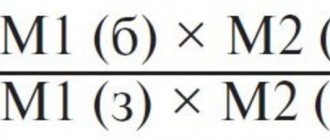This article will focus on children over 1 year old. The causes and course of dysbiosis in infants and older children are different, so it is better to immediately outline the boundaries of the issue under consideration, this will facilitate the understanding and practical application of the advice.
So, first of all, it is necessary to define what is meant by the concept of intestinal dysbiosis (dysbiosis). This is an imbalance between the number and/or activity of microorganisms in the gastrointestinal tract.
When many people hear the word bacteria, they associate it with something harmful, dangerous, and alien. However, this is not entirely the correct understanding and attitude. There are beneficial “native” bacteria, there are simply loyal ones, and there are downright hostile ones. If the balance of power between “good” and “bad” is maintained, then the body is fine.
When a baby is born, from the very first seconds of his life, a unique microbiota begins to form in the body, the interaction and coexistence of various microorganisms. Viruses, bacteria, protozoa, fungi and other microorganisms can make up up to 60% of the total body weight; these are not just “passengers” - they are part of us. The intestine contains the maximum number and concentration of these microorganisms; in an adult, microflora bacteria (microbiota) can reach 2.5 kg; this is practically a separate organ, even if it does not have a place of fixation and shape.
A mutually beneficial relationship is established between the body and bacteria, the waste products of the body are an excellent environment for the proliferation of bacteria, and humans, in turn, also benefit greatly from such neighbors, this is what beneficial bacteria do in the gastrointestinal tract:
- help break down food into its component nutrients for complete absorption;
- help the body independently synthesize some vitamins (C, K, group B, etc.), enzymes, amino acids;
- ensure the absorption of minerals, micro and macro elements;
- take part in regulatory and metabolic processes;
- provide sanitation, self-cleaning of the intestines, removal of toxins, waste, support motility and peristalsis;
- suppress the vital activity of pathogenic microorganisms (Shigella, Salmonella, a number of fungi, etc.);
- provide the creation of conditions for the production of immune cells in the intestine through Peyer's patches; about 70% of all immune cells are produced in the intestine.
It becomes clear what an important role beneficial bacteria play and how important it is to maintain a healthy microbiota.
Intestinal microflora in children
The intestinal microflora consists of various types of microorganisms that live in various parts of the digestive organ. In a normal state, these bacteria do not cause harm to the body and are involved in many metabolic processes. Human waste products are an ideal habitat for them.
Bacteria produce substances necessary to ensure the functioning of the digestive system, natural bowel movements and increase local immunity.
The role of bacteria that make up the intestinal microflora for the child’s body:
- completion of food digestion processes;
- synthesis of nutrients, vitamins and enzymes;
- increasing local and general immunity;
- ensuring the absorption of useful elements in the intestines;
- binding and removing toxins and other harmful substances from the body;
- protecting the body from pathogenic microorganisms;
- ensuring normal contraction of the intestines;
- neutralization of toxic effects on the digestive system;
- stimulating the process of bowel movement.
How to treat infant dysbiosis
The best treatment is breast milk. It contains all the substances that help the body grow and prevent the development of harmful bacteria. If the child is developing normally, and even if lumps, a small amount of mucus or greens appear in the child’s stool, there is no need to treat him. But if you experience the symptoms listed above, you need to seek medical help.
Colic gets worse in the evening
At the first stage of treatment, the growth of pathogenic organisms is suppressed. That is, these unnecessary organisms are either completely removed or their number is reduced. There are specific viruses for this. It is they who cause harm to a certain type of bacteria, without affecting other, necessary “good” bacteria. Such viruses are “tamed”. Their effect is on conditionally pathogenic and pathogenic bacteria.
Causes of dysbiosis in children
The intestines of a newborn baby are sterile. From the first days of a baby’s life, the process of populating its digestive system with microflora begins. The main one in this case is breast milk, which contains lactobacilli, bifidobacteria, vitamins and other useful elements.
It is recommended to put the baby to the breast in the first two hours after birth. If this process is carried out later, the baby may experience disturbances in the microflora. Late breastfeeding may be due to the serious condition of the newborn or his mother.
Factors provoking dysbacteriosis:
Symptoms in children manifest themselves quite clearly and cause discomfort. Artificial feeding (including a mixed version);- violation of the diet (including the predominance of sweets in the child’s diet);
- consequences of intestinal infections;
- negative environmental impact;
- diseases of the digestive system;
- giardiasis and other helminthic infestations;
- consequences of long-term or uncontrolled treatment with antibiotics;
- progressive chronic diseases;
- complications after surgery in the digestive system;
- negative consequences of frequent stressful situations and psycho-emotional stress;
- tendency to colds;
- vegetative-vascular dystonia;
- immunodeficiency (congenital or acquired form);
- hormonal changes in the body during puberty;
- tendency to allergic reactions of various etiologies.
