Treatment of reflux esophagitis is based on lifestyle changes: special nutrition, giving up bad habits (smoking, drinking alcohol, overeating).
With reflux esophagitis, partially digested food and stomach acid return from the stomach back into the esophagus. The acid irritates the mucous membrane, causing heartburn, pain and inflammation.
For the prevention and during treatment of gastroesophageal reflux disease, it is recommended to reduce the consumption of foods that contribute to increased production of stomach acid and long-term storage of food in the stomach. The menu should include dishes that have undergone thermal, mechanical and chemical processing, soft enough so as not to cause pain when swallowing and not irritate the esophagus. You need to eat 5-6 times a day in small portions, avoid carbonated drinks, fatty foods, sour foods and sweets.
What is reflux esophagitis and how to get rid of it?
Reflux esophagitis (gastroesophageal reflux disease, GERD) is a disease of the esophageal mucosa. The first signs of esophagitis - heartburn and difficulty breathing - arise from the entry of acid and bile from the intestinal tract into the esophagus. Heartburn may get worse when lying down or during physical activity. At the same time, nausea, belching, hiccups, and pain behind the chest, reminiscent of heart pain, are possible. Sometimes cough, shortness of breath, and discomfort when swallowing food appear.
If you ignore the symptoms of GERD, life-threatening complications may develop: internal bleeding, cancer of the esophagus, stomach or duodenum.
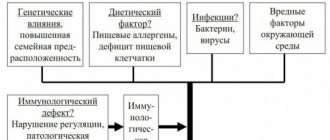
GERD affects up to 30% of the adult population. Among the causes of esophagitis are:
- mechanical injury to the esophagus (small objects, fish bones);
- chemical and thermal burns of the mucous membrane;
- consumption of fatty, spicy, fried foods, fast food, alcohol abuse;
- overweight;
- gastrointestinal diseases;
- taking antiallergic and sedative medications;
- pregnancy.
Treatment of GERD can be conservative or surgical; the choice of therapy depends on the cause of the disease. A mandatory component of treatment is taking medications that neutralize stomach acid. Another important means of preventing and treating reflux esophagitis is diet. In patients who do not follow a proper diet, smokers, and those who drink alcohol for esophagitis, treatment may be ineffective or more complicated.
Pharyngeal-esophageal (Zenker's) diverticulum.
The main role in the pathogenesis of the formation of this type of diverticula is achalasia (inability to relax) of the cricopharyngeal muscles, which results in a violation of the opening of the upper esophageal sphincter in response to swallowing. Excessive intraluminal pressure pushes the submucosal layer into the resulting muscle defect. The diverticulum then descends between the posterior wall of the esophagus and the spine. The inner surface of the diverticulum is covered with a mucous membrane; it may have superficial erosions, foci of inflammation and scars.
Diet for esophageal esophagitis
The diet for esophageal esophagitis should be as gentle as possible so as not to cause irritation of the mucous membrane of the gastrointestinal tract. Typically, gastroenterologists advise patients to take diet menu option No. 1 as a basis for nutrition, which is designed specifically for the treatment and prevention of gastrointestinal diseases.
The menu for reflux should consist of soft dishes without seasonings:
- pureed vegetables and fruits;
- well-cooked, viscous rice, oatmeal, buckwheat and semolina porridges;
- lean meats (beef, turkey, chicken) and steamed fish;
- soups in lean broth with well-cooked or pureed vegetables and cereals.
The bread can be white, dried, yesterday's bread, it will help reduce acidity and fermentation processes. As for drinks, it is better to give preference to jelly, liquid tea with milk and still mineral water at room temperature. Mineral water reduces stomach acidity and helps restore the esophageal mucosa.
Following the basic rules of eating for reflux will speed up recovery:
- It is necessary to eat in small portions, not to overeat;
- food should be warm, neutral in taste;
- salt, sugar and spices should be limited;
- It is better to give preference to dishes with a soft consistency, so as not to irritate the esophagus;
- within 2 hours after eating, you should not lie down or exercise, so as not to provoke the release of partially digested stomach contents back into the esophagus.
