The symptoms of gastritis are familiar to many - heartburn, heaviness in the stomach, pain in the sternum. According to many doctors, the causes of gastritis are poor nutrition - quick snacks, incorrect and strict diets, eating too spicy and fatty foods. A proper diet for gastritis and pancreatitis is the first step to a quick and successful recovery. Remember that the menu for patients should be prepared by a nutritionist. There are general rules and recommendations, but the table for ulcers should be prepared individually, taking into account the characteristics of the body and general health.
Allowed foods for gastritis
Gastritis cannot be treated solely with medications; in order to alleviate its symptoms, it is necessary to eat properly. The basic rule is regular meals and a limited table. A diet for gastritis is prescribed to the patient after a full examination, because the disease comes in two types - with low and high acidity. A diet for gastritis with low acidity should include those foods that will stimulate the production of gastric juice; in the second case, such foods, on the contrary, are completely excluded from the diet. With hyperacid gastritis, gastric secretion is increased, so diet therapy should primarily focus on reducing secretory function. The diet for superficial gastritis is not as strict as for the acute form, but you should still adhere to some rules.
A diet for gastritis and pancreatitis, as well as cholecystitis, should be prescribed by a doctor, but there are general rules:
- Avoid taking liquid and solid foods at the same time;
- Foods that contain fiber should be removed from the diet;
- discard seasonings and hot peppers;
- eat less salty foods.
The table for patients with ulcers should consist of soft food - porridge, pureed soups, boiled vegetables. A diet for gastritis with low acidity is a complete rejection of fried, fatty, spicy salted, smoked, full-fat milk, and fresh baked goods.
Treatment of cholecystitis
Treatment of cholecystitis can be medicinal and surgical. Surgical techniques include removal of the gallbladder (cholecystectomy) laparoscopically (minimally invasive procedure) or conventional access. It is used in the acute inflammatory process, if conservative actions are ineffective, with the development of jaundice, routinely in the presence of stones in the bladder (in order to prevent painful attacks and acute inflammation in the future).
Drug therapy for cholecystitis is aimed at eliminating the infection (antibiotics, antiparasitics), normalizing the motility of the biliary tract and the outflow of bile (therapeutic diet, antispasmodic drugs, choleretic drugs, therapeutic duodenal intubation).
Treatment of cholecystitis can be medicinal and surgical
Diet for cholecystitis is very important, since unhealthy diet plays an important role in the development of the disease. The basic principles of nutrition include frequent but fractional meals with the exception of fatty, fried, spicy foods. You need to lead a healthy and active lifestyle. It is necessary to move more, which will prevent stagnation of bile and the development of the disease. It is also necessary to get rid of bad habits (smoking and drinking alcohol).
Treatment of chronic cholecystitis
During a period of severe exacerbation of the disease, the patient must be hospitalized in a therapeutic hospital. In mild cases, treatment is usually carried out on an outpatient basis. During the period of exacerbation, patients with chronic cholecystitis are recommended to rest in bed for 7-10 days. Food should be mechanically and chemically gentle and not have a cholekinetic effect. After eliminating signs of exacerbation of chronic cholecystitis, diet No. 5 is prescribed.
Drug therapy includes the use of drugs to relieve pain, normalize the function of the autonomic nervous system and the rational use of choleretic drugs described in the previous section. As an antispasmodic, it is advisable to prescribe duspatalin 200 mg (1 drop) 2 times a day. In the treatment of chronic cholecystitis, the use of enzyme preparations (digestal, festal, panzinorm, creon) for 3 weeks during meals, as well as antacid preparations (maalox, phosphalugel, remagel, protab), used 1.5-2 hours after meals, is indicated.
Prevention of cholecystitis
The most important factor in the prevention and treatment of cholecystitis is the normalization of diet. It is necessary to restore the function of the gallbladder and organize adequate passage of bile. In order for bile not to stagnate, it is necessary to eat regularly, and in order for it to be released in full, food must be in adequate quantity.
The most important factor in the prevention and treatment of cholecystitis is normalization of diet
If you do not normalize your diet and eat frequently (there are such recommendations), then the gallbladder will be constantly in a contracted state, bile will flow into the intestines directly from the liver, and the bile that is in the bladder will remain there, without a chance to be replaced by fresh bile. Stagnation of bile is a direct cause of inflammation and stone formation. Also, with chronic cholecystitis, it is necessary to work on normalizing weight and physical inactivity. The composition of bile and the functioning of the gallbladder are directly related to metabolism and lifestyle.
Taking honey dissolved in a glass of warm water on an empty stomach is a well-known method for treating gastrointestinal diseases, prescribed in the sunnah. For chronic cholecystitis, it is also effective - it helps cleanse the entire upper floor of the gastrointestinal tract, remove excess mucus and relieve spasms, and remove bile. You can take honey every morning for both prevention and treatment - without the risk of side effects.
Also in the treatment of chronic cholecystitis, black cumin seed oil can be used, a teaspoon twice a day: if tolerated well, you can take it with honey on an empty stomach; if tolerated poorly, try taking it after meals. Black cumin oil has a choleretic effect, and bactericidal properties help cope with the infectious component.
Basic principles of a diet with high stomach acidity
The diet for gastritis with high stomach acidity should contain boiled vegetables, dairy dishes, cereals, berries and fruits, jelly and compotes. The food should be soft, the ideal consistency is puree. For ulcers, lean meat is allowed - steamed cutlets, soufflés, rolls, purees. For hyperacid gastritis, vegetable milk soups are recommended (with the exception of cabbage). It is also worth noting that if you have high acidity, you should not consume low-fat milk, onions, or garlic.
With hyperacid gastritis, food should be consumed slowly, chewed thoroughly, and eaten often, but in small portions. After eating, be sure to rest for 10-15 minutes. It is unacceptable to eat in front of the TV or at a fast pace, or to overeat. Any chewing gum is contraindicated, as it stimulates gastric secretion.
General rules
Gallbladder diseases are quite common diseases. In their development, a certain stage can be traced: dyskinesia (functional disorders of the gallbladder with symptoms of hypo- and atony) - dyscholia (impaired composition of bile, cholesterosis of the gallbladder wall) - inflammation.
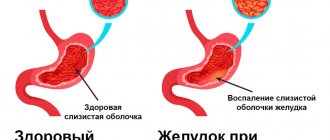
Chronic cholecystitis is considered an inflammatory disease of the gallbladder wall, in the development of which infection plays a major role. Long-term cholecystitis causes disturbances in other organs of the digestive system. Typically, patients have concomitant gastritis or pancreatic diseases. Gastritis can accompany cholecystitis at any stage of its development, and is most often associated with biliary reflux . The incidence of gastritis is 68-83%.
The constant reflux of duodenal contents containing bile has a direct damaging effect on the mucosa. The degree of changes in the mucosa depends on the duration of biliary reflux. In addition, bile acids, changing the chemical composition of the gastric mucosa, can enhance the effect of other factors: Helicobacter pylori infection and hydrochloric acid and pepsin of gastric juice. Patients may develop catarrhal or erosive gastritis , the motor function of the stomach and secretory function are impaired (secretion is usually reduced).
For cholecystitis and gastritis, it is also important to change your lifestyle and diet:
- timely eating and frequent small meals;
- reduction in animal fats in the diet;
- refusal to drink alcohol and sweet carbonated drinks;
- exclusion of spicy and fried foods, which irritate the mucous membranes;
- elimination of inactivity;
- getting enough sleep at night;
- stopping smoking.
The main table for these diseases during the period of remission can be Table No. 5 , and in accordance with the stage of gastritis (exacerbation), diet correction is carried out. The gentle regime corresponds to fractional meals. More frequent meals (4-6 times) improves the outflow of bile, and small portions do not overload the stomach, are better digested and evacuated from the stomach, preventing stagnation of chyme.
The diet for cholecystitis and gastritis contains the physiological norm of proteins and carbohydrates. Protein restriction is not advisable, since it stimulates the formation of bile acids, increases the cholate-cholesterol index , and this in turn prevents stone formation.
At the same time, it is necessary to limit the extractive substances formed during cooking broths, stewing meat and fish, and during frying. Strong stimulants (broths, mushrooms, coffee, carbonated drinks, alcohol, smoked meat and fish) and irritants (fried foods, coarse vegetables - radishes, garlic, onions, radishes, pickled dishes, seasonings and hot spices and dishes) are excluded from the diet. .
It is advisable to enrich the diet with foods rich in lipotropic substances - these are essential amino acids that protect the liver from fatty degeneration and reduce the risk of stone formation. Therefore, cottage cheese, oatmeal and buckwheat porridge, bran bread, egg whites, cod, pike perch and other low-fat fish, beef, soybeans (if well tolerated), whey, and buttermilk are introduced into the diet of patients.
Most authors recommend limiting fat content. However, it cannot be completely excluded, since fats stimulate the secretion of bile and are necessary for better absorption of fat-soluble vitamins. Refractory fats, lard, fatty meat and poultry are harmful to gastroenterological patients. You can use butter from animal fats.
At the same time, vegetable oils containing beneficial unsaturated fatty acids are introduced, which stimulate bile secretion and generally improve the condition of the liver. These oils are not contraindicated for gastritis with high acidity (if low, they are contraindicated in large quantities). Vegetable oils can be added to vinaigrettes, boiled and raw vegetables, and ready-made dishes. Limit/exclude vegetables containing a lot of fiber (white cabbage, turnips, radishes).
Carbohydrates are limited to simple ones (sweet pastries, preserves, jams). The amount of fluid is not limited, as it improves the flow of bile.
Exacerbation of gastritis dictates the prescription of a more gentle diet:
- pureed soups with cream, egg-milk mixture, minced boiled meat;
- pureed, non-coarse vegetables in the form of puree (potato, carrot and beetroot), to which milk or cream is added, you can eat vegetable baby food or prepare a steam soufflé from vegetables;
- boiled turkey, beef and chicken in the form of minced meat several times rolled and products in the form of soufflés, pates and quenelles;
- chopped or rolled fish;
- milk jelly, well-mixed cottage cheese, boiled porridge with milk.
As inflammation decreases, the diet expands and the degree of mechanical sparing of the stomach decreases. The patient can already eat meat and fish in pieces and use baking, as in Diet No. 5 . Fresh, not rough fruits are introduced into the diet, and vegetables are best consumed boiled or stewed until stable remission is achieved.
Diet for low acidity
A diet for gastritis with low acidity should include the following foods:
- lean meat and fish;
- stewed and steamed vegetables (ideal carrots and cabbage);
- baked fruits.
Fried foods, fast food, and sweet sodas should be completely excluded from your diet. Before meals, it is recommended to drink a glass of slightly carbonated mineral water, for example, Essentuki-17. Drinking herbal teas with sugar is allowed.
Special diets for stomach ulcers
For stomach diseases, ulcers and cholecystitis, the therapeutic diet 1a has proven itself well, which can also be used as a disease prevention. Diet 1a reduces irritation of the mucous membrane, accelerates recovery, reduces irritation and excitability of receptors. The basis of the therapeutic diet 1a for patients with gastritis is pureed dishes, slimy soups, porridge with water or diluted milk. Eggs, lean fish and meat, vegetable oil, diluted fruit juices, teas and herbal infusions are allowed. The diet for gastritis and cholecystitis completely excludes:
- coffee and cocoa;
- legumes;
- cheese;
- pasta;
- sauces;
- tomatoes and products containing them;
- dried fruits;
- alcohol.
Based on the basic rules and recommendations, you can easily create a menu for the week, but for this you need to consult a doctor.
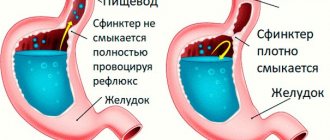
Reflux gastritis
The symptoms of reflux gastritis are almost the same as a regular stomach ulcer. This is heartburn, belching, chest pain. Such symptoms usually begin to worsen immediately after eating or while lying down. The therapeutic diet for reflux gastritis completely excludes fried and fatty foods, spices, coffee, and alcohol.
The diet for gastritis is aimed primarily at restoring the inflamed mucous membrane of the stomach and esophagus; such a disease cannot be treated exclusively with medication, it must include therapeutic nutrition. Very often, for this disease, diet 1a is prescribed. The diet for reflux gastritis does not have strict restrictions, but all recommendations must be strictly followed.
Gastritis pancreatitis and cholecystitis and treatment of the pancreas
Gastritis and pancreatitis are inflammations, in the first case of the stomach wall, in the second - of the pancreas. Both of them have a chronic form and periods of exacerbations, foci of inflammation, and similar symptoms.
