What to do if you have high stomach acidity?
Stomach problems are one of the most common ailments that plague a huge number of people. Sometimes it is severe pain, sometimes constant nausea, and often vomiting and lack of appetite. There are many reasons for the occurrence of such problems, but one of the main reasons why a person feels discomfort is increased stomach acidity.
The natural physiological increase in acidity that occurs after eating occurs relatively unnoticed in a healthy person. It is also considered normal if the pH temporarily increases after eating certain foods - citrus fruits, tomatoes and tomato juice (paste, sauce), alcoholic drinks, etc. A condition in which the level of hydrochloric acid significantly exceeds the norm, regardless of food intake, is considered pathological.
Causes
The most common cause of increased stomach acidity is a nutritional factor, i.e., improper, irrational nutrition. Spicy, salty, fatty foods, and alcoholic drinks have an irritating effect on the gastric mucosa, as a result of which the parietal cells begin to secrete hydrochloric acid in greater quantities than required.
The nutritional factor also includes too rapid absorption of food. In this case, a poorly chewed bolus of food enters the stomach, not sufficiently moistened with saliva, containing too large particles. To digest it, a larger amount of gastric juice is required, and therefore hydrochloric acid, which leads to increased acid production, and therefore to an increase in the acidity of gastric juice.
Other causes of increased stomach acidity may include:
- Infection with the bacterium Helicobacter pylori. This is a unique microorganism that can survive in an acidic environment. Once in the stomach, bacteria produce urease, which has an irritating effect on its walls. In an effort to destroy these bacteria, stomach cells intensively synthesize hydrochloric acid and pepsin.
- Chronic stress. In itself, it does not have a negative effect on the state of the digestive system, however, being in a depressed state, a person stops eating properly, often smokes, drinks alcohol, which negatively affects the gastric mucosa.
- Long-term use of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and/or corticosteroids, as they have an irritating effect on the gastric mucosa.
- Smoking. Nicotine has a stimulating effect on parietal cells, resulting in an increase in stomach acidity.
Causes
Increased stomach acidity can provoke the development of severe pain syndrome
Before moving on to the main symptoms of increased stomach acidity, it is worth saying what gastric juice is and why pathology can develop. Gastric juice is the juice that is produced by various cells of the mucous membrane of this organ. Thanks to this juice, the normal digestion process occurs and the necessary nutrients are absorbed in the body. One of the main indicators of normal stomach function will be the concentration of acid in gastric juice. Very often people experience increased acidity, which can be caused by the following reasons:
- Poor nutrition. Abuse of alcohol, spicy and fatty foods, large amounts of food consumed or, conversely, irregular meals in small portions
- Poor chewing of food. Often, when a person eats in a hurry, many large unchewed pieces of food end up in the stomach, which are very difficult to digest. And in order to do this, the stomach is forced to produce more gastric juice, and as a result, increase its acidity
- Long-term use of certain medications that have a harmful effect on the gastric mucosa. Such drugs usually include paracetamol, aspirin, hormonal medications, analgin
- Stress. Severe emotional overload, as well as constant tension, can provoke the development of various health problems in a person. Very often, the first thing this affects is the gastrointestinal tract, since in most cases, when experiencing stress, a person forgets to eat, or takes a large amount of alcoholic beverages, which have a detrimental effect on the gastric mucosa
- Smoking. Tobacco smoke, despite the fact that it is most concentrated in the lungs, negatively affects the normal functioning of the stomach. Smokers often have digestive problems. Tobacco smoke causes the greatest harm when a person smokes on an empty stomach. It is at this moment that toxic substances have the greatest effect on the mucous membrane, provoking increased secretion of gastric juice and an increase in its acidity
- Helicobacter. More recently, scientists discovered this bacterium, which is the cause of such diseases. Like stomach ulcers and gastritis. Helicobacter is one of the few bacteria that, due to its good adaptive abilities, can live in the stomach. If it enters the body, specific enzymes will be produced that damage the gastric mucosa. Separately, it should be noted that this bacterium is transmitted through saliva. Therefore, it is easy to become infected with gastritis by drinking from the same cup with someone who has it.
- Infection. After a person has suffered an infectious disease, be it even a simple influenza virus, complications may arise that sometimes affect the gastric mucosa. Any infection can spread very quickly throughout the body and find a further place for development in absolutely any organ.
Despite the fact that almost every person knows the main reasons why gastritis can develop and the content of hydrochloric acid in the gastric juice can increase, few people pay attention to them until the problem hits them.
Symptoms
Increased acidity very often occurs against the background of an imbalance in the process of regulating the acidity of the juice, as well as its neutralization. That is why, when acidity increases, a person may experience the following symptoms:
- Bloating.
- State of apathy, bad mood.
- Heartburn. It usually occurs either immediately after eating, or at the moment when a person takes a lying position. Heartburn is the reflux of stomach acid into the esophagus. The juice irritates the mucous membrane and therefore a strong burning sensation occurs, which is localized mainly in the Adam's apple area.
- Feeling of heaviness. This usually happens even after a small meal or snack.
