Pregnancy is a special state in a woman’s life, but it is not always as carefree as we would like. This is due to the increasing load on the body: body weight and blood volume increase, hormonal levels change, reserves of vitamins and microelements are depleted, and the excretory system suffers serious overload. Even for a completely healthy body, this is a serious test of 40 weeks, and for those who already experienced health problems, pregnancy can cause an exacerbation of chronic diseases and the emergence of new diseases.
Which doctor should I contact?
Sometimes pregnant women are at a loss if they have to deal with any health problems that are not directly related to carrying a baby. In fact, there is nothing wrong with this. If you experience pain in the abdomen or general malaise, you should consult a therapist at the antenatal clinic. After the initial examination, he will give a referral to a gastroenterologist, if necessary.
Pain in the epigastric region is always frightening and raises a lot of questions, but if it overtakes a pregnant woman, then fears and concerns can become serious and not groundless. At the first manifestation of discomfort, including those associated with eating, you should immediately consult a doctor.
Non-compliance with the diet
Pregnant women often tend to overeat. That is why healthy nutrition has always been and will be the most important condition for good health.
The idea of “eating for two,” which has its roots in the distant past, has nothing to do with reality, since when carrying a child, the body requires only 300–500 kcal more than usual
If pain occurs in the pancreas associated with overeating or eating junk food, the doctor usually prescribes antispasmodics and painkillers, after which he recommends following a certain diet:
- meals should be divided, up to 5–6 times a day and in small portions;
- do not overload the gastrointestinal tract at night;
- exclude fried, smoked, fatty foods;
- reduce to a minimum or eliminate spicy and salty foods;
- exclude carbonated drinks;
- remove spices and herbs from the diet;
- Alcohol and coffee are strictly prohibited.
Treatment of chronic pancreatitis in pregnant women
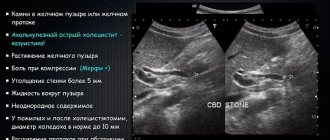
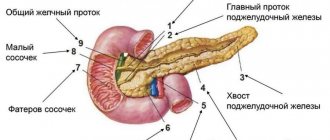
chronic pancreatitis is a group of chronic diseases of the pancreas of various etiologies, predominantly of an inflammatory nature, manifested by varying degrees of disruption of exocrine and endocrine functions. The diagnosis of chronic pancreatitis in pregnant women is quite a difficult task for doctors working in obstetric clinics. Exacerbation of chronic pancreatitis in pregnant women must be differentiated from diseases such as irritable bowel syndrome, Crohn's disease, ulcerative colitis, intestinal obstruction, exacerbation of chronic cholecystitis, chronic hepatitis, as well as pathologies of the hepatobiliary system associated with pregnancy - early toxicosis of pregnancy, excessive vomiting of pregnant women, preeclampsia, acute fatty liver. Often in the first trimester of pregnancy, exacerbation of chronic pancreatitis occurs under the guise of early toxicosis. It is generally accepted that symptoms of dyspepsia that occur before 12 weeks of pregnancy are signs of early toxicosis and are regarded after 12 weeks as an exacerbation or manifestation of a chronic disease of the hepatobiliary system. In the second and third trimesters, exacerbation of chronic pancreatitis must be differentiated from intrahepatic cholestasis of pregnancy, preeclampsia, acute fatty liver degeneration and HELLP syndrome. Factors that provoke exacerbation of pancreatitis in pregnant women include poor diet, decreased physical activity, impaired motility of the gastrointestinal tract associated with the hormonal effects of estrogens, diseases of the gallbladder and biliary tract, protein deficiency, infections, and polypharmacy. Unfortunately, it is not always justified to prescribe a large number of medications and multicomponent vitamins to pregnant women, which can have