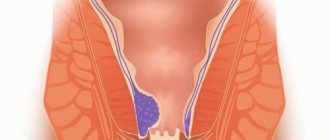
What is bleeding hemorrhoids
Hemorrhoids are accompanied by pain and itching in the rectal area, and a sensation of a foreign body in the rectum. In advanced forms of the disease, bleeding develops. In the initial stages, a drop of blood from the patient may be detected after a bowel movement. But soon there may be profuse bleeding from the anus.
The main cause of this pathological condition is damage to the hemorrhoids due to constipation.
This pathological condition can be cured by using hemostatic drugs for hemorrhoids. They are produced mainly in the form of:
- rectal suppositories;
- drugs for oral administration;
- ointments for external use.
Let's consider the most effective means that belong to these groups.
Hemostatic tablets for hemorrhoids
For bleeding hemorrhoids, medications for internal use are prescribed. These include the following tablets:
- Chemoroidin,
- Detralex,
- Asklezan A,
- Pilex,
- Ginkor Fort,
- Etamzilat,
- Litovit-B,
- Dicynon,
- Vikasol.
Chemoroidin
Contains plant substances that act on the walls of the rectum. Prescribed when hemorrhoids bleed. Chemoroidin has the following effects on the body:
- reduces inflammation in the anus;
- stops bleeding;
- eliminates burning and itching in the anus;
- With long-term use, it reduces the size of knots.
Detralex
Detralex is an effective tablet for hemorrhoids. Most often used for blood pathologies.
The active substances of the medicine relieve swelling in the anus and pain
This drug increases venous tone and restores blood supply. Thanks to these properties, bleeding stops.
Asklezan A
The drug is classified as a dietary supplement. Helps with acute hemorrhoids. Used for mild bleeding from anal fissures.
Pylex
The drug is based on herbal substances that help eliminate inflammation of the rectum, stop bleeding, and reduce burning and itching in the rectal area.
For the greatest therapeutic effect, it is necessary to use the tablets simultaneously with other drugs for hemorrhoids (medicines for topical use).
Ginkor Fort
Prescribed for minor hemorrhoidal bleeding. The pharmacological properties of the tablets include:
- normalization of venous tone;
- relieving pain in the anus;
- blood thinning;
- restoration of normal blood supply;
- preventing blood clots;
- increasing the permeability of the capillary system.
Litovit B is a safe dietary supplement that helps women cope with hemorrhoids during pregnancy
Litovit-B
The tablets contain herbal ingredients that help eliminate the symptoms of the pathological condition. Most often prescribed for hemorrhoids for women during pregnancy.
The substances that make up the drug stop the development of the disease and promote the healing of affected tissues in the rectal area. In addition, the tablets normalize the functioning of the intestines.
Etamsylate, Dicynon and Vikasol are used for emergency treatment of severe internal bleeding. In addition to tablets, drugs are also available in the form of injection solutions.
It is important to remember that such medications may have restrictions on their use and cause side effects. Therefore, self-medication for illness is strictly prohibited. Only the attending physician prescribes tablets for hemorrhoids with bleeding.
Effective rectal suppositories for bleeding
To treat hemorrhoids that bleed, suppositories are used. These drugs not only reduce bleeding, but also eliminate other signs of pathology. Suppositories stimulate regeneration processes and eliminate pain in the anus. Rectal suppositories are commonly used to treat internal hemorrhoids.
The peculiarity of these suppositories is that at normal room temperature they will not melt, however, when they are introduced into the rectum, a rapid effect is observed, especially with severe bleeding.
The following drugs effectively help with hemorrhoids during bleeding:
- Anuzol;
- Methyluracil;
- suppositories with propolis;
- Hepatrombin;
- suppositories with adrenaline;
- Relief (Relief Advance or Relief-ultra);
- homeopathic suppositories.
Anuzol
The drug contains bismuth, zinc and belladonna extract.
