Where to contact
FGDS or EGDS is performed by a doctor trained in endoscopy in residency, or who has undergone retraining in this specialty. In particular, at La Salute gastroscopy is performed by a diagnostician with many years of experience who is proficient in all methods of examination and treatment. In the clinic, the procedure is carried out in comfortable conditions, using high-quality Japanese Pentax equipment, in compliance with sanitary safety requirements.
You can make an appointment for the procedure by phone or contact the endoscopy room directly.
What should the patient take with him?
It is recommended to wear something loose for a gastroscopy. This will help you relax when the endoscope is inserted. Clothing should not restrict movement, put pressure on the abdomen in the stomach area, or tighten the neck. You need to take with you: a sheet or towel for the couch and a non-alcohol napkin for your chin so as not to stain the collar area with saliva. In addition to the direction, the documents you must have:
- passport;
- medical policy and insurance certificate;
- results of previous gastroscopy;
- in special cases, tests and outpatient records.
Also take with you non-carbonated water and medications taken on a regular basis. For example, from pressure.
You need to have shoe covers with you. Not everywhere they issue this protective product or it is possible to purchase a kit. At our La Salute clinic you will be given the things necessary for the procedure: shoe covers, disposable sheets, napkins. But if you wish, you can take your own.
Description of the procedure
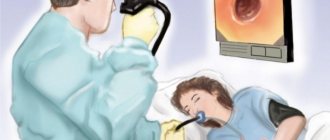
Diagnostics are carried out in a separate specially equipped room. In addition to the diagnostician, there is a nurse in the office who helps perform gastroscopy. After discussing the procedure with your doctor and immediately before the start of the session, dentures and glasses should be removed. It is advisable to disinfect your hands in any way. The further FGDS algorithm is as follows:
- The patient lies on the couch on his left side, with his knees bent and slightly tucked to his chest. In this case, the head lies on a bolster or pillow, and the person himself is facing the equipment.
- In order to relax the muscles of the oral cavity, reduce the gag reflex and sensitivity, the doctor sprays the throat and root of the tongue with a local anesthetic, for example, Lidocaine. Once the anesthetic has taken effect, the doctor inserts a jaw retainer, called a mouthpiece, into the mouth to prevent reflexive closing of the teeth during the procedure.
- The doctor inserts an endoscope into the mouthpiece hole, moves it towards the throat and the patient swallows the tip with the camera. While in a relaxed state, the person breathes slowly and deeply, and the specialist carefully moves the flexible tube step by step along the esophagus to the stomach. Once the probe reaches the desired location, the patient is asked to breathe through the nose and not swallow.
- From the moment it is immersed in the esophagus, the endoscope camera transmits an image of the mucous membrane to the monitor, and the doctor examines the condition of the internal walls of the digestive organs in real time. For better visibility, air or a little water can be supplied through the tube. In the first case, this straightens the folds on the walls of the organs, and in the second, it washes the endoscope chamber.
- After completing the examination, the endoscopist carefully removes the probe. At the same time, the patient feels normal, nothing prevents him from going home.
At the end of the procedure, the doctor makes recommendations and presents a conclusion. A gastroenterologist or therapist will look at and interpret the results.
FGDS under sedation
As a rule, gastroscopy is painless and tolerated calmly. But there is a certain discomfort. People are bothered by the sensation of a foreign body inside. Many people are overcome by a gag reflex. The situation is aggravated by the inability to relax, which complicates the procedure. Panic attacks make it difficult to breathe. For such patients, gastroscopy under anesthesia or sedation is possible, which is discussed in advance with the endoscopist.
In this case, before the procedure you will need to take tests, conduct additional examinations and visit other doctors. During diagnostics, an anesthesiologist is present in the endoscopy room, who administers anesthesia and at the same time monitors the patient during the examination.
How else does performing FGDS under the influence of drugs differ from conventional gastroscopy? The main difference is that a person immersed in medical sleep does not experience discomfort. The patient's muscles are relaxed, which allows for a better examination.
Endoscopy under general anesthesia and gastroscopy under sedation also differ. And not only because in the first case it is deep sleep, and in the second it is superficial sleep. During general anesthesia, it is necessary to use devices that monitor the patient's condition and breathing equipment, and the drugs administered are quite toxic. After such a diagnosis, a long recovery will be required. The same cannot be said about sedation, the principle of which is simpler and safer.
Thus, during medicated sleep, no serious equipment is used: the patient breathes on his own. After a mild hypnotic and dosed administration, a person wakes up faster and does not feel the reactions characteristic of emerging from anesthesia - weakness, drowsiness or nausea. Examination under sedation is well accepted by the body of a person who has recently undergone surgery, as well as by children. The only relative disadvantage of the technique is the possible allergy to the administered drug.
The progressiveness of the study under sedation makes it possible for almost everyone who wishes to undergo the diagnosis without physical and psychological discomfort. This can be done in our clinic, where the procedure will be carried out professionally and competently. In addition, La Salute’s own express laboratory will allow you to take preparatory tests on site and get results within half an hour. This will eliminate queues at the clinic and save time.
