The lifestyle followed by most of the world's population does not always mean a healthy lifestyle and nutrition. One of the most common health problems is disorders of the gastrointestinal tract. Discoveries in the medical field in recent years make it possible to painlessly carry out various diagnostics of the human body.
The presence of pathologies can be detected in conditions that are comfortable for the patient and as efficiently as possible. Diseases of the gastrointestinal tract can be detected at any stage and even without obvious clinical signs and symptoms. Only a qualified medical professional can make a correct diagnosis.
Modern scientists offer several types of intestinal diagnostics, differing in the type of problem, severity and characteristics of a particular patient. Bowel examination methods include:
- Capsule examination;
- Endoscopic examination;
- Colonoscopy;
- Irrigoscopy.
Capsule examination and its features
Capsule examination is used for abdominal pain and suspicion of a tumor.
A capsule examination is performed by swallowing an enterocapsule with a video camera built into it. This method came into domestic medicine thanks to the Israeli scientists who invented it.
The big advantage of capsule diagnostics is minimal invasiveness and high information content. The doctor performing the procedure will be able to specifically assess the internal state of the patient’s gastrointestinal tract. A similar diagnostic method is recommended for those patients who have the following symptoms:
- abdominal pain;
- hidden bleeding;
- suspected congenital disease;
- suspicion of a tumor.
The diagnostic process begins with attaching a recording device to a person's body, after which he must swallow a video capsule. The device moves through the gastrointestinal tract due to peristalsis waves.
After these manipulations, the data obtained as a result of the survey is processed by special computer programs. The duration of data processing can reach about 8 hours. The specialist will determine the presence of polyps, tumors, including cancer, as well as all other intestinal pathologies. The capsule is excreted from the body naturally.
In some cases, namely when the patient has weak intestinal motility, a slightly different capsule called Patency is used. Its purpose is to identify narrowed areas of the intestine.
Chemotherapy
If adenocarcinoma cancer cells have spread to the lymph nodes, adjuvant chemotherapy is given after surgery to prevent recurrence. In case of adenocarcinoma with metastases, chemotherapy drugs are used for palliative purposes to slow down the progression of the tumor, improve the patient’s condition, and prolong life.
Combinations of chemotherapy drugs are often prescribed for adenocarcinomas:
- FOLFOX: leucovorin + fluorouracil + oxaliplatin.
- FOLFORI : leucovorin + fluorouracil + irinotecan.
If relapse occurs after surgery, fluorouracil may be prescribed in combination with radiation therapy. This therapy is called chemoradiotherapy .
Endoscopic examination
Endoscopic examination is used to detect tumors and polyps.
This diagnostic method is used to determine the patient’s hidden pathologies, such as polyps and tumors. The process is safe for the patient and also painless.
Thanks to endoscopy, the condition of the intestinal mucosa can be accurately assessed. The doctor examines the lining of the esophagus, stomach, duodenum, large intestine and small intestine.
The process is carried out on an empty stomach. The patient must first stimulate cleansing with laxative medications. The next stage is the introduction of an ultrasound sensor into the rectum.
Then, when the device reaches the required area of the intestine, the doctor assesses the condition of the formation or other pathology and, based on what he sees, takes further actions and treatment methods.
Contraindications. Endoscopy is not recommended for people with heart or lung disease due to exposure to special medications. But in any case, this issue is resolved individually with each patient, based on the conditions of the particular case.
Choosing a research method depending on the expected pathology
A consultation with a gastroenterologist includes the collection of anamnestic information and a clinical examination, based on the results of which the doctor gets an idea of what disease the patient is suffering from. To clarify the diagnosis, examinations are prescribed that are aimed at clarifying various details.
| Suspected pathology | Eligible Studies |
| Inflammation of the small intestine (acute and chronic enteritis) | X-ray, ultrasound, various types of endoscopy |
| Tumors, oncology | Fluoroscopy, balloon enteroscopy, capsule endoscopy, ultrasound, FGDS, MRI |
| Celiac disease or gluten intolerance | X-ray, ultrasound, various types of endoscopy |
| Duodenal ulcer | FGDS with biopsy, radiography, MRI, capsule endoscopy |
| Intestinal obstruction | Ultrasound, FGDS |
| Dyskinesia | All types of examination |
| Diverticula | All types of examination |
| Irritable bowel syndrome | All types of examination |
| Malabsorption syndrome | All types of examination |
| Crohn's disease | All types of examination |
Diseases of the small intestine are diverse; only a gastroenterologist can understand everything. The earlier treatment is started, the less the entire body suffers, and the less time it will take to recover.