The product effectively helps if hemorrhoids are bleeding. Anuzol relieves pain and has a hemostatic effect. In addition, it reduces the inflammatory process in the rectum and eliminates burning and itching sensations.
Methyluracil suppositories
This medicine for hemorrhoids treats wounds and fissures of the anus, helps reduce bleeding from hemorrhoids. Restores damaged tissue and protects against pathogenic bacteria. Excellent for heavy bleeding from the anus.
Side effects may rarely occur when using methyluracil suppositories.
Suppositories with propolis
Propolis, which is part of the drug, increases blood clotting, as a result of which bleeding stops. The drug fights inflammation of the rectum and stops the growth and reproduction of pathogens in the anus. It is recommended to insert one candle into the anus before bed every day.
The use of propolis-based suppositories is permitted during pregnancy and lactation.
Ready-made suppositories can be purchased at any pharmaceutical establishment. In addition, such candles can be prepared at home. To do this, simmer Vaseline and cocoa butter in a water bath, and add propolis to the mixture. Then the product is poured into foil forms and frozen in the refrigerator.
Hepatrombin
Candles contain the following active ingredients:
- heparin;
- allantoin;
- lemon oil;
- dexpanthenol, a B vitamin;
- pine oil.
Thanks to the pharmacological properties of these substances, bleeding quickly stops and swelling in the anal area is relieved. In addition, the product prevents blood clots.
At the local level, under the influence of suppositories, blood supply and metabolic processes improve. Candles allow you to speed up the recovery of damaged tissue.
Adrenaline suppositories
The active component stops blood in the rectum, due to its ability to increase blood clotting.
These candles have some restrictions on their use. An adverse reaction of the drug is an increase in blood pressure. Therefore, it is not recommended to use the medicine to treat hemorrhoids in elderly patients.
The use of decoctions and infusions
Herbs for hemorrhoids are used as components in decoctions and infusions with their further use not only for oral use as a vasodilator, but also as a component in the manufacture of oral suppositories and addition to sitz baths.
It must be remembered that if hemorrhoids are bleeding, the use of microenemas, even those based on decoctions, is not recommended.
Traditional medicine recipes have a good effect and have been tested by many generations of our ancestors
Recipes:
- Chamomile (2 tsp) is poured with boiling water (1 tbsp), kept in a water bath for 10 minutes, filtered. Intended for internal use, like tea, and external use.
- Oak bark (2 tbsp.) is poured with boiling water (1 tbsp.), Placed in a water bath for 30 minutes. Next, it is infused for 2 hours and filtered. It is taken orally three times a day after meals in the dosage prescribed by the doctor, and also as an external remedy.
- Dry cucumber tendrils (50 g) are filled with water (500 ml), placed on fire and brought to a boil. Next, the broth should be cooled and strained. Take ½ cup three times a day.
- Dry calendula herb (1 tsp) is filled with water (100 ml), boiled for 7 minutes, infused for 30 minutes, filtered.
- Dried calendula inflorescences (1 tbsp) are poured with boiling water and infused for an hour in a thermos. They are filtered. The remaining mass can be used as compresses.
- Water pepper (2 tbsp) is filled with water (1 l) and brought to a boil. Strained.
- Yarrow herb (2 tablespoons) is poured with boiling water (200 ml) and cooked for 15 minutes. Next, it is infused for 1 hour and filtered. After diluting the decoction with boiled water to 200 ml, it is ready for use. Take 1/3 tbsp. three times a day or ½ glass twice. It is possible to use dried yarrow leaves as tea. For this, 2 tbsp. l. plants are brewed in boiling water (1 l).
In addition, you can wash the anal area with decoctions and infusions after bowel movements.
Effective ointments for bleeding hemorrhoids
When treating hemorrhoids with bleeding, I also use ointments, gels and creams. The following are considered effective in this regard:
- Fleming's ointment. It is a homeopathic remedy. Therefore, use does not depend on age criteria and other characteristics of the body. This remedy can be used even during pregnancy.
