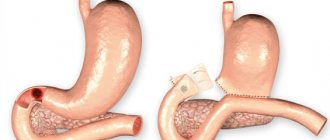
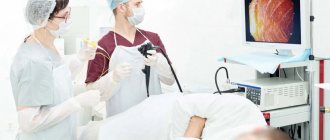
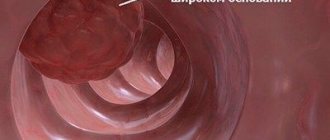
Fibrogastroduodenoscopy is a special method for diagnostic examination of the organs of the digestive tract, namely the stomach, esophageal cavity and duodenum. The purpose of such manipulation is to detect gastrointestinal diseases, take a tissue sample and monitor the results of therapy.
FGDS: what is it?
FGDS is an endoscopic examination of the digestive system. This procedure is considered the most effective for identifying various pathologies and tumors localized in the gastrointestinal tract.
Fibrogastroduodenoscopy can be prescribed to patients for the purpose of treatment and early diagnosis of diseases.
Thanks to this procedure, a number of important medical procedures can be performed:
- Remove the foreign body from the stomach cavity.
- Obtain a sample of pathological tissue from the digestive tract for further cytological and histological examination.
- Introduce some pharmacological agents.
- Remove a small benign tumor.
- Cauterize the blood vessel to stop internal bleeding.
- Apply a special ligature or clips for blood loss from the intestines or stomach.
- Conduct monitoring of therapeutic measures for ulcerative process and other gastrointestinal diseases.
The endoscopic procedure can be performed routinely or urgently.
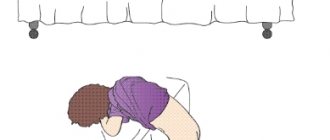
Fibrogastroduodenoscopy is performed in a separate room, where all the necessary equipment and facilities are available. The patient is placed on his left side, with his hands placed on top of his stomach. Taking into account the purpose of the study, the patient is offered a choice of local or general anesthesia. In the first case, Aeroflot is used, and in the second, a sleeping pill is administered intravenously. Afterwards, a fibrogastroscope is inserted into the cavity of the digestive tract through the mouth and the organs, their structure and mucous membrane are examined for the presence of pathological processes.
The duration of the procedure is 5-15 minutes, however, for the purpose of therapy, the duration can be increased to 20-25 minutes.
After the procedure, the patient is sent home and given an examination report.
At what age do children undergo FGDS? Nuances of the procedure and possible alternatives
Endoscopic examination of the gastrointestinal tract is considered one of the most informative methods for diagnosing diseases of internal organs in children. Its variety is FGDS (fibroesophagogastroduodenoscopy), which allows you to examine the upper parts of the digestive tube (esophagus, stomach, duodenum) using a flexible endoscope equipped with an optical system (fibrogastroscope) and identify pathological changes in them.
Despite the information content, this procedure is used to a limited extent in pediatrics, as it is associated with certain difficulties - the anatomical and physiological characteristics of the digestive organs in childhood and the child’s stress reaction to the insertion of an endoscope. In order to understand in which cases this study is necessary for a child to perform, and in which cases you can do without it, we will consider in our article:
- Do FGDS do children and at what age ?
- what are the indications and contraindications;
- how to properly prepare for FGDS of the stomach;
- what it is and how it is made;
- what diagnostic methods exist that can replace it .
CONTENT
Thanks to the achievements of modern medicine, FGDS can be used to diagnose diseases of the gastrointestinal tract in children of different age groups, and
even newborns . However, for a safe and effective study, it must be performed by pediatric endoscopists with special training, experience and technical equipment.
- In children under 5 years of age, of less than 6 mm are used for the procedure . In addition, they must have a sufficient atraumatic functional bending of the working part and be adapted to a given age in terms of technical characteristics.
- In patients older than 5-7 years, the examination is done with an endoscope with a diameter of 6-8 mm.
- Standard adult endoscopes are safe for examining the upper gastrointestinal tract in individuals weighing over 25 kg .
In pediatrics, FGDS is performed according to strict indications and only in cases where it is not possible to establish the correct diagnosis using simpler diagnostic methods. Typically, their role is played by clinical manifestations of diseases of the digestive system or their complications:
- persistent nausea, vomiting;
- prolonged diarrhea;
- recurrent abdominal pain of unknown origin;
- swallowing disorder;
- weight loss;
- anemia, the cause of which is unknown;
- signs of bleeding from the upper gastrointestinal tract (vomiting “coffee grounds”, black feces);
- ingestion of caustic substances.
In newborns and children under one year of age, gastric gastric gastroscopy is performed in the absence of appetite and weight gain against the background of retarded physical development and general irritability. After all, they still cannot talk about their condition, and if the doctor does not find the reason for the child’s poor health, then in some cases they have to resort to endoscopy.