a toxic effect on the organs of the hepatobiliary system and contribute to the exacerbation of chronic pancreatitis. Classification of chronic pancreatitis (Marseille-Roman): – Chronic obstructive pancreatitis (develops as a result of obstruction of the main pancreatic duct). –Chronic calcific pancreatitis (protein precipitates, cysts and pseudocysts, stenosis and atresia of the ducts, atresia of acinar tissue are found in the ducts). – Chronic parenchymal pancreatitis (characterized by the development of fibrosis, infiltration of mononuclear cells that replace the pancreatic parenchyma). Diagnosis of pancreatitis in pregnant women In the clinic of chronic pancreatitis in pregnant women, mild pain syndrome, maldigestion and malabsorption syndrome, and endocrine insufficiency predominate. Relative pancreatic insufficiency is caused by a drop in the intraduodenal pH level below 5.5 (due to inactivation of enzymes), motor disorders of the duodenum (disruption of the process of mixing enzymes with food chyme), excessive bacterial growth in the small intestine (destruction of enzymes, decreased level of intraintestinal pH) , deficiency of bile and enterokinase (impaired activation of lipase and trypsinogen). Clinical signs of pancreatitis with exocrine insufficiency: diarrhea with fatty, foul-smelling feces, weight loss with preserved or increased appetite, nausea, vomiting. Laboratory tests recommended for the diagnosis of exocrine pancreatic insufficiency are currently not available in most Russian obstetric institutions. Thus, the quantitative determination of neutral fat in stool over 72 hours (more than 6 g per day is pathology), and the determination of elastase in stool (a level of less than 200 mcg in 1 g of stool indicates pancreatic insufficiency) seems problematic. The low sensitivity of the amylase test (determination of amylase activity in the blood and urine) is associated with the short duration of hyperamylasemia and hyperamylasuria in pancreatitis. With exacerbation of pancreatitis, an increase in the level of ALT and AST to 2 norms may be detected. An increase in bilirubin, mainly direct bilirubin, cholesterol and alkaline phosphatase is characteristic of the developed cholestasis syndrome, which may be due to a block of the common bile duct and the development of reactive hepatitis. During pregnancy, abdominal radiography, retrograde cholangiopancreatography, and CT are not used. Up to 32 weeks, EGDS can be performed. Ultrasound of the internal organs reveals an increase in the size and changes in the structure of the pancreas, uneven and unclear contours, dilation of the ducts, cysts and pseudocysts, pathology of the biliary tract, primarily cholestasis. Most often in pregnant women, diseases of the hepatobiliary system occur with symptoms of cholestasis. The main causes of cholestasis in pregnant women: • Recurrent cholestasis of unknown etiology • Exacerbation or manifestation of a chronic disease of the hepatobiliary system • Toxic liver damage • Viral infections (HBV, HCV, HAV, CMV, HSV, adenovirus, enteroviruses, Coxsackie viruses, Epstein-Barr virus) • Parasitic invasion (opisthorchiasis) • Benign non-hemolytic hyperbilirubinemia • Oncological diseases As a rule, all these diseases are accompanied by dysfunction of the pancreas of varying severity. Treatment of chronic pancreatitis in pregnant women Treatment of pregnant women with pancreatitis is no less difficult than its diagnosis. In our pregnancy pathology clinic, we adhere to the following principles for the management of pregnant women with chronic pancreatitis. 1.Minimization of drug therapy. 2. Diet with limited fat, fresh vegetables and fruits. 3.Increasing the amount of protein to 150 g per day (mainly due to animal proteins). Eat at least 5 times a day in small portions. All dishes are prepared boiled or baked. 