- Benefits of gastroscopy during sleep
- What is the procedure
- Without anesthesia
- Using anesthesia
To carry out the most effective diagnosis of the condition of the upper gastrointestinal tract, specialists conduct an internal examination of the mucous membrane of the esophagus, stomach and the initial part of the small intestine.
The process is carried out using an endoscope - a thin long tube at the end of which there is a camera and a flashlight. The image of the examined area is transmitted to the monitor, which allows the doctor to study the object in detail. This procedure is called gastroscopy, or more precisely, esophagogastroduodenoscopy (EGD). Such an examination allows you to most accurately identify pathological processes and changes in the structure of the above sections of the digestive system.
The specialist conducting the research has the opportunity to enlarge the picture and thoroughly examine the risk zone. This makes it easier to determine the nature of destructive changes and accurately diagnose an ulcerative lesion, an inflammatory process or a neoplasm. Gastroscopy is performed both under anesthesia and without it, depending on the patient’s health condition, the characteristics of his body and medical indications.
For what diseases is examination prescribed?
This method has the greatest accuracy necessary for differential diagnosis of various gastric diseases. For example, chronic gastritis, polyps, cancer, gastrointestinal bleeding. Gastroscopy is also used to confirm or refute a suspected malignant tumor of the stomach.
Gastroscopy is advisable to use when complaints arise that indicate disruption of the digestive tract, or when X-ray signs of the disease are identified. This study helps to obtain the necessary information about the condition of the gastric mucosa.
It can also be prescribed in the following cases:
- when pain occurs in the epigastric region, which is associated with meals, occurs on an empty stomach or a few minutes after eating food;
- when heartburn occurs;
- vomiting with blood;
- when you experience belching that has a sour taste;
- in the event of various dyspeptic disorders: nausea and vomiting of food eaten the day before;
- the occurrence of a constant feeling of heaviness or schedule that occurs after eating food.
- Gallery
- News
- Reviews
- Vacancies
- Licenses
- Insurance partners
- Controlling organizations
- Schedule for receiving citizens for personal requests
- What you need to know about coronavirus infection?
- Rules for patients
- Online consultation with a doctor
- Preparing for research
- to corporative clients
- Documentation
Transnasal gastroscopy is a gastroscopy without swallowing the probe. The gastroscope is inserted through the nose - transnasally. This newest method uses an ultra-thin gastroscope (less than 6 mm in diameter!). Administration through the nose guarantees the absence of a gag reflex and sore throat. In addition, when performing transnasal gastroscopy, there is no need to use sedatives, which allows the patient to drive immediately after the examination and minimizes the risk of any complications.
The study begins with ingesting a tablespoon of medicine to suppress foaming in the stomach, as well as determining which nostril breathes better. Nasal congestion, in most cases, was not an obstacle to transnasal examination. Before the study, I just need to blow my nose and that’s it!
A small amount of a mild anesthetic is injected into the selected nostril (by the way, this procedure can be carried out without any anesthesia at all, but patients often feel more comfortable with pain relief), and a little gel is also injected into the nostril to make the endoscope glide better.
The endoscope is carefully inserted into the nostril, while the process is monitored on the monitor screen. The sensations, of course, are a little strange, but they cannot be called unpleasant.
The examination lasts a few minutes, which is associated with much better examination conditions, because the stomach is calm and there are no gag reflexes. During the study, the mucous membrane is examined, the vessels of the gastric mucosa are examined in a special mode, the acidity in the stomach is analyzed, a Helicobacter test is taken, and, if necessary, a tissue biopsy is performed for further histological examination.
Advantages of the transnasal method:
- The procedure is comfortable. The endoscope does not touch the root of the tongue, and the procedure does not cause a swallowing reflex or vomiting.
- The patient can speak freely with the doctor during the examination, which minimizes discomfort.
- Improved examination conditions, no gag reflexes.
- Reduced examination time due to the absence of strong painkillers or anesthesia.
- Ability to drive a car immediately after the study.
- Increases readiness for repeated research.
According to the results of a patient survey, 94% of respondents would prefer the transnasal method to conventional gastroscopy.
Sign up for an examination by phone
Services and prices
Appointment with a gastroenterologist, therapeutic and diagnostic, primary, outpatient
2,000 rub.
Appointment with a gastroenterologist, candidate of medical sciences, therapeutic and diagnostic, primary, amb.
2,500 rub.
Biopsy of the digestive tract mucosa during endoscopy (up to 3 fragments)
1,300 rub.
Transnasal video esophagogastroduodenoscopy diagnostic
4,300 rub.