FGDS with video in a German clinic
FGDS (fibrogastroduodenoscopy), or gastroscopy, or fibrogastroscopy is a method of examining the upper gastrointestinal tract using a flexible device with fiber optics.
This instrument is inserted through the mouth and esophagus and makes it possible to examine the stomach, duodenum, and the walls of the esophagus. This technique has been used since 1868. The German family clinic offers an FGDS (gastroscopy) examination at the clinic on the square. Chernyshevsky, 11, Business. Make an appointment by phone 432-32-32.
For patients of our clinic, there is a comfortable opportunity to undergo the procedure under intravenous anesthesia (you will sleep), and we can also do a comprehensive examination of FCS and FGDS at the same time. The procedure is performed under intravenous anesthesia using the drugs “Propofol” or Diprivan®
In order to use the intravenous anesthesia service, you must have an ECG (electrocardiographic study) no more than 14 days old.
- What is revealed through the FGDS procedure?
- In what cases can FGDS not be done?
- How does the FGS procedure work?
- Our prices
Contraindications to gastroscopy
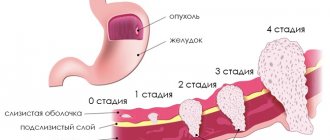
Gastroscopy is performed to make an accurate diagnosis of gastritis or cancer.
Despite the fact that the study makes it possible to study the mucous membrane of the digestive tract and is highly informative, it is characterized by the presence of certain contraindications.
If a patient has gastric bleeding, he needs to undergo an emergency gastroscopy.
When is it necessary to do an FGDS?
Fibrogastroscopy is performed on the direction of a doctor
for the purpose of diagnosis or treatment monitoring. This procedure is currently the only way to obtain information about the internal structure of the gastrointestinal tract of the upper section and makes it possible to assess the condition and make a final diagnosis.
Indications for gastroscopy of the stomach may include:
- pain in the abdominal area, which is periodic, short-term, or long-lasting;
- discomfort in the abdomen, esophagus;
- periodic vomiting and nausea of unknown etiology;
- frequent belching of air and/or food, particularly after eating;
- frequent heartburn;
- loss of appetite;
- a sharp drop in body weight;
- low hemoglobin content;
- the need to prepare for abdominal surgery;
- monitoring the effectiveness of treatment;
- age over 45 years (WHO recommends an annual planned procedure);
- postoperative period (gastric polyp removal procedure)
In addition, if a gastric ulcer, duodenal ulcer, disease of the pancreas, liver, gall bladder was previously diagnosed, or a malignant neoplasm was detected, fibrogastroscopy will be periodically required.
It is very important to identify various kinds of destructive processes in the early stages. Many diseases of the upper gastrointestinal tract may be asymptomatic at first, making it impossible to begin timely treatment. That is why it is recommended to undergo examination at the slightest sign of discomfort in the abdomen and esophagus, and even in the absence of such, for preventive purposes. The price of FGDS is low and quite affordable.
Stock
Promotion "FGDS (gastroscopy)"
FGDS with comfort at an attractive price
2000 a until 31.03.2022
Promotion “FKS (Video colonoscopy)”
Early diagnosis of gastrointestinal tumors
2500 a until 31.03.2022
Currently, work is underway on the website to change the price list; for current information, please call: 640-55-25 or leave a request, and an operator will contact you.
What is revealed through the FGDS procedure?
The endoscope allows not only to record and assess the condition of the gastrointestinal tract, but also:
- remove foreign bodies that have entered the esophagus or stomach;
- remove benign tumors (for example, polyps);
- perform a biopsy for in-depth tissue analysis and diagnosis of a number of serious diseases, such as cancer, jaundice;
- administer medications;
- perform electrocoagulation of a vessel that is bleeding;
- in case of severe bleeding, apply clips and ligatures;
- determine acidity;
- do a test for bacteria, in particular Helicobacter Pylori
Feelings and experiences
Local anesthesia makes the swallowing procedure difficult, but all these discomforts quickly disappear after the examination. At first, the endoscope may feel like it is interfering with breathing, which can trigger a panic attack. To calm down, it is recommended to breathe deeply through your nose. Discomfort can be created by air that will distend the esophagus, stomach and intestines. A biopsy is a completely painless procedure. Taking sedatives on the eve of diagnosis will help you calm down and endure all actions without worry or panic. The gas pumped into the stomach is removed from the body quickly and without negative consequences.
In what cases can FGDS not be done?
Typically, FGDS occurs under anesthesia, more precisely, using a local anesthetic - lidocaine in the form of a spray, which makes the throat insensitive to unpleasant sensations when a tube is inserted into the esophagus. At the patient's request, general anesthesia can be used. In fact, the procedure is painless and not particularly difficult. However, there are a number of contraindications, including:
- serious condition of the patient;
- pre-infarction condition, or recent heart attack;
- recent stroke;
- hypertensive crisis;
- exacerbation of bronchial asthma of any severity;
- hemophilia;
- damage to esophageal tissue;
- various types of mental disorders
However, if the benefits of the study are obviously higher than the risks of consequences, then while the patient is in the hospital under the supervision of specialists, the FGDS (gastroscopy) procedure can still be performed.
