If a person experiences pain in the area of the left side of the hypochondrium, the first suspicions immediately fall on the pancreas or stomach. However, another, neighboring organ may also be disturbing.
The spleen is one of the most mysterious organs, the functions of which are not fully understood. This is the most important organ that helps the immune system: it is the one that copes with filtering blood cells infected with viruses. The spleen is a reservoir organ, a blood depot.
Pain syndrome in the spleen without the influence of external factors occurs only in one case - when it is significantly enlarged. Often, patients simply complain of discomfort, a pulling sensation in the left half of the abdomen.
Diseases that cause pain in the spleen:
- Infectious diseases (typhoid fever, hepatitis, anthrax, infectious mononucleosis, syphilis, tuberculosis) Many infectious diseases affect the spleen, causing pain and starting a destructive process.
- Traumatic conditions of the spleen They are divided into two types: open and closed type. The first includes stab and gunshot wounds of the chest area on the left or the upper part of the abdominal cavity. Closed injuries - bruises and fractures. In some cases, the spleen may rupture, which is accompanied by internal bleeding. Damage to an organ is usually characterized by acute pain radiating to any part of the body, as well as a general deterioration of the condition.
- Organ infarction Occurs as a result of thromboembolism, as well as thrombosis. The condition of a person with a splenic infarction is directly related to the magnitude of the pathology. If it is small, then it is probably asymptomatic. With a large heart attack, pain occurs in the left hypochondrium with irradiation to the back area, which responds to breathing.
- Spleen abscess The pathology picture is fever, pain in the abdomen and chest, muscle tension.
- Parasitic diseases (most often echinococcosis)
- Benign and malignant neoplasms
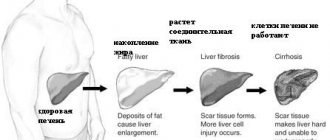
- An enlarged spleen is often combined with an enlarged liver (hepatolienal syndrome), which is observed in liver cirrhosis, portal hypertension, and blood diseases.
Any pain in the body is a signal for help.
Do not blindly ignore it and take painkillers indiscriminately. Pain and discomfort in the left hypochondrium may indicate several problems.
Only a doctor can identify the exact cause.
If you experience pain of an unclear nature in the left hypochondrium, you can contact our clinic. To make a correct diagnosis, specialists will conduct an examination and interview, and also prescribe the necessary tests. During the consultation, you can discuss all the symptoms in order to choose the most effective and safe therapy.
The role of the spleen in the body
The spleen is an organ of the immune system. It is involved in blood filtration, ensures the synthesis of antibodies, leukocytes, and can also perform hematopoietic functions. At the same time, its presence is not vital, and in some cases the spleen can be removed¹.
What happens if the spleen is removed?
Removal of the spleen is necessary:
- for some types of cancer, if the tumor or metastases affect the organ;
- if the spleen enlarges so much that it begins to put pressure on the stomach;
- when an organ ruptures, which can occur after severe damage or severe trauma;
- in cases of spleen dysfunction due to infections that cannot be treated.
After the spleen is removed, other organs take over its functions. Mainly the liver, as well as bone marrow and other organs of the immune system. Of course, this puts additional stress on them, and people with weakened immune systems may be at increased risk of contracting infections².
Diagnosis and treatment
Diagnosis of spleen diseases begins with a thorough examination by a doctor. After palpation and history taking, additional studies will be required - ultrasound, radiography, MRI or puncture. Laboratory diagnostics are also required.
The primary task is to correctly diagnose in order to prescribe effective treatment. It should only occur under the supervision of an experienced specialist.
Preventive measures to maintain the organ in a healthy state are very simple: proper nutrition and a healthy lifestyle. The spleen begins to work better with regular physical activity, as well as with special breathing exercises.
Pain in the spleen occurs when the organ has significantly increased in size. This may indicate various diseases, which can only be diagnosed by a qualified doctor. It is highly recommended not to make a diagnosis on your own, much less select a treatment.
After all, the spleen is one of the important organs responsible for supporting human immunity.
Timely contact with specialists will help you solve the problem at an early stage with minimal damage.
For early diagnosis of health problems, you can undergo a comprehensive diagnostics of the body at our center.
