Polyps in the gastrointestinal tract are common among patients over 40 years of age.
Elena Gennadievna Biryukova, an endoscopist at the Department of Endoscopy and Endoluminal Surgery at the Research Institute of Emergency Medicine named after A. N.V. Sklifosovsky DZM.
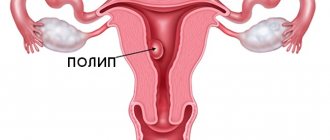
What is a polyp?
The term “polyp” is translated from ancient Greek as “many-legged.” In medicine, it is used to identify tumors in various organs. If we talk about the gastrointestinal tract, then we are talking about a benign tumor that protrudes into the lumen of a hollow organ and is connected to it either by a stalk or a wide base. Polyps are found in both the upper gastrointestinal tract (stomach) and the colon. Their size can vary from a few millimeters to 5–8 centimeters.
When performing gastroscopy in people over 50 years of age, polyps are found in up to 6% of cases, and during colonoscopy - up to 40% of patients.
Nutritional recommendations and diet
With reduced acid production, the patient needs to supplement the diet with meat and mushroom broths, pasta, cheese and boiled sausage, ham. If acid production, on the contrary, is increased, then the diet will include vegetable soups, cereals, and purees. In this way, intestinal function can be normalized.
It is important not to force yourself to eat; it is better to drink more water or juices. It is recommended to consume berries or juice of viburnum and sea buckthorn. Hazelnuts have a beneficial effect on the functioning of the stomach and intestines.
What types of polyps are there?
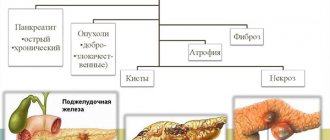
Polyps are classified according to a number of characteristics: number, size, location, appearance and many others. However, the most important thing for determining further treatment tactics is the division of polyps according to the severity of malignancy potential - the ability to degenerate into cancer.
There are two large groups of polyps:
- 1. Neoplastic
(have a high risk of malignancy). These include true tumors - adenomas. - 2. Non-neoplastic
(with minimal risk): hyperplastic, hamartomas and inflammatory polyps.
It takes about 5-10 years for cancer to arise from a polyp in the gastrointestinal tract, but everything is extremely individual. The potential for malignancy varies; no one can give exact dates or give guarantees.
Other recipes
Nutritious, rich in vitamins and fatty acids, the medicine is offered by traditional medicine to cure polyps of any etiology and location. You need to grind 6-7 tablespoons of unroasted, peeled pumpkin seeds in a coffee grinder and place them in a saucepan. Add to them 7 boiled yolks, which must be ground, and pour in a half-liter bottle of any vegetable oil (ideally olive oil). Stir the mixture thoroughly and place in a water bath. Stirring occasionally, simmer for 20 minutes.
This medicine should be taken for 5 days, after waking up, one teaspoon at a time. Then take a 5-day break. By the time the medicine runs out, not only polyps, but even moles on the skin should disappear. Tar medicine has been known to Russian healers since ancient times. You need to regularly take 5 drops of tar per glass of milk in the morning. The course lasts 20 days. Then take a break. After 5 days, repeat the course again. For many, polyps disappear after the first stage of treatment.
Traditional medicine has accumulated a huge number of recipes that give excellent results. But for successful treatment, it is important to believe in yourself, in your body, follow a diet and lead a healthy lifestyle.
Today, science knows why polyps appear?
There is no single theory on this matter. There is an assumption that the mechanism of occurrence of polyps is based on a violation of the regeneration (healing) processes of the mucous membrane of internal organs.
Provoking factors include poor nutrition (an abundance of refined foods and a lack of fiber), Helicobacter pylori infection, dysbacteriosis, diverticular intestinal disease, and exposure to radiation.
The hereditary theory of the origin of polyps has been confirmed in relation to a large group of diseases - hereditary polyposis (Gardner's disease, familial adenoma, etc.). In approximately 15% of cases, colorectal cancer is familial.
Nutritional recommendations and diet
No matter how effective the selected treatment is, it is impossible to cure stomach diseases without strict adherence to the diet. Here are the main points that such patients need to remember and observe.
When treating any disease of the digestive system, it is necessary to remember the need for constant monitoring by a gastroenterologist. No matter how miraculous the treatment method used may seem, periodic examinations of the state of the digestive organs are mandatory. Only based on data on the dynamics of the disease can one choose the optimal treatment that will help in each individual case.