4. Pregnancy imposes certain restrictions on drug therapy. Proton pump inhibitors and H2-histamine receptor blockers are contraindicated during pregnancy. In exceptional cases, when it comes to saving a woman’s life, the possible harm from the use of these drugs is immeasurably lower than the expected therapeutic effect. Thus, in severe cases of pancreatitis or in the presence of ulcerative lesions of the gastrointestinal tract, parenteral use of omeprazole or famotidine is possible. 5. The prescription of antispasmodics is indicated. Preference is given to the selective antispasmodic Duspatalin - 200 mg twice a day 20 minutes before meals for 3-4 weeks in combination with pancreatic enzymes. Pancreatic enzymes containing only pancreatin, for example, Creon 25,000 U, are prescribed 40 minutes before meals in order to achieve an analgesic effect, followed by a transition to Creon 10,000 U at the beginning of each meal for at least 3-4 weeks. 6. Considering the almost always present dysfunction of the hepatobiliary system, the prescription of drugs that help resolve cholestasis is indicated. Depending on the clinical situation, ademetionine or ursodeoxycholic acid preparations, or artichoke extract preparations are prescribed. 7.Buffer antacids (aluminum phosphate) are prescribed for heartburn before meals and 30–40 minutes after meals and before bed. 8. In case of bacterial overgrowth syndrome in the intestines, inflammatory process in the intestines, as well as in the presence of systemic lesions, no effect of therapy without the use of antibacterial agents, amoxicillin 1000 mg 2 times a day is prescribed before 18 weeks of pregnancy, after 18 weeks of pregnancy it is possible to prescribe metronidazole 250 mg 4 times a day. In the absence of bacterial overgrowth syndrome in the intestines, the main ways to influence the intestinal microflora is the use of probiotics and prebiotics. Probiotics are live microorganisms - lactic acid bacteria, often bifidobacteria and lactobacilli, sometimes yeast, which are normal inhabitants of the intestines of a healthy person and improve the microbial balance of the intestine. Prebiotics are non-digestible food ingredients that selectively stimulate the growth or metabolic activity of one or more groups of bacteria found in the colon. For the treatment of dysbiosis in pregnant women, a combination of one of the enteric forms of the probiotic with a prebiotic is ideal. A number of studies have established the prebiotic effect of the lactulose drug Duphalac, which was the basis for its inclusion in the complex therapy of intestinal dysbiosis in pregnant women. Thus, the problem of diagnosing and treating chronic pancreatitis in pregnant women is an urgent task and requires the interaction of doctors of various specialties - obstetricians, therapists and gastroenterologists.
Patient S., 32 years old, resident of the Sverdlovsk region, birth history No. 608, was admitted to the intensive care unit of UrNIIOMM on March 21, 2007 with the diagnosis: “Pregnancy 31–32 weeks. Bichorionic, biamniotic twins. Ulcerative-necrotizing esophagitis. Erosive gastritis. Chronic pancreatitis, exacerbation. Pregnant anemia 2nd degree.” When questioned, the patient denied the presence of chronic diseases, but noted heartburn and flatulence that occurred due to errors in diet before and during pregnancy. On March 13, after an error in her diet (she ate salted sprat with fried potatoes), the woman began vomiting, first with food, and later with coffee grounds up to 20 times a day, and therefore was hospitalized at her place of residence in the department of pathology of pregnant women. The examination revealed ulcerative necrotizing esophagitis. Ultrasound reveals diffuse changes in the pancreas, dilatation of the splenic vein at the hilum of the spleen. Clinical tests determined a reduced amount of hemoglobin to 88 g/l, hematocrit to 25.3, hyperbilirubinemia to 30.6 µmol/l, hypoproteinemia to 55.4 g/l. In the hospital at the place of residence she received detoxification therapy, famotidine, antacids, antispasmodics, iron supplements, metronidazole. On March 21, she was transferred to the Research Institute of OMM. Upon admission, she complained of heartburn, unbearable