- Pain. It can be either strong or not very strong. It occurs at the moment when acid enters the duodenum, or rather into its lumen. In addition, another cause of pain will be acid getting into damaged mucous areas. At the moment when their interaction occurs, the person feels a strong pain attack, which can last for several minutes. At the same time, it is difficult for a person to even move, the pain is so severe.
- Belching, which usually tastes either sour or bitter. Moreover, it appears mainly after eating.
- Problems with appetite. Due to the fact that after each meal a person suffers from pain or heartburn, appetite gradually decreases.
- Problems with stool. In some people this may be diarrhea, which is very difficult to relieve even with medications, and in some people it may be constipation for a long time.
- A feeling of constant discomfort in the stomach area, which can be manifested by stretching. Heaviness, tingling, etc.
And most importantly, not a single person has yet managed to independently relieve the symptoms of high stomach acidity. Of course, there are several medications that can help temporarily alleviate the condition. But only a specialist can find out the true cause of the increase in acidity and prescribe treatment.
1.General information
Every adult has heard about such a functional indicator of the digestive system as acidity. And not only adults: a school chemistry course includes information about the pH value, acid-base balance, as well as litmus paper and phenolphthalein as indicators of acidity.
The pH value of the gastric environment should normally be significantly shifted to the acidic side: if approximately seven is considered a neutral value, then the pH of gastric juice is 1.5-2.5. This is one of the evolutionary protective measures that, to some extent, prevents the introduction and reproduction of numerous infectious pathogens that enter the body in large quantities with food. In addition, a strongly acidic environment is provided as a normative condition for food processing in such a complex biochemical synthesizer as our digestive (digestive) system.
However, acid has an aggressive and destructive effect not only on pathogenic microorganisms and food products; it can also corrode its own mucous membrane lining the inner surface of the stomach. Therefore, it is necessary, firstly, precise control and constant “adjustment” of the acidity level, and secondly, physicochemical protection of one’s own tissues. The regulatory function is ensured by the fact that the stomach produces, along with hydrochloric acid, special mucus with an alkaline pH reaction, which, as necessary, neutralizes excess acid and acts as a surface protector for the gastric walls.
Any deviations from the natural pH level for the stomach, if they are persistent or chronic, are dangerous. So, low acidity, i.e. рh>5, leads to the development of antacid gastritis and is considered a precancerous condition. Increased acidity in recent decades has become a real scourge of modern man.
Excessive “acidification” of the gastric environment (acidosis, ph
A must read! Help with treatment and hospitalization!
Diagnostics
The degree of acidity can be accurately determined only on an outpatient basis. For this purpose, the following gastroenterological studies are used:
- gastroduodenoscopy - endoscopic examination using a probe;
- daily pH-metry - a procedure carried out using acidogastrometers for 24 hours;
- assessment of the acidity level by the degree of staining of urine with ion exchange resins;
- fractional sounding of the digestive organ, during which a special tube sucks out the contents in different parts of the stomach with further laboratory analysis.
In modern practice, the method of daily pH-metry is recognized as the most accurate, since it allows you to measure the acidity of the stomach directly in its cavity, which allows you to minimize distortion of the analysis results.
Causes and symptoms of pathology
The causes of hypersecretion of hydrochloric acid can be both external and internal. The second category usually includes various gastrointestinal diseases (gastritis, ulcers), hormonal imbalance during pregnancy or menopause, as well as metabolic disorders in the body. External factors that increase stomach acidity are:
- unhealthy diet with abuse of fatty, fried or smoked foods;
- lack of sleep and rest;
- psycho-emotional experiences;
- pregnancy at any stage;
- bad habits.
Increased acidity of gastric juice can be easily determined by a burning sensation in the lower part of the sternum and pain under the ribs. The pathology is always accompanied by dyspeptic disorders in the form of belching, sour taste in the mouth and nausea. A person is haunted by a constant feeling of hunger, possible disturbances in the functioning of the intestines (constipation, colic, diarrhea, flatulence). Another symptom is reflux or the reflux of the contents of the duodenum along with bile back into the esophagus.
Consequences
Due to the excess hydrochloric acid content in the stomach and the resulting indigestion, the patient may experience a sharp loss of body weight. A deficiency of nutrients, vitamins and minerals leads to brittle hair and nails, deterioration in the appearance of the skin - it becomes gray, dull, dehydrated, loses tone and becomes vulnerable to mites. Teeth are also subject to negative effects.
A more serious complication of increased gastric pH is the occurrence of gastritis and peptic ulcers. However, the development of these diseases most often requires the presence of additional negative factors (Helicobacter pylori infection, unhealthy lifestyle, unhealthy diet).
Opportunities for quickly eliminating symptoms and normalizing the level of stomach acidity allow us to make favorable prognoses for patients who are attentive to their health and follow the doctor’s recommendations.
Basic nutrition rules
Regardless of what purpose the specialist or patient is pressing, which will cause an increase or, conversely, a decrease in stomach acidity, it is necessary to follow several basic rules, which include the following measures:
- Changing the nature of nutrition. Meals should always be frequent and small. It is forbidden to eat large portions of foods, as the stomach becomes overstretched and the parietal cells do not produce enough acid. This causes fermentation, bloating and abdominal pain.