Causes
The reasons for the weakening of beneficial intestinal flora can be the following factors:
- Antibiotics. The entry of antibiotics into the intestinal tract increases the proliferation of pathogenic microbes and fungi. Dysbacteriosis manifests itself especially strongly after taking broad-spectrum antibiotics.
- Unbalanced diet. An incorrect diet leads to an imbalance of flora if animal proteins and fats predominate in the food, while fermented milk products, fresh fruits and vegetables are absent. The processes of rotting and fermentation cause the death of normal flora and the development of pathogenic bacteria.
- Radiation treatment, chemotherapy . Potent medical procedures greatly reduce the immune system, as a result of which the normal flora in the intestines is disrupted.
- Acute intestinal infections. For example, dysentery kills beneficial flora, helping harmful bacteria to develop.
- Parasites in the gastrointestinal tract. For example, roundworms produce toxins that kill normal microorganisms.
- Conditions that weaken the immune system. Serious diseases (oncology, diabetes), the elderly and children.
Symptoms and signs of intestinal dysbiosis in children
Symptoms of dysbiosis in children differ depending on age. Newborn and infant babies cannot explain deviations in the digestive system.
The development of a pathological process in this case may be indicated by frequent crying of the child, excessive passage of gases, bloating and too frequent bowel movements (up to fifteen times a day, undigested food particles or foam are present in the stool). In older children, symptoms appear with additional manifestations.
The main symptoms of dysbiosis:
- pain in the abdomen (intensifies in the afternoon);
- excessive irritability and sleep disturbance;
- lactose intolerance (comorbidity);
- manifestation of flatulence and rumbling in the stomach;
- alternating diarrhea with constipation;
- pain in the digestive organs after eating food;
- weight gain at a slow pace;
- allergic manifestations (skin reactions);
- green stool with mucus (in newborns);
- bad breath;
- presence of a metallic taste in the mouth;
- tendency to frequent colds.
The health of the children of the Southern Urals is our concern!
Dysbacteriosis has recently become a very common condition in children, especially in infants. It causes discomfort to babies, worsening their general condition and well-being, interferes with the child’s normal weight gain and causes a lot of worry to their parents. In addition, microflora plays an important role in human life. It regulates intestinal motility, supports and stimulates the immune system, synthesizes many vitamins, provides antiviral protection for the host, normalizes metabolic processes, helps absorb many trace elements and amino acids, helps cleanse the body of toxins and prevents the penetration of foreign microbes into the blood. In total, in the human body in the intestines there are 1.5 kilograms of beneficial microbes in dried form - this is a whole “organ”. Their activity and significance can be compared with the function of the two organs of the liver and kidneys combined! The head of the pediatric gastroenterology department of the Chelyabinsk Regional Children's Clinical Hospital, a doctor of the highest category, Vadim Zemlyakov, talks about the causes of dysbiosis and methods of combating it.
— Vadim Leonidovich, some doctors consider dysbiosis to be a disease. What is your opinion on this matter? — Dysbacteriosis is a condition that can develop due to various diseases or unfavorable environmental conditions of a person. Let me give you a simple example: you are sitting at a lecture or in a movie, and the amount of carbon dioxide in the air is stuffily increasing in the hall. In this situation, a state of dysbiosis gradually begins to develop. The boss scolded him at work, the person received a new portion of stress, intestinal motility increased, and the beginning of the development of a state of dysbiosis was laid. The normal intestinal flora, and not only the intestinal flora, but also the flora of all abdominal organs, is affected by: poor nutrition, poor ecology, climate change, various ionizing radiation that surrounds a person in everyday life, inflammatory diseases, and taking medications. But this is not a disease - it is a change in flora (temporary condition) depending on external conditions of influence. — Can dysbiosis occur only in the intestines or is all mucous membranes of the body susceptible to this? — Disturbed intestinal flora will have a negative effect on the mucous membrane of all abdominal organs in which it is present (oral cavity, esophagus, stomach, intestines, vagina, etc.). Here a chain of relationships appears: disease of the intestinal mucosa affects the state of the microflora, disturbed microflora affects the mucous membrane. — By what signs can parents determine that their child has a dysbacteriosis condition? — Parents should think about it if their child’s appetite decreases, the child is pale with bluish circles under the eyes and under the nose. If a child periodically experiences nausea, grumbling and abdominal pain, the stool changes, and there are greens or pieces of undigested food in the stool. The child does not gain weight well, spits up, and often begins to get colds. Perhaps in the evening, namely at seven o'clock, a low-grade fever is noted - 37.1-37.2. Provided that you hold the mercury glass (and not electronic) thermometer for exactly 10 minutes, this is very important. These signs may indicate diseases of the digestive system and, in particular, the condition of dysbiosis. — How much does the state of the intestinal flora affect the child’s immunity? — When a child’s intestinal microflora changes for the worse, immunity decreases. When a child develops frequent colds, this also indicates that the digestive organs do not allow one to have 100% immunity. After all, 98% of a person’s immunity depends on the state of the colon microflora. And when it is disrupted, immunity drops, which means frequent colds appear. — That is, if parents have a child who is often sick, they