pain behind the sternum in the projection of the esophagus, flatulence, mushy stools up to 4 times a day, nausea, vomiting coffee grounds, which brings temporary relief, and slight itching of the skin. On examination, the condition is of moderate severity. The skin is pale. Vesicular breathing. Heart sounds are muffled and rhythmic. BP = 110/70 mm Hg, heart rate = 80 beats per minute. The abdomen is soft, moderately painful on palpation in the projection of the head of the pancreas. Liver + 1.5 cm. Edema of the lower extremities. Ultrasound of internal organs: diffuse changes in the pancreas. The splenic vein is dilated to 13 mm. The pancreas is painful on examination. EGDS: Erosive-fibrinous esophagitis. Sliding hiatal hernia. Gastroesophageal reflux. Duodenogastric reflux. Diagnosis: Pregnancy 30–31 weeks. Bichorionic, biamniotic twins. Gastroesophageal reflux disease: sliding hiatal hernia, grade 3 reflux esophagitis, acute erosion of the middle and lower third of the esophagus. Chronic pancreatitis, exacerbation. Cholestatic hepatosis of a pregnant woman. Anemia of the 2nd degree of combined genesis. Received treatment: 1. Fractional meals (broths, pureed soups, viscous porridges). 2. Gentle mode. 3. Infusion of saline solutions, omeprazole intravenously, before and after meals. 4. Creon 25,000 units 40 minutes before meals 3 times a day. 5. Duspatalin 1 dose, 2 times a day. 6. Liquid iron preparations. During the observation period, by March 26, 2007, the symptoms of pancreatitis and esophagitis stopped, and the patient’s well-being improved significantly. She was delivered by Caesarean section on March 27, 2007. The weight of the fetuses was 1780 g and 1770 g. In the postpartum period, she received Creon 10,000 units 3 times a day, Duspatalin 1 dose, 2 times a day for 1 month. On the 7th day, in satisfactory condition, she was transferred to the rehabilitation department of the children's clinic to care for children.
Literature 1. Grigoriev P.Ya., Yakovenko E.P. Recommendations for prescribing enzyme preparations for the syndrome of impaired digestion and absorption // Attending physician, 2001. – No. 5–6. – pp. 48–52. 2. Ivashkin V.T. Treatment of chronic pancreatitis // Russian Journal of Gastroenterology, Hepatology, 1996. – T. 4. – P. 10–18. 3. Lebedev V.A. Treatment of dysbacteriosis in pregnant women // Issues of gynecology, obstetrics and perinatology, 2005. – T. 4. – No. 2–3. – P. 3–5. 4. Maev I.V. Chronic pancreatitis (Algorithm for diagnosis and treatment tactics). – M., 2006. – 104 p. 5. Murashkin V.V., Lebedeva A.A., Votyakova N.V. Treatment of irritable bowel syndrome in pregnant women // Issues of gynecology, obstetrics and perinatology, 2005. – T. 4. – No. 2–3. – P. 6–9. 6. Podymova S.D. Liver diseases. – M.: Medicine, 1993. – 544 p. 7. Sarkisov D.S., Gelfand V.B., Tumanov V.P. Problems of early diagnosis of human diseases // Clinical. Medicine, 1983. – No. 7. – p. 6–14 8. Sorinson S.N. Viral hepatitis. St. Petersburg : TEZA, 1998. – 325 p. 9. Sherlock S., Dooley J. Diseases of the liver and biliary tract. – M.: Geotar-Med. 10. Boisson J., Coudert Ph., Dupuis J., Laveredent Ch. Tolerans de la mebeverine a long terme. Act Ther 1987, 16:289–292. 11. Le Gat M. Peloux Ch. Colopathe fonction–neile impact Medecin 1989; 3 Juin: 2–4.
Pancreatitis
One of the organs that most often fails during pregnancy is the pancreas. The most common problem associated with it is pancreatitis.
Inflammation of the pancreas is extremely dangerous because in the early stages of pregnancy it is extremely difficult to diagnose due to symptoms similar to toxicosis:
- poor appetite or its complete absence;
- nausea;
- vomit;
- pain in the abdomen.
It is often simply impossible to independently determine that pancreatitis lies behind toxicosis
What to do when the first symptoms of illness appear? You should consult a doctor who will prescribe the necessary tests in this case:
- Urinalysis (by which diastasis is easily determined);
- Biochemical blood test (with pancreatitis, amylase is detected in it).
Which doctor treats the pancreas
The disease can be completely asymptomatic or painful. The most dangerous form of the disease during pregnancy is considered dyspeptic, which is accompanied by a host of unpleasant manifestations:
- diarrhea;
- vomit;
- lack of appetite;
- weight loss, etc.
With this manifestation of the disease, the intestinal microflora is disrupted, which entails general dysbiosis and vaginal candidiasis. All this has an extremely negative impact on the health of women and children. In order to minimize the likelihood of any complications, probiotics and prebiotics are usually prescribed for such problems with the pancreas.
Why does pancreatitis make itself felt during pregnancy?
If in ordinary life the pancreas ache a little, then when carrying a child these symptoms can intensify many times and lead to serious illnesses. This happens for several reasons:
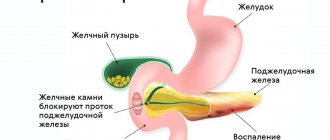
- The enlarged uterus sometimes compresses the liver ducts, which blocks its functions, provokes the growth of pathogenic flora and the development of infections.
- General immunity decreases.
- Chronic diseases are getting worse.
- Under the influence of hormones, the muscular system of the digestive organs relaxes and their tone decreases.
- Sometimes prescribed medications have a negative effect on the body due to their toxicity.
Pregnancy is a time during which a woman’s body works to the limit of its capabilities.
Treatment of pancreatitis
During pregnancy, the treatment of any disease should be approached sensibly and responsibly, since the question is not only about the health of the woman, but also her child.
There are several steps to pay attention to:
- Any vitamins and other medications can be taken only as prescribed by the attending physician and strictly in accordance with his recommendations.
- If problems with the pancreas occur, you must immediately give up bad habits (smoking, alcohol) and adhere to a therapeutic diet.
- It is possible to take additional enzymes that promote good digestion (Mezim, Allochol, etc.).
- Fight against dysbiosis.
Pancreatitis during pregnancy
When developing obstetric tactics, the peculiarities of the course of the disease in a particular patient are taken into account. Women with stable remission, preserved secretion in the absence of complications (pancreatogenic diabetes, etc.) are recommended to undergo dynamic observation, periodic examinations by a gastroenterologist, and diet correction with limited amounts of spicy, fatty, fried foods, and complete abstinence from alcohol. When prescribing medications for the treatment of concomitant disorders, it is necessary to take into account their possible pancreatotoxic effect. Acute pancreatitis that develops before the 12th week of pregnancy is an indication for its termination, and for a gestational age of 36 weeks and beyond - for early delivery.
A patient with active pancreatitis is hospitalized in a surgical hospital. The main therapeutic objectives are relief of pain, inflammation, restoration of the secretory functions of the organ, removal of intoxication, and prevention of possible complications. An important stage of treatment is to ensure functional rest of the damaged gland: to suppress the secretion of pancreatic juice for 3-7 days (taking into account the severity of inflammation), a regime of hunger and thirst is observed with parenteral nutritional support, the contents of the stomach are aspirated every 4-6 hours through a nasogastric tube, local hypothermia of the epigastric region. The drug therapy regimen includes:
- Gastric secretion blockers
. The drugs consolidate the effect of the created functional rest of the pancreas. A decrease in the volume of secreted gastric juice is accompanied by a decrease in the activity of pancreatic secretion, which makes it possible to localize damage and prevent further autolysis of the organ. - Anti-enzyme agents
. Antiproteolytic drugs allow you to inactivate pancreatic enzymes that destroy gland tissue. More effective when the process is active. For chronic variants of the disease, drugs with a metabolic effect that selectively inhibit trypsin are preferred. - Analgesics
. To eliminate pain, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and antispasmodics are prescribed. In more complex cases, glucocorticosteroids are used. In case of intense pain and signs of pancreatogenic shock, epidural anesthesia with mepivacaine and buprenorphine is possible. - Detoxification drugs
. Since active pancreatitis is accompanied by massive tissue destruction, pregnant women may develop severe intoxication syndrome. To remove toxic metabolites, infusion therapy with drip administration of crystalloid and colloid solutions is used.