- It is not recommended to consume fried or smoked foods, as the carcinogens they contain increase the risk of not only acidity disorders, but also malignant processes.
- Drinking enough liquid. According to many patients, the most beneficial is water with lemon added. It leads to increased acidity, which is dangerous for patients with initially reduced acidity levels.
- Complete exclusion of alcohol-containing products from the diet. To give up smoking.
- Limiting the use of medications. It is recommended to exclude medications as much as possible if they do not affect acidity. Continuation of therapy is mandatory when their deficiency can be life-threatening.
- Elimination of stress, emotional overload and other problems with the functioning of the nervous system.
Normalizing nutrition prevents the development of high stomach acidity. In order to prevent hydrochloric acid from accumulating in the stomach cavity, it is necessary to regularly adhere to fractional meals.
Among the foods that reduce the level of hydrochloric acid are:
- Dairy products that are not fermented include milk, cottage cheese and cheese.
- Fruit and vegetable dishes.
- Low-fat boiled meats.
- Boiled lean fish.
- Whole grain porridge.
Before creating the required diet, it is imperative to consult with a specialist. Only a doctor will be able to accurately identify the cause and, based on it, choose the most suitable and missing products for the body. A prerequisite is the selection of products taking into account calorie content and nutrient composition.
If necessary, the doctor selects a medicinal drink consisting of mineral waters and other drinks. Including them in the diet without prior examination can cause serious consequences for the body.
Taking water
Water with bicarbonate will help normalize acidity
Currently, in pharmacies and stores you can find a large amount of water that is used for medicinal purposes. Among them are sulfate, alkaline, chloride and other types of drinks.
The choice depends on the type of pathology for which the patient consults a doctor. Against the background of increased acidity, which leads to gastritis and peptic ulcers, it is recommended to include water containing bicarbonates in the diet.
The use of this mineral water leads to a decrease in the level of hydrochloric acid due to the entry of its ions with bicarbonate, which is an alkaline solution. As a result of a complex chemical reaction, neutralization occurs.
In addition, bicarbonates absorbed into the internal environment come into contact with a hydrogen ion. It is these ions that are involved in the production of gastric acid. During the treatment, the patient notes an improvement in well-being, a decrease in nausea and heartburn.
Great importance is also paid to its temperature; it is recommended to use heated water, which eliminates excess carbon dioxide content. The volume of liquid drunk should be up to a liter. It must be taken before eating food, since on an empty stomach the amount of hydrochloric acid is high.
How to reduce stomach acidity?
Treatment for high acid levels involves the use of the following medications:
- Proton pump blockers. These include Omeprazole and Lansoprazole.
- Histamine blockers. Doctors often prescribe Ranitidine and Famotidine. They normalize digestion and reduce the amount of acid.
- Antiacid drugs. The most effective are Almagel and Maalox. They are prescribed for inflammation of the stomach and to normalize the level of hydrochloric acid secretion.
- To eliminate stomach pain, experts prescribe Motilium or Domidon.
A well-known remedy for neutralizing hydrochloric acid is baking soda. However, experts recommend not to abuse it during treatment.
Leya Yu.Ya. pH-metry of the stomach. Chapter 1. Zones of formation and neutralization of hydrochloric acid in the stomach
Chapter 1ZONES OF FORMATION AND NEUTRALIZATION OF HOLARIC ACID IN THE STOMACH
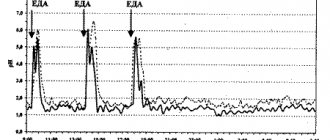
Physiologists and morphologists have established that there is a significant difference between the functions of different parts of the stomach, and they emphasized the leading importance of the region of the lesser curvature of this organ in secretory processes. There are at least 2 groups of gastric glands - their own (fundic) and pyloric glands (pyloric). Own glands are located in the body, fundus and intermedial part of the stomach. They contain parietal (producing hydrochloric acid), main (producing a complex of proteolytic enzymes) and mucoid, or accessory, cells (secreting mucins - mucus, mucopolysaccharides and gastromucoprotein - Castle’s “internal factor”, necessary for the absorption of vitamin B12). The pyloric glands are located in the distal part of the stomach, occupying about 1/5 of the mucous membrane of this organ. These glands are primarily composed of mucoid cells, but they may contain a small number—about 1%—of parietal cells. However, the experiments of I.P. Pavlov have already proven that the secretion of the pyloric antrum of the stomach, obtained on an empty stomach, is very viscous in consistency and has an alkaline reaction. This secret has a certain significance in protecting the mucous membrane from chemical influences and mechanical injuries. Despite the fact that the secretory function of the stomach is not necessary for life, it is very important. Hydrochloric acid creates the best conditions for the action of proteolytic enzymes (their optimum action is observed at pH 1.5-2.0, but activity remains even up to pH 5.0), causes swelling of food, increases the permeability of cellular structures, and promotes protein denaturation. In addition, hydrochloric acid is involved in the barrier function of the digestive system, promotes the separation of iron from food substances and converts ferric iron in food into a divalent ion, which is necessary for its absorption. Consequently, according to the function of the glands in the stomach, one should distinguish the upper - acid-forming - and lower - acid-neutralizing (neutralizing) zones [Leya Yu. Ya., 1976]. The first corresponds to the fundus, body and intermedial section, and the second corresponds to the pyloroantral section of the stomach (Fig. 1). It is the intermedial compartment that is distinguished by the most pronounced activity of acid formation. Often (for example, during surgery) the boundary of the acid-forming and neutralizing zones is determined. To do this, the pH probe probe is moved from the neutralizing zone to the acid-forming zone. The transition zone discovered in this case turned out to be narrow - changes in intragastric pH from more than 7 to less than 3 are usually observed over a period of 2-3 mm.