You need to follow the diet for at least 3 months, during which time the mucous membrane is completely restored. To prevent recurrent esophagitis, it is necessary to limit the consumption of spicy and sour foods, carbonated and alcoholic drinks.
Prevention of esophagitis
The best prevention of esophagitis and other gastrointestinal diseases is:
- Mode.
- Proper nutrition.
- Normalized intake of biostimulants.
- Consuming warm (but not hot) food.
- Quitting smoking and excessive alcohol consumption.
- Do not take antibiotics or other drugs without a doctor's prescription.
In case of chronic esophagitis, the patient must undergo regular medical examinations from the attending physician and go to sanatorium-resort treatment once or twice a year.
This article is posted for educational purposes only and does not constitute scientific material or professional medical advice.
What should you not eat if you have esophagitis?
If you have esophageal esophagitis, you should not eat foods that increase the acidity of the stomach and take a long time to digest. You must stop using:
- fresh baked goods, rye bread, pasta;
- strong broths, stir-fried soups;
- fatty meats and fish;
- sausage products, smoked dishes, canned food;
- millet, pearl barley, barley, peas, beans;
- alcoholic drinks;
- foods high in fat, including chocolate, fatty cheeses, snacks.
Carbonated drinks, strong tea, tomatoes, onions, garlic and citrus fruits can cause or increase pain, so they should be excluded from the diet during treatment for esophagitis. Coffee and chocolate provoke excess secretion of gastric juice and negatively affect the smooth muscles of the esophagus, causing reflux of stomach acid and heartburn.
Hot, cold, spicy, salty dishes, which can irritate and damage the esophageal mucosa, are contraindicated. It is necessary to minimize the consumption of fats and oils when preparing dishes: they suppress gastrointestinal motility, food remains in the stomach for a long time, acidity and gas formation increase. Most of these foods weaken the esophageal sphincter, which is supposed to close after food enters the stomach. If it remains open, partially digested food and stomach acids enter the esophagus and cause inflammation.
When composing a diet for reflux esophagitis, it is necessary to take into account your well-being. If any product provokes heartburn or pain in the stomach, you should avoid it.
Diagnosis of esophagitis
Localization of painful symptoms in acute esophagitis in most cases allows you to quickly identify the pathology and prescribe the necessary laboratory and computer tests.
In the acute stage of the disease, the following is carried out:
- fluoroscopy with barium (if necessary);
- endoscopic biopsy;
- X-ray of the esophagus
; - Abdominal ultrasound
; - esophagoscopy;
- histology.
In case of congenital malformations of the esophagus, impaired motor function can be detected by esophagomanometry. The study gives an accurate picture of the contractile activity of the esophagus, displays peristalsis, the work of the upper and lower esophageal sphincters. Esophagomanometry is prescribed to patients with suspected atypical functioning of the esophagus (dysphagia, dyspepsia, odynophagia), as well as at the preparatory stages for antireflux operations.
Vegetables for reflux esophagitis
For reflux esophagitis, it is recommended to consume vegetables in soft (boiled or mashed) form. It is better to steam or boil vegetable dishes. It is better to avoid frying and stewing. You should also not eat pickled, salted or pickled vegetables.
The best for the diet are carrots, potatoes, beets, and cauliflower. You can make puree or soufflé from them. Potatoes are one of the recommended vegetables. Particularly nutritious is puree, which has an enveloping effect. Baked potatoes are healthy, but without adding vegetable oil or butter.
Roasted vegetables should not be consumed as they worsen the symptoms of GERD. Dishes with tomatoes provoke heartburn, and white cabbage, radishes, and cucumbers are difficult to digest, so they are not recommended during treatment.
List of fully or partially restricted products:
| bread | Butter pastries, fresh wheat and rye bread, pancakes, pancakes, fried pies |
| Vegetables | White cabbage, radish, radish, legumes, bell pepper, turnip, radish, onion, garlic, sorrel, spinach |
| Groats | Millet, pearl barley, corn, barley |
| Fruits and berries | All sour fruits: citrus fruits, currants, green apples |
| Meat | Goose, duck, pork, canned meat, lard, sausages, sausages, smoked meat, dried meat |
| Soft drinks | Strong tea, coffee, kvass, sparkling water, sweet fruit drinks |
Can you eat sweets if you have GERD?
