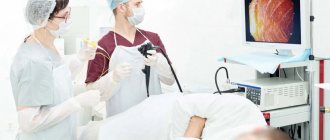
A healthy esophagus along its entire length has sufficient width for the free passage of swallowed food. However, in some cases, a narrowing of the lumen of the esophagus occurs due to a scar stricture: this is the name for the pathological growth of scar tissue in the wall of the organ. Dysphagia occurs - a complex of unpleasant symptoms associated with disruption of the process of swallowing and passage of food into the stomach.
Endoscopic bougienage of the esophagus is the best way to help the patient in such a situation. Bougienage may also be necessary before stenting the esophagus: the lumen of the organ must be sufficient for endoscopic insertion of the stent.
Indications and contraindications for urethral dilation
The procedure is carried out for therapeutic and diagnostic purposes. The main indication for bougienage is urethral stenosis, which develops due to various factors, namely:
- congenital developmental disorders;
- past infectious and inflammatory processes, sexually transmitted diseases;
- mechanical damage to the urethra;
- errors during medical procedures associated with penetration of the urethra;
- scarring of tissue after surgery.
Despite the large number of indications, there are patients who are better off refraining from this procedure. An experienced specialist will definitely conduct a conversation or diagnostic measures that will help identify or exclude such contraindications as:
- cystitis;
- suspicion of the presence of neoplasms;
- pyelonephritis;
- inflammatory processes in the acute stage;
- narrowing of the foreskin in men;
- poor blood clotting;
- renal failure in acute and chronic form.
Are there any contraindications?
Despite the fact that the procedure is classified as minimally invasive, when prescribing it it is important to take into account the existing limitations:
- mediastinitis;
- acute esophagitis and periesophagitis;
- exacerbation of somatic diseases;
- disorders of the coagulation system;
- oncology;
- symptoms of general intoxication;
- fever;
- congenital stenosis with complete or partial fusion;
- serious mental disorders that are accompanied by motor and speech disorders.
After surgery, the esophagus is dilated only after the wound has healed and the risks of suture dehiscence are minimized. The presence of diverticula in the digestive tract, perforations, fistulas, and complete scarring of strictures is also a limitation to bougienage of the esophagus.
Varieties and selection of bougies for therapeutic purposes
Depending on the material, instruments can be metal or synthetic.
The former are extremely rarely used in modern therapeutic practice, since their use leads to urethral injuries. Synthetic instruments are made of elastic material, which minimizes the risk of urethral puncture. Depending on the shape, straight and curved bougies are distinguished. The former are used to treat women, and are sometimes used for bougienage in men with an affected lower part of the urethra. Curved bougies are intended for male patients only. With their help, you can influence different parts of the organ, which ensures the effectiveness of treatment.
How is the operation performed?
In the laparoscopic technique - through 5 punctures with a diameter of less than 1 cm and under the control of a microvideo camera - the bandage is inserted into the abdominal cavity using microsurgical instruments. It is fixed just below the level of the junction of the esophagus with the stomach. The punctures are sutured with self-absorbing suture material. A sterile bandage is applied on top.
The internal cavity of the silicone ring is not filled at the time of application. After surgery, its volume is gradually increased with saline (by microinjections through the peritoneal skin). In this way, the degree of compression of the band around the stomach is smoothly adjusted.
Preparation for the procedure
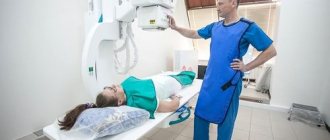
Before the procedure, an ultrasound is prescribed, which allows you to determine the diameter of the organ, the location of the stone or the characteristics of the narrowing.
In addition, you will need to undergo a general urine and blood test and undergo a computed tomography scan. Sometimes it is necessary to consult with other specialists, for example, a therapist or gynecologist for women. If there are no contraindications, a date for the examination is set. A few days before your visit to the doctor, avoid alcoholic beverages, and on the day of the procedure you should avoid food. If you take any medications on an ongoing basis, be sure to inform your specialist.
Before inserting the instrument, the patient is dressed in a sterile uniform, after which he is placed in a reclining position on a special chair. The procedure is carried out by a doctor and his assistants.