Please note It is considered inappropriate to perform FGDS in case of functional digestive disorders, pyloric stenosis (narrowing of the opening leading from the stomach to the duodenum) and uncomplicated gastroesophageal reflux disease.
Also, gastroscopy in children can be used for therapeutic purposes , for example, to stop gastric bleeding or remove a foreign body.
For some patients, FGDS is undesirable, as it can be harmful to health. The following pathological conditions limit its use in children:
- severe disorders of the functioning of the cardiovascular and respiratory systems;
- bleeding disorders;
- mental disorders due to organic damage to the nervous system;
- acute inflammatory processes in the upper respiratory tract;
- pronounced narrowing of the esophagus or changes in its location with grade 3-4 scoliosis, mediastinal tumors (it is difficult to pass the device without damaging the mucous membrane).
The lack of appropriate endoscopic equipment (with the required diameter of the fiber gastroscope tube) is also considered a contraindication to FGDS.
However, if the benefits of the study outweigh all the risks, then it is carried out. If the patient has a disease that poses a direct threat to life , endoscopy is absolutely justified.
Each child is prepared for FGDS individually. The preparation process is very important, because it determines how the research will go and how informative it will be .
- The first thing parents should know is that the procedure is carried out on an empty stomach . The last meal is allowed 8-10 hours before the expected procedure. It is advisable not to drink water within 2 hours before it. In children of the first year of life, the period of fasting before FGDS is reduced to 6 hours.
- special diet is required at the study planning stage . A doctor will prescribe therapeutic nutrition for each child, taking into account his condition, symptoms and preliminary diagnosis.
- The next stage of preparation is the right psychological attitude . The child should be explained that the procedure is extremely necessary and short-term. Tell him how it is carried out, what sensations he will feel. It is also important for the parent himself to be calm and nearby, as children take on the emotions of adults.
- Immediately before the study, medication preparation is carried out. It consists of local anesthesia of the throat and the prescription of sedatives (calming) and anticholinergics (inhibiting secretion and motility of the gastrointestinal tract).
You can read more about preparing for the procedure: diet, how to swallow the tube correctly and breathe during the procedure here.
How to eat properly after completing the procedure is written in this article. Advice from doctors will help avoid complications and discomfort.
If necessary, the procedure can be performed under anesthesia or sedation, which allows the doctor to quickly and painlessly insert the endoscope into the digestive tube and calmly examine it. The indication for general anesthesia is severe anxiety in young children (under 5 years). For older children, sedatives are usually sufficient. If the child is calm, then you can do without it.
FGDS under anesthesia is also used in patients for whom the study is planned for therapeutic purposes.
Sometimes, parents independently insist on conducting FGDS in a state of medicated sleep in order to protect the child from stress. However, they must understand that anesthesia involves the additional introduction of medicinal substances into the body with their own effect on the body and possible adverse reactions.
The study is carried out in a specially equipped room. The child is placed on a table or couch on his left side , positioned in such a way that the left leg is straightened, the right leg is bent at the knee joint and brought to the stomach, or both legs are bent and pulled up. Hands are pressed to the body. An oilcloth pillow is placed under the child's head.
Sometimes during the procedure it becomes necessary to change its position (turn it on the stomach or on the right side), so it is good if a special table with a rising head and foot end is used for endoscopy, with the possibility of turning it in one direction or another.
Before introducing the fibrogastroscope into the digestive tract, a mouthpiece is put on it and placed in the oral cavity . It protects the device from damage and prevents the mouth from closing. The assistant fixes the subject's head, tilting it back a little. Then the patient is asked to make a swallowing movement at the height of a small inhalation.
At this point, the specialist carefully advances the endoscope into the cavity of the esophagus, and then into the stomach and duodenum.
Help During the procedure, the child is recommended to breathe evenly and calmly and make swallowing movements only at the request of the doctor.
After examining the internal surface of these organs, if necessary, tissue samples can be taken for analysis .
At the end of the procedure, the endoscope is also carefully removed from the digestive tract. The patient needs to turn on his stomach and burp air . If a biopsy was performed, then to prevent bleeding from damaged areas of the mucous membrane, a solution of Vikasol is injected intramuscularly. Eating is allowed 1.5-2 hours after endoscopy.
FGDS of the stomach
FGDS is an invasive study that not only causes discomfort and fear in the child, but can also lead to the development of complications (trauma to the esophagus or stomach). Therefore, if the child’s condition allows, then first they resort to safer and more easily tolerated procedures:
- Ultrasound of the stomach;
- X-ray examination with contrast;
- video capsule endoscopy;
- transnasal gastroscopy using ultrathin video endoscopes.