Rice. 1. Stomach areas.
1 - acid-forming; 2 - intermedial; 3 - neutralizing. Consequently, according to the function of the glands in the stomach, one should distinguish the upper - acid-forming - and lower - acid-neutralizing (neutralizing) zones [Leya Yu. Ya., 1976]. The first corresponds to the fundus, body and intermedial section, and the second corresponds to the pyloroantral section of the stomach (Fig. 1). It is the intermedial compartment that is distinguished by the most pronounced activity of acid formation. Often (for example, during surgery) the boundary of the acid-forming and neutralizing zones is determined. To do this, the pH probe probe is moved from the neutralizing zone to the acid-forming zone. The transition zone discovered in this case turned out to be narrow - changes in intragastric pH from more than 7 to less than 3 are usually observed over a period of 2-3 mm. Gastrin-producing cells are not detected in the body of the stomach; they are found in the pyloroantrum. Gastrin is released when food comes into contact with the mucous membrane of the mentioned section of the stomach, when it stretches or increases peristaltic activity. Under the influence of hydrochloric acid on the mucous membrane of the antrum, gastrin is released until then. until the pH of the gastric contents reaches 2.5-3.0. With a further increase in the concentration of hydrogen ions, the release of gastrin stops. Acetylcholine, as a mediator of the vagus nerve, enhances the release of gastrin and sensitizes parietal cells to its effects. The study of the topography of the acid-forming and neutralizing zones of the stomach is important both in theoretical and practical aspects. Ulcers are often found at the borders of the pyloric glands with other parts of the gastrointestinal tract. In addition, it is advisable to study the intragastric environment not only in the pyloroantral region, from where gastric contents are taken for titration, but also in the acid-forming zone, and precisely in the zone of maximum acid formation. This makes it possible to obtain information about the activity of gastric acid formation in the area of hydrochloric acid secretion even before its neutralization in the antrum. During the development of the disease, the glandular apparatus of the stomach is not affected to the same extent. The parietal cells, compared to the main cells, change earlier and to a greater extent. It follows from this that in a pathological process or disease, the acid-forming function of the stomach is first disrupted. The sizes of the acid-forming and neutralizing zones of the stomach can vary significantly in different patients. In patients with gastric body ulcers, the acid-forming zone is relatively small; at the same time, the neutralizing zone is larger than in patients with duodenal ulcer [Pokrotnieks Yu. Ya., 1983], and occupies 1/2 - 5/6 of the entire gastric mucosa [Antsans A. Ya. et al., 1980]. It can even cover up to 70-80% of the lesser and half of the greater curvature of this organ. In extreme cases, the neutralizing zone extends along the lesser curvature of the stomach - from the esophagus to the duodenum - even a few centimeters below the pylorus. The increase in the size of this zone appears to be the reason for the increase in acid-neutralizing function in patients with gastric ulcers. Consequently, in clinical practice it often happens that after the “correct” installation of the probe in the stomach, both pH sensors are located below the acid-forming zone, and the researcher does not receive information about the function of this region. On the other hand, in patients with highly active acid production, the neutralizing zone of the stomach is relatively small, which makes it difficult to place a pH sensor in this zone. In case of peptic ulcer, heterotopia of parietal cells was found in the mucous membrane of the pyloric antrum of the stomach in 8% of cases - in the form of elements interspersed with the pyloric glands; in one of the observations, focal heterotopia of the mucous membrane of the fundus of the stomach was found in the mucous membrane of the duodenum [Samsonov V. A., 1977]. In the literature, the terms “gastric secretion”, “contents”, “juice” are often not separated, but there is a difference between them. The secretion of the entire stomach or certain of its glands without admixtures of saliva, duodenal contents, residual fluid, food, etc. is a product of their activity. At the same time, when using the term “stomach contents”, its specific composition is not specified - in addition to the secretion of the gastric glands, the “contents” may contain various impurities. "Gastric juice" is a traditional, but not scientific, term. A pure gastric secretion, and even more so a pure secretion from the acid-forming and neutralizing zones of the stomach, cannot be obtained from a person: firstly, because the secretion from the acid-forming zone falls down into the neutralizing zone and is more or less neutralized by its contents; secondly, the stomach is a hollow organ, into which, both normally and in pathology, the contents of the esophagus and duodenum enter, and its contents are evacuated into the duodenum. In particular, when studying the acid-forming function of the stomach, possible impurities in its secretion, as well as loss of gastric contents through the pylorus, are usually not taken into account. When assessing the pH of the acid-forming zone of the stomach, it is apparently necessary to take into account that a certain part of hydrochloric acid, after reaching the surface of the mucous membrane, is immediately neutralized by the secretion of mucoid cells. During the study, the pH sensor is located over a large number of acid-producing glands, and the neutralization process always reduces the intragastric acidity indicated by the electrode. It should be noted that the term often used in the literature and in practice - the “neutralizing” zone of the stomach - is more correctly understood conditionally, since the neutralization of the secretion of the acid-forming zone by the secretion of the pyloric glands is only part (and there is reason to believe - not the main one) of the processes occurring in the pyloric antrum. In particular, in experiments on dogs, A. Ya. Antsans (1984) received an average of 1.12 ± 0.12 ml of secretion from the isolated neutralizing zone of the stomach in 1 hour under basal conditions, and from the isolated acid-forming zone - 3.14 ± 0 .50 ml of secretion. Within 1 hour after stimulation with pentagastrin, an average of 1.08 ± 0.09 ml was obtained from the isolated neutralizing zone, and 44.45 ± 2.10 ml from the acid-forming zone. In addition, it is necessary to take into account the “transit” function through the relatively short and small area of the mucous membrane of the pyloroantral canal. Through this channel, the contents of the acid-forming zone of the stomach move from top to bottom, and the contents of the duodenum often rise from bottom to top. The volumes of these transit juices often significantly exceed the volume of secretion of the pyloric glands, and neutralization of the contents of the acid-forming zone during duodenogastric reflux is mainly carried out by the contents of the duodenum. Consequently, the pH of the antrum of the stomach is a summary indicator and indicates the final result of neutralization of hydrochloric acid both by the secretion of the pyloric glands and, in the presence of reflux, by the contents of the duodenum. Currently, the distance between the centers of the body electrode (for studying the acid-forming zone) and the antral electrode (for studying the neutralizing zone) in pH probes produced by factories is about 11 cm. However, E. Yu. Linar et al. (1974) indicated that it is necessary to be able to change the distance between the olives of the pH probe within 8...12 cm for children and adults, depending on the objectives of the study, but such probes are not produced. A practical difficulty also lies in the fact that the distance between the zones of maximum acid formation and the neutralizing zone can vary significantly in different patients. At the same time, using a probe with a certain distance between the pH electrodes for each patient is currently unrealistic, since the specified distance before the study is unknown and there are no probes with different distances between the pH electrodes. At the same time, the production of pH probes with a distance between electrodes of less than 11 cm for the study of children is quite realistic.
Rice. 2. Position of the tube in the stomach. The area of maximum acid formation (3) is located between the body (1) and antral (2) electrodes.
Theoretically, it can be expected that when examining patients, the pH of the neutralizing zone, as a result of the release of alkaline secretions, will always exceed the pH of the acid-forming zone. However, often there is practically no difference between the readings of the antral and body electrodes, or even vice versa - the pH of the neutralizing zone is more acidic than the pH of the acid-forming zone. The reasons for the latter may be the location of the area of maximum acid formation between the body and antral pH electrodes (Fig. 2), the upward shift of the antral pH electrode by antiperistalsis, the cessation of acid formation when the pH of the acid-forming zone increases, and the pH of the neutralizing zone remains acidic until the gastric contents are evacuated. To carry out accurate pH measurements of the acid-forming and neutralizing zones of the stomach, it is obvious that it is necessary to ensure the correct position of the pH probe (see Chapter 5).
Drug treatment
The possibilities of modern medicine in treating high acidity of the stomach are quite large. There are a huge number of drugs with different mechanisms for suppressing the acid-forming function of parietal cells. But you need to be able to find a competent approach to their differentiated use. The basics for the correct use of such funds are outlined below.
- Pantoprazole, omeprazole, lansoprazole, razol, Proxium, Nexium, etc. Today, they are rightfully considered the main antisecretory drugs. Most effectively and selectively block the production of hydrochloric acid. The only drawback of drugs in this group is that they cannot be used in pediatric practice.
- Maalox, Almagel, Phosphalugel, Venter, Gastal. They have a combined effect on the mucous membrane: neutralizing acid and protecting the inflamed mucous membrane from irritation due to the formation of a barrier film. The drugs do not affect the level of secretory activity of acid-forming cells. Can be used as a basic remedy for hyperacid gastritis.
- Rennie, Gaviscon. They have a quick healing effect. Prescribed to relieve periodic attacks of heartburn. They cannot be used as a basic treatment, although they do not cause rebound syndrome. They can be classified as drugs of purely symptomatic therapy.
- Ranitidine, quamatel (famotidine). Effectively reduce the level of general gastric secretion, including hydrochloric acid. They have a symptomatic and pathogenetic effect, stopping not only painful manifestations in the form of heartburn, but also influencing the root causes of its occurrence.