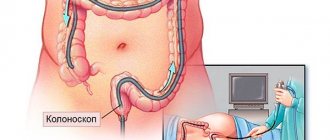
Colonoscopy
Colonoscopy is a method of studying and assessing the condition of the walls of the gastrointestinal tract.
This is a diagnostic method that many patients do not like. You can’t call it painful, rather it’s unpleasant, but its effectiveness is very high.
Colonoscopy is performed using a fiber colonoscope, which is inserted into the patient’s body after cleansing the intestines with a special laxative. The procedure lasts about 30 minutes, during which the patient may feel bloating.
A fiber colonoscope is a medical tourniquet that has a flexible texture and is equipped with an optical system. Thanks to this device the following manipulations are possible:
Intestinal irrigography: what it is, how it is carried out, preparation - MEDSI
Table of contents
- What is irrigoscopy?
- What does the study show?
- Stages of irrigography
- Indications for irrigography
- Contraindications
- Preparing for the examination
- Advantages of carrying out the procedure at MEDSI
The intestines are an important part of the human body, which is responsible for both the digestion process and the removal of feces from the body.
It consists of several parts:
- Small intestine:
- Duodenum - food eaten from the stomach enters here
- Small intestine - here food is digested, nutrients are absorbed, after which the rest of the food is sent to the next section
- Valve - through it, unnecessary remnants of processed food enter the colon
- Large intestine - where stool is formed
- Rectum - through it feces are removed from the body
Disruption of any of these areas leads to problems in the functioning of the entire organism as a whole.
What is irrigoscopy?
Irrigoscopy of the small intestine is a type of x-ray examination in which a barium contrast solution is injected into the patient's body. The use of contrast is necessary for the intestines to be visible on an x-ray (since they are not normally visible on x-rays). A barium solution is injected into the rectum, after which images are taken.
This analysis is used to find out whether the patient has disorders or pathologies in the structure of the intestine, whether there are neoplasms or other diseases of this organ.
The procedure is non-invasive - it does not require abdominal incisions - and not endoscopic (in a standard situation, no sensors are inserted into the human body to carry it out). It is painless and does not cause discomfort to the patient.
What does the study show?
Irrigoscopy is used to examine and assess the condition of different parts of the intestine. It allows you to determine:
- The presence or absence of disturbances in the operation of the valve (bauhinium valve) - it should open only in one direction
- Condition, location, diameter, elasticity and shape of the colon
- The quality of functioning of the intestinal sections
- Presence of gastric pathologies
- Presence of obstruction
- Qualitative condition of the inner lining of the intestine (presence of polyps, ulcers, ruptures, scars, cracks)
- Does the patient have any neoplasms (tumors) or diverticula (protrusion of the intestinal wall)
- Are there pathologies of interaction between the intestine and adjacent organs?
Stages of irrigography
Irrigoscopy of the large and small intestines takes place in two stages:
- General x-ray examination of the lower abdominal cavity
- Barium contrast examination
The first stage is used to diagnose the presence of surgical pathologies of the intestine. At this time, the patient lies on his back.
A barium solution is then injected into the patient's body through the rectum. After it has spread through the intestines, several pictures are taken. For this stage, the patient takes the following position: lying on his left side, pressing his legs to his stomach and placing his hands behind his back. After this procedure, the patient has a bowel movement, and doctors take another picture.
If there is a suspicion of cancer or another tumor, the doctor may do a double contrast study. In this case, after the previous stage, air is pumped into the rectum and then another series of pictures is taken.
When examining children using irrigoscopy, there are several nuances:
- If necessary, an ultrasound probe may be inserted into the intestine during the examination.
- If the procedure is prescribed for a small child, it will be performed under general anesthesia.
Indications for irrigography
This study is prescribed in the following cases:
- The patient has nonspecific ulcerative colitis
- There is a suspicion of cancer or another tumor
- The doctor suspects the appearance of polyps, ulcers or other disorders of the mucous membrane
- Possibility of having Crohn's disease (irreversible changes in the intestines)
- Possibility of obstruction
- There is a suspicion of a foreign body in the intestine
- Diagnosed with tuberculosis or Grishsprung's disease (congenital anomaly in organ development)
- Suspected injury or damage
Also, irrigoscopy of the large and small intestines is prescribed in the presence of symptoms such as:
- The appearance of bloody and mucous discharge in the stool
- Sudden weight loss for unknown reasons
- Permanent abdominal pain, discomfort in the anal area
- Regular bowel dysfunction (constipation, diarrhea)
It is worth undergoing a similar examination in the event of a decrease in hemoglobin levels, which occurred for unclear reasons. It is also prescribed if it is impossible to do a colonoscopy.