Author. Shabanova Irina Viktorovna,
What symptoms may indicate the presence of polyps in the intestines or stomach?
The main insidiousness of the disease lies in the fact that in most cases it is asymptomatic. However, when villous tumors reach large sizes (2-3 centimeters), the following symptoms may occur:
- - bloody and mucous discharge;
- - pain in the abdomen and anus;
- - constipation or diarrhea;
- - anal itching.
If the polyp begins to bleed, this indicates the process of ulceration, which is no longer an early symptom. And intestinal or duodenal obstruction also indicates that the neoplasm has grown to a large size and completely blocks the lumen. Therefore, unfortunately, the patient cannot somehow “feel” the presence of polyps in the intestines or stomach. Most often, the disease is an accidental discovery during an instrumental examination for another reason.
Causes of the disease
The occurrence of this disease is typical for people of an older age group, most often it affects people after forty years, however, the disease can also develop in younger patients. According to medical statistics, gastric polyposis is more common in men than in women.
There are a number of factors that cause the occurrence of polyposis. The following people are at risk for this disease:
- those who have reached the age of forty;
- having a hereditary predisposition, which is a characteristic prerequisite for the formation of polyposis in the intestines;
- survivors of infectious inflammation of the gastrointestinal tract, including those provoked by the bacterium Helicobacter pylori;
- suffering from chronic gastritis;
- having an incorrect diet and an unbalanced diet;
- taking a large number of medications, especially uncontrolled;
- workers in hazardous industries associated with constant contact with chemicals and radioactive radiation;
- having bad habits.
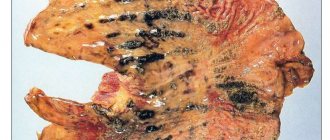
Polyps, as a rule, form on the damaged and inflamed mucosa lining the stomach, since the damaged tissue begins to intensively scar, “triggering” the mechanism of intensive cell division.
What examinations are necessary for early detection of polyps?
The only way to early diagnose polyps is mass screening, even in the absence of any complaints. A fecal occult blood test, which is included in the list of free examinations during the annual medical examination, is the main non-invasive method to suspect the presence of villous tumors and cancer. But the “gold standard” for diagnosing polyps is an endoscopic examination of the colon, which can detect almost any formation (less than 0.5 centimeters in size).
The best prevention of the appearance of polyps in the gastrointestinal tract is regular examinations, including gastroscopy and colonoscopy.
What surgical methods are used to remove polyps?
Depending on how the polyp is attached, various surgical techniques are used to remove it.
If the polyp is located on a stalk, then an endoscopic loop is placed on it and cut off using the electrocoagulation method in a special frequency mode. In the case when the polyp is located on a wide base, several options for surgery are possible:
- 1. As a rule, for tumors up to 1 centimeter, the “cold loop” method is used - without the use of diathermocoagulation.
- 2. To remove larger polyps, they resort to the use of electrocoagulation. In order to avoid bleeding and perforation, lifting of the formation is carried out: a special solution is injected into the submucosal layer, which lifts the mucous membrane above the surface of the wall, and a loop is placed around the polyp on externally unchanged tissue. Both techniques can be used on an outpatient basis for certain sizes of polyps without signs of malignancy.
What method is used to remove large polyps?
To remove giant formations en bloc, the dissection method in the submucosal layer is used. The operation is performed under general anesthesia and may take several hours. Afterwards, the hospital stay takes from one to three days.
!!! Regardless of which method was chosen to remove the polyp, after extraction it is sent for histological examination in order to determine the nature of the neoplasm and exclude oncology.
The probability of relapse (re-appearance) of hyperplastic polyps in the stomach is quite high, while in the colon such phenomena are isolated.
Juice therapy
Traditional methods of treating gastric polyps involve the use of freshly squeezed juices. It is worth remembering that you need to consume them in small quantities, in small sips.
Carrot juice is an excellent antioxidant. It helps fight malignant neoplasms. You should take this product only after first passing it through gauze so that all starchy substances remain on the fabric. To enhance the effect, you can add a small amount of onion juice.
A good remedy is potato juice, which should be mixed in an amount of 200 ml with 1 tsp. honey Take the prepared product strictly on an empty stomach. This remedy prevents the formation of tumors.
Cabbage juice helps soothe acute gastritis and significantly reduce existing hyperplastic growths. Every day you need to drink 1 tbsp. cabbage juice Juice therapy should be long-term, however, the treatment process should be strictly controlled by the attending doctor.