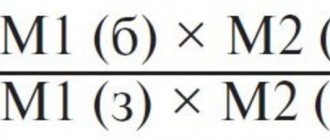Remedies for spasms in children are antispasmodic drugs (antispasmodics). Antispasmodics for children are a group of drugs that can eliminate excessive contraction of smooth muscle cells, that is, they can eliminate spasm. Spasms are quite common during early childhood. As a rule, they manifest themselves in pain, as a result of which the baby begins to cry. The severity of pain varies. Children can often be restless during the day and especially at night.
The main causes of spasms in children
The diseases and causes that can lead to this problem are quite extensive. It is worth noting that in children, spasms and pain are most often observed in the gastrointestinal tract and accompany various organic and functional diseases of the stomach and intestines. The difference between organic and functional diseases lies in the presence of structural or biochemical changes in organs and tissues. Organic diseases have them, but functional ones do not. Functional pathology is caused by changes in the regulation of these organs, which can also cause symptoms similar to organic ones. In young children, spasms are more often observed against the background of functional pathology. With age, the incidence of organic pathology increases. The most common causes of excessive contraction and abdominal pain in children are:
- Intestinal colic.
- Functional diarrhea and constipation.
- Acetonemic syndrome.
- Biliary dyskinesia, inflammation of the gallbladder.
- Gastritis, peptic ulcer.
- Diseases accompanied by malabsorption syndrome. Malabsorption is a malabsorption of substances in the small intestine.
- Inflammatory bowel diseases.
- Chronic colitis, intestinal infections, parasitic infestations.
There are also many other diseases that are accompanied by excessive contraction of muscle cells and pain. We list only the most common of them. Often spasms are accompanied by inflammatory diseases of the urinary tract (cystitis, pyelonephritis). In this case, they occur in the urinary tract. Often, during the formation of the menstrual cycle, teenage girls may experience severe cramps and pain in the lower abdomen. This problem is called dysmenorrhea. Vascular spasms often develop when the temperature rises in children, which is characterized by the appearance of “white fever”. In this article we will briefly talk about the main causes of spasms in children, as well as the diseases that lead to them. Let us explain the basic principles of use and the mechanism of action of drugs used for this pathology.
There are many other diseases that are accompanied by excessive contraction of muscle cells and pain.
How to choose tablets for stomach pain
Drugs are selected depending on the type of pain, its cause and the mechanism of action of the drug, as well as the patient’s age and existing concomitant diseases. It is important that tablets for stomach pain are prescribed by a doctor; only a specialist can take into account all the nuances. He can choose medications from the following groups:
Antispasmodics. They help with smooth muscle spasms and pain due to gastric ischemia (circulatory disorders in small vessels). Typically, the pain due to spasm is dull, constant or stabbing, sometimes intensifying and then receding depending on the position of the body or exposure to heat. Drugs can have a myotropic effect, that is, they directly affect the muscle fibers themselves, or neurotropic - they inhibit the transmission of impulses from nerve endings, which is why the muscles relax. The drugs work especially well in the area of the upper part of the digestive tube - the esophagus, stomach and the initial part of the small intestine. An undoubted advantage is the fact that they do not mask the main cause of pain and do not interfere with the diagnosis carried out by the doctor.
Analgesics. These drugs suppress pain sensations in the brain coming from tissues and organs. They can help with both severe, mild or moderate pain, but do not eliminate its cause itself, plus, they often interfere with diagnosis by suppressing pain. They should be used only in extreme cases, and when the diagnosis is already known, no emergency interventions are required.
Proton pump inhibitors. These are drugs that suppress the synthesis of acid in the stomach, thereby reducing its irritating effect on the mucous membrane. They are indicated for gastritis and ulcers, especially when there is an exacerbation.
Antacids. They neutralize excess stomach acid, helping to relieve heartburn and stomach pain. Enveloping the walls of the stomach, they help the mucous membrane to calm down and relieve its irritation.
To the point
Bloating: Diet and Treatment Methods
Enveloping and astringent agents. They help in relieving pain associated with irritation and inflammation of the stomach wall due to excess acid. By forming a protective film covering the mucous membrane, they prevent the contents of the stomach from contacting the cells and irritating them.
Enzymes. These drugs have practically no effect on the stomach itself, but they help to digest food as quickly as possible, eliminating it from the stomach and thereby reducing the severity, discomfort, and pain when overeating.
Motor stimulants. They are indicated for stagnation of contents in the stomach and sluggish peristalsis. Due to their action, the stomach empties faster, and food does not irritate its walls.
Combination products usually contain several different components that have complementary effects.
It is impossible to definitely name the best pills for stomach pain; depending on different causes and diagnosis, the doctor will select his own medications for each patient, and sometimes a combination of them.
Symptoms of spasms in children
As mentioned above, the most common cause of spasms in children is pathology of the gastrointestinal tract.
