Types and causes of occurrence
There are two types of belching - physiological and pathological. The first type is characterized by the release of gases up to two times daily. Often the process occurs when snacking on the run, constantly talking during meals, dry snacks, overeating and abuse of soda and dairy products. This process is considered a normal variant and does not require treatment.
Pathological belching is a symptom of diseases of the digestive tract, worsening up to ten times a day. Repeated cases of belching indicate dysfunction of the liver, gallbladder, and stomach. Most often, the release of gases through the mouth occurs with gastritis, gastric and duodenal ulcers, gastroduodenal reflux, gastroduodenitis, esophageal hernia, impaired gastric pH, impaired outflow of bile.
Belching can be empty or airy, bitter, sour, with food residues, with the taste of acetone, rotten.
Treatment
Help before diagnosis
The taste of acetone, which is caused by conscious dietary restrictions, can be eliminated independently. To reduce the level of ketone bodies, you need to add a sufficient amount of carbohydrates to your diet (at least 45-50% of your daily caloric intake). At the same time, it is important to increase fluid intake to 2.5-3 liters, due to which toxins will be eliminated from the body through urine.
Athletes need to strictly control their menu and increase the caloric content of their food during periods of intense training or preparation for competitions. To eliminate the nauseating acetone taste, you need to regularly rinse your mouth with water or a special herbal solution for oral care. When an uncomfortable taste is combined with weakness, severe headaches, and disturbances in consciousness, emergency medical attention is required.
Conservative therapy
In severe ketoacidosis, accompanied by an acetone taste in the mouth, medical tactics do not depend on the cause of the disorder. First, general measures are taken to detoxify the body and eliminate the immediate threat to health; after stabilization of the condition, etiotropic and pathogenetic medications are prescribed. Most often, the treatment regimen includes medications such as:
- Infusion solutions
. To normalize blood composition and remove ketone bodies from the body, massive infusions of saline and colloid solutions in combination with loop diuretics are recommended - the method of forced diuresis. In case of coagulation disorders, fresh frozen plasma is added. - Insulin
. Ketoacidosis caused by diabetes mellitus, regardless of its type, requires rapid intravenous administration of insulin. The dosage is selected according to the person’s weight and blood sugar level. To improve glucose utilization, potassium preparations and solutions with ascorbic acid are additionally infused. - Antibiotics
. If there is an acetone taste in the mouth due to a bacterial cause, etiotropic treatment is necessary. In the case of a septic condition, a combination of two antimicrobial agents is used, which act on the maximum number of gram-positive and gram-negative microorganisms. - Thyrostatics
. To relieve thyrotoxicosis, Mercazolil and similar drugs that inhibit the secretory activity of the thyroid gland are effective. They are combined with intravenous administration of iodine solutions. Heart rate is normalized with beta blockers. - Immunosuppressants
. For autoimmune processes (hepatitis, thyroiditis), corticosteroids are indicated, which are inducers of remission and quickly improve the patient's condition. In severe forms, antimetabolites are additionally used in minimal therapeutic dosages.
Which doctor treats belching
If belching is a frequent occurrence, then you need to consult a gastroenterologist.
To make an appointment with a doctor, choose any method:
- call the clinic +7 (495) 103-99-55,
- order a call back,
- leave a request for an appointment using a convenient form on the website:
Many people think that belching is a symptom that does not require much concern. This is true if belching occurs as a physiological phenomenon.
IMPORTANT! If belching becomes permanent, then you should consult a gastroenterologist, because the symptom may indicate the development of serious diseases of the gastrointestinal tract.
Make an appointment with an experienced and qualified gastroenterologist at the Kuntsevo Medical and Rehabilitation Center to understand the individual causes of belching, as well as get advice on how to eliminate the symptom.
SIGN UP
What are the reasons for the violation
The most likely cause of the acetone odor is diabetes. With this disease, there is a lack of insulin as a result of metabolic disorders. The smell will be the first sign of this disease, as will lethargy, apathy, fatigue and other manifestations of intoxication.
Another factor is disruption of the hepatobiliary system and kidneys. They remove toxic substances from the body. In various diseases, organ function is disrupted and harmful components, including acetone, accumulate in tissues.
An acetone odor is noted in renal failure. This phenomenon is also present during fasting.
One of the most dangerous signs will be the appearance of odor against the background of thyroid pathologies. With hyperthyroidism, increased hormone synthesis occurs, which, with the right approach, can be eliminated with medications. In some cases, there is a critical deviation from the norm, which causes increased metabolism.
The infectious process can also be manifested by an acetone odor. This is the result of protein decompositions. Therefore, during infections, it is recommended to drink more to remove acetone from the body.
Other reasons may be:
- poor oral hygiene;
- smoking;
- dry mouth;
- binge eating;
- dental diseases.