The best diagnosis of pain in the spleen is MRI of the spleen
You can sign up for a consultation right now: online or by phone
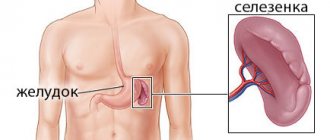
Where is the spleen located?
The spleen is located just below the ribs on the left side (Figure 1). It concerns the left kidney, left adrenal gland, posterior wall of the stomach, pancreas, diaphragm. This is a small organ, 10-15 cm long. It weighs about 150 grams, its shape is round and oblong. Normally, the spleen cannot be felt, but after injury or illness it can become greatly enlarged and even noticeably protrude from under the ribs³.
Figure 1. Where is the spleen located. Image: rob3000/Depositphotos
Structure of the spleen
The shape of the spleen is similar to a bean; it is elongated, with rounded outlines, connected by layers of the peritoneum (ligaments) to the stomach, diaphragm, and colon. When the position of these organs changes, the spleen is also affected. There are several surfaces in its structure:
- Diaphragmatic. It is convex, oriented towards the diaphragm.
- Visceral. It is divided into gastric, renal and colonic surfaces in contact with the corresponding organs.
The blunt lower and sharp upper edges separate the visceral and diaphragmatic surfaces. The anterior, facing forward and downward, and posterior, facing back and upward, poles are also distinguished.
The main part of the spleen is formed by two zones that perform different functions: the red and white pulp. The red pulp accounts for about 80% of the organ's volume, and the white pulp for about 20% (Fig. 2).
Figure 2. Structure of the spleen. Image: Seamartini / Depositphotos
Functions of the red pulp:
- blood filtration;
- destruction of viruses, fungi, bacteria by phagocytes;
- regulation of red blood cells (destruction of old, damaged, abnormal cells);
- accumulation, storage of leukocytes, platelets.
The white pulp provides the production of lymphocytes to produce antibodies.
Also in the structure of the spleen there is a marginal (marginal) zone located between the white and red pulp. It contains macrophages necessary for antibacterial protection.
What kind of special spleen is it?
Sometimes the spleen has a non-standard structure. There are several types of congenital anomalies:
- Accessory spleen - development of additional lobules of the spleen. They can be located either near the organ itself or in other places - for example, in the pancreas, epididymis, etc. A person may have several dozen additional spleen lobes. This usually does not affect your health or well-being in any way.
- Cysts are cavities in the structure of an organ. The larger the size of the cyst, the more it affects the functioning of the spleen.
- Asplenia or alienia is the congenital absence of the spleen. A rare dangerous pathology, which is often combined with severe heart and vascular defects and in this case leads to death during the first year of life. With asplenia, disturbances in the functioning of the immune system and blood clotting occur.
- Microsplenia is a reduction in the size of the spleen while maintaining its functions. Usually does not affect quality of life or health status.
- Polysplenia is a division into several equal lobules. Like asplenia, it is often combined with disorders of the cardiovascular system.
- Ectopia is an abnormal location of the spleen. It may end up in a diaphragmatic or umbilical hernia, in the retroperitoneal space. If there is a transposition of the internal organs (they are located mirror-image), the spleen will be located not in the left, but in the right hypochondrium. Sometimes the malposition of the spleen affects the functioning of the bladder or stomach³.
Inflammatory diseases
Acute splenitis in ultrasound diagnostics is indicated by enlargement of the organ with rounding. The echostructure is homogeneous, fine-grained. Sometimes there are foci of acute necrosis. In chronic splenitis, the enlarged size of the spleen remains due to the proliferation of fibrosis. The echogenicity of the tissue is higher than normal. Foci of necrosis may be calcified. Calcifications are visible on ultrasound as small hyperechoic formations.
Often, ultrasound reveals splenomegaly - a pathological increase in the size of the spleen. It can be a sign of various diseases: Gaucher disease, amyloidosis, tuberculosis and others. In 75% of cases, splenomegaly is a symptom of diseases of other organs: liver cirrhosis, active hepatitis. In the initial stage, ultrasound diagnostics shows an increase in the diameter of the splenic vein. Fibrosis gradually sets in with an increase in echostructure.