- Relief Advance. The ointment contains shark liver oil, which has a wound-healing effect and reduces the inflammatory process in the lesion. The ointment contains phenylephrine hydrochloride, which constricts the vessels of the rectum and eliminates bleeding in it.
- Hepatrombin. The active ingredient is heparin, which prevents blood from clotting quickly. Therefore, the ointment not only reduces bleeding, but also prevents the formation of blood clots. The medicine eliminates swelling and relieves inflammation of the walls of the rectum.
- Proctosan. The ointment contains bismuth, which treats maceration of the skin and relieves pain.
- Heparin ointment. Heparin contained in the product has hemostatic and anti-inflammatory properties.
- Troxevasin. The main properties of the gel are considered to reduce venous permeability, reduce inflammation and improve blood circulation. Proctologists recommend the simultaneous use of Troxevasin gel and tablets.
- Bezornil. Helps with various complications of hemorrhoids, including bleeding.
- Proctoglivenol. The ointment is used for external hemorrhoids. It has an anti-inflammatory, hemostatic, softening and analgesic effect on hemorrhoids and fissures. Also available in the form of rectal suppositories.
- Boro Derm. Herbal preparation. Its main action is aimed at relieving pain and discomfort in the rectal area. Eucalyptus extract has antiseptic properties, and horse chestnut perfectly strengthens blood vessels and stops bleeding.
- Aurobin. Thanks to the vitamins contained in the preparation, wounds and cracks heal faster.
- Berzonil. Use ointment to treat chronic hemorrhoids.
- Vishnevsky ointment. Helps with external manifestations of the disease. It is recommended to apply compresses with this remedy to the affected area.
These ointments are applied to damaged areas several times a day. In addition, compresses can be made using these products. Before doing this, it is recommended to wash the rectal area with baby soap.
Hemorrhoids: emergency care, treatment strategy, prevention
G
Emorrhoids have been one of the most common human diseases for more than four thousand years. Equally common in men and women, children and adults, this disease brings a lot of physical and mental suffering, makes it impossible to work, and reduces the quality of life.
The ability to accurately determine what hemorrhoids are appeared in the 18th century, when cavernous vascular plexuses surrounding the anal canal were discovered. It has been proven that in addition to veins and arteries, these vascular formations contain elastic connective tissue and smooth muscle cells. By regulating blood flow in the anal canal area, hemorrhoidal plexuses provide the basic functions of the rectum: retaining feces and defecation, providing an effective immune barrier between the internal environment of the body and the outside world.
The anatomy and physiology of the internal hemorrhoidal plexuses, located proximal to the dentate line of the anal canal, and the external ones, located distal to it, differ significantly. The dentate (or comb) line is the mucocutaneous junction, the zone of closure of ectodermal (skin) and endodermal (rectum) tissues and forms the upper border of the anal canal. The anal canal is lined from the inside with anoderm, which is essentially a continuation of the skin and covered with stratified squamous epithelium. The anoderm and adjacent skin are richly supplied with somatic sensory nerves and are very sensitive to painful stimuli. The lining of the rectum is a mucous membrane covered with transitional and columnar epithelium. It is innervated by autonomic fibers and is relatively insensitive to pain. Venous drainage from areas located above the dentate line occurs through the portal system. Outflow from the anal canal and areas located below the dentate line occurs into the inferior vena cava system. Venous blood from the anorectal junction can enter both the portal and caval systems. The lymph flow from the rectum is directed to the inferior mesenteric and aortic nodes, while the lymphatic vessels from the anal canal approach the internal iliac and inguinal nodes, to the posterior wall of the vagina. The distribution of the venous and lymphatic vessels of the anorectal zone determines the different routes of spread of infection, malignant lesions and drugs from the zones to and above the dentate line.
