Abdominal pain can develop both during the day and at night; the time of day is rarely of diagnostic value. But some diseases are characterized by nighttime stomach pain.
To find out the exact cause of the symptom, it is necessary to undergo an examination of the gastrointestinal tract. Treatment for severe night stomach pain may include medications, surgery, and psychotherapy. Diet adherence is mandatory.
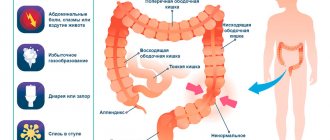
Severe stomach pain at night can occur due to various pathologies that cause:
- disruption of the intestines and stomach;
- increased acidity of gastric juice;
- inflammatory response of mucous tissues;
- contraction of smooth muscles (spasm);
- thrombosis.
With peptic ulcer and cholelithiasis, gastritis, abscess and pancreatitis, the pain is constant, but if during the daytime a person concentrates less on sensations, then at night the discomfort no longer allows him to fall asleep, making the pain seem much stronger. In some cases, the stomach hurts at night due to objective reasons.
Pathologies caused by increased acidity of gastric juice
“Hungry” abdominal pain appears at night because the concentration of hydrochloric acid in the gastric juice increases and the process of autolysis begins, that is, self-digestion of the stomach walls. Acid-dependent diseases include the following pathologies.
Gastritis
Normally, the walls of the stomach are protected from the aggressive effects of secretions by mucus. Under unfavorable factors, this protection is destroyed and an inflammatory process begins in the mucous membrane.
Against the background of inflammation, erosions appear, which, if the course is favorable, can regenerate within three days, and if unfavorable, transform into an ulcer. The ulcer may heal within two weeks, otherwise a chronic peptic ulcer develops.
Peptic ulcer
When the disease occurs, ulcers appear on the mucous membrane of the stomach or duodenum. Pathology occurs due to toxins secreted by Helicobacter, taking non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, heart disease, lung disease, liver disease, and exposure to stress.
An ulcer appears due to the fact that, against the background of a deterioration in the evacuation function of the gastrointestinal tract, the protective function of the mucous membrane is impaired and it is affected by the aggressive environment of gastric juice (hydrochloric acid, pepsin, bile).
During an exacerbation, pain is felt in the epigastric region (under the stomach), which can spread to the left side of the back, chest, shoulder blade, lower back, sometimes pain begins from the center of the spine. If an ulcer has developed in the pylorus, then pain often occurs at night or late pain (3-4 hours after eating), and its intensity increases.
Also, with a peptic ulcer, nausea, vomiting, heartburn, bloating, abnormal bowel movements, bad breath, and coating on the tongue occur. Gagging usually occurs at the peak of pain and brings relief. Artificial induction of vomiting leads to the development of the disease.
Functional dyspepsia
It develops as a result of increased secretion of hydrochloric acid, infection with Helicobacter pylori infection, drug therapy, malnutrition, and hypovitaminosis. Under unfavorable factors, the sensitivity of visceral receptors in the gastric mucosa increases, which leads to impaired motor and secretory function.
The disease manifests itself as pain in the upper abdomen, nausea, vomiting, and a feeling of early satiety. In the ulcer-like form of the disease, severe night or “hungry” pain occurs, which manifests itself against the background of emotional stress. The symptom subsides after eating or taking antacids.
Often during an attack, patients develop fear and obsessive thoughts about the incurability of the disease.
Gastroesophageal reflux disease
With pathology, the walls at the bottom of the esophagus are inflamed, as there is a reverse movement of acidic gastric and intestinal contents. The disease occurs due to a violation of the canal’s ability to evacuate food into the stomach and a decrease in the protective function of the mucous tissue.
Causes of stomach pain after eating
The aggressive environment irritates the esophageal mucosa, which leads to deep ulcerations and greatly increases the risk of developing cancer.
Symptoms of reflux include heartburn, belching, and chest pain. If this occurs more than twice a week, then it is necessary to conduct an examination.
As a rule, these pains go away if you eat. To avoid reflux, it is recommended to eat small meals every 3-4 hours and no later than three hours before bedtime, avoid taking medications that affect the functions of the esophagus and act aggressively on the mucous membrane, and raise the head of the bed by 15 centimeters.
For peptic ulcers, pain can be relieved by applying a cold heating pad or an antispasmodic
To reduce the production of hydrochloric acid, antacids (magnesium carbonate, magnesium oxide, aluminum phosphate, aluminum hydrochloride), H2-histamine blockers, and proton pump inhibitors are prescribed. The patient is advised to follow a diet and adhere to a diet, not to overeat and not to take long breaks between meals. After eating, you can’t go to bed to rest, you need to move.
Should you be afraid of Helicobacter pylori?
The bacterium Helicobacter pylori (Helicobacter) is capable of breaking down mucus, exposing the stomach wall. Its “goal” is to get to the latter and provoke permanent inflammation or ulcers, and then cause a precancerous condition - metaplasia. It is interesting that most people have Helicobacter (for example, in Russia - 80% of the population) - and this has been going on for more than fifty thousand years.
To the question “why has humanity not yet died out from stomach cancer?” The answer is simple: in most carriers of the infection, inflammation still does not develop. This happens due to the fact that the immune system and Helicobacter achieve “armed neutrality”: bacteria interact with the human immune system in a complex manner and only sometimes win. However, the risk still remains - and it is not difficult to make it easier for microorganisms to gain access to the stomach if you often take painkillers or abuse alcohol.
Just a few years ago, it was believed that it was necessary to identify and destroy Helicobacter only in individual cases. Today this is indicated for almost all adult patients: experts are confident that the bacterium is the main provocateur of stomach cancer. According to the recommendations of the Kyoto Global Agreement on Helicobacter pylori-associated gastritis, it is necessary to be examined and treated from the age of twelve. European consensus recommendations are slightly different: everyone who lives in countries at high risk for stomach cancer (in particular in Russia and Japan), patients who have bad heredity, gastritis, peptic ulcer disease, any “stomach” complaints, iron deficiency should get rid of Helicobacter , vitamin B12 deficiency, as well as for those taking painkillers and anticoagulants.
Alexey Paramonov points out that the damage caused by Helicobacter varies from person to person, but the risk of developing a malignant stomach tumor is increased in each carrier. According to the doctor, it is especially important to eliminate the bacteria for those who are forced to take antacid medications (omeprazole, lansoprazole, esomeprazole) for a long time. These drugs contribute to the development of atrophy of the gastric mucosa - and this is the first step to cancer if the microbes are not destroyed. But there is good news: timely methods of combating these bacteria allow the mucous membrane to fully recover.
Pathologies leading to reflux
Night abdominal pain can also develop because all organs of the gastrointestinal tract are at the same level. Pain and heartburn occur because stomach contents can more easily enter the esophagus. For this reason, pain often appears at night due to the following pathologies.
Achalasia cardia
Pathology of the esophagus, in which peristalsis and muscle tone change during swallowing, which leads to disruption of the passage of food from the esophagus to the stomach. Since reflexive relaxation of the sphincter does not occur, difficulties appear when swallowing food (at the early stage it is solid, at the later stage it is difficult even to drink), and regurgitation occurs.
The reflux of food mass from the esophagus into the oral cavity can occur during meals or after 2–3 hours. Sometimes this happens during sleep (nocturnal regurgitation), which causes a “night cough” as food gets into the airways. Pain occurs on an empty stomach or while eating.
They are localized behind the sternum and can extend to the jaw, neck, and area between the shoulder blades. The disease is characterized by paroxysmal pain that occurs during anxiety, at night or during physical activity, lasting from two minutes to an hour.
Diaphragmatic hernia
Pathology is formed when part of the organ, which normally should be located under the diaphragm, is displaced into the thoracic region. The disease provokes chest pain, heartburn, regurgitation, difficulty swallowing, hiccups, and arrhythmia.
The pain is localized in the epigastric region, spreads along the esophagus, extends to the area between the shoulder blades or the back, and can be encircling. Pain occurs when lying down, during physical activity, coughing, and after eating.
An acquired hernia is formed as a result of weakening of the esophageal ligaments. A systematic, sharp increase in intra-abdominal pressure (constipation, severe vomiting, bloating, obesity, blunt trauma, lifting something heavy, sudden bending) increases the risk of developing the disease.
Even in the absence of sphincter pathology, casting can occur when bending over, exercising, or at night.
To avoid stomach pain at night, it is recommended not to eat 3 hours before bedtime and raise the head of the bed so that your head is slightly higher than your stomach. Pain with achalasia goes away after vomiting, food entering the stomach, and taking antispasmodics.
If the cause of the pain is a diaphragmatic hernia, then it will go away after belching, taking a deep breath, vomiting, changing position, and drinking fluids.
Diagnosis of pain in the epigastric region
Epigastric pain is a non-unique symptom, the presence of which makes it impossible to make a diagnosis. An in-depth examination is required using the following methods:
- gastroscopy (FGDS) of the stomach and intestines;
- general and biochemical blood test;
- Ultrasound or CT scan of the abdominal cavity;
- analysis of stool and urine.
With the help of FGDS, it is possible to carefully examine the stomach and duodenum using an endoscope. A blood test gives a general idea of the condition of the body. If gastritis or peptic ulcer is detected, a breath test is additionally prescribed to determine the presence of Helicobacter bacteria.
To make an accurate diagnosis, it is important to use instrumental, hardware and laboratory diagnostic methods. If a person is admitted to the hospital with acute pain, differential diagnosis is used. First of all, the most dangerous pathologies are excluded.
Recommended video:
Other reasons
Severe cramping pain may appear in the lower abdomen due to increased gas formation, causing stretching of the intestinal walls, nervous tension and stress, as well as due to disruption of peristaltic waves. During sleep, intestinal motor activity is reduced, as nervous stimulation decreases.
Therefore, in some diseases associated with the evacuation function of the intestines, symptoms may worsen at night. Signs of diseases caused by slower peristalsis are constipation, false urge to defecate, heaviness in the abdomen, lack of vitamins and microelements.
In the evening, the level of the adrenal cortex hormone (glucocorticoid), which suppresses the inflammatory process and the pain caused by it, reaches a minimum, so any discomfort associated with inflammation intensifies.
Diet for gastrointestinal diseases
If epigastric pain is associated with gastrointestinal pathology, you will need to use a gentle diet. The main principles of proper nutrition are:
- fractional meals in small portions 4-6 times a day;
- exclusion of too hot and cold dishes;
- exclusion of hard-to-digest foods;
- exclusion of fried, salted, spicy and smoked.
It is recommended to give preference to liquid dishes. The basis of the diet can be various cereals and soups. It is also very important not to drink alcohol throughout the entire therapy.