- Vikalin, vis-nol, de-nol, vikair, gastro-norm. They are used as drugs of choice for high acidity, accompanied by the formation of ulcers of the mucous membrane of the gastroduodenal complex associated with Helicobacter pylori infection.
- Gastrocepin. It is considered a remedy from the reserve group for reducing acidity and is mainly used for severe diseases accompanied by hyperacid conditions.
- Gastromax. It is a combination of famotidine with enveloping agents.
Important to remember! Sodium bicarbonate (soda) is included in many medications for the treatment of high acidity. It is often used by many patients as the only treatment. This approach is unacceptable, since prolonged use of soda, in addition to a short-term decrease in acidity, causes rebound syndrome. This means that the positive effect is soon followed by an even greater increase in acidity!
Treatment
Based on the results of the diagnosis and taking into account the existing symptoms, the doctor prescribes a course of treatment for the patient. Low stomach acidity, the symptoms of which are the main guideline in developing a course of treatment, can be successfully restored. The doctor pays special attention to the choice of drugs, since the problem is specific, and the properties of some drugs may have a negative effect on its manifestation.
In most cases, in practice, a method is used that involves increasing the production of hydrochloric acid, which helps normalize digestion and, as a result, helps solve the problem.
To do this, the doctor is recommended to take HCl preparations and enzyme medications that replenish the deficiency of endogenous digestive enzymes.
As part of the treatment, the patient follows a diet, during meals he takes a solution of hydrochloric acid, concentrated gastric juice, pepsin, the dosages of the drugs are prescribed by the doctor.
How to improve low stomach acidity?
If your stomach hurts after eating and a doctor’s appointment is diagnosed with low stomach acidity, then it is recommended to include foods that increase stomach acidity in your diet. It is necessary to regularly eat vegetables and fruits high in vitamin C, ginger root (ginger tea), fermented vegetables (fermented), and fermented milk products.
Pumpkin seeds, potatoes, beans, peanuts, whole grains, bread and brown rice can increase your body's zinc levels, which have a big impact on HCl production. You can improve the absorption of zinc by taking vitamin complexes.
Prevention
At this point in time, the prevention of low acidity consists of reducing the consumption of animal proteins. Instead, it is recommended to include foods containing plant proteins in your diet. Another important recommendation is to reduce or completely eliminate sugar, while consuming enough fiber.
If your stomach hurts after eating, but you need to pay attention to your diet and reconsider it. It is best to switch to separate meals, when proteins and carbohydrates are taken separately, and fruits are also consumed separately, after completing the main meal.
Consumption of probiotic products has a positive effect on the formation of a normal balance of intestinal and stomach microflora, therefore their consumption has a positive effect on stabilizing acidity levels.
Forecast
What to do if your stomach hurts after eating? First of all, consult a doctor and get examined. If low stomach acidity is diagnosed, then you need to undergo a course of treatment and follow the doctor’s recommendations. Predicting the consequences of low stomach acid is a difficult task. To solve it, it is necessary to follow an integrated approach, take into account all the symptoms, the patient’s health status, possible risks and complications, and only make a prognosis based on all this information. But you need to take into account that the worst-case scenario is often oncology.
We provide paid medical services to our clients; you can make an appointment with a doctor using a form on the website or by phone; all messengers are also available.
To find out the cost of seeing any of the specialists or to get answers to questions, you can call the 24-hour hotline: +7.
Watch a useful video about the causes of low stomach acidity
Diet
During the period of exacerbation (when pain is tormented), you need to endure at least a week on dietary soups without frying, porridges, stewed or boiled potatoes, small portions of boiled meat. During this period, you can drink teas, jelly, compotes (not sour), juices - only pumpkin, and then only a little. Alcohol, smoked, spicy, salty foods, carbonated drinks, sour fresh vegetables and fruits are completely excluded. The bread is stale, optimally dried. All food is neither hot nor cold (the best option is warm).
During the period of remission, the diet expands. The patient can eat low-fat varieties of fish (hake, cod, pink salmon), meat (rabbit, chicken, beef); The side dish is porridge, potatoes, maybe pasta, but not much and not often. Eggs, fresh non-acidic fruits and dairy products are also included in the diet. It is useful to drink fresh cabbage juice. Restrictions on the intake of fatty foods, smoked peppers, alcohol and strong teas and coffee remain.
2. Reasons
There are so many possible reasons for a persistent increase in acidity that they are usually divided into two large groups: endogenous and exogenous (internal and external, respectively).
The most common endogenous factors include:
- hereditary predisposition;
- chronic infections and/or presence of parasites;
- persistent hypoxia (lack of oxygen supply to tissues and organs);
- metabolic (metabolic) disorders;
- hypovitaminosis, deficiency of microelements, amino acids, etc.
Main exogenous factors:
- smoking and drinking alcohol, especially strong drinks;
- distortions in the daily diet (infatuation with spicy, fatty, spicy, over-salted, too hot and other dishes that irritate the mucous membranes of the gastrointestinal tract);
- long-term or amateur use of medications without prior consultation and supervision of a gastroenterologist;
- work in some hazardous industries, which involve, in particular, constant contact with nitrates;
- physical inactivity, sedentary lifestyle, haphazard eating with long breaks and a predominance of sandwiches, fast food, sour juices, coffee, carbonated drinks and similar “stomach killers.”
Visit our Gastroenterology page
Menu for the week
The diet used for stomach acidity is based on food that is gentle on the functions of the gastrointestinal tract. During such a diet, fatty and spicy foods, sausages, pickles, marinades, carbonated drinks, and fast foods are excluded from consumption. The basis of the diet consists of foods that reduce acidity levels.
Day 1−2:
- Breakfast: ground buckwheat porridge (with milk), cottage cheese soufflé, herbal tea.
- Lunch: soft-boiled egg, vegetables.
- Lunch: light vegetable soup, meatballs, carrot puree, jelly.
- Dinner: fish cutlets, pasta.
- Before bed: milk or kefir.
Day 3−4:
- Breakfast: oatmeal, carrot puree, tea.
- Lunch: pancakes.
- Lunch: zucchini soup, steamed cutlets, pasta, compote.
- Dinner: lazy dumplings, plum soufflé.
- Before bed: milk or kefir.
Day 5−6:
- Breakfast: baked omelette, avocado toast, tea.
- Lunch: carrot-apple soufflé.
- Lunch: rice soup (milk-based), boiled meat, jelly.
- Dinner: mashed potatoes, a little spinach, low-fat cottage cheese.
- Before bed: milk or kefir.
Day 7:
- Breakfast: semolina porridge, dry cookies, tea with milk.
- Lunch: egg soufflé.
- Lunch: chicken soup with croutons, baked apples with honey, fresh vegetable salad, dried fruit compote.
- Dinner: baked chicken with rice, boiled potatoes, stewed vegetables.
- Before bed: milk or kefir.
Don't go to bed on a full stomach. Lying down immediately after eating can cause stomach acid to move back up the tract instead of down. As a result, this only contributes to the stimulation of an increase in acidity levels.
Drug therapy
To reduce acidity levels, a comprehensive medicinal approach is used. Drugs are used to normalize the process of hydrochloric acid secretion, helping to restore damaged elements of the gastric mucosa. They can be divided into several medicinal groups:
- Antibiotics (Tsiprolet, Metronidazole)
. One of the reasons for increased acidity of gastric juice is the activity of the bacterium Helicobacter pylori. Antibacterial agents are used to suppress it. - Proton pump inhibitors (Omez, Omeprazole)
. Their action is aimed at stopping the destruction of the walls of the gastrointestinal tract. - Antacids (Phosphalugel, Almagel)
. Stop spasms and neutralize excess hydrochloric acid. - Sorbents (Polysorb)
. Effectively reduce acidity and prevent further intoxication of the body.
Additionally, doctors prescribe symptomatic therapy. If the patient is concerned about pain in the epigastric area, antispasmodics are recommended. When the cause of increased acidity is depression or nervous tension, neurotropics (Aprofen, Buscopan) are used.
Review of popular drugs
As additional medical assistance, patients are prescribed combination drugs that reduce the acidity of gastric juice. The list of them is very extensive. Such medications have a complex effect on the body. They allow you to relieve not only increased acidity, but also other unpleasant symptoms (for example, pain or vomiting).
Most often, doctors prescribe Maalox. This drug belongs to the group of antacids. It quickly destroys free hydrochloric acid and has an adsorbing and enveloping effect. The standard dosage involves 1-2 tablets three times a day. The duration of therapy should not exceed 3 months.
Another combined antacid drug is Gastal. Its use should not exceed 2 weeks. The medication helps reduce the acidity of juice in the stomach and at the same time relieves dyspeptic disorders in the form of heartburn or belching. While using the tablets, side effects may occur in the form of changes in the taste of food, nausea or constipation.
Folk remedies
The patient can feel better with the help of infusions and decoctions based on medicinal herbs for high stomach acidity.
- A decoction based on mint, fennel herb and caraway seeds. It is necessary to take all the ingredients in equal proportions, pour boiling water over them and consume 100 ml 2 times a day before meals.
- Chamomile tea. It is enough to pour 150 ml of boiling water 1 tbsp. l. chamomile herbs purchased at a pharmacy. Leave for half an hour. Take before meals. This tea stabilizes digestion.
- A decoction of St. John's wort herb. Mix 50 g of herb with a glass of boiling water. Consume strictly before meals.
- Mint decoction. To prepare the product you will need a glass of mint and 500 ml of boiling water. Bring the resulting mixture to a boil over low heat and cook for 10 minutes, then leave the broth for half an hour. It should be taken at least 6 times a day, half a glass. The decoction has a calming effect on the gastric mucosa and enhances metabolism.
It is not recommended to use ginger, plantain and rosehip during treatment. They contain substances that irritate the gastric mucosa.