Splenomegaly with normal echostructure is observed with:
- infections,
- liver pathologies,
- sickle anemia,
- congenital spherocytosis,
- leukemia,
- hemolysis,
- chronic anemia,
- Still's disease
- Felty's syndrome,
- Wilson's disease
- reticulocellular sarcoma.
Hypoechogenicity with an enlarged spleen:
- hepatocellular disease,
- lymphogranulomatosis,
- myeloma,
- non-caseating granulomatous inflammation,
- leukemia.
Abscesses are rare but possible. They appear as anechoic or hypoechoic lesions with poor borders but visible walls. There are gas bubbles inside, creating zones of high echogenicity. To diagnose abscesses, the clinical picture is also used; hematoma and splenic infarction must be excluded.
Functions in the body
The spleen is the largest lymphatic organ. As part of the immune system, it performs several important functions:
- Participates in the functioning of the immune system, ensuring the formation of lymphocytes. The spleen is directly involved in the production of B-lymphocytes - cells of the immune system. They recognize foreign structures and produce antibodies against them.
- Purifies the blood by capturing and destroying old, damaged platelets and red blood cells. Their breakdown products are then sent to the liver, where they are used in the formation of bile.
- Accumulates and stores blood, as well as platelets. Up to a third of all platelets in the body are stored in the spleen. The organ can also hold about 50 ml of blood. By dilating the blood vessels, the blood volume can be greatly increased if necessary.
- During fetal development, the spleen performs hematopoietic functions. By the time of birth, the bone marrow begins to perform them, but even after this, the spleen retains the ability to participate in hematopoiesis. In case of blood diseases, it can again begin to perform these functions⁴.
Treatment of an enlarged spleen
The main target of treatment is the pathology that has caused serious deviations in the functioning of the organ. In some cases, the spleen itself becomes the target for radical measures. For example, organ removal is resorted to in the following cases:
- large-scale infarction and abscess of the spleen;
- thalassemia;
- some forms of leukemia;
- failure of conservative therapy.
Identification and elimination of the causes and consequences of hypersplenism (and/or splenomegaly) can be carried out using traditional medicine methods (acupuncture, homeopathy, osteopathy, herbal medicine, qigong therapy, hirudotherapy). In this case, the “target” of diagnosis and treatment becomes the body in the totality of its numerous relationships.
Herbs for treating spleen
Herbal medicine is a method of holistic medicine. Therefore, despite the fact that there are herbal preparations for the treatment of spleen diseases, it is better to prepare them individually, based on the diagnosis “here and now”. For example, based on iridology. In this case, the action of the herbal collection will not only be more accurate and effective, but also softer and more gentle. As a result, the effectiveness of treatment will increase, and side effects will be minimal. That’s why you should prefer visiting a herbalist to searching for recipes on the Internet.
Make an appointment
Signs of spleen diseases
Pain in the left hypochondrium may indicate problems with the spleen.
Photo: actiongp / freepik.com Problems with the spleen can occur due to physical injury, infection, blood disease, liver disease, or any condition in which blood cells are destroyed too quickly, overloading the organ. The symptoms that appear in this case will depend on the type of spleen disease:
- In case of injury, damage, or rupture of an organ on the left under the ribs, acute pain appears. It can give under the shoulder blade. Blood pressure also drops, severe thirst, sweating, and possible vomiting appear. If such symptoms appear after a strong blow to the stomach, a broken rib, a fall, or any other injury, you should immediately consult a doctor.
- If the spleen is enlarged, discomfort or pain occurs in the left hypochondrium. If the enlargement is too strong, it may rupture (accompanied by acute pain and other symptoms of spleen injury). The spleen can become enlarged during severe infections, blood cancer, liver diseases, and some metabolic disorders.
- When the spleen is enlarged due to an infectious disease, pain appears in the left hypochondrium, which is accompanied by high temperature. Symptoms characteristic of a specific infection also appear.
- If, due to an increase in size, the functions of the spleen increase, this affects the results of a clinical blood test (possible leukopenia, thrombocytopenia, anemia).
- If a splenic infarction occurs, pain appears in the left hypochondrium even without previous trauma. It intensifies with deep breathing and can radiate to the left shoulder blade. The condition develops with coronary heart disease, endocarditis, and other heart diseases. It is accompanied by symptoms from the cardiovascular system.