Comprehensive transnasal videoesophagogastroduodenoscopy
5,600 rub.
Histology of biopsy material obtained during endoscopic examination. up to 3 teachers.
1,650 rub.
Bakhvalova Tatyana Aleksandrovna Gastroenterologist Doctor of the highest category Work experience: 47 years
Prilepskaya Svetlana Ivanovna Gastroenterologist Doctor of the highest category Work experience: 34 years
Make an appointment
Preparing for a stomach examination
Preparation for the procedure includes specific features that the patient should take into account. Firstly, the research is carried out strictly on an empty stomach, because food interferes with the necessary examination of the gastric mucosa. That is why 6-8 hours before the diagnosis it is necessary to give up food and cigarettes.
It is also best to limit the amount of liquid you drink. If you need to take medications that are used systematically, you need to drink a small amount of water and warn the diagnostician in advance about this before conducting the study.
Recommended video:
Benefits of gastroscopy during sleep
Endoscopic examination has its own characteristics, and not all patients can tolerate it without stress. Many people actively experience a gag reflex, coughing and spasms of the laryngeal muscles. Manipulations with a flexible hose penetrating inside cause a negative reaction in especially sensitive patients and children with increased nervous excitability.
Gastroscopy of the stomach under anesthesia, which proceeds quickly and almost imperceptibly for the patient, will help get rid of unpleasant sensations, unnecessary anxiety before the procedure and negative memories. It is also easier for a doctor to perform an endoscopy when the subject does not have physiological or emotional resistance to the process.
Endoscopic examination during sleep allows for more than just a visual examination. You can additionally do:
- Tissue collection for histological analysis.
- Stop bleeding.
- Removal of polyps.
- Endobiliary manipulation.
Contraindications to gastroscopy
There are a number of contraindications for which gastroscopy is not recommended. However, their validity may be relative in some situations. For example, the introduction of a gastroscope in the presence of gastrointestinal bleeding will be advisable even in case of acute myocardial infarction.
When conducting a routine examination, contraindications usually include:
- severe degree of respiratory failure;
- heart rhythm disturbance;
- hypertensive crisis;
- acute myocardial infarction;
- heart failure;
- history of hemorrhagic or ischemic stroke;
- recovery period after a recent myocardial infarction or acute cerebrovascular accident;
- presence of serious mental illness;
- aneurysms of the great vessels or carotid sinuses.
If there are any contraindications from the above list, you should consult with your doctor regarding the selection of another diagnostic method that will not be inferior to gastroscopy in its information content.
Anesthesia and sedation
If performing gastroscopy is difficult due to the psychological status of the patient or the presence of epilepsy or organic diseases of the central nervous system, then the study is best carried out under sedation or intravenous anesthesia.
For everyone else, this may be a good way to get through the procedure without unnecessary worry and stress. Sedation for EGD is widespread throughout the world. Read more about it in our article.
General anesthesia is often used in young children, which makes the procedure easier tolerable and easier.
Alternative methods of checking the stomach without gastroscopy
Diagnosis of various functional and organic abnormalities is carried out taking into account three directions: physical examination, laboratory diagnostics and instrumental examinations. The latter includes gastroscopy. Despite the wide range of its information content, today it can easily be replaced by other diagnostic methods.
Diagnostics by capsule
According to the diagnostic principle, capsule endoscopy is extremely similar to fibrogastroscopy. The only difference is that instead of a probe, the patient must swallow a small capsule, which is surrounded by LEDs and a camera. The size of this capsule is 10x25 mm. During the examination, the patient wears a special vest containing a recording device. The capsule moves along the esophagus on its own.
Who is suitable for gastroscopy in a dream?
- You are terrified of undergoing the endoscopy prescribed for you.
- You are not sure that you can control your gag, cough and swallowing reflexes.
- You are experiencing severe stress from the upcoming manipulations.
- You don't want any unpleasant or painful sensations in the process.
- You have no contraindications to the use of anesthetics and sedatives.
To carry out the most effective endoscopy in a dream, it is important to choose the best clinic, where real masters of their craft work, there is new high-quality equipment and comfortable living conditions.
If you want to have a gastroscopy under anesthesia in Moscow, feel free to contact the Central Clinical Hospital of the Russian Academy of Sciences. Here you will meet highly qualified specialists with extensive experience in performing endoscopy using the most modern equipment.
Our largest multidisciplinary clinic, which is part of the Russian Academy of Sciences, has everything necessary to carry out therapeutic and diagnostic procedures both in outpatient and inpatient settings. You will be provided with European-level service, diagnostics and treatment that meet the highest international standards.