For those who are afraid to do FGDS, but do not see an alternative, a separate article has been written that talks about how it is easier to endure the procedure. Tips on choosing a doctor, psychological attitude and proper breathing techniques will help make gastroscopy as comfortable as possible.
To summarize the above, I would like to note that in some situations, FGDS can be an indispensable method for diagnosing and providing assistance to a sick child (for example, with ongoing gastric bleeding). But medical science does not stand still and is developing new endoscopy techniques that are no less informative, but are easier to tolerate for young patients .
Have you, dear readers, ever had to do an FGDS for your child? Did you manage to properly prepare him for the study? And did this procedure help solve your problem?
Advertising
Indications for gastroscopy
At the moment, FGDS is the most effective way to diagnose various gastrointestinal diseases. In addition to assessing the external condition of the internal organs, during such manipulation it is possible to carry out therapeutic and surgical interventions.
The main indications for gastroscopy are:
- Pain in the epigastric region, often after eating. Such a sign may indicate the presence of gastritis and ulcers.
- Intense and prolonged heartburn.
- Bloating, abdominal discomfort.
- Regular belching after food and regardless of it.
- Sudden loss of body weight.
- Hungry nagging and general pain that occurs 5-6 hours after eating. This symptom indicates pathology of the duodenum.
- Profuse and systematic vomiting.
- Suspicion of blood loss from the digestive system.
- Swallowing dysfunction.
- Preoperative period for the treatment of the heart, joints and other organs.
- Inflammatory lesions of the mucous surface of the stomach and intestines.
- Gastroesophageal pathology.
What affects the time of gastroscopy?
Despite the fact that the average duration of an endoscopic examination of the stomach is 5-10 minutes, this period can be extended under the influence of several internal and external factors.
Among them:
- Psychological mood
. Most patients (especially those undergoing this examination for the first time) associate endoscopy with painful sensations. This creates a persistent fear in them, which negatively affects the formation of contact with the doctor. - Failure to comply with proper preparation
. If the patient did not adhere to the diet and consumed any food within a few hours or minutes, performing an FGDS may be difficult or even canceled. In this situation, active digestion of incoming food will occur in the stomach cavity, as a result of which it becomes impossible to assess the condition of the walls of the organ. - Use of anesthesia
. As mentioned above, if there are indications or personal desire, endoscopic examination of the stomach is possible under local or general anesthesia. This will require the involvement of an anesthesiologist, who individually selects the optimal drug and its dosage.
Contraindications for FGDS
The main contraindications to endoscopic examination are:
- Scoliosis.
- Acute myocardial infarction.
- Poor blood clotting.
- Atherosclerotic plaques.
- History of stroke.
- Attacks of bronchial asthma during exacerbation.
- Pathological conditions of the mediastinum.
- Narrowing of the esophagus.
Manipulation is carried out with caution in patients who have angina pectoris, mental disorders, severe hypertension, acute infections of the nasopharynx and tonsils.
How to prepare for gastroscopy of the stomach
For the FGDS procedure to be successful, it is necessary to properly prepare for it. To do this, just follow the following recommendations:
- 3-4 days before the procedure, it is important to exclude spicy foods, seeds, nuts, chocolate and alcoholic beverages from the diet.
- In the presence of some severe gastrointestinal pathologies, such as stenosis of the esophagus and impaired passage of food through the duodenum, patients must follow a strict diet prescribed by a doctor for several days.
- The evening before the study, dinner should be no later than 6 pm and consist of easily digestible foods.
- In the morning before the manipulation itself, it is forbidden to eat, drink, or perform hygiene procedures.
- To avoid discomfort during the procedure, you should take a bulky napkin or towel with you.
- You should not swallow during the examination.
- After FGDS, it is not advisable to eat for 2 hours.
FGDS with video in a German clinic
FGDS (fibrogastroduodenoscopy), or gastroscopy, or fibrogastroscopy is a method of examining the upper gastrointestinal tract using a flexible device with fiber optics.
This instrument is inserted through the mouth and esophagus and makes it possible to examine the stomach, duodenum, and the walls of the esophagus. This technique has been used since 1868. The German family clinic offers an FGDS (gastroscopy) examination at the clinic on the square. Chernyshevsky, 11, Business. Make an appointment by phone 432-32-32.
For patients of our clinic, there is a comfortable opportunity to undergo the procedure under intravenous anesthesia (you will sleep), and we can also do a comprehensive examination of FCS and FGDS at the same time. The procedure is performed under intravenous anesthesia using the drugs “Propofol” or Diprivan®
In order to use the intravenous anesthesia service, you must have an ECG (electrocardiographic study) no more than 14 days old.
- What is revealed through the FGDS procedure?
- In what cases can FGDS not be done?
- How does the FGS procedure work?
- Our prices