What medications are suitable during pregnancy
Pregnant women often complain of increased stomach acidity
Everything related to pregnancy and pregnant women is always a sensitive issue, especially in relation to any substances. Any medications must be prescribed by a doctor. And the usual reason for prescribing a drug is if the risk to the mother's health from the disease outweighs the harm the drug could cause to the fetus. Therefore, they try to solve the situation with high acidity by adjusting the diet.
However, your doctor may prescribe enzyme preparations, which are usually a biological product rather than a chemical compound.
Prevention
To prevent increased acidity, you need to follow a number of rules. They are not heavy and do not require serious effort, but will help keep your stomach acidity in order. Of course, proper nutrition comes first in importance. The amount of proteins, carbohydrates, fats, fiber, vitamins must be balanced. It is important to follow a meal schedule. The last meal is 3 hours before bedtime. If we are talking about light meals, for example, low-fat dairy products, you can eat them even 30 minutes before bedtime.
Try to avoid hunger and mono-diets, do not overeat, but eat dry. It is better to avoid fried, fatty foods and dishes. Eat warm food, not hot or cold. It is better to give up bad habits (alcohol, smoking) if you decide to get your acid-base balance in order. Observe the storage conditions and terms of food products.
It is necessary to maintain individual hygiene and sanitize the mouth in a timely manner. Treat any illnesses on time, since all organs and systems in the body are connected. And the most unexpected disease can affect the balance of the stomach. Any medications should be taken only as prescribed by a doctor. Try to think positively and avoid stress; it is with psycho-emotional stress that most gastrointestinal diseases begin.
Causes leading to impaired stomach acidity
Increase acidity:
- poor quality nutrition, irregular food consumption, abuse of coffee, smoked meats, diet;
- there are many diseases that require long-term use of anti-inflammatory drugs;
- stressful situations;
- smoking, excessive nicotine intake;
- Helicobacter pylori infection.
Reduce acidity:
- Helicobacter pylori infection;
- eating disorder;
- bad habits;
- genetic disorders;
- diseases of the liver and pancreas;
- pathology of the endocrine system and metabolic processes.
As we can see, the reasons are largely similar. But in each individual person they will cause different manifestations of the disease, depending on the person’s initial health status, his lifestyle and diet, and the presence of concomitant pathology.
Diet is another stage of therapy
The use of medications will be ineffective if the daily diet is not adjusted. The purpose of the diet for this pathology is to relieve dyspeptic symptoms and reduce the acid factor. It is necessary to adhere to such a diet both during the period of exacerbation and during remission. Its main principles boil down to the following rules:
- You need to eat often (up to 5-6 times a day) and in small portions.
- The diet must be balanced to saturate the body with the necessary proteins, fats, carbohydrates and vitamins.
- It is important to exclude all mechanical, chemical and physical irritants.
- Do not consume excessively hot or cold food/drinks.
- It is necessary to follow a diet and eat at approximately the same time.
- You should use foods that neutralize gastric acid in your diet.
Diet No. 1 meets the listed requirements. They first learned about it many years ago. The diet was developed by Soviet specialists under the leadership of M. Pevzner. Today, its use among patients with various gastrointestinal pathologies can significantly speed up the recovery process.
Permitted and prohibited products
A diet with increased production of hydrochloric acid involves proper preparation of foods. They are usually boiled, baked or steamed. The finished dish is served pureed and always warm. Prohibited and permitted foods in this diet are listed in the table below.
| Product category | Allowed | Prohibited |
| Pasta, cereals | Pasta, vermicelli, buckwheat, semolina and rice | Pearl barley, barley, all legumes |
| Meat, poultry | Rabbit, turkey, chicken | Duck, goose, all fatty meats, sausages |
| Fish | Pike, pike perch, hake, pollock | Trout, salmon, salmon |
| Bread | Biscuits, dried wheat bread | Rye bread, pastries and sweets |
| Vegetables | Carrots, potatoes, cauliflower | Mushrooms, radishes, onions, cucumbers |
| Fruits | All sweet fruits | All sour fruits and berries |
| Dairy | Milk, cream, kefir, cottage cheese | All high fat foods |
It is imperative to exclude from the diet all food components that provoke excessive irritation of the gastric mucosa or increase the secretion of hydrochloric acid. As a result, all spices and marinades, fatty and smoked foods are prohibited. Patients are advised to abstain from alcohol, carbonated and overly sweet drinks for the entire period of therapy.
Fasting day
With an increased level of stomach acidity, it is recommended to carry out fasting days, but not more than once every 10 days. During this period, you only need to eat oatmeal. It is important to choose regular Hercules and not for instant cooking.
For stomach problems, oatmeal is cooked only in water.
To do this you will need a glass of rolled oats and 2.5 glasses of water. The cereal is dipped in boiling water and cooked until fully cooked (about 5-7 minutes). You can add butter, salt and sugar to the porridge.
It is useful to cook oatmeal with rosehip decoction, which is rich in vitamin C. This drink has a positive effect on irritated stomach mucous membranes. In addition to oatmeal, fasting days can be spent on other cereals (for example, buckwheat). Only approved products should be used. It is also important to remember the dangers of overeating.