Historical reference
In the 17th century, doctors began to use gastric tubes not for diagnosis, but for treatment purposes. There is information that Hermann Boerhaave was the first to administer an antidote through a tube to a poisoned patient in order to save a man who could not swallow it on his own.
The placement of a gastric tube for diagnostic purposes was first carried out by the German scientist and physician Adolf Kussmaul in 1869. He obtained the contents for analysis through the tube by aspiration.
Further, gastroenterologists from different countries developed a method for a more detailed study of the secretion of the stomach and duodenum and its role in pathology: single-stage and fractional intubation, stimulation with breakfast and the introduction of chemicals.
Endoscopists also consider Kussmaul to be the founder of the method. Schindler invented a bendable gastroscope with an optical system. Since the middle of the 20th century, controlled soft gastroscopes have come into practice, providing a panoramic view, and Basil Hirschowitz created a model of a fiber gastroscope.
In the new device, the image passed through bundles of the finest glass fibers. The optical part was called fiber optics. Industrial production began in Japan. Until now, equipment from Japanese companies is considered the best and is most common in medical institutions in Russia.
Technology does not stand still; today it has become possible to broadcast the fibrogastroscopy procedure to an audience of doctors and students.
Probeless methods for endoscopic examination of the gastrointestinal tract
Ultrasound
Ultrasound diagnosis of diseases of the stomach and intestines is a relatively new phenomenon in gastroenterology, as it was previously used only for examining parenchymal organs (liver, spleen, kidneys, pancreas) and bile outflow tracts.
The method is safe and informative. Ultrasound allows you to visualize the organ through the anterior abdominal wall and provides the doctor with a spatial image of it in different projections.
Usually ultrasound is prescribed in any case as an addition to FGDS. It is excellent as the first stage of examining the gastrointestinal tract system and can identify emergency cases . A detailed analysis and comparison of these two methods: FGDS and ultrasound can be read here.
X-ray
X-ray techniques are widely used to detect pathology of the gastrointestinal tract. They are distinguished by their accessibility, ease of use, and sufficient information content , but, at the same time, they are associated with radiation exposure.
Some of them are carried out with contrast enhancement, which puts additional stress on the body and causes unwanted reactions. X-rays are most often prescribed for emergencies in hospitals . A detailed comparison of stomach X-rays and FGDS can be found in this article.
CT and MRI
Computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging are prescribed in gastroenterology as additional research methods when there is a need to confirm the diagnosis or clarify the nature of pathological changes, as well as when a tumor process is suspected.
Computed tomography (CT) exposes body tissue to radiation that is several times higher in dose than conventional radiography. MRI has certain limitations in use. You can learn more about this in a separate article.
Electrogastroenterography
The method is absolutely safe and non-invasive. It is used in clinical practice to assess the motor function of the stomach and intestines by recording the electrical potentials emanating from them. The absence of contraindications and side effects makes it possible to prescribe it to different categories of people - young children, seriously ill patients, pregnant women.
What is single-stage and fractional probing?
Both options for checking the stomach by first swallowing a rubber tube-probe differ in the frequency of aspiration. The one-step method is not currently used. It was carried out with a thick probe (10–13 mm in diameter) with a rounded end and two holes. Through them, the contents of the stomach were sucked out with a syringe.
In gastroenterology, it is impossible to draw conclusions about acidity from one fraction. For fractional probing, a thin probe with a diameter of 2–3 mm and a length of 110–150 cm is used; several fractions are aspirated. The stages of secretory activity are studied.
Standard probes vary in size
The gastric probing algorithm involves sequential aspiration of material:
- the probe is advanced into the stomach by swallowing movements of the patient to the desired level;
- put a syringe on the free end and suck out the contents for five minutes (the first or “skinny” portion);
- remove the plunger from the syringe and inject through it into the stomach cavity 200 ml of a test breakfast warmed to body temperature;
- apply a clamp to the outer end;
- after 10 minutes, the second portion (10 ml) is removed, it determines the basal secretion;
- then suction is performed every 15 minutes (the third portion is stimulated secretion) and another 4 per hour, for a total of 7 portions;
- the probe is removed;
- All materials are numbered in order and sent to the laboratory.
The estimated duration of the procedure is about two hours. The patient does not feel pain.
Based on the results, total, free, bound acid, pepsin content, and hydrochloric acid production rate are studied. The production of gastric juice reflects the intensity of acid neutralization, the reflux of alkaline contents from the duodenum into the stomach (the presence of duodenogastric reflux).
Probing of the stomach shows the functionality of the organ, but does not allow us to see the reasons for their failure or pathological changes. Insertion of a probe is contraindicated:
- with bleeding from the stomach;
- varicose veins of the esophagus;
- obstruction of the esophagus;
- acute stage of inflammation of the esophagus and stomach;
- ulcers in the mouth and stomach;
- hypertension;
- tendency to attacks of angina pectoris;
- difficult nasal breathing.
The study of all fractions gives a complete picture of the secretory activity of the stomach
How gastroscopy is performed at the Yauza Clinical Hospital
The procedure requires preliminary preparation. It is carried out on an empty stomach, so you should not eat food 8-10 hours before gastroscopy. If pre-sedation is planned, cardiac data must be obtained. An ECG can also be performed in our clinic to evaluate your condition. You won't have to spend a lot of time on research if you do everything you need in one hospital.
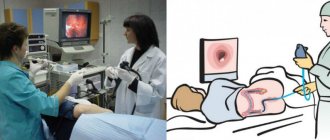
The patient's stomach is filled with air to improve vision. Next, a backlit camera on a thin and flexible cord is inserted into the esophagus. With its help, the doctor assesses the condition of the organ and records the collected data.
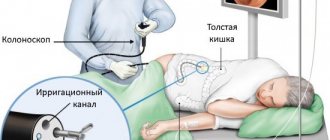
Often, in order to fully assess the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract, gastroscopy and colonoscopy are performed. In the latter case, the examination is carried out through the intestines, inserting an endoscope into the rectum.
Gastroscopy of the stomach in Moscow at the clinical center on Yauza is carried out in the iScan expert mode. High-precision endoscopic equipment allows you to obtain high-quality images and detect even small changes.
The equipment allows you to take a targeted biopsy precisely from the lesion. In addition, if necessary, tumors and polyps can be removed using an endoscope. When using this method, the operation occurs with minimal tissue damage and does not require a long period of rehabilitation.
Carrying out the procedure
Gastroscopy is carried out according to strictly established rules.
Gastroscopy must be carried out according to strictly established rules, which will ensure its high efficiency. Initially, the doctor administers anesthesia to the root of the tongue.
For this purpose, a spray or a special anesthetic solution can be used. The patient needs to lie on the couch on the left side.
Next, the doctor inserts a mouthpiece into the patient’s mouth. It helps protect the patient's teeth from injury. This device also protects the endoscope from biting.
A special gel is applied to the tip of the endoscope. Next, it is carefully introduced into the patient’s esophagus through the oral cavity. To move the endoscope through the digestive tract, the patient must take a sip.
During gastroscopy, patients, as a rule, do not have problems with swallowing a medical instrument. The patient's breathing remains smooth. To avoid negative consequences during endoscopy, a person is strictly prohibited from swallowing movements.
If saliva accumulates in the patient’s mouth during the examination, the nurse removes it with a special suction. The doctor slowly moves the endoscope through the digestive system.
Using an eyepiece and a monitor, the mucous membranes of the digestive tract are assessed. If it is impossible to see the walls, then water or air is supplied to the digestive system. For this purpose, a special channel of the endoscopic tube is used. Excess air and water are removed using suction.
Survey results
It is necessary to do an FGDS, EGDS or FGS to check the condition of the following organs:
| esophagus | stomach | duodenum |
|
|
|
If abnormalities are detected, the patient is recommended to undergo gastroscopy annually or every six months, depending on the diagnosis. The cost of refusing preventive examinations may be a deterioration in health.
Based on the examination results, the doctor can diagnose:
- areas with damage (cracks, bleeding, perforations);
- changes in the structure of the mucous membranes (erosions, ulcers);
- inflammatory diseases (gastritis, duodenitis);
- scar tissue changes, the presence of diverticula (protrusions) of organ walls;
- the presence of benign and malignant neoplasms;
- narrowing of the lumens of the sphincters separating the stomach from the esophagus and intestines;
- violation of peristalsis with reflux - reflux of the contents of the duodenum into the stomach or from the stomach into the esophagus;
- changes in the acidity of the stomach and other pathologies.
What can be replaced?
If the patient has contraindications to FGDS, the doctor prescribes an examination using alternative methods. It is considered advisable to combine several diagnostic procedures to obtain more accurate data and prevent errors at the diagnostic search stage.
Sometimes patients themselves look for an alternative to gastroscopy, experiencing discomfort or fear of the study. In such cases, it is better to coordinate your actions with your doctor and choose a diagnostic method together . After all, to make a diagnosis in each case, a different amount of examination may be required. Below we list the main alternative studies and briefly discuss each of them.