Stomach
Considering the emergence of highly effective antiulcer therapy and a significant reduction in the frequency of ulcer recurrences after successful HP eradication, balloon dilatation can be successfully used for cicatricial narrowing of the pylorus and duodenum as an alternative to surgical intervention. Of course, there is no point in dilation with decompensated stenosis. Dilatation is also possible for malignant ones, as palliative treatment, and after burn strictures, anastomotic strictures. Solt J., et al., published long-term results of dilatation in patients with benign gastric outlet stenosis (after surgery, peptic, corrosive and post-vagotomy strictures) [15]. He performed 117 balloon dilations on 72 patients and had a mean follow-up of 98 months. The average diameter of the stenosis was 6 mm before treatment and 16 mm after it. Reduction and disappearance of symptoms was observed in 80% immediately after the procedure and in 70% after three months. In 16 patients, restenosis was observed within 1-18 months after the intervention. Complications included one case of arterial bleeding and two perforations. Boylan JJ, and Gradzka MI, emphasize that proper antiulcer treatment, especially HP eradication and cessation of NSAIDs, is necessary to maintain the result of successful dilatation for gastric outlet stricture of peptic nature [2]. Anastomotic strictures and strictures of a malignant nature are more prone to rapid recurrence [11].
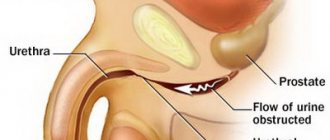
Dilation of the urethra in women, men and children
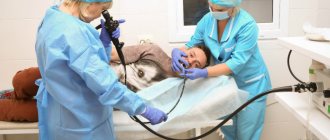
For diagnosis and therapy, a straight-shaped rigid bougie is used.
The specialist treats the tube with Vaseline for easy penetration, injects medication with an anesthetic into the urinary canal, and then places the rod in the urethra to the point of narrowing. After some time, the bougie is removed and the urethra is treated with an antiseptic substance. After 8-48 hours the procedure is repeated. In the next session, the therapist may use a wider bougie. To completely dilate the urethra, 3-5 procedures are required.
In men, the procedure takes a long time and requires a careful approach due to the anatomical features of the organ. The manipulation is carried out using rigid or flexible bougies, the latter are considered more comfortable for the patient. Rods made of synthetic material are often used, at the end of which there is a special cylinder with water. With this device, the instrument can be easily moved along the canal.
Before the procedure, the man may be given a sedative medication intravenously, and antiseptics are injected into the cavity of the urethra. The doctor slowly inserts the bougie while monitoring the patient's condition. Forced penetration may cause organ damage. When feeling pain, the patient should tell the specialist about it, in this way it is possible to detect the localization of the stenosis. The expanded part of the bougie is placed at the site of stenosis and left in this position for several minutes, after which it is carefully removed. During one procedure, bougies of different diameters can change. To restore urethral function, 2-14 sessions are required. Between procedures it is necessary to take breaks of at least 8 hours.
Congenital anomalies in children are eliminated exclusively under general anesthesia. The doctor carefully selects the appropriate instruments for the procedure and acts as carefully as possible to avoid injury. The technique of bougienage in this case is similar to the technique of manipulation in adults.
Using flexible rods, the doctor examines the location of stenosis in the urethra. During diagnosis, it is possible to obtain information about the condition of the organ. The main difference between the diagnostic procedure and the therapeutic method is that it is carried out once (repeated sessions are required for treatment).
During the diagnosis, it is important that the patient is as relaxed as possible, since nervous and physical tension leads to contraction of the canal, which means the procedure will be painful, uncomfortable and ineffective. In case of severe anxiety, the patient is offered sedatives, and in some cases, the diagnosis is carried out under general anesthesia.
What is bougienage of the esophagus?
The esophagus, narrowed due to scar stricture, must be expanded to its normal diameter in order to restore its natural functions. Bougienage is the process of expanding an organ using a bougie.
This is the name of a special device that is effective specifically for such manipulation. Properly performed bougienage has a lasting effect, removing or significantly reducing the symptoms of dysphagia.
Reasons for the formation of scar strictures:
- Chemical or thermal burns of the esophagus;
- Benign tumors of the esophagus;
- Radiation therapy for oncological diseases;
- Destructive esophagitis;
- Hereditary diseases.
This pathology is treated either surgically or endoscopically. Endoscopic surgery to bougienage the esophagus has great advantages:
- Using an endoscope, the doctor sees with his own eyes how the process of expansion of the esophagus is progressing, which helps to ideally select the size of the bougie for the expansion of the organ.
- The endoscopic method is minimally invasive, that is, it does not cause injury and does not require rehabilitation.
- The operation has almost no risks of complications.