should think about visiting a gastroenterologist? - Like one of the moments. We know that many diseases: skin, teeth, mucous membranes, even bronchial asthma, are sometimes a complication of diseases of the digestive system. When people ask me questions like this, I immediately remember one incident: the entertainer comes on stage and says: “I have a headache today.” His partner replies: “You probably ate something wrong.” The audience in the hall laughs, but he said everything correctly. Headache can be a direct consequence of gastrointestinal problems. — How does a doctor determine whether a child has a dysbacteriosis condition? — There are various methods for studying microbial flora in humans. When assessing a stool test for dysbacteriosis, it is very important to take into account the patient’s age, the principles of his diet, the sowing period: how it was collected, and when the stool was donated. And without taking these factors into account, it is impossible to correctly evaluate the result obtained. Because the numbers will ultimately be different. Let me give you a simple example: if a patient consumes more fermented milk products, then he will have significantly less coli bacteria, but this does not mean that this is a disease. If he eats more meat, he will have more coli bacteria, less bifidum, and so on. Therefore, the analysis itself must be interpreted taking into account all these points. — When a child is tested, are all these factors examined in detail? - Of course not. — Then it turns out that it is impossible to accurately determine the presence of dysbacteriosis in a child? — Without taking these factors into account, it is impossible. Therefore, many parents, when they turn to us for help, are often surprised why we ask all the subtleties and details of nutrition, which, in principle, no one ever asks. Therefore, we differ positively both in terms of treatment, and in terms of diagnosis, and in terms of results. And that’s why there’s always a huge queue for us. — What methods of treating dysbiosis exist and is it necessary to treat it at all? - You definitely need to treat! It is necessary to begin treatment with the underlying disease that led to this condition or with the cause that led to it. Naturally, medications are initially prescribed that act directly on eliminating the underlying cause. Let’s assume that a child has gastritis, it is treated, and drugs are prescribed that improve the child’s intestinal microflora. If the child is in rooms where there are various household “emitting devices” (TV, computer, microwave oven, radiotelephone, etc.), then, accordingly, they must be used as rarely as possible. If medications are a factor leading to the disease (antibiotics, etc.), then, if possible, they should be replaced or eliminated completely. That is, it is first necessary to remove factors that negatively affect the normal intestinal flora of the child. And only after that, it becomes possible to restore it. - The doctor will be able to determine exactly why it is dysbiosis that has developed? - Most often, we see the reason. - Is there a way to prevent dysbiosis? - First of all, it is necessary to monitor the child’s health. It is imperative to adhere to the principles of a healthy diet. The child’s daily diet should contain plant fiber (vegetables, fruits, grains) porridge), which helps restore intestinal microflora. Naturally, the set should be complete: microelements, vitamins, enzymes. Plant foods should predominate in the diet; the child must consume fermented milk products and proteins, in the form of eggs, meat, chicken, and fish. This will help restore normal intestinal flora. — You can lead a healthy lifestyle, but it’s much more difficult to protect yourself from stress and radiation. What is the solution in this case? — The only thing is to get rid of the source of negativity. If, for example, you are stressed at work, then you need to change your place of work. And this is absolutely serious, because we only live once. Being under constant stress and being treated for illnesses is not the best solution to the problem. It just doesn't make sense. It’s not for nothing that the Japanese believe that you should change your job once every five years. And at each enterprise they have an unloading room in which there are models of bosses. If the boss offends you, you go into this room and use the stick there to hit this dummy. The boss whose dummy is destroyed faster than others is fired from the enterprise. This is the prevention of illness among employees and the struggle for higher productivity in the enterprise. — It turns out that it is also not rational to live in the Chelyabinsk region, where the ecology is not the best? — Of course, living near the Mediterranean Sea or in the mountains of Georgia is much more useful than living in the Chelyabinsk region. Let me give you a simple example: in 1991, through the Green Cross, we took children with gastroenterological pathologies to Karlovy Vary for recovery. I took with me a huge box of medicines in case of exacerbation of illnesses, because every child had a serious digestive disease. And after living there for 1.5 months, none of the children complained of feeling unwell. But as soon as we crossed Brest and went to a restaurant on the train, within exactly two days that we were traveling, all the medicines we had stored were used up. Children began to have health problems due to deteriorating quality of food, water and air. — What is the role of heredity in the development of gastrointestinal diseases? — Of course, the health of his parents plays a big role in the health of a child. They convey to him a predisposition to diseases of the digestive system. If the mother is unhealthy, then the quality of her breast milk will be low, which is the next factor not in favor of the baby. — During breastfeeding, should the mother follow a special diet or diet? — Nutrition should be complete and varied. If the mother has gastrointestinal diseases, medications that improve her condition can be prescribed for preventive purposes. The mother herself should draw the attