Conservative treatment of duodenogastric reflux
The goal of conservative therapy is to neutralize the aggressive effect of duodenal contents on the mucous membrane of the stomach and esophagus, improve the evacuation capacity of the stomach and antroduodenal coordination. For this purpose, drugs are prescribed that normalize the motility of the upper gastrointestinal tract, prokinetics, enhancing the peristalsis of the stomach and duodenum and improving the evacuation of their contents, antacids, etc.
In addition, since duodenogastric reflux is often combined with other diseases of the digestive system, drugs are also needed to treat the underlying pathology. In addition, great importance is given to following a diet and giving up bad habits. Conservative treatment is difficult, and although the clinical manifestations of reflux decrease with medication, this is only a temporary improvement. It is possible to achieve good results with conservative therapy only in case of functional disorders that cause reflux.
Symptoms of reflux
Signs of reflux vary depending on the type of disease. The following symptoms are considered common to all types of reflux:
- belching;
- heartburn;
- nausea.
With duodenogastric reflux, a yellow coating appears on the tongue, and abdominal pain with unclear localization is possible. Gastroesophageal reflux is characterized by sour belching and chest pain. With pharyngolaryngeal reflux, hoarseness in the voice, cough, and a feeling of a lump in the throat appear.
Surgical treatment of GHD
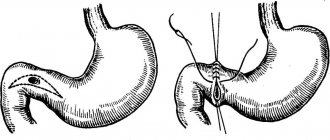
If conservative correction is ineffective, surgical intervention is indicated; the purpose of the operation is to strengthen the pyloric valve, as well as reduce the volume of bile thrown into the stomach. The operation is carried out in several directions:
- elimination of the causes that led to duodeno-gastric reflux;
- pyloroplication – performed to reduce symptoms of pyloric dehiscence;
- in the presence of hiatal hernia and calculous cholecystitis, fundoplication with crurorrhaphy and cholecystectomy is indicated.
In our clinic, laparoscopic access is used for surgical treatment of patients with GHD - all surgeon actions are performed through 3-4 punctures on the abdominal wall, and the length of the incision does not exceed 10 mm. Moreover, the operation itself is low-traumatic and painless; during its implementation, the likelihood of complications and blood loss are excluded. As a rule, the patient can go home within 2-3 days; work capacity is restored 2-3 weeks after surgery.
Causes of bile accumulation in the stomach
Doctors name several reasons that can trigger the release of bile into the stomach.
- Physiological disorders. Gastroduodenal reflux can develop on the basis of a congenital pathology called “bile bend”.
- Benign and malignant neoplasms. Only an experienced and qualified gastroenterologist will be able to diagnose the presence of neoplasms based on an analysis of the examination and the patient’s complaints. After palpation, gastroscopy and ultrasound procedures, the doctor prescribes the necessary treatment.
- Surgical intervention. Recent surgery can also cause gastroduodenal reflux. If during surgery the mucous membranes of the stomach are affected or damaged, this can provoke the release of bile, which results in inflammation and erosion.
- Hidden chronic duodenitis. Most often, the patient may not even know that he has a chronic stage of duodenitis, since he does not observe any acute symptoms, however, after eating, such patients tend to experience a feeling of heartburn or frequent bloating. It is these symptoms that indicate improper functioning of the digestive system and hidden inflammation of the duodenum, caused by an abundant accumulation of bile inside the stomach.
- Pregnancy. Changes in hormonal levels caused by pregnancy can also cause problems with the proper functioning of the digestive system. As the fetus develops, significant pressure is exerted on the duodenum, which provokes abundant production of bile into the stomach cavity.
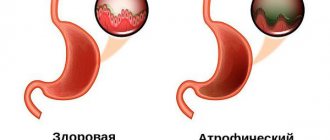
- Chronic gastritis. Any inflammation of the chronic type is often the cause of reflux , as it occurs against the background of disruption of the biliary tract.
- Irregular and sedentary lifestyle. Overeating, a sedentary lifestyle, smoking, alcohol abuse, fatty and spicy foods - all this undoubtedly affects the functioning of the entire body, in particular the digestive system.
- Use of medications. With long-term use of certain medications, the tone of the sphinters and muscles of the digestive canal decreases, most often this leads to the development of duodenitis.
- Nervous system failure. Frequent stress, breakdowns and depression cause disturbances not only in the gastrointestinal tract, but also in the general functioning of the body.
Gastroduodenal reflux: causes
Doctor's comment
If you are worried about heartburn and nausea, and your usual medications and strict adherence to a diet do not bring relief, if you often experience abdominal pain that gets worse after eating, perhaps the cause of this condition is duodenogastric reflux. You can determine its presence in our clinic, where for a high-quality examination you can undergo all the necessary diagnostic procedures - at any time convenient for you. Treatment tactics depend on the degree of the disease. This may be drug therapy or surgical treatment, which is indicated when conservative methods are ineffective. Our patients have the option of treatment in a day hospital. The operation in the clinic is carried out using laparoscopy: all actions are carried out through 3-4 punctures on the abdomen, which subsequently become invisible. During the operation, which is painless and bloodless, the likelihood of complications is virtually eliminated. After 1-3 days, our patients are discharged from the clinic; in the future, there is no need to take medications or strictly follow a diet. Therefore, do not delay treatment, because with advanced duodeno-gastric reflux, treatment will be more difficult and longer.
Head of the surgical service at SwissClinic Konstantin Viktorovich Puchkov
What causes the reflux of bile into the stomach?
This pathology is called gastroduodenal reflux . The cause of reflux is the insufficiency of the pyloric closing element and increased pressure in the duodenum. The disease is caused by impaired functioning of the gastrointestinal tract.