Recovery after the procedure
After removing the urethral stricture, the specialist prescribes antibiotic therapy to prevent infectious complications.
Antibiotics are prescribed on an individual basis and taken in a strictly defined course. For some time after the manipulation, the patient may feel pain and burning when urinating, and observe the presence of a small amount of blood in the urine. After some time, the discomfort goes away; in the first few days, you can take painkillers. After bougienage, it is necessary to monitor the patient’s condition, measure body temperature and monitor the amount and characteristics of urine. If you experience acute pain in the lower abdomen, purulent discharge, or a large amount of blood, you should consult a doctor as soon as possible to rule out serious infectious processes.
Complications are characterized by:
- opening of bleeding;
- acute pain when urinating that does not go away for a long time;
- sharp pain in the lower abdomen;
- elevated body temperature.
Particular attention should be paid to the child’s condition after bougienage. If the baby is restless, redness and swelling of the genitals, and bleeding are observed, then it is necessary to urgently seek medical help.
Principle of the technique
Using a silicone ring, the stomach is divided into two sections according to the hourglass principle.
The volume of the upper part is made ~20-30 ml. The small volume is quickly filled with a small portion of food, after which the brain receives a command about saturation. Food slowly moves through the stomach through a narrowed opening in the band area, and the person feels full for several hours. As a result, the amount of food consumed can be reduced several times - to the minimum physiological norm. The inert biocompatible material of the bandage is not perceived by the body as foreign and does not cause rejection or negative side reactions.
Where to do it: cost of the procedure
You can sign up for the medical and diagnostic procedure of bougienage at the medical office.
We offer specialist consultations and treatment from a professional urologist at an affordable cost. You can find the exact prices in the price list. Bougienage is a therapeutic and diagnostic manipulation to expand the lumen of the urethra, which is carried out on an outpatient basis using modern instruments. You can make an appointment for a preliminary consultation with a urologist by phone or on the clinic’s website.
Advantages and disadvantages of bandaging
Gastric banding is performed using laparoscopic technology; patients can easily tolerate the operation. During the first two years, excess weight in operated patients decreases by ~62.5%. In addition, secondary pathologies caused by excess body weight, such as diseases of the joints and cardiovascular system, stop progressing. The associated risks of infertility, breast and colon cancer, and obesity-related mortality rates are reduced.
The bandage system can be adjusted after surgery, thereby creating a nutrition system that is comfortable for the patient and controlling weight. At the request of the patient or according to indications, it can be completely removed (without changing the diet, this can lead to weight gain again).
Of all the surgical treatments for obesity, banding has the lowest risk of complications. However, with a BMI ≥ 45, a number of decompensated conditions - bronchial asthma, reflux esophagitis, hypercholesterolemia and clinically significant type 2 diabetes mellitus - biliopancreatic bypass and gastric bypass operations are more effective.
After the operation, diet therapy is indicated: the patient is helped to change eating habits, since even in a limited amount, high-calorie foods will interfere with weight loss. With regular overeating, it is possible to increase the volume of the upper stomach and reduce the therapeutic effect. If the surgical technique is performed incorrectly, the bandage may spontaneously slip off (therefore, patients should carefully choose a clinic).
Small and large intestine
The main indications for dilatation are strictures due to Crohn's disease or UC and anastomotic strictures. Although there are reports of the use of this method for diverticular, tumor and ischemic strictures [8]. A retrospective analysis of balloon dilatation of strictures through a colonoscope in 59 patients with Crohn's disease (53 with anastomotic strictures and 6 with primary strictures) showed that a long-term positive result was achieved in 41% of patients, and in 17% after one dilation. However, in 59% of patients during the observation period, there was a need for surgical treatment as a result of stricture recurrence. Complications included two perforations [17]. Brooker JC, et al., reported the combination of balloon dilatation with the administration of long-acting steroids for strictures resulting from Crohn's disease [3]. In 50% of patients, remission was achieved after one dilatation with the introduction of steroids, in 28.5% several interventions were required, and, finally, in 21.4% of cases dilation was not effective.
When dilating colonic anastomotic strictures, balloon dilatation has proven to be more effective than bougienage [14]. Virgilio C., et al., using a balloon intended for the treatment of achalasia to dilate anastomotic strictures with a diameter of 2 mm or less, achieved results in 94% of cases [18].
Tumor strictures of the colon are dilated both for the purpose of emergency decompression [1] and for better preoperative preparation [16] or palliative treatment, in the latter case the installation of metal self-expanding stents is preferable.