,6 | 42 |
Non-alcoholic drinks | ||||
| cola | 0,0 | 0,0 | 10,4 | 42 |
| sprite | 0,1 | 0,0 | 7,0 | 29 |
| tonic | 0,0 | 0,0 | 8,3 | 34 |
| Fanta | 0,0 | 0,0 | 11,7 | 48 |
| energy drink | 0,0 | 0,0 | 11,3 | 45 |
Juices and compotes | ||||
| grape juice | 0,3 | 0,0 | 14,0 | 54 |
| * data is per 100 g of product | ||||
How is intestinal irrigoscopy performed?
During the procedure, the patient lies on the X-ray machine table. First, an X-ray of the intestine is taken without contrast to ensure the absence of waste products. Then a tube is inserted into the patient’s anus, through which a solution of radiopaque contrast agent heated to 34–36°C is supplied. When the intestines are filled with contrast material, X-rays are taken from several positions. After this, the intestines empty naturally.
During irrigoscopy using the double contrast method, another procedure is performed - the colon is filled with air and irrigograms are made again. The entire procedure takes on average 40–60 minutes.
Structure of the apparatus
Irrigoscopy - procedure
The irrigoscopic device, based on the examination of various areas of the intestine, is designed quite simply. The basis of this device is a small container with two tubes attached to it. The existing container can hold from one to three liters of a special substance. A special contrast agent necessary for the examination is poured into the bottom of the container. By the way, without this substance it is simply impossible to study the structure of the intestine.
Next, a special bulb is attached to one end of the tube to allow air to be pumped. At the second end of the other tube there is a special tip, which is inserted directly into the intestine when examining the intestines. The material from which the tubes are made is silicone. The choice of this composition by the designers is not accidental; the tubes can be used repeatedly, cleaning them from various microorganisms through conventional sterilization. At the same time, this material is absolutely safe for the human body.
The metal parts of the device are made of high quality stainless steel. The tips of this device are made in different dimensional units. This condition helps to use the device for both adults and children. This simple structure of this device makes it possible to detect quite serious malfunctions in the intestines. Along with the device, the kit includes detailed operating instructions and relevant certificates that guarantee the quality of the manufactured device.
Popular questions and answers
Irrigoscopy is considered a safe and informative research method and is often used to diagnose pathologies of the large intestine. Therefore, many are interested in how safe and painless this procedure is and how it differs from another popular research method - colonoscopy. Our experts answer popular questions from readers: candidate of medical sciences, doctor of the highest category, therapist Yulia Esipenko and candidate of medical sciences, doctor of the highest category, surgeon Maksud Magomedov .
How does intestinal irrigoscopy differ from colonoscopy?
Both diagnostic methods make it possible to assess the condition of the large intestine and identify pathological processes. But they are fundamentally different in the way they are carried out. Irrigoscopy is a study using a radiopaque substance that fills the large intestine. Colonoscopy is performed using a colonoscope - endoscopic equipment with optics, which provides high image clarity when examining tissues and parts of the intestine. Colonoscopy is a more informative method, since it can be used to assess the condition of the peri-intestinal lymph nodes and detect the most minor pathological changes, including malformations and tumors. During the examination, other medical procedures may be performed, such as stopping bleeding or taking tissue for a biopsy. Irrigoscopy allows you to quickly and accurately examine the large intestine, including those sections where a colonoscope cannot reach. Thanks to the contrast agent, the doctor receives a clear image, which can be used to assess the anatomy of the intestine and the presence of large pathological formations. However, with the help of irrigoscopy it is difficult, and often impossible, to detect inflammation, a small polyp or tumor at an early stage.
Will it hurt during intestinal irrigoscopy?
According to patient reviews, intestinal irrigoscopy is a painless procedure. Minor discomfort may occur when the intestines are filled with radiopaque material using an enema. During the examination, there may be a urge to defecate and a feeling of heaviness in the abdomen.
What should you do after irrigoscopy?
After the procedure, they lead a normal life. Do not worry if the stool becomes lighter within 2-3 days - this is due to the release of residual barium. Short-term constipation may occur, so a single dose of a laxative is allowed.
What complications may arise?
Complications during and after irrigoscopy are extremely rare.
Sometimes, when the intestinal walls are stretched, abdominal pain and painful urge to stool appear, which disappear within 2–3 hours and do not require treatment. To relieve pain, you can take an antispasmodic. A very rare and more serious complication is intestinal perforation and release of radiopaque substance into the abdominal cavity. In this case, nausea, vomiting, weakness, fever, abdominal pain, diarrhea and bleeding from the rectum are observed. If such symptoms occur, you should immediately consult a doctor. Sources
- Irrigoscopy. Memo for the patient https://nmcs.ru/infopat/diagnostics/%D0%98%D1%80%D1%80%D0%B8%D0%B3%D0%BE%D1%81%D0%BA%D0% BE%D0%BF%D0%B8%D1%8F.pdf
- Radiation diagnostics of diseases of the esophagus, stomach and intestines. https://disk.yandex.ru/i/4cYCbOkWs5GzjA
- The procedure for preparing for X-ray examinations. https://disk.yandex.ru/i/K19kT5_kXU4sIg
Kinds
There are two forms of irrigoscopy.
Procedure with a simple contrast method
This form of irrigoscopy involves the use of barium alone.
This research method should be done for older people and patients whose health has deteriorated in the postoperative period. It is done to determine intestinal motility.
With such filling of the intestine, this method allows you to obtain the clearest contours.
Double contrast procedure
This method involves the use of barium suspension and air.
It reveals tumors, ulcerative defects of the intestine, polyps in the intestinal lumen, intestinal obstructions and diverticula.
Quitting the diet
After completion of irrigoscopy, a gradual gradual exit from the slag-free diet is required for approximately 5-7 days. If you violate the rules and quickly include fatty meat products and various root vegetables in your diet, there is a risk of constipation and the formation of fecal stones.
Expand your diet first with foods that are easily digestible in the body (vegetables, cereals, fruits), and if you feel normal, introduce fatty meats and previously prohibited foods on the 3rd-4th day. Continue to stay hydrated. After irrigoscopy, in order to normalize the intestinal biocenosis, it is recommended to take probiotics , which will also help improve digestion processes.