Below we consider the main symptoms of gastrointestinal diseases accompanied by spasms in children:
- Intestinal colic. This pathology is characterized by sudden and severe bouts of crying in the baby. Colic appears during the neonatal period. Intestinal colic is associated with immaturity of the nervous regulation of intestinal activity and increased gas formation against the background of intestinal dysbiosis.
- Functional diarrhea and constipation. Spasms in these pathologies are not the main symptom. They can only appear periodically. The diseases are functional disorders of young children, which are accompanied by diarrhea or constipation, respectively. At the same time, an in-depth examination does not reveal any other pathology.
- Acetonemic syndrome. Often occurs in children, especially during early childhood. As a rule, the cause of its development is an error in diet. Other reasons include ARVI, harmless excitement (birthdays, etc.), stress. In this case, the pain is no longer caused by spasm, but by irritation of the mucous membrane with ketone bodies (those substances that cause acetone syndrome). Characteristic symptoms of this disease are the smell of acetone in the exhaled air, nausea, vomiting, lethargy, and drowsiness.
- Biliary dyskinesia, inflammation of the gallbladder . Dyskinesia is a functional disorder of the gallbladder and bile ducts, which may be accompanied by spasms in these organs. As a result, children experience pain, often in the right hypochondrium. In addition, children feel heaviness in the right hypochondrium, bitterness in the mouth, and yellowness of the skin and eyes appears.
- Gastritis and peptic ulcer. The causes are often Helicobacter pylori. Children experience: nausea, often vomiting, abdominal pain, heartburn, tendency to constipation, bad breath.
With gastritis, children often experience nausea, vomiting, and abdominal pain.
- Malabsorption syndrome . Among the pathologies in this group, it is worth highlighting celiac disease and lactase deficiency. Celiac disease is a gluten intolerance that is accompanied by a variety of symptoms, including abdominal pain. Lactase deficiency is an intolerance to dairy products, after consuming which occurs bloating, abdominal pain and diarrhea.
- Inflammatory bowel diseases. These include Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis. It is most often characterized by the appearance of blood in the stool and abdominal pain. Subsequently, symptoms intensify and other signs appear.
- Intestinal infections. Acute intestinal infections are manifested by fever, often vomiting and diarrhea, which is characterized by persistent progression. As a rule, it can develop after eating bad foods or after contact with a sick person.
In addition to pathology of the gastrointestinal tract, other diseases can lead to the development of spasms and pain. Urinary tract infections are quite common, especially in girls. This is due to the short and wide urethra, through which pathogenic bacteria can quickly penetrate. The development of cystitis is accompanied by the appearance of symptoms such as pain when urinating, pain, frequent urination, burning and pain in the urethra and bladder. Teenage girls often develop dysmenorrhea, which is characterized by pain and heaviness in the lower abdomen.
Phosphodiesterase inhibitors (PDE) type IV
These are traditionally widely used antispasmodics: drotaverine hydrochloride and papaverine. Their injectable forms are sold with a prescription, while their tablet forms are available without a prescription. PDE IV is widely present in smooth muscle along the entire length of the intestine, as well as in the biliary and urinary tracts. Thus, blocking PDE IV has a universal antispasmodic effect regardless of the severity of the spasm or its cause. In addition, drotaverine has anti-edematous and anti-inflammatory effects. Drotaverine can be used for acute abdominal pain - both to relieve acute spasms and for long-term treatment of biliary dyskinesia, cholelithiasis, chronic intestinal diseases with spastic syndrome, which are accompanied by colicky or bursting pain. Unlike M-anticholinergics, drotaverine can be used in elderly men with prostate pathology, as well as with concomitant pathology and combined use with other drugs. The therapeutic concentration of drotaverine in plasma when taken orally is achieved after 45 minutes.
Sodium channel blockers
These drugs block intracellular calcium stores through a cascade of reactions. The most famous drug is a derivative of veratric acid - mebeverine. Unlike anticholinergics, it does not cause hypotension of the colon. Most often, this drug is prescribed for functional disorders of the gastrointestinal tract or as an adjuvant for organic diseases of the gastrointestinal tract. Mebeverine is used only for course treatment. Mebeverine is most effective in combination with other pathogenetic drugs. Mebeverine is mainly available by prescription, but there is a dosage form in tablets that does not require a doctor's prescription.
We will not dwell on calcium channel blockers in more detail, since these drugs do not have any over-the-counter forms.
The over-the-counter myotropic antispasmodic trimebutine stands apart. Trimebutine acts on the enkephalinergic system of the intestine and peripheral opiate receptors - µ, κ and δ. Having an affinity for receptors that enhance and suppress peristalsis, it stimulates the contraction of intestinal smooth muscles in hypokinetic conditions and is an antispasmodic in hyperkinetic conditions. Trimebutine reduces the tone of the esophageal sphincter, promotes gastric emptying and increased intestinal motility, as well as the response of the smooth muscles of the colon to food irritants. It is used for various functional disorders of the gastrointestinal tract.