Despite the deep historical roots of research into the study of anorectal pathology, only in the middle of the 20th century did it become generally accepted that the normal physiological role of the hemorrhoidal plexuses does not imply the development of many pathological symptoms, which are usually combined into the symptom complex of hemorrhoids. The appearance of hemorrhoids is the result of impaired hemodynamics and inflammation in the vessels of the hemorrhoidal plexuses
, which is often accompanied by thrombosis, varicose veins and sclerosis of the veins, bleeding.
Classification
Hemorrhoids are divided depending on the location of the hemorrhoids relative to the dentate line of the anal canal. With internal hemorrhoids (IG), the nodes are located medially, and with external hemorrhoids (IG), the nodes are located distal to the dentate line. It is customary to classify I–IV severity levels of VH decompensation. For stage I VH
swollen and possibly bleeding, but non-prolapsed hemorrhoids are found.
In case of II degree VH,
the nodes fall out and can be reduced independently.
In case of stage III VH,
prolapsed nodes can only be set instrumentally or with the help of manual manipulation.
And finally, with grade IV VH
, it is not possible to straighten the nodes at all.
Typical locations for hemorrhoids (HU) are the left lateral, right anterior and right posterior walls of the anal canal. The technique often used by proctologists to describe the localization of a GU using the analogy of a watch dial (for example, “a large GU is located at 9 o’clock”) often creates confusion in medical documents, since it can only be used if the patient is examined in the knee-elbow position.
Etiology
The etiological factors of hemorrhoids traditionally include constipation, a long-term spastic state of the internal sphincter of the rectum
, developing due to various reasons and leading to frequent straining, as well as
pregnancy
. Among the causes of VH, a special place is occupied by chronic portal hypertension, as well as subclinical disorders of the portosystemic blood flow of various origins (in particular, with overeating, drinking alcohol, taking anabolic steroids, contraceptives, and other chronic drug intoxications). The development of NG is undoubtedly facilitated by chronic inflammatory diseases of the anorectal zone and pelvic organs, such as bacterial salpingoophoritis, prostatitis or cystitis, leading to hemodynamic disturbances and lymphogenous spread of infection into the hemorrhoidal plexuses.
However, the etiology of hemorrhoids, according to most researchers of the problem, has not been fully studied, and among the factors that could theoretically be associated with the development of the disease, the study of hereditary, social and cultural aspects of the problem deserves the most attention [1,2].
Symptomatology
Pathognomonic symptoms of NG are pain, bulging nodes and bleeding
, which usually develops after or during bowel movements and rarely leads to significant blood loss and anemia. NG should be considered the cause of significant rectal bleeding only if other diseases that most often lead to this condition are excluded. In most cases, hemorrhoidal bleeding is noticed by traces of blood on toilet paper.
Exacerbation of NG is always painful to one degree or another. Ulceration or thrombosis of nodes can cause severe pain, in some cases disabling the patient. A very severe pain syndrome develops in a special form of the disease - an acute attack of hemorrhoids, which is understood as the infringement of sharply swollen or thrombosed hemorrhoids. NG thrombosis can lead to bulging of the perianal region and a characteristic sensation of a foreign body in the anorectal area and, in some cases, is complicated by gangrene of the hemorrhoids.
Decompensation of VH is in most cases less painful than NG. VH is characterized by a feeling of incomplete defecation or its impossibility, a feeling of fullness in the rectum, and “laced” rectum syndrome [3].
Main criteria for the diagnosis of decompensation of hemorrhoids
|
With VH, it is also possible for mucus or pus to pass during bowel movements.
VH stages III and IV can be complicated by thrombosis, ulceration and gangrene of unreducible or strangulated GU, which is accompanied by increased pain, the appearance of signs of systemic intoxication and/or fever. As a result of the often recurrent course of VH, incompetence of the internal sphincter of the rectum and fecal incontinence may develop.
Diagnostics
When interviewing a patient, in addition to collecting active complaints, they must clarify the nature of bowel movements, stool parameters, and the mode of use of laxatives.