To prevent infection of foci of necrosis, it is possible to prescribe antibiotics that have no contraindications for use during pregnancy. In severe cases of pancreatitis, according to indications, the volume of circulating blood is replenished, under the control of diuresis, disorders of water and electrolyte metabolism are corrected, and antiplatelet agents are used. After stopping the active process in the presence of functional organ failure, replacement therapy with multienzyme drugs is carried out.
To prevent infectious complications, the patient is recommended to have a natural birth with adequate pain relief (usually epidural anesthesia). Due to the significant risk of infection, cesarean section is performed in exceptional cases for obstetric indications. If conservative therapy is ineffective, the destruction of the gland increases, the inflammatory process spreads to the retroperitoneal tissue and peritoneum, sanitizing and drainage interventions and pancreaticoduodenal resection are indicated. Usually, in the 3rd trimester before abdominal surgery, pregnancy is completed with surgical delivery, which allows saving the life of the child.
Diabetes
One of the main functions of the pancreas is the production of insulin, which is responsible for the level of glucose in the blood. Against the background of serious overloads that the body experiences, gestational diabetes mellitus (pregnant diabetes) may well occur. Its peculiarity is that after childbirth, all its manifestations can disappear without a trace, but at the same time, colossal damage will be caused to the health of the mother and child.
There is no need to be afraid of this diagnosis. Usually, regular monitoring and dietary adjustments are enough to bring sugar levels back to normal.
It is usually very difficult to detect diabetes mellitus at the initial stage, since all the symptoms appear when the disease progresses quite seriously.
The manifestation of diabetes mellitus is recognizable:
- excruciating thirst;
- frequent urination;
- constant insatiable hunger;
- drop in visual acuity.
In order to start treatment on time, today all pregnant women undergo a glucose tolerance test (GTT) at 24–28 weeks. Many people do not like it because of its complexity and unpleasant sensations (you have to drink a strong sugary glucose solution on an empty stomach).
If gestational diabetes is detected, the woman is prescribed a strict diet and constant monitoring of blood sugar. You shouldn’t be afraid of this, because if you follow all the recommendations, then everything will be fine.
About the influence of the pancreas, or how to save pregnancy
Pregnancy is a certain test for a woman’s body. During pregnancy, many organs of the abdominal cavity experience additional stress, in particular the pancreas, which we are discussing with the head of the Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology No. 1 of KSMU Albir Almazovich Khasanov , works in an enhanced mode: on the one hand, the body of a pregnant woman must process large quantities of food , and on the other hand, large amounts of insulin are needed in order to ensure the development of the fetus. Unfortunately, disruptions to the functioning of this organ can cause a number of complications that affect the course of pregnancy. In this article, we talked about pancreatitis and diabetes mellitus (DM).
— How common are pancreatic diseases in pregnant women today?
— If we talk about inflammation of the pancreas - pancreatitis, its prevalence among pregnant women is approximately 1-2 per 4000 women. During pregnancy, acute pancreatitis can occur at any stage, but more often in the second half of gestation. The prevalence of type 1 and type 2 diabetes mellitus among women of reproductive age is about 2%, in 1% of cases a pregnant woman has pregestational diabetes, and in about 5% of cases gestational diabetes occurs or manifests true diabetes.
— Is it possible to prevent these diseases in pregnant women to avoid complications?