For GERD, sweets can be in the form of jelly, jelly, soufflé, or sweet fruit puree. The main rule is that the dishes do not cause irritation to the throat and esophagus and are easy to swallow and digest. Gastroenterologists do not recommend consuming chocolate; it provokes acid reflux and can cause exacerbation of esophagitis. Cakes and sweets are slowly digested, so they should not be consumed during an exacerbation of GERD. In a state of remission, a small portion of sweets is allowed, but not on an empty stomach.
The main problem when eating desserts is appetite control, especially in overweight people. Eat sweets after the main course, but do not allow yourself to feel heavy and overeated.
If candidal esophagitis is being treated, sweets must be completely abandoned. This will avoid the growth of pathogenic microflora.
Clinical presentation and diagnosis of pharyngoesophageal diverticulum.
Small diverticula are manifested by a sore throat, dry cough, foreign body sensation, and increased salivation. When it is filled with food, swallowing problems (dysphagia) may develop. A protrusion may appear in the neck, especially when the head is pulled back. As the size of the diverticulum increases, spontaneous reflux of undigested food appears from the lumen of the diverticulum into the esophagus. As a result of compression of the trachea, difficulty breathing may occur, and when the recurrent nerve is compressed, hoarseness may occur. When food is retained for a long time in the diverticulum, a putrid odor from the mouth appears. All these manifestations lead to eating disorders and weight loss.
Puchkov K.V., Ivanov V.V. and others. Technology of dosed ligating electrothermal effects at the stages of laparoscopic operations: monograph. - M.: ID MEDPRACTIKA, 2005. - 176 p.
Puchkov K.V., Bakov V.S., Ivanov V.V. Simultaneous laparoscopic surgical interventions in surgery and gynecology: Monograph. - M.: ID MEDPRACTIKA, 2005. - 168 p.
Puchkov K.V., Rodichenko D.S. Manual suture in endoscopic surgery: monograph. - M.: MEDPRACTIKA, 2004. - 140 p.
Zenker's diverticula can be complicated by the development of diverticulitis (inflammation of the wall), then phlegmon of the neck, mediastinitis, development of an esophageal fistula, etc. Regurgitation (reflux) and aspiration (entry into the respiratory tract) of the contents of the diverticulum lead to chronic bronchitis, repeated pneumonia, and lung abscesses. Bleeding from the eroded mucous membrane of the diverticulum may occur, as well as the development of polyps and mucosal cancer.
My approach to treatment
When surgically treating patients with reflux esophagitis, I, like most specialists in European clinics, use a more effective technique that does not have the above-mentioned disadvantages - partial Toupet fundoplication with a cuff rotation of 270°. The technique I improved has a number of advantages:
- the physiological functioning of the esophageal sphincter is restored;
- maintaining a functional esophagogastric valve allows the patient to do without medications throughout his life;
- the ability to belch and vomit—the body’s natural defense reactions—is preserved;
- no pain after overeating or carbonated drinks;
- the number of relapses does not exceed 2% within a year after surgery, after 5 years this figure is about 4%.
A Russian Federation patent has been issued for an improved technique - Toupet 270° fundoplication.
Reflux esophagitis
Symptoms of laryngopharyngeal reflux
- Dysphonia or hoarseness;
- cough;
- feeling of a lump in the throat;
- discomfort and feeling of mucus in the throat;
- dysphagia (impaired swallowing).
Some researchers believe that chronic irritation of the larynx may lead to the development of carcinoma in patients who do not drink alcohol or smoke, although there is no data to support this.
Symptoms characteristic of LPR may also be caused by the following conditions:
- postnasal drip;
- allergic rhinitis;
- vasomotor rhinitis;
- upper respiratory tract infections;
- habitual coughing;
- use of tobacco or alcohol;
- excessive use of voice;
- changes in temperature or climate;
- emotional problems;
- environmental irritants;
- vagal neuropathy.