Treatment methods
First of all, the doctor is interested in the diet and prescribes an examination to examine in detail the condition of the digestive tract. Modern equipment installed within the walls of our clinic allows gastroscopy to be performed quickly and without pain.
Next, based on the diagnostic results, the gastroenterologist establishes a diagnosis and develops treatment tactics for each patient individually.
Drug therapy involves taking adsorbent, antacid drugs, and anti-inflammatory drugs to combat the inflammatory process of the tissues of the internal organs of the gastrointestinal tract. They create a protective layer on the walls of the stomach, collapse gases, and speed up the process of digesting food. In some cases, the gastroenterologist recommends taking a course of physical therapy to improve intestinal motility.
Treatment of belching is impossible without correcting the diet. So, you need to exclude foods such as cabbage, brown bread, baked goods with yeast, legumes, and carbonated drinks. Along with the main therapy, alkaline mineral water is prescribed to reduce stomach acidity.
The main causes of acetone odor from the mouth
The unpleasant odor of acetone from the mouth may be a consequence of:
- poor nutrition, prolonged fasting;
- acute alcohol poisoning;
- physical fatigue;
- acetonemic syndrome;
- pregnancy;
- diabetes mellitus;
- ketoacidosis;
- thyrotoxicosis;
- severe disturbances in the functioning of the liver and kidneys;
- schizophrenia.
Let's look at each reason in more detail.
Hunger
If you follow a low-carbohydrate diet for a long time, the body will begin to use up reserves of proteins and fats as sources of energy. With the active breakdown of lipids, ketone bodies are formed. They are responsible for the taste of acetone in the mouth.
The symptom is especially pronounced in the morning, immediately after waking up . If a person does not stop fasting, his urine will also begin to smell.
Alcohol poisoning
As a result of alcohol intoxication, many biochemical reactions begin to proceed incorrectly. Catabolic processes come to the fore. Ketone components are actively synthesized. Then in the morning after a feast, the addict is faced with an unpleasant acetone aroma.
Physical fatigue
An increase in the level of ketone bodies is often observed in professional athletes and people involved in strength sports. Their body actively breaks down fats to get an additional portion of energy. This is the reason for the increase in dimethyl ketone concentration.
If an unpleasant symptom persists for several days in a row, you cannot ignore it. It is recommended to visit a doctor and undergo laboratory tests.
Acetonemic syndrome
Most often, this condition is found in preschool children. The child is very nauseous and vomits periodically. He becomes lethargic, passive, pale, refuses to eat, and sleeps poorly. The patient smells strongly of acetone.
Often acetone syndrome is caused by severe viral and infectious diseases , fever, and dehydration. If it develops, you should urgently consult a pediatrician.
Pregnancy period
While carrying a child, the load placed on a woman’s body increases many times over. Important hormonal changes occur. Some expectant mothers experience changes in their sense of taste in the first trimester. They begin to smell dimethyl ketone when they eat or drink something.
There is no need to worry about such changes. As a rule, they go away on their own along with toxicosis. But you still need to notify your obstetrician-gynecologist about strange sensations.
Diabetes
The smell can occur during a long and complex course of the disease. This symptom is not characteristic of the initial period of diabetes. At the same time, the patient begins to suffer due to a constant feeling of thirst, drying out of the mucous membranes of the oral cavity, and decreased appetite.
Ketoacidosis
A dangerous complication of diabetes. It is characterized by a rapid increase in the concentration of ketone bodies against the background of cessation of insulin production. This can happen with a fever, and also if a person forgot to take the next insulin injection, the day before he worked a lot and hard.
The situation with this diagnosis worsens gradually. First, the patient notices that he constantly feels the taste of dimethyl ketone. His thirst increases. Then weakness appears and breathing quickens. It is important not to wait for the complication to progress and to seek medical help as soon as possible.
Thyrotoxicosis
With thyrotoxicosis, the content of thyroxine in the blood increases. As a result, the breakdown of protein structures in the human body is activated. A strange chemical taste appears in the mouth, which disappears temporarily after brushing your teeth. If the patient drinks little and eats poorly, the manifestations of the disease become more obvious.
Liver diseases
The liver is the natural filter of the human body. It is responsible for neutralizing toxins and harmful substances, removing incompletely oxidized metabolic products.
If severe liver disease has developed, a specific acetone taste very often occurs. He is accompanied by:
- weakness;
- nausea;
- pain in the right hypochondrium;
- constipation or, conversely, diarrhea.
Among the main liver disorders in which the aroma of acetone appears are:
- Viral diseases. Among them: hepatitis B and C, cytomegalovirus infection.
- Failure in the functioning of the liver parenchyma due to severe intoxication of the body.
- Liver failure, Reye's syndrome, drug overdose.