Symptoms of the three diseases appear immediately, the common signs are:
- alternating salivation and dry mouth;
- dizziness;
- weakness, apathy, anxiety;
- nausea and vomiting.
Constant inflammation turns the disease into a chronic one, and the combination of the two dramatically increases the likelihood of death. Taken together, the three diseases guarantee a long, difficult treatment. All organs are prone to self-destruction, since they contain enzymes that digest food.
Doses of antibiotics are prescribed by the doctor as well as blockers and inhibitors metronidazole clarithromycin ranitidine and omeprazole, respectively
Treatment of gastritis and pancreatitis, traditional and innovative
Fasting at the time of exacerbation is traditional for all three diseases (the disappearance of symptoms is a signal to begin careful eating on a strict diet). Vitamin preparations, mucosal restorers, antispasmodics, antimicrobial drugs help the stomach. Depending on the acidity, the remaining glands, including the pancreas, are reduced or stimulated.
Doses of antibiotics are prescribed by the doctor, as well as blockers and inhibitors - metronidazole, clarithromycin, ranitidine and omeprazole, respectively. New techniques include bioresonance therapy, which is based on suppressing vibrations of diseased organs and cells, replacing them with vibrations causing resonance of healthy cells. Therapy is performed using the same equipment as diagnostics, reducing treatment time and increasing its effectiveness. Gastritis and the pancreas require the same prevention, which makes life much easier for patients.
How to distinguish the symptoms of gastritis from pancreatitis
Chronic gastritis and pancreatitis, in many ways, have similar symptoms. Due to the close location of the organs, it is not immediately possible to distinguish which one is inflamed. However, there are differences, and they relate, first of all, to the location of the pain. With gastritis, they occur in the central upper part of the abdomen, manifesting themselves in the form of spasms, colic, or are dull and aching. And with pancreatitis, their character is encircling, constant and cramping, and they manifest themselves more intensely and last longer.
Chronic gastritis and pancreatitis have many similar symptoms due to the close location of the organs, it is not immediately possible to distinguish which one is inflamed
If inflammation has affected the head of the pancreas, pain will be noted in the upper right part of the epigastric region. When the body is affected, they are localized in the left upper abdomen; if the tail is affected, the pain will be in the left hypochondrium. In addition, pain can radiate to the back and chest. Also, in these diseases, one can clearly trace the connection between the occurrence of pain and food intake.
As a rule, with gastritis it occurs immediately after eating, especially in diseases with high acidity. Basically, gastritis worsens when the diet is violated. With pancreatitis, the connection with food intake is not so obvious; pain can occur after a few hours, and when drinking alcohol, even after a day. Naturally, from these symptoms one can roughly estimate which organ is inflamed. Clinical and instrumental diagnostic methods will help to most accurately identify and distinguish diseases.
Gastritis in a child
If a child suffers from stomach diseases, drawing up the correct menu is mandatory. The symptoms of the disease in children are the same as in adults - pain in the stomach and chest, heartburn, and possible belching. The therapeutic diet for gastritis in children is not much different from that in adults, but it is still worth taking into account some features of the growing body. A child's diet with an ulcer should be as balanced as possible and include all the necessary nutrients and vitamins. Breakfast for children with gastritis should be hearty and satisfying - porridge, dairy products, steamed omelet. If you have a stomach ulcer, completely avoid soda and sandwiches. The therapeutic diet for gastritis should include protein foods in sufficient quantities, vegetables and fruits, and the menu should be varied. The exception is citrus and sour berries. Coffee and strong tea are not recommended; give preference to compotes and jelly.
Diet 1a for gastritis is well suited for a child; it can rightfully be considered universal for stomach diseases. But it is worth noting that the diet for gastritis 1a for a child cannot be permanent; after a week it is recommended to take a break and switch to a different diet.
Reviews and results
During the period of remission of gastritis and cholecystitis, there is no need for strict restrictions, however, restrictions on spicy, excessively fatty and fried foods should be maintained. Nutrition during this period is quite varied and can be carried out for a long time. Strict restrictions are advisable only during periods of exacerbation and patients themselves feel the need for this. The exclusion of foods that provoke deterioration, bloating and pain, against the background of adequate treatment, quickly normalizes the condition of patients. Reviews indicate the positive impact of nutrition on the condition of the intestines and pancreas.