Treatment of Barrett's esophagus
The following treatment methods for Barrett's esophagus are used:
- Medication . Conducted by gastroenterologists. Antacids that reduce acidity, prokinetics that stimulate motility and the movement of food through the gastrointestinal tract, and proton pump inhibitors are often prescribed.
- Endoscopic . And here the endoscopist has a large choice, it all depends on the volume of the lesion, the severity of dysplasia, the depth of invasion (penetration) and other factors.
- argon plasma coagulation;
- endoscopic resection (dissection) of the mucous membrane;
- endoscopic ablation of the esophageal epithelium with a bipolar electrode;
- photodynamic therapy;
- cryodestruction;
- laser ablation.
- Surgical . To prevent the development of Barrett's esophagus, a Nissen fundoplication is performed. The essence of the operation is that a cuff is made around the esophagus from the bottom of the stomach, which should prevent the reflux of stomach contents into the esophagus.
Another commonly used and very radical method is removal of the lower part of the esophagus.
Surgical treatment of pharyngeal-esophageal (Zenker) diverticula.
Indications for surgical treatment are as follows: complications (perforation, penetration, bleeding, stenosis of the esophagus, cancer, development of fistulas), large diverticula complicated by at least short-term retention of food masses in them, long-term retention of food in the diverticulum, regardless of its size. Ineffectiveness of conservative therapy.
The essence of surgical treatment is complete removal of the diverticulum.
(cutting off from the esophagus, followed by suturing the organ wall) - diverticulectomy: the diverticulum is isolated from the surrounding tissues to the neck, a myotomy is performed, it is excised and the hole in the wall of the esophagus is sutured.
We isolate pharyngoesophageal diverticula from the cervical approach. A cosmetic skin incision is made in the projection of the anterior edge of the left sternocleidomastoid muscle. We mobilize the left lobe of the thyroid gland, retract it medially, and the neurovascular bundle laterally. Before surgery, a thick probe is inserted into the esophagus, which greatly facilitates the surgical treatment of esophageal diverticula. Then we perform extramucosal esophagomyotomy
several centimeters long, making sure that all the fibers of the m. cricopharyngeus (cricopharyngeal myotomy). We isolate the diverticulum up to the neck and stitch its base with an EndoGia-30 endoscopic stapler (Switzerland). The specimen is sent for pathohistological examination. The duration of stay in the clinic is 2-3 days. You can eat after 1-2 days.
Watch a video of operations performed by Professor K.V. Puchkov. You can visit the website “Video of operations of the best surgeons in the world.”
Epiphrenic diverticula
Epiphrenic diverticula, usually pulsational, are located along the posterior or right wall of the esophagus 2-11 cm above the diaphragm. Diverticula are spherical or mushroom-shaped. The leading factors in the formation of epiphrenic diverticula are the following factors: weakness of the muscular wall, increased intra-esophageal pressure and pressure of the food bolus on weak areas of the esophageal wall. Muscular weakness can be congenital or acquired. An increase in intra-esophageal pressure occurs due to uncoordinated peristalsis of the esophagus and its lower sphincter.
Authorized Products
- For esophageal esophagitis, soups are prepared only with vegetable broth, and cereals and vegetables in soups are pureed. Ready-made soups are seasoned with egg-milk mixture and butter. Sautéing vegetables for soups is not permitted.
- Dried wheat bread is allowed in quantities up to 200 g.
- Beef, lamb, turkey and chicken, lean pork are prepared boiled and rolled; cutlets, soufflés and quenelles can be made. Baking without a crust with sauces (milk or sour cream) is not contraindicated.
- Dishes from low-fat varieties of fish are consumed in the form of cutlets or in pieces.
- It is better to choose more gentle cereals - semolina, buckwheat or rice. They are boiled in water or with milk. Buckwheat and rice porridges are pureed and brought to a semi-viscous state with milk.