- As the spleen tumor develops, it increases in size, heaviness appears in the left hypochondrium, and dull or, less commonly, acute pain may appear. With malignant tumors, this is accompanied by weight loss, anemia, and fever.
- If a splenic abscess develops, pain in the left hypochondrium is accompanied by fever. The pain can spread to the chest and radiate to the left shoulder. The spleen increases in size so much that it can be felt. In this case, there is tension in the muscles of the anterior abdominal wall⁵.
Problems with the spleen can be accompanied by several syndromes:
- Lymphoproliferative - enlarged lymph nodes, pain in the right hypochondrium, sweating, fever, itching, the appearance of leukemic infiltrates in the skin.
- Immunodeficiency - the appearance of purulent-inflammatory complications, frequent infections.
- Syndrome of autoimmune disorders - the development of autoimmune thrombocytopenia, autoimmune anemia.
- Hemorrhagic - nasal, gingival bleeding, subcutaneous hemorrhages.
- Anemic - pallor, weakness, shortness of breath, dizziness, headache, sweating, drowsiness.
These syndromes are associated with an underlying disease (eg, autoimmune disorder, blood disorder, cancer). They may develop before the first signs of spleen problems appear⁵.
Important!
With diseases of the spleen, the efficiency of blood filtration decreases, and the functioning of the immune system is disrupted. This is dangerous, so it is important to consult a physician if any problems with the spleen occur.
Spleen diseases
As a rule, primary diseases of the spleen are quite rare; much more often it is affected secondarily, and more often than this happens to other organs. Below are the main dysfunctional conditions of the spleen that can be diagnosed as a disease.
- Congenital malformations.
There are cases when a person does not have a spleen from birth. There are also cases when the size of the spleen does not fit into the usual framework; its shape and structure are non-standard. Sometimes additional spleens are identified, there may even be several of them. If the position of the spleen is poorly fixed due to weak abdominal muscles, it may move in the abdominal cavity; This phenomenon in medicine is called “wandering spleen”, and it occurs more often in women than in men.
- Splenic infarction
is a phenomenon that occurs quite often, although the area of infarction is usually very small. Leukemia and some other infections contribute to the occurrence of a heart attack.
- Volvulus of the spleen
(or twisting of the leg) requires the mandatory intervention of a surgeon, since it leads to a serious disruption of the blood circulation of this organ.
- Abscesses.
The causes of a splenic abscess can be different - it could be a splenic infarction or typhoid fever. As a rule, this process is painless, which in most cases ends in self-healing.
- Cysts.
Various types of cysts can be observed in the spleen, but epithelial cysts are extremely rare. But serous cysts are observed more often, but they usually arise, like ruptures, as a result of a person being injured.
- Various degenerative irreversible processes.
In old age, splenic atrophy occurs quite often.
- Tumors.
A typical tumor of the spleen is lymphosarcoma. Primary malignant tumors rarely affect the spleen, and metastases to the spleen are even rarer.
- Enlarged spleen
(so-called splenomegaly). This may be associated with various pathological conditions of the human body. With enlarged lymph nodes, with fever or jaundice, with an enlarged liver or severe anemia - in all these cases splenomegaly can be detected. In the case of certain cardiovascular diseases, infectious diseases - these can be measles, meningitis, scarlet fever, malaria, etc., with blood diseases - leukemia or hemolytic jaundice, an enlargement of the spleen may also occur.
Since splenomegaly is only the body’s reaction to another disease, first of all, it is necessary to establish what caused this pathological condition of the organ.
How does the spleen hurt?
Pain associated with the spleen appears under the ribs on the left side. The nature of the pain depends on the cause of its occurrence. Pain due to damage or rupture of the spleen occurs after an injury to the abdomen or chest - a strong blow, broken ribs, a fall on the stomach, a sports injury. Rupture does not always occur immediately after injury. Sometimes it takes up to several weeks for symptoms to appear. Wherein:
- A sharp pain appears behind the ribs on the left side. It can intensify when touched or pressed on this area.
- When lying down, the pain may radiate to the left shoulder.
- There are signs of blood loss and low blood pressure - rapid heartbeat even with light exertion, weakness, dizziness.
If these symptoms occur, you need to call an ambulance. A ruptured spleen is life-threatening.