How is probing carried out?
This diagnostic method takes quite a long time and can last up to two and a half hours. This depends on the condition of the patient and on the procedure used.
It is usually carried out in a standard way:
- First, all its contents are aspirated from the stomach.
- Then, every 10 minutes for an hour, the secretion produced by the stomach on an empty stomach is collected. The fluid collection time is five minutes.
- Afterwards, a so-called test breakfast is introduced into the stomach. This could be cabbage broth, light broth, or medicinal secretion stimulants: insulin, pentagastrin or gestamine. These drugs have their own contraindications for use, so a trial breakfast is now practically not carried out. In addition, it does not give the desired stomach reaction.
- Half an hour after the introduction of breakfast, the secretion caused by stimuli is again selected. The collection is also carried out within an hour at intervals of fifteen minutes.
Each portion of liquid received is tested in the laboratory. The smell, appearance, consistency and total amount of the resulting contents are assessed.
The use of gastroscopy and sounding for treatment
The gastroscopy method is used in medical procedures. The specialist can simultaneously:
- remove polyps;
- remove foreign bodies;
- stop the bleeding of the ulcer;
- Apply the medication directly to the damaged area.
Carrying out these procedures increases the duration by 10–15 minutes. The insertion of a probe in the form of an ambulance hose is used in the hospital for gastric lavage in emergency cases of poisoning.
Gastroenterologists often prescribe “blind probing.” So, this is a technique that does not require the insertion of a probe. It has nothing to do with diagnosis; it involves cleansing the bile ducts during stagnation and dyskinesia. Another name is tubage. It is carried out at home. Not recommended for cholelithiasis, as it “displaces” the stone and provokes an attack.
The drug has a pronounced choleretic effect
The essence of the method: in the morning on an empty stomach you need to drink Xylitol, Sorbitol, a solution of magnesium sulfate, heated mineral water without gas, then lie down for 30 minutes on a warm heating pad on your right side with your knees tucked to your chest. Thanks to the choleretic effect, a portion of bile acids is released into the intestines. After the procedure, loose stools may occur.
Reviews
Boris, 47 years old: I don’t want to be biased, but I’ve suffered enough fear. And in the office they quickly persuaded me like a child. It doesn't hurt at all. You can endure it.
Raisa Mikhailovna, 64 years old: The capsule is a way out, I saw it in the movies. Where can pensioners get money? You need to get examined. It would be nice if our innovative technologies offered something domestic!
Nadezhda, 53 years old: She underwent both fractional sounding and fibrogastroscopy. I had to have surgery and remove part of my stomach. Now I undergo an annual examination.
Oleg, 32 years old: Much depends on your own mood. If your health fails, then where to go, you swallow a pipe.
Price
The cost of examining the stomach using the above methods in the Russian Federation varies depending on the region, the prestige of the clinic and the qualifications of the specialist and equipment.
The price for the same procedure can differ significantly in the center of the capital and on the outskirts. Therefore, if there is a need to undergo examination in private clinics, it is better to familiarize yourself with their capabilities and pricing policy in advance.
Table 2. Cost of FGDS and other studies in the Russian Federation (in rubles).
| Moscow | St. Petersburg | Voronezh | Ekaterinburg | Krasnoyarsk | Ufa | |
| Ultrasound of the stomach | 800-3300 | 800-2800 | 540-1500 | 500-1500 | 450-1200 | 150-3080 |
| X-ray of the stomach | 1000-13000 | 1450-4500 | 650-2400 | 200-2500 | 200-1900 | 400-4200 |
| FGDS | 1000-36000 | 200-12000 | 400-3000 | 730-6800 | 250-2000 | 500-3030 |
| Video capsule endoscopy | 6000-111000 | 10000-78000 | From 55000 | 37000-50000 | From 53000 | From 65000 |
What does gastroscopy show?
The doctor will make the first conclusions about the presence or absence of pathologies at the stage of conducting a visual examination of the walls of hollow internal organs. Medical research makes it possible to fairly accurately establish a number of diseases and anatomical features of the structure of the gastrointestinal tract.
Doing an FGDS or undergoing other endoscopic diagnostic methods is required to promptly detect:
- hidden bleeding;
- inflammation of the mucous membrane;
- ulcerative processes;
- oncological neoplasms;
- phlebeurysm;
- polyposis and other diseases.
Based on the results of the examination, the patient receives recommendations and referrals to specialists for further treatment. Early diagnosis in many cases allows you to prescribe effective conservative therapy and avoid surgical intervention. You can undergo a gastroscopy procedure in Moscow at an affordable cost in our clinic.