- Milk, low-fat cream (in dishes) and non-acidic kefir, you can make milk jelly and milk cream. Cottage cheese is chosen with medium fat content and consumed in its natural form (well mashed and slightly diluted with milk), as well as in the form of a soufflé or pudding. Avoid fermented milk drinks with high acidity from the diet.
- Butter in the amount of 20 g and refined sunflower oil are used in ready-made dishes.
- Vegetables with low fiber content are allowed (potatoes, beets, cauliflower, pumpkin, carrots). They are consumed boiled and pureed. You can eat vegetable puddings.
- Drinks include milk tea, fruit teas, sweet fruit juices, herbal teas (mint tea is excluded). Sugar or honey is added to teas and decoctions.
- You can make purees, jelly, jelly and compotes from sweet fruits. Avoid eating raw fruits.
Table of permitted products
| Proteins, g | Fats, g | Carbohydrates, g | Calories, kcal | |
Vegetables and greens | ||||
| zucchini | 0,6 | 0,3 | 4,6 | 24 |
| cauliflower | 2,5 | 0,3 | 5,4 | 30 |
| potato | 2,0 | 0,4 | 18,1 | 80 |
| carrot | 1,3 | 0,1 | 6,9 | 32 |
| beet | 1,5 | 0,1 | 8,8 | 40 |
| pumpkin | 1,3 | 0,3 | 7,7 | 28 |
Cereals and porridges | ||||
| buckwheat (kernel) | 12,6 | 3,3 | 62,1 | 313 |
| semolina | 10,3 | 1,0 | 73,3 | 328 |
| cereals | 11,9 | 7,2 | 69,3 | 366 |
| white rice | 6,7 | 0,7 | 78,9 | 344 |
Bakery products | ||||
| wheat bread | 8,1 | 1,0 | 48,8 | 242 |
Confectionery | ||||
| jelly | 2,7 | 0,0 | 17,9 | 79 |
Raw materials and seasonings | ||||
| honey | 0,8 | 0,0 | 81,5 | 329 |
| sugar | 0,0 | 0,0 | 99,7 | 398 |
| milk sauce | 2,0 | 7,1 | 5,2 | 84 |
| sour cream sauce | 1,9 | 5,7 | 5,2 | 78 |
Dairy | ||||
| milk | 3,2 | 3,6 | 4,8 | 64 |
| cream 9% | 2,8 | 9,0 | 4,0 | 107 |
Cheeses and cottage cheese | ||||
| cottage cheese | 17,2 | 5,0 | 1,8 | 121 |
Meat products | ||||
| boiled beef | 25,8 | 16,8 | 0,0 | 254 |
| boiled veal | 30,7 | 0,9 | 0,0 | 131 |
| rabbit | 21,0 | 8,0 | 0,0 | 156 |
Bird | ||||
| boiled chicken | 25,2 | 7,4 | 0,0 | 170 |
| turkey | 19,2 | 0,7 | 0,0 | 84 |
Eggs | ||||
| chicken eggs | 12,7 | 10,9 | 0,7 | 157 |
Oils and fats | ||||
| butter | 0,5 | 82,5 | 0,8 | 748 |
Non-alcoholic drinks | ||||
| mineral water | 0,0 | 0,0 | 0,0 | — |
Juices and compotes | ||||
| jelly | 0,2 | 0,0 | 16,7 | 68 |
| rose hip juice | 0,1 | 0,0 | 17,6 | 70 |
| * data is per 100 g of product | ||||
Symptoms and clinical manifestations of epiphrenic diverticula
Almost half of epiphrenic diverticula are detected incidentally as a radiological finding. Usually these are diverticula with a diameter of up to 2-3 cm. With epiphrenic diverticula, patients complain of a feeling of heaviness, pain in the lower part of the sternum or in the area of the xiphoid process, and progressive difficulty swallowing. Some patients experience aerophagia, putrid breath, and regurgitation of old decomposed food. In some cases, attacks of bronchial asthma and angina may occur. The severity of the symptoms of the disease depends on the size of the diverticulum and the degree of its filling with food masses.