— Timely treatment of diseases that cause pancreatitis and diabetes, elimination of chronic intoxications (industrial, alcoholism) is necessary. At the same time, it is important to ensure a balanced diet, as well as a clear eating regimen. In these matters, health education work is of great importance. Sanatorium-resort treatment is indicated in the phase of complete remission or in the absence of frequent exacerbations. Resorts with drinking mineral waters and healing mud are recommended. If we talk about the prevention of diabetes, it is important to mention that the prevention of pregestational diabetes depends on the pathogenetic form of the disease and is one of the most pressing, still unresolved problems of modern healthcare. Prevention of gestational diabetes is carried out by correcting avoidable risk factors (obesity, hyperandrogenism and hypertension). Prevention of complications of gestational diabetes is carried out with early detection, active treatment of the disease, as well as teaching the patient self-monitoring of glycemic levels using portable glucometers and insulin therapy skills.
— Can early diagnosis contribute to further treatment tactics for pancreatic diseases in pregnant women?
— Today, many doctors unanimously speak out about late diagnosis of the disease in pregnant women. This is due to the lack of clear criteria for exacerbation of pancreatitis in pregnant women and precise additional research methods that could be used for diagnosis in this category of patients. It is also important that doctors often forget about the possibility of developing pancreatitis in pregnant women. In this regard, preventive measures aimed at preventing possible exacerbations during pregnancy are not carried out. When diagnosing diseases, it is necessary to take into account the duration of the disease, the degree of its compensation at the time of pregnancy, and the presence of vascular complications of diabetes. Doctors should first of all collect in detail a complete family history, features of the formation of menstrual function, the presence of infectious and inflammatory diseases (especially chronic pyelonephritis).
— Can pancreatitis and diabetes serve as contraindications for pregnancy?
— In general, pregnancy does not always affect the course of chronic pancreatitis and is not a contraindication in most patients. In addition, pancreatitis does not disrupt fetoplacental blood flow. At the same time, women suffering from this disease must be registered at the dispensary; it is necessary to take measures aimed at preventing the development of possible exacerbations or complications of the disease. With stable remission of the disease, in the absence of severe pancreatic dysfunction and complications, pregnancy with chronic pancreatitis is allowed. From the first weeks, patients with this disease are observed by an obstetrician-gynecologist and therapist, so that when the first signs of an exacerbation of the disease appear, appropriate treatment is carried out. As for patients with diabetes, a slightly different picture is observed here. These pregnant women are at risk for the development of various obstetric and perinatal complications such as spontaneous abortion, gestosis, polyhydramnios, premature birth, growth retardation and congenital malformation of the fetus, birth trauma of the mother and fetus, and more. Patients are included in this risk group, taking into account their relationship to such groups as: women who have been ill for more than 10 years, patients suffering from ovarian dysfunction, diabetic polyneuropathy, retinopathy, urinary tract infections and much more.
— What tactics should be followed when managing such patients?
— Of course, success in treatment cannot be achieved without active, competent self-control carried out by the patient at home. Therefore, women with diabetes should undergo training in diabetes schools according to a structured program before planning a pregnancy. A woman should be able to independently measure her glycemic level, change the dose of insulin depending on the results obtained, and have the skills to prevent glycemic conditions. Diet and exercise program are required. Diet therapy is also the main link in complex therapy for chronic pancreatitis. Treatment of this disease should be carried out strictly under the supervision of a doctor, and in acute forms - in surgical hospitals.
— Could you recall an interesting clinical case from practice related to the management of pregnant women with pancreatic diseases?
— At 25-26 weeks of pregnancy, a patient (21 years old) was admitted to us. She was taken to one of the city hospitals with complaints of epigastric pain, nausea, and vomiting. A diagnosis of acute pancreatitis was made. Two days after delivery, laparoscopy and laparatomy were performed, during which a purulent effusion was obtained. Sanitation and drainage of the abdominal cavity and omental bursa were performed. It was decided to terminate the pregnancy, and if the condition worsened, extirpation of the uterus and tubes. Two years later, this patient became pregnant again and gave birth to a healthy baby without complications.
Alfiya Khasanova