Kidney diseases
With kidney problems, the body cannot normally eliminate toxic ketone substances. Then the taste of dimethyl ketone remains permanently. There is a failure of nitrogen metabolism. The patient's appetite worsens and nausea appears.
People who have been diagnosed with acute renal failure often complain of an acetone taste. Then, in addition to a strange discomfort, urination becomes rare and the mucous membranes of the oral cavity dry out.
Schizophrenia
Very often, patients with schizophrenia complain about unpleasant acetone symptoms. This symptom is associated with an obsession with poisoning - it seems to a schizophrenic that they are trying to poison him.
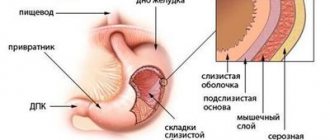
Causes of belching
Belching with rotten eggs occurs as a result of failures in the process of digesting food and its stagnation in the body. Subsequently, rotting and fermentation begin, bacteria are formed, causing belching of hydrogen sulfide, bad breath, and abdominal pain. Sour belching occurs when the acidity of the gastric juice is increased, air belching occurs when there is increased gas formation in the gastrointestinal tract, and bitter belching occurs when bile is released into the stomach.
In addition to gastrointestinal pathologies and liver diseases, belching may occur due to:
- addiction to fried, fatty, spicy foods, alcoholic beverages, as well as regular overeating;
- intolerance to certain types of foods, in particular hypolactasia (lactose intolerance), fructose intolerance, celiac enteropathy (gluten intolerance)
Belching in Gilbert's disease
Gilbert's syndrome is a genetic liver disease characterized by a constant increase in unconjugated bilirubin and metabolic disorders. It can be congenital and manifest (develops after a viral infection).
Gilbert's disease is characterized by belching with a bitter aftertaste.
Belching with antral gastritis
Antral gastritis is an inflammation of the gastric mucosa that is chronic. One of the main causes of its occurrence is pathogenic Helicobacter.
Antral gastritis is characterized by belching with a sour taste.
Belching with ascites
Ascites is characterized by the accumulation of free fluid in the abdominal cavity. The development of ascites can be caused by a large number of different diseases.
Ascites is characterized by frequent belching, often with a rotten taste.
Belching with atrophic gastritis
Atrophic gastritis is a type of chronic gastritis, which is characterized by thinning of the gastric mucosa, a reduction in the number of glands and secretory insufficiency. It is considered the most dangerous, precancerous condition.
Atrophic gastritis is characterized by belching of air and a rotten taste.
Belching with autoimmune gastritis
Autoimmune gastritis is a chronic inflammatory process affecting the gastric mucosa. In this disease, antibodies produced by the body attack the epithelial cells of the stomach, causing atrophy of the mucosa. This is a fairly rare pathology.
Belching with autoimmune gastritis may have a rotten taste.
Belching with achalasia of the esophageal cardia
Achalasia of the esophageal cardia is a disease in which the reflex relaxation of the lower esophageal sphincter is absent or insufficiently expressed, due to which the patency of the esophagus is impaired.
Achalasia of the esophageal cardia is characterized by belching with a rotten taste.
Belching with acalculous cholecystitis
Acalculous cholecystitis is an inflammation of the gallbladder in which gallstones do not form. The motor function of the organ is impaired, and bile stagnation occurs. This disease occurs several times more often in women.
Acalculous cholecystitis is characterized by belching of air and a bitter aftertaste.
Belching with biliary pancreatitis
Biliary pancreatitis is a chronic inflammatory disease of the pancreas that occurs as a result of pathologies of the liver and bile ducts. It is often combined with other diseases of the digestive system.
Biliary pancreatitis is characterized by belching with a bitter taste and a characteristic odor of bile.
Belching during bulbitis
Bulbit is an inflammation of the duodenal bulb. Can be acute or chronic. The focal and diffuse nature of inflammation is also distinguished. Bulbit is a secondary disease; it is isolated very rarely on its own.
Belching with bulbitis may have a sour taste.
Belching with gastritis
Gastritis is an inflammatory disease during which dystrophic changes in the gastric mucosa and disruption of its functions occur. Gastritis is distinguished with high, normal and low acidity of the stomach. Gastritis is the most common disease that causes belching
For gastritis with high acidity
Gastritis with high acidity is characterized by increased production of hydrochloric acid, which helps dissolve food. As a result, the walls of the mucous membrane become inflamed and erosion occurs.
Belching with gastritis with high acidity has a sour taste.
For gastroesophageal reflux disease
Gastroesophageal reflux disease is a pathology in which regular reflux of gastric or duodenal contents into the esophagus and inflammation of the walls of the lower esophagus occur.
Gastroesophageal reflux disease is characterized by belching with gas and a sour taste.