It is necessary to undergo irrigography for preventive purposes for people over fifty years of age whose family has a predisposition to colorectal cancer (one of the relatives suffered from this disease).
Contraindications
Irrigography cannot be used in such cases as:
- The patient has been diagnosed with cardiovascular disease
- The patient suffers from an infectious disease accompanied by fever
- The man is in a coma
- Woman pregnant
- The patient is in lactation period
- The patient has swelling or inflammation of the brain
- Exacerbation of ulcerative colitis diagnosed
- Allergy to contrast agent
- The patient's intestinal patency is extremely impaired
- There is injury or rupture of the intestinal wall
In the last two cases, the barium solution may enter the abdominal cavity, which will lead to serious complications in the patient's condition.
Preparing for the examination
Irrigoscopy of the large and small intestines requires simple preparation. But it is important to remember that the accuracy of the research results depends on its quality, so you must strictly follow the doctor’s instructions.
Preparatory procedures include two important stages:
- Compliance with diet rules
- Colon cleansing before the procedure
Two to three days before the examination, you need to start following a diet, namely, exclude foods such as:
- Vegetables (cabbage, carrots, beets)
- Legumes (corn, beans, peas, lentils)
- Porridge (barley, oatmeal, millet)
- Fruits (apples, apricots, bananas, oranges)
- Bakery products
- Dairy
- Sweet
- Fast food
- Fatty and smoked foods
Such products lead to excessive gas formation and take a long time to digest.
The last meal should be on the eve of the study, no later than 6 pm.
Also, the day before and in the morning of the test, it is necessary to do a cleansing enema or use drugs that stimulate the release of feces from the intestines.
Advantages of carrying out the procedure at MEDSI
- In the MEDSI network of clinics, the procedure for irrigoscopy of the large and small intestines is performed by experienced coloproctologists, oncologists and surgeons of the highest qualification categories, candidates of medical sciences
- Clinical centers have high-tech modern equipment that uses gentle X-ray radiation, but allows you to take the most accurate images
- Specialists will help you prepare correctly for the procedure to ensure the best possible result.
- To make an appointment for a consultation, you do not need to go to the reception desk, since you can easily make an appointment by calling 8 (495) 7-800-500
Irrigoscopy
Irrigoscopy is an examination of the gastrointestinal tract using x-rays.
Irrigoscopy is an examination of the gastrointestinal tract using x-rays. It is first necessary to cleanse the intestines as much as possible, using enemas and laxatives. On the eve of irrigoscopy, the patient should not eat.
Before diagnosis, the patient takes barium sulfate orally, which is a radiopaque substance. The substance fills parts of the intestine and helps the doctor examine its contours and the degree of lumen, which will later help identify the presence of pathologies.
In some cases, it is necessary to carry out a double contrast method. What does it mean? After the intestine is cleared of the radiopaque substance, it is filled with air. Thanks to this, it is also possible to determine the outlines of all parts of the intestine.
Based on the contours seen, the doctor determines the presence of fistulas, tumors, diverticulosis, congenital pathologies, ulcerative formations, scars, and so on. Irrigoscopy is safe and painless, the patient is minimally exposed to radiation. In what cases is irrigoscopy recommended:
- discharge of mucus and pus from the intestines;
- pain in the anus and colon;
- chronic stomach upset (diarrhea, constipation);
- bleeding from the rectum;
- suspicion of a tumor in the gastrointestinal tract;
- inability to perform a colonoscopy to accurately formulate a diagnosis;
- intestinal obstruction (the presence of this diagnosis is confirmed using x-rays and ultrasound examinations).
Indications for ultrasound of the distal colon
- Malformations of the distal colon
- Chronic constipation
- Fecal incontinence
An intestinal ultrasound should be performed in the morning on an empty stomach, since the body does not digest food for 6-8 hours at night. Before performing an ultrasound of the child’s colon, it is cleared of feces. On the day of the study, before the procedure, a cleansing enema is given with a 1% solution of sodium chloride at 37-38 °C in a volume of 200-400 ml. For 2 days before an ultrasound of the colon, you are given an adsorbent to drink - activated carbon. After cleaning the intestine with an enema, you need to fill it with warm water using a Zhanna syringe.
It is important to psychologically prepare the child for the study, explain why it is necessary and what it will give. Both parents and the doctor play an important role in this process.