With proper functioning of the body, after eating, food passes through the esophagus and enters the stomach, after which the digestive system secretes gastric juice from the bile ducts, that is, bile, which helps digest food. If this sequence is violated, bile begins to be produced into the empty stomach, thereby irritating and damaging its walls, which causes a deterioration in the patient’s well-being, a feeling of heartburn and nausea. Ignoring these symptoms can lead to the development of ulcers, internal inflammation and other serious pathologies.
Advantages of treatment of duodeno-gastric reflux at the Swiss University Hospital
- Our Center is equipped with modern equipment produced by leading European and American companies, which allows us to carry out the most complex diagnostic and therapeutic procedures with high accuracy and efficiency.
- The clinic employs specialists of the highest and first categories who have extensive experience; each of them is fluent in all techniques in their specialization.
- Our specialists have performed more than 600 surgical interventions related to duodenal obstruction.
- Patients who have concomitant diseases of the abdominal cavity and pelvis and require surgical treatment can undergo simultaneous surgery in our clinic. During one intervention, you can get rid of 3-4 pathologies (for example, kidney cysts, ovarian cysts, nephroptosis, fibroids and a number of other diseases).
FAQ
Duodeno-gastric reflux - symptoms
This pathology is characterized by belching of air or sour contents, heartburn, nausea and even vomiting of bile. Often a person is bothered by bitterness in the mouth. The discomfort does not disappear even with taking medications. There is also pain in the epigastrium, which intensifies after eating. The patient is also bothered by periodic abdominal pain of a cramping nature, often occurring during stress or after physical activity.
Diagnosis of duodenogastric reflux
Our clinic performs 24-hour pH measurements to determine intraventricular pH levels and the height of reflux. Bilimetry is also performed - using scrapings from the tongue, the presence of bile acids can be detected. In addition, patients undergo an ultrasound - on an echogram with water stress, the retrograde movement of fluid in the direction from the pylorus to the body of the stomach and gas bubbles in echogenic areas are determined. DGR can also be detected using fibrogastroduodenoscopy, fluoroscopy, and biopsy of the gastric mucosa. Fiberoptic spectrophotometry is very effective for diagnosis; it is based on determining the absorption spectrum of bilirubin. This study can be replaced by radionuclide biliary scintigraphy. In addition, to determine the cause of duodenal obstruction, probe duodenography is performed.
Why is DGR dangerous?
As a result of pathological reflux, the course of many gastrointestinal pathologies can be complicated. GHD can lead to severe gastritis and esophagitis, cause metaplasia of the stomach and esophagus, as well as squamous cell carcinoma of the esophagus, which develops against the background of metaplasia; this is confirmed by clinical studies. There is also evidence that, against the background of duodenogastric reflux, symptoms of damage to the respiratory system develop, along with chest pain that is not associated with coronary pathology. In addition, in some patients, GHD can cause catarrhal pharyngitis and laryngospasm.
Rehabilitation after surgical treatment
After surgery, only a few incisions no longer than 10 mm will remain on the skin of the abdomen. Already on the day of surgery, patients get up, are allowed to drink, and the next day - take warm liquid food. Our patients are usually discharged within 1-3 days, depending on the severity of the condition. After 2-3 weeks, the person returns to his usual lifestyle. Compliance with a strict diet is necessary in the next two months, a softer one is allowed six months after the operation. In the future, a person can do without medications and does not need to strictly adhere to a diet.
Duodenogastric reflux. Recommendations
It has been noted that apparently healthy people can also have symptoms of GHD. Gastroenterologists have not reached a consensus regarding duodenogastric reflux. Some believe that the signs of GHD are the onset of the disease, others that almost all healthy people are susceptible to these signs. We are talking about a feeling of heaviness in the stomach or belching, which sometimes occurs during strength and physical exercise or even in sleep.
The advice may be very simple - consult a doctor, even if the symptoms of the disease are mild, in order to prevent further development of the disease.
What symptoms of duodenogastric reflux should serve as a signal to visit a gastroenterologist? Pay attention to spastic pain in the epigastric region that periodically occurs after eating, as well as nausea, belching of air or eaten food, and vomiting of bile. You may feel disturbed by a feeling of abdominal distension or bloating. Symptoms of the disease include a yellow coating on the tongue and a bitter taste in the mouth. Diagnosis of GHD is not difficult; when you contact a specialist with complaints, the doctor gives a referral for fibrogastroduodenoscopy (FGDS), in some cases it is recommended to do contrast radiography of the stomach and duodenum. After the research, the doctor prescribes treatment. It must be comprehensive, and first of all, aimed at curing the underlying disease.
Nutrition for duodenogastric reflux
Recommendations and principles of treatment The main condition for successful therapy is adherence to nutritional rules and maintaining a healthy lifestyle. The doctor will advise you to give up bad habits - smoking, drinking alcohol. If you are additionally taking medications - aspirin, caffeine, choleretic drugs, you must notify your doctor about this and consult with him about the need to change or shorten the course of treatment.
One of the ways to solve the problem of GHD may be to follow a diet and control body weight.
The doctor will prescribe the necessary diet, which will become an important and integral part of the therapy. Patients are advised to monitor their lifestyle. Eat five or six times a day in small portions, avoiding overeating. You may need to grind your food in a blender, or make sure you chew it thoroughly. Preference should be given to dishes baked in a steamer or oven. Fill your diet with pureed cereals, bran, puree soups, lean meats and fish. You should have milk, yogurt on your table, as well as non-sour berries, fruits and vegetables. A diet for duodenogastric reflux requires excluding the following foods: onions, garlic, tomatoes, citrus fruits, sour fruits, fresh soft bread, carbonated drinks, chocolate and coffee. Do not eat smoked, spicy, fatty and salty foods, as well as some fermented milk products. After eating, you should not engage in any type of physical activity, and also do not lie down or bend over.