Causes of enlarged spleen in children
In children, an enlarged spleen can be associated with a number of diseases.
Most often these are bacterial, viral or parasitic infections: measles, rubella, viral hepatitis, infectious mononucleosis, babesiosis and others. The cause may be some autoimmune diseases, for example, systemic lupus erythematosus, as well as stagnation of venous blood in the liver, hemolytic anemia, granulomatous inflammation, leukemia. An enlarged spleen should be diagnosed by ultrasound. In this case, the pediatrician will prescribe blood tests. He can also give a referral to a specialized specialist, for example, an infectious disease specialist or a hepatologist. The spleen can enlarge after an injury, against the background of a severe infection and some other diseases. At first, organ enlargement may not cause any symptoms at all. However, then:
- Pain appears in the left hypochondrium. It may feel like slight discomfort.
- If the enlarged spleen presses on the stomach, you will feel full very quickly while eating.
Even if the pain accompanied by signs of an enlarged spleen is mild or almost absent, you should consult a doctor as soon as possible. This condition is dangerous. If an organ is greatly enlarged, the risk of rupture increases⁵.
Figure 3. Healthy and enlarged spleen. Image: rob3000/Depositphotos
Publications in the media
Types of injuries • Penetrating wounds (knife, gunshot). Injury to the spleen can occur with injuries to the abdomen, middle or lower chest • Blunt closed trauma often occurs in road traffic accidents. Damage to the spleen leads to profuse internal bleeding and shock. In 5% of cases with blunt injuries, splenic rupture can be delayed (two-stage) • Two-stage rupture •• First, a subcapsular hematoma occurs. As a result of lysis of red blood cells, the osmolarity of the contents of the hematoma increases, which leads to its enlargement and rupture of the wall (splenic capsule) •• About 75% of delayed ruptures occur 2 weeks after the initial injury and are manifested by acute shock resulting from profuse internal bleeding • Iatrogenic injuries are formed due to strong traction on the splenic ligaments or incorrect position of retractors during abdominal operations. In 20% of cases, the indication for splenectomy is iatrogenic trauma • Spontaneous ruptures occur as a result of splenomegaly of various origins (for example, with mononucleosis, leukemia, malaria).
Clinical picture • Internal bleeding and shock: pallor of the skin, cold sweat, tachycardia, decreased blood pressure, Hb, Ht with accumulation of blood in the subdiaphragmatic space - a “vanka-stand” symptom (increased pain when the patient is horizontal, dullness of percussion sound in sloping places abdominal cavity) • Symptoms of peritoneal irritation: muscle tension in the abdominal wall, Shchetkin-Blumberg, Voskresensky symptoms, etc. • If the chest cavity is injured, there are signs of pneumo- and hemothorax.
TREATMENT . It is rarely possible to save an organ, only with superficial and minor injuries.
• With small ruptures of the capsule, bleeding can sometimes be stopped by electrocoagulation and the application of a hemostatic sponge.
• Splenectomy is the method of choice for massive injuries, especially in combination with damage to other organs •• Indications for splenectomy: extensive trauma to the spleen, bleeding from dilated veins of the esophagus caused by thrombosis of the splenic veins •• Complications after splenectomy ••• Atelectasis of the lower lobe of the left lung ( occurs often) ••• Subphrenic abscess in combination with left-sided effusion pleurisy ••• Postsplenectomy sepsis. The disease begins with nonspecific symptoms resembling moderate pneumonia, then high fever appears, and shock is possible. In adults who undergo splenectomy due to trauma, the risk of developing sepsis is 0.5–0.8%.
ICD-10 • S36 . 0 Spleen injury
Prevention of spleen diseases
Sometimes spleen disorders cannot be prevented - for example, if they are caused by autoimmune diseases, cancer or blood diseases. However, many problems can be avoided if you take precautions:
- Reduce the risk of contracting infections. To do this, you need to strengthen your immune system, follow hygiene rules, and try not to contact sick people.
- Protect yourself from sexually transmitted infections. It is enough to use a condom during sex, especially with new and untested partners.
- Reduce the risk of physical injury. When playing football, wrestling, or contact sports, you need to use protective equipment. When driving in a car, you should always wear a seat belt⁴.