Indications for surgical intervention for epiphrenic diverticula do not differ from the treatment of Zenker's diverticula. The operation is indicated for complications: perforation, penetration, bleeding, stenosis of the esophagus, cancer, development of fistulas, large diverticula complicated by at least short-term retention of food masses in them, long-term retention of food in the diverticulum, regardless of its size. Lack of effectiveness from conservative therapy.
Very important! A feature of my approach to choosing treatment tactics for patients with esophageal diverticula is the earlier determination of indications for surgical treatment using the laparoscopic method (through several punctures of the abdominal wall), without waiting for complications to develop and without wasting time on useless conservative treatment methods.
Typically, the traditional approach, which most clinics use, to epiphrenic diverticula is to perform a left-sided thoracotomy along the VII - VIII intercostal space.
Currently, in the surgery of esophageal diverticula, methods for their removal using video thoracoscopic or laparoscopic (which is even less traumatic) techniques are becoming increasingly widespread.
My experience in treating patients with esophageal diverticula is more than 14 years
.
During this time, I was able to successfully operate and treat more than 100 patients
.
Very important! Unlike other clinics, I use a minimally invasive laparoscopic approach, which allows, without opening the pleural cavity, to isolate the epiphrenic diverticulum at a distance of up to 8-10 cm from the cardia, remove it and reliably close the esophageal wound. To do this, I stitch the base of the diverticulum with an endoscopic stapler EndoGia-30 (Switzerland), which allows you to apply a 3-row titanium suture.
The basis of a precision technique for bloodless isolation of a diverticulum from surrounding tissues is the use of the LigaSure dosed vessel ligation system (Switzerland).
Very important! I always remove the esophageal diverticulum under the intraoperative control of fibroesophagoscopy; this allows during the operation (by means of illumination) to give the surgeon an excellent reference point in the surrounding tissues and, most importantly, to excise the diverticulum under double visual control (laparoscopy and fibroisophagoscopy). This double control, in turn, guarantees the completeness of its excision and the absence of narrowing of the lumen of the esophagus after suturing the diverticulum stalk with a stapler.
In the case of a combination of epiphrenic diverticula and achalasia cardia, hiatal hernia, chronic reflux esophagitis
I perform simultaneous simultaneous surgical intervention: diverticulectomy and correction of the hiatal hernia or cardiomyotomy in my own modification.
The patient begins to walk the next day after surgery and eat food 1-2 days later. Discharged on the 3rd day, after a control chest x-ray.
Thus, the earlier (before complications develop) surgery is performed for esophageal diverticulum, the better the treatment results.
Pharyngeal-esophageal diverticula are operated on by a thoracic surgeon using access to the neck, through a cosmetic incision using the LigaSure dosed vascular ligation system (Switzerland) to isolate the diverticulum and the endoscopic stapler EndoGia-30 (Switzerland), which allows you to apply a safe 3-row titanium suture to the wall esophagus.
Rice. 2. Removal of esophageal diverticulum using an endoscopic stapler using laparoscopic access.
Epiphrenic diverticula (from 1 to 10 cm from the cardia) I operate laparoscopically
through punctures, also using the LigaSure dosed vessel ligation system (Switzerland) to isolate the diverticulum and the EndoGia-30 endoscopic stapler (Switzerland) (Fig. 2).
In this case, I perform all stages under double visual control - laparoscopic and fibroesophagoscopic from the side of the lumen of the esophagus.
All of the above measures make it possible to perform surgical interventions for esophageal diverticula reliably, with a minimum number of complications, with a short hospitalization period and a quick return to normal life.
Postoperative follow-up
After the operation, 3-4 incisions 5-10 mm long remain on the skin of the abdomen. From the first day, patients begin to get out of bed, drink, and on the second day take liquid warm food. Discharge from the hospital is carried out on 3-4 days, depending on the severity of the disease. The patient can begin work in 2 - 3 weeks. A strict diet should be followed for one and a half to two months, a softer diet should be followed for 2-3 months. Further, as a rule, the patient leads a normal lifestyle - without medications or diet.
At the request of patients, the clinic can undergo a full examination before surgery to determine the optimal treatment tactics and choose the method of surgical intervention.