The diagnosis of an acute attack of hemorrhoids, NG or thrombosis of hemorrhoids is easy to make by examining the anus and rectum in a normal state, as well as when the patient strains in the knee-elbow position and under good lighting conditions. Perianal and rectal digital examination, rectovaginal examination for complicated hemorrhoids may be accompanied by severe pain and, therefore, require terminal superficial anesthesia.
Detailed diagnosis of VH, as well as differential diagnosis with other diseases of the anorectal area, is carried out during anoscopy
or
sigmoidoscopy
to a level of 15–60 cm above the anus. To formulate a diagnosis and select adequate treatment tactics, it is important to remember the anatomical and physiological differences between external and internal hemorrhoids, which determine different pain sensitivity and the risk of systemic complications in these two forms of the disease [3]. In clinical practice, combined localization of hemorrhoids is often encountered.
Treatment
The choice of tactics and method of treating hemorrhoids in each specific case is based on: an assessment of the severity of the patient’s general condition, the severity of the pain syndrome and the degree of the patient’s disability; location and severity of hemorrhoids; the presence of complications, such as strangulation or thrombosis of hemorrhoids; the patient's plans for future treatment of the disease. Figure 1 shows all currently known methods of treating hemorrhoids.
Conservative therapy
Drug therapy is widely used for a course of planned and preventive treatment of hemorrhoids, as well as in preparation for radical surgical or non-invasive surgical treatment, as well as as part of combined treatment in the postoperative period. For decompensated hemorrhoids, conservative pharmacological treatment, in the vast majority of cases local, is a means of providing emergency care to the patient [1].
The main component of conservative therapy is the use of local agents for quick and effective pain relief
anorectal zone. For this purpose, superficial local anesthetic drugs are traditionally used: anesthesin, dicaine, etc., which can be used by application, but more often - as part of combined ointments, creams and suppositories. Traditionally, in official formulations for the treatment of hemorrhoids, anesthetics are combined with local anti-inflammatory and astringent agents or glucocorticoids. As part of complex pre- or postoperative therapy, as well as for complicated forms of hemorrhoids, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are increasingly used for pain relief and anti-inflammatory purposes.
For acute thrombosed hemorrhoids, locally acting agents are widely used, which, in addition to the above components, include heparin (Hepatrombin G, Nigepan). Included in Gepatrombin G
heparin and allantoin cause a thrombolytic effect, and panthenol stimulates the epithelization of damaged tissues.
The combined use of anesthesin and heparin in Nigepan
causes analgesic, anti-inflammatory, antispastic and antithrombotic effects. Preparations containing heparin are, of course, the means of choice for acute thrombosis of hemorrhoids, but are no less effective for any form of hemorrhoids and in the postoperative period, providing a powerful and physiological anti-inflammatory, anti-edematous and capillary-protective effect. When prescribing topical heparin-containing drugs, complete resorption of thrombotic masses should be expected no earlier than after 4–8 weeks of regular use.
A special place in the arsenal of means for the conservative treatment of hemorrhoids is occupied by drugs used to reduce straining and facilitate bowel movements. For this purpose, it is advisable to prescribe laxatives with emollient and osmotic effects:
psyllium preparations, lactulose and macrogol. Drugs that reduce the tone of the internal sphincter of the rectum are mainly used in the early postoperative period, although their use is fully justified in providing emergency care for complicated forms of hemorrhoids. For this purpose, ointments and creams containing nitroglycerin, isosorbide dinitrate, nifedipine, as well as suppositories containing belladonna extract are used [11–14].
In the planned conservative treatment of hemorrhoids, capillary stabilizing agents (rutin) and venotonic agents (bioflavonoids - diosmin, escin) are now widely used. When prescribed as a course, these drugs can be used or administered orally [4].