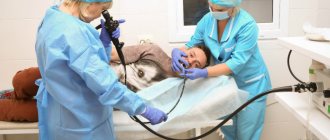
How is video gastroscopy performed?
For the examination, the patient is placed on the couch on his left side. Then a special mouthpiece is inserted into the oral cavity so that the insertion of the device does not damage the teeth or diagnostic equipment. After this, the doctor begins to slowly insert a flexible tube with a light and camera into the throat. At this time, the patient is advised to breathe evenly and deeply, not to swallow saliva and not to touch the tube of the diagnostic equipment with his tongue.
From the very beginning of the examination, the doctor carefully examines the mucous membranes. Since the esophagus and stomach have a folded structure, to examine the entire area of the mucous membrane, the doctor periodically pumps air into the location of the gastroscope camera. At such moments, the patient may experience a feeling of fullness. Air may be expelled as burps.
During the examination, the doctor records the following indicators:
- relief of the mucous membrane;
- state of the lumen of the esophagus;
- elasticity of walls;
- vascular pattern on the mucous membrane;
- the presence of hyperemia, erosions, ulcers, polyps and other changes.
As prescribed by the gastroenterologist and if clinically necessary, additional manipulations are performed during the examination of organs:
- a biopsy is taken for further research;
- mucous membranes are stained with special compounds (chromoscopy);
- a urease test is performed to determine Helicobacter pylori;
- a rapid test for lactase deficiency is performed;
- the acidity of gastric juice is determined.
Additional manipulations do not cause discomfort and only take a few seconds. After they are carried out, the doctor slowly removes the flexible tube from the esophagus, again examining the mucous membranes if necessary.
On average, the procedure takes from 5 to 15 minutes. At the end of it, the patient can go home and do his usual activities. For more details about the procedure, watch the video:
Important! It is not recommended to eat or drink within 20 minutes after VEGDS. If a biopsy was performed during the examination, you should refrain from eating hot food and drinks for 2 hours.
Carrying out the FGDS procedure in St. Petersburg
Preparation
The main thing to consider is the requirement to undergo the procedure exclusively on an empty stomach
. The last dinner before the FGDS should take place no later than 20.00 and be as dietary as possible. If the procedure is scheduled for the second half of the day, then in the morning it is recommended to drink weak, not too sweet tea or still mineral water. Drink in small sips. Foods such as chocolate, nuts, seeds, spicy foods, salads and alcohol should be excluded from the diet for two days before the appointed FGDS. Smoking on the day of the procedure is extremely undesirable - it can provoke a gag reflex.
Preparing for the study
Before carrying out the procedure, it is necessary to undergo preparation.
Before swallowing the tube, it is necessary to determine the presence of contraindications in the patient. Gastroscopy is performed only if the patient agrees to this procedure.
Before the procedure, the patient signs a special form. At the same time, the patient and the doctor discuss the possibility of complications and the specifics of the procedure.
A few weeks before gastroscopy, you should stop taking iron medications. Patients are also prohibited from taking aspirin. If for certain reasons it is impossible to exclude the use of medications, then it is necessary to discuss with your doctor the specifics of their use and dosage.
Methods for painless passage
In the last decade, techniques have begun to be actively used that can significantly reduce discomfort or even painlessly undergo gastroscopy of the stomach:
- Sedation. Sedation will help you survive FGDS calmly without fear. The patient is injected intravenously with a drug from the group of benzodiazepines, after which he falls asleep. The procedure is widely carried out and makes it easier to endure unpleasant sensations and painlessly perform FGDS of the stomach for adults and children. A few minutes after completion of the study, the patient wakes up. In an hour he can go home. The risk of side effects is low.
- Anesthesia (general anesthesia). Used more rarely under the supervision of an anesthesiologist. The patient is given several drugs for pain relief, but mechanical ventilation is not required. Usually performed before planned surgery.
- Capsule endoscopy. This is an innovative technique in which the patient does not have to swallow the tube. Instead, it swallows a small capsule-shaped chamber that travels all the way through the digestive system. The image is recorded and then viewed by a doctor without any problems. Among the disadvantages of capsule endoscopy is the impossibility of a more thorough examination of the changed area of the mucosa, conducting a Helicobacter test or biopsy. Helps those who cannot undergo the standard FGDS procedure.
Insertion of a probe through the nose (transnasal technique) is also used. This technique provides a more comfortable FGDS, since it causes nausea much less often and does not affect hemodynamic parameters (which is important for patients with cardiovascular diseases). A probe with a significantly smaller diameter is used - 5.4 mm (standard - 11 mm). When asked whether it is painful to do gastroscopy of the stomach in this way, many patients answer in the negative. Some diseases can be diagnosed with less unpleasant procedures: x-rays of the stomach and ultrasound of the abdominal cavity. In this article we have presented all the alternative methods of FGDS.