Belching with gastroenterocolitis
Gastroenterocolitis (foodborne toxic infection) is a disease in which an inflammatory process occurs in several parts of the gastrointestinal tract - the mucous membranes of the stomach, small and large intestines, and digestive function is disrupted.
With gastroenterocolitis, belching of food or with a rotten taste occurs.
For hepatomegaly
Hepatomegaly is a pathological or physiological increase in the size of the liver. The cause may be a number of diseases, including liver cirrhosis, viral hepatitis, mononucleosis, fatty degeneration, oncology, and cardiovascular diseases.
Belching with hepatomegaly is frequent and prolonged with a rotten taste.
Belching with hernia of the white line of the abdomen
A hernia of the linea alba is a protrusion of the abdominal organs and intestinal loops through the gap between the tendon plexuses along the midline of the abdominal muscles. Pathology occurs due to weakness and thinning of connective tissues.
With a hernia of the linea alba, belching with a sour taste may occur.
Belching due to hiatal hernia
Esophageal hernia (diaphragmatic hernia, hiatal hernia) is a common chronic recurrent pathology in which the initial abdominal section of the digestive tube moves into the supradiaphragmatic zone through the esophageal opening of the diaphragm.
A hiatal hernia may be characterized by frequent belching of air and a bitter taste.
Belching with esophageal diverticulum
Esophageal diverticulum is an abnormal protrusion of the esophageal wall into the mediastinal cavity, which is represented by mucous, muscular and serous or only mucous membranes. In this regard, true and false diverticula are distinguished. As a result, swallowing functions and the movement of food in the esophagus are impaired.
With esophageal diverticulum, belching with a rotten taste often occurs.
Belching with dysbacteriosis
Dysbacteriosis is the occurrence of an imbalance of microflora. The ratio of normal and opportunistic microorganisms is disrupted. This phenomenon can occur in the intestines (most often) and in the reproductive organs.
Dysbacteriosis is characterized by belching of air, with a bitter or rotten taste.
Belching treatment
If you experience constant belching with an unpleasant taste that causes discomfort, you should consult a specialist. To determine its causes, after interviewing the patient, a number of studies are carried out:
- clinical and biochemical blood tests - to identify inflammatory processes, pathologies of kidney, pancreas, and liver function;
- stool analysis for occult blood, coprogram - to detect poorly digested food fragments, undigested fat, the presence of coarse dietary fiber;
- assessment of gastric acid production - to determine the level of stomach acidity;
- esophagogastroduodenoscopy - to assess the condition of the inner surface of the duodenum, stomach and esophagus, performed through an endoscope with the obligatory taking of a biopsy;
- impedance-pH-metry of the esophagus - to detect gastroesophageal release and assess the frequency, duration and severity of reflux;
- ultrasound examination of the abdominal organs - to identify the presence of tumors on the pancreas, duodenum, and stomach walls;
- checking for the presence of the pathogenic Helicobacter pylori, which lives in the pyloric part of the stomach and provokes the development of many diseases of the gastrointestinal tract;
- colonoscopy – to assess the condition of the inner surface of the colon using an endoscope.
After examination and diagnosis, treatment for diseases that cause belching is prescribed. It is extremely undesirable to independently treat constantly occurring belching using traditional methods or medications. This can lead to extremely negative health consequences.
Poor nutrition
A strict diet can lead to serious disorders in the body. In an effort to quickly lose weight, many people turn to fad diets from the Internet and the press, without thinking about the consequences. And they go to the doctor only after developing symptoms of dangerous diseases.
Diets with acetone can lead to belching when it is recommended to consume only one of the components: proteins or carbohydrates. Poor nutrition has never been beneficial.
A healthy body needs a supply of fats, proteins and carbohydrates, minerals and vitamins. All components must be supplied in a certain proportion, and a deficiency of one of them can lead to serious symptoms.
If an imbalance occurs, the body tries to replenish the supply by breaking down its own fat or muscle tissue and converting it into the desired substance. This process is unnatural for the body and can have negative consequences. As a result of a complex chemical reaction, the smell of acetone appears.
Belching acetone necessarily accompanies patients with anorexia. In addition, all organs of the body suffer, metabolism is disrupted, mucous membranes become inflamed, kidneys and liver suffer.
Thyroid diseases
The thyroid gland is one of the main organs, and failure of its functioning can lead to serious consequences. An increased amount of hormones produced by the thyroid gland is called hyperthyroidism. This condition is treated by taking oral hormonal drugs.
Hormone levels can increase noticeably when:
- pregnancy;
- surgical intervention;
- stressful situations;
- incorrectly chosen treatment tactics.
Metabolism suddenly speeds up. As a result, the following symptoms appear:
- smell of acetone from the mouth;
- excited or inhibited state;
- abdominal pain;
- increased body temperature;
- jaundice.
The condition requires immediate therapeutic intervention.