Diagnosis of the large intestine
A blood test provides a lot of information about a person's health status.
To determine diseases of the colon, doctors prescribe a number of required examinations and tests.
Initially, a blood test is performed for clinical and biochemical composition. To determine dysbiosis, the patient submits stool to the laboratory. Five main techniques for examining the rectum:
- anoscopy;
- sigmoidoscopy;
- fibrocolonoscopy;
- laboratory diagnostics of stool for dysbacteriosis;
- blood analysis.
A digital rectal examination is necessary, which should be performed at any hint of pelvic organ disease. This procedure is carried out by a doctor using special devices.
To begin with, the condition of the anus muscles is analyzed, which will help identify a number of diseases: hemorrhoids, anal fissures, narrowing in the intestinal lumen, tumor formations, scars, and so on. In some cases, a rectoscope is used, which is necessary for diagnosing more deeply removed areas of the colon.
Diagnosis of the small intestine
The examination begins with diagnosing the condition of the duodenum, jejunum and ileum. The localization of these areas of the gastrointestinal tract is between the large intestine and the stomach. A specialist in this field is a gastroenterologist. For diagnostics use:
- fiberoscopy;
- irrigoscopy;
- endoscopy;
- ultrasonography;
- X-ray.
An appointment for a comprehensive examination can only be obtained from a gastroenterologist. Before making a diagnosis, it is important to follow a diet for several days to unload the gastrointestinal tract.
Thanks to endoscopy, it is possible to identify pathologies of varying degrees of severity in a patient. Just as often as endoscopy, to diagnose the small intestine, the rectoscopy method is used (examination of the internal walls of the intestine with a sigmoidoscope). Thanks to endoscopy, the following problems are solved:
- getting rid of polyps;
- stopping bleeding;
- installation of a feeding tube;
- removal of foreign objects.
Another highly effective way to detect diseases of any part of the small intestine is double-balloon enteroscopy, performed on the patient under general anesthesia. It is used if the patient has:
- tumor formations;
- adenomatosis;
- polyps;
- bleeding in the small intestine;
- the presence of foreign bodies in the small intestine.
Small bowel cancer
Small intestinal cancer causes pain and problems with intestinal patency that disappear.
Colorectal cancer (cancer of the small intestine) is often very difficult to identify. This disease may be hidden behind the mask of another pathology; doctors need to work hard to identify it.
The main signs of small intestine cancer are persistent pain in the abdomen and problems with intestinal patency. Especially if the pain is increasing in nature, then it is necessary to schedule one or more examinations.
Bowel cancer may be present even if the ultrasound is negative. Since cancers are often hidden, doctors often fail to see them the first time.
Many, in order to unambiguously determine the presence of the disease, turn to specialists in Israel and Germany for help, since they have the most modern techniques and equipment. If there is even the slightest suspicion of a cancerous tumor, then examinations will have to be continued until a definite diagnosis is known.
In addition to the diagnostic methods already mentioned, there is a procedure called enteroscopy. This procedure involves an endoscopic examination, sometimes accompanied by a biopsy.
When should you contact a gastroenterologist?
The key to successful treatment of any disease is a timely visit to a doctor. You should consult a gastroenterologist if you are bothered by one or more of the following symptoms:
- Stomach pain, whether or not related to meals;
- Nausea;
- Vomit;
- Heartburn;
- Bitterness in the mouth;
- Heaviness or pain in the right hypochondrium;
- Bloating;
- Problems with bowel movements (constipation or diarrhea);
- Pain in the left hypochondrium or lower abdomen;
- Feeling of quick satiety while eating;
- Unmotivated weight loss.
All these symptoms indicate a disruption in the normal functioning of the digestive organs. You should also visit a gastroenterologist for preventive purposes if you already have any chronic gastrointestinal disease. This is especially important for those who do not fully adhere to the principles of proper nutrition and have such a bad habit as smoking.
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI)
Magnetic resonance imaging is a painless method for examining the intestines.
Magnetic resonance imaging is a safe method for examining the intestines, without causing pain to the patient.
MRI will allow you to find out whether the patient has chronic diseases of the gastrointestinal tract. Before starting, it is important to cleanse the intestines with an enema. Next, the patient receives the contrast agent. The duration of the procedure is very short (only 10 minutes).
Thanks to the MRI method, a doctor specializing in this problem will be able to accurately determine the severity of the disease, examine each section of the intestine, and find metastases (if any). Also, thanks to magnetic resonance imaging, the presence of malignant tumors can be detected.