Surgical hemorrhoidectomy and minimally invasive instrumental treatment
The effectiveness of conservative therapy for hemorrhoids as an independent method of treatment, in general, is not assessed very highly, since the disease continues to progress and degenerative changes in hemorrhoids and the anorectal area also increase over time [3,5]. However, experts unanimously believe that active conservative therapy is a necessary step in preparation for a radical cure for the disease and at the same time a means of reducing the number of emergency hemorrhoidectomies
, in 25% of cases accompanied by early postoperative complications [6,7]. Moreover, according to a retrospective European study conducted in 2000, about 10% of patients after emergency excision of nodes require reoperation, and an equal number of cases develop anal stenosis in the long term [7]. Nevertheless, acute thrombosed, strangulated or ulcerated hemorrhage, as well as massive hemorrhoidal bleeding with portal hypertension, continue to be considered indications for emergency surgical hemorrhoidectomy.
Planned surgical hemorrhoidectomy is indicated for 10–30% of all patients suffering from hemorrhoids of III–IV severity [5,8]. In case of hemorrhoids of I, II severity, as well as in a significant part of patients with III degree, complete cure can be achieved by using minimally invasive instrumental aids, which are also carried out without exacerbation of the disease [3]. A widespread and least expensive method of minimally invasive care is ligation of the hemorrhoid with a rubber ligature.
.
The method is used to treat large internal and external hemorrhoids, and it consists of grasping and pulling the node with a rubber loop with a diameter of 6 mm in an area of the mucous membrane insensitive to pain, which leads to its necrosis and subsequent rejection. Every 14 days, one node is ligated for 3–6 procedures. Ligation may be complicated by perineal sepsis. Sclerotherapy is also indicated for patients with hemorrhoids of I and II severity, but in practice it is used less and less due to the high risk of severe complications that develop with dystopia of sclerosing drugs (impotence, neurogenic bladder, liver abscesses) [9,10]. Among the safest and most effective today are infrared light, high-frequency radio and laser coagulation of hemorrhoids
. The procedures are performed on an outpatient basis, affecting one hemorrhoid during one visit to a specialist. Coagulation is not accompanied by systemic complications, however, in 10–20% of cases, the effectiveness of treatment is significantly less than expected [1,3].
The course of the disease and its prevention
In most cases, hemorrhoids develop relatively benignly with periodic “unmotivated” exacerbations, leading to short-term disability.
Often the disease is primarily chronic, without causing clinically significant pathological symptoms. However, the steady increase in symptoms is proportional to the frequency of exacerbations and over time determines the widespread desire among doctors for a radical cure of hemorrhoids at the first time the patient seeks medical help. On the other hand, there is a widespread reluctance among patients to undergo surgical treatment for this reason. The situation is illustrated by reports from epidemiological studies conducted annually in the United States, which indicate a progressive decrease in the number of radical surgical operations for hemorrhoids. Thus, the number of surgical hemorrhoidectomies in the United States decreased from 165,000 in 1982 to 30,000 in 1994 [5]. There appear to be several reasons for this dramatic decrease in the number of surgical hemorrhoidectomies. And not the most significant of them is the reluctance of patients to undergo an expensive operation, endure a painful postoperative period and the associated long-term disability [17]. The reduction in the need for radical surgical care in recent decades has resulted from a significant improvement in the quality of conservative and minimally invasive therapy undertaken in the early stages of the disease, as well as a resulting decrease in the number of emergency surgical interventions. The trend towards non-invasive treatment is greatly facilitated by the development and implementation in the practice of family and prehospital medicine of the thesis “the best strategy for the treatment of hemorrhoids is its prevention” [1,15]. One of the most important places in the prevention system is the correction of constipation with a diet enriched with plant fiber, consumption of sufficient amounts of water and osmotically active nutrients such as juices, and increased physical activity of patients. Prevention of hemorrhoids also involves ensuring normal activity of the internal sphincter of the rectum, coordinated with the propulsive function of the colon, which is achieved by correcting emotional disorders, quitting smoking and using drugs [16]. References:
1. Brisinda G.BMJ 2000 Sep 9; 321(7261):582–3.
2. Bruch HP, Roblick UJ. Chirurg 2001 Jun; 72(6):656–9
3. Pfenninger JL. BMJ 1997; 314:1211–2.
4. Diana G, Catanzaro M, Ferrara A, Ferrari P. Clin Ter 2000 Sep–Oct; 151(5):341–4.
5. Pfenninger JL. BMJ 1997; 315:881–881a.
6. Kurbonov KM, Mukhabbatov DK, Daminova NM. Klin Khir 2000 Dec; (12):33–4.
7. Ceulemans R, Creve U, Van Hee R et al. Eur J Surg 2000 Oct; 166(10):808–12.
8. Pigot F.Rev Prat 2001 Jan 15; 51(1):21–5.
9. Murray–Lyon IM, Kirkham JS. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol 2001 Aug; 13(8):971–2.
10. Pilkington SA, Bateman AC, Wombwell S, Miller R. Ann R Coll Surg Engl 2000 Sep; 82(5):303–6.
11. Wasvary HJ, Hain J, Mosed–Vogel M, Bendick P, Barkel DC, Klein SN. Dis Colon Rectum 2001 Aug; 44(8):1069–73.
12. Perrotti P, Antropoli C, Molino D, De Stefano G, Antropoli M. Dis Colon Rectum 2001 Mar;44(3):405–9.
13. Briel JW, Zimmerman DD, Schouten WR. Int J Colorectal Dis 2000 Aug;15(4):253–4.
14. Coskun A, Duzgun SA, Uzunkoy A, Bozer M, Aslan O, Canbeyli B. Dis Colon Rectum 2001 May; 44(5):680–5.
15. Brisinda G. BMJ 2000 Sep 9;321(7261):582–3.
16. Muller-Lobeck H. Chirurg 2001 Jun;72(6):667–76.
17. Cheetham MJ, Mortensen NJ, Nystrom PO, Kamm MA, Phillips RK. Lancet 2000 Aug 26; 356(9231):730–3
Combined drug for the conservative treatment of hemorrhoids –
Gepatrombin G (trade name)
(Hemofarm)
Antihemorrhoidal suppositories –
Nigepan (trade name)
(Nizhpharm)
Other means
Microlax, which is available in a solution for rectal administration using microenemas, will help cure hemorrhoids that are bleeding.
This drug is a combination drug that has a laxative effect. The components included in the medicine help soften stool during constipation, which often causes bleeding.
In addition, Microlax affects the receptors of the intestinal mucosa, as a result of which peristalsis is stimulated. Thanks to this action, bowel movements are improved.
Thus, there is a large selection of pharmaceutical agents for the treatment of internal or external bleeding due to hemorrhoids. They are available in the form of tablets, injection solutions, microenemas, ointments, creams and rectal suppositories.
However, it is important to remember that some of them have adverse reactions or may be contraindicated in various conditions. Therefore, it is necessary that such drugs be prescribed by a qualified specialist.
Product table
| The product's name | Fastens | Weakens | Gives gas formation |
| Cabbage | + | + | |
| Whole milk | + | + | |
| Sour milk | + | ||
| Beet | + | ||
| Bakery | + | ||
| Peas | + | ||
| Egg | + | ||
| Semolina | + | ||
| Cream | + | ||
| Potato | + | ||
| Fatty meat | + | + | |
| Plum | + | ||
| Chokeberry | + | ||
| Pear | + | ||
| Black bread | + | ||
| Rice | + | ||
| Pomegranate | + | ||
| Apricot | + | ||
| Persimmon | + | ||
| Black tea | + | ||
| Walnut | + |
Find out about the most effective candles from the video:
This article has been verified by a current qualified physician, Victoria Druzhikina, and can be considered a reliable source of information for site users.
Bibliography
1. https://www.gastroscan.ru/literature/authors/9497
Rate how useful this article was
4.2 19 people voted, average rating 4.2
Did you like the article? Save it to your wall so you don’t lose it!