- “... Exacerbation usually occurs in spring and autumn. This forces you to switch to proper nutrition for a month or a month and a half. At this time I eat only steamed dishes (cutlets, omelettes, pates), soups, various cereals and vegetable purees. I make it not only from potatoes, but also pumpkin, zucchini, and cauliflower. I add a little salt, add ground bay leaf and butter - it turns out delicious. Steamed cutlets are not very tasty, but they can last for 1.5 months. During this time, heartburn and stomach pain disappear. Even without an exacerbation, I don’t eat spicy, fried, pickled vegetables or fatty foods”;
- “... I start to eat properly during an exacerbation, although at other times I don’t eat spicy or fried foods. I have long excluded onions, garlic, radishes, mayonnaise, smoked sausage, ketchup, and tomato sauce, as they cause pain in the stomach and right hypochondrium. Eating white cabbage (and in any preparation) increases pain in the intestines and causes bloating. I also don’t tolerate overeating well. I switch to boiled meat and fish, porridges, light, not fried soups. Eating for a month helps restore the stomach, reduces bitterness and bloating”;
- “...I eat irregularly and dry food. This led to the development of cholecystitis first, and a year later gastritis. I feel especially bad when there is an exacerbation: heaviness and pain in the stomach, constantly increased appetite and heartburn, terrible bloating. I don’t go to the hospital, but receive treatment on an outpatient basis and go on a diet. After 20 days, heaviness and discomfort in the stomach disappear. I only eat boiled, chopped at first. Nothing spicy or fried, much less fatty or smoked. My family does not support such a diet, so I have to cook for myself separately. In this regard, my proper nutrition ends in a month, and it’s difficult to combine it with work.”
Therapeutic diet for cholecystitis and gastritis - features and differences
Many diet rules for gastritis and cholecystitis are the same. The menu includes soups, cereals, properly prepared vegetables and fruits. The table must be as balanced as possible. In case of acute cholecystitis, it is recommended to completely abstain from food in the first days of illness. After a few days, you can expand the menu to include slimy soups and thoroughly pureed porridges. A week later, for cholecystitis, a therapeutic diet No. 5 or 1a is prescribed. Diet menu No. 5:
- a large number of vegetables and fruits;
- vegetable fats;
- butter.
Fatty meat, garlic, spices, canned food should be excluded in case of acute cholecystitis and other diseases.
The therapeutic diet for reflux esophagitis and gastritis, cholecystitis also has a lot in common, but in any case, if you have been given an unpleasant diagnosis, you should not create a menu for the week yourself, this should be done by a specialist. If you are interested in a diet for weight loss with gastritis, then it is worth remembering that fasting and strict abstinence from food are contraindicated for this disease. If a diet for gastritis is needed for weight loss, only a professional can develop it, since in solving this issue it is necessary to take into account many individual characteristics and the general condition of the body, as well as the stage and symptoms of the disease.
What kind of diseases: gastritis, cholecystitis, pancreatitis
The digestive system is one of the main ones in our body. It is from it that a person receives the energy that is necessary for work and rest. And the stomach and intestines occupy the main positions in this system, since these are two border links in the process of food processing.
The digestive system is one of the main ones in our body; it is from it that a person receives the energy that is necessary for work and rest.
But according to statistics, almost every person experiences one or another problem with the gastrointestinal tract. For many diseases, the symptoms are quite similar. These include abdominal pain, nausea, diarrhea, and lack of appetite.
Gastritis is a disease in which there is inflammation of the gastric mucosa. Causes: alcohol, nicotine, eating disorders, possibly disease of other organs. Depending on the nature of the pain and its frequency, doctors can diagnose acute or chronic gastritis.
Acute gastritis can appear suddenly. The patient begins to experience discomfort in the stomach, loss of appetite, severe headaches, and sometimes vomiting. If gastritis spreads to the intestines, this is accompanied by acute colic and diarrhea. As a treatment, first of all, gastric lavage is performed, thereby eliminating the causes of the disease. After this, a special course of nutrition is required, consisting of liquid soups and cereals.
At the same time, medications are prescribed. Recovery occurs in 3-5 days. If acute gastritis is not cured in time, it will recur and then develop into a chronic disease. It is much more difficult to treat. Plus, you will have to switch to a very strict diet, in which almost everything is prohibited.
Cholecystitis is inflammation of the gallbladder. As a result, the outflow of bile from it, as well as the blood flow in the walls of the gallbladder, is disrupted. The main cause of cholecystitis is the presence of stones in the bladder. This leads to infection by microflora from the intestines. Again, there are acute and chronic forms of the disease.
Cholecystitis is inflammation of the gallbladder as a result of which the outflow of bile from it and the blood flow in the walls of the gallbladder are disrupted.
Symptoms of acute cholecystitis are pain in the right side of the abdomen, radiating to the shoulder or shoulder blade. As well as vomiting, fever and chills. Even itching and jaundice are possible. The chronic version is dangerous. It may develop into hepatic jaundice. In this condition, the patient requires urgent hospitalization. Treatment of cholecystitis consists of medications, a special diet, but in some cases it can even go as far as surgery.
Inflammation of the pancreas is called pancreatitis. As a result of the disease, enzymes and toxins cannot enter the intestines and begin to destroy the gland itself. At the same time, they can easily enter the blood, and through it reach other organs. For example, hit the heart or brain. Therefore, any type of pancreatitis requires prompt treatment.
First of all, ice is applied to the pancreas. This slows down the destructive process. After this, all affected organs should remain at rest for several days. At this time, the patient is prescribed a course of medications. Intravenous nutrition is also possible. But if gland cysts occur, they are removed surgically. By the way, every second person with pancreatitis has problems with alcohol. In other cases, the cause may be injury, infection, or congenital abnormality.
Possible recipes
Do not think that with such stomach diseases your nutrition will be limited. There are special recipes for delicious and healthy dishes that you can prepare yourself and diversify your diet for every day.
Recipes for first courses - rice soup, cabbage soup. For the first one you will need rice, chicken fillet, potatoes, carrots, onions. Separately cook the fillet and vegetables, then finely chop the vegetables, chop the meat and combine. Let the soup boil, the dish is ready. The recipes for cabbage soup are varied; if you follow a diet for duodenitis and gastritis, the following will do. Place chopped potatoes and shredded cabbage in a saucepan with water. Simmer the onion, carrots and tomato (previously doused with boiling water and without the skin) over low heat until half cooked, add to the pan with the vegetables after the water boils. Cook the cabbage soup until fully cooked for 10-15 minutes.
Recipes for second courses are full of variety, so don’t despair, you just need to look, and you can eat tasty and healthy on a diet for gastritis. The main recipes for second courses are casseroles, stews, and salads. You can also make desserts.
Self-treatment
The diet for gastritis, cholecystitis and other diseases has many general rules, but a doctor should be involved in developing the menu. If it is not possible to turn to specialists, pay attention to the general rules, completely eliminate prohibited foods from your diet, do not indulge in fast food and do not overeat. Try diet table for gastritis No. 1a.
As soon as possible, contact a nutritionist who, based on the results of the examination and the general condition of your body, will help you create a menu for the week. Pay attention to your health; proper nutrition will help you get rid of many diseases and problems.
Diagnostic methods
After the first signs of the disease appear, you should seek help from a gastroenterologist. A preliminary diagnosis is made by the attending physician based on the patient’s complaints, taking into account the nature of the described pain, the frequency of its manifestation and other symptoms.
It is possible to reliably confirm the diagnosis and determine treatment methods after a complete diagnosis:
- Blood test study in the laboratory. With cholecystitis, especially in the acute period, ESR levels will be increased, and neutrophilic leukocytosis will be detected.
- Ultrasound. The examination allows you to visually assess changes in the organ. The doctor determines the shape of the organ, the thickness of the walls and its dimensions, evaluates the contractile function and the number of dense formations, if any. In advanced stages of cholecystitis, you can notice deformation of the organ and thickening of the walls.
- Probing, during which three portions of bile are collected. Further microscopic examination is used to assess the consistency of the bile and its color. At this stage, the pathogen that is the cause of the infectious process is also determined. This will determine how to treat cholecystitis and which drugs will be more effective.
- X-ray contrast method - allows you to assess the degree of impairment of the motor function of the organ.
In doubtful cases, the patient may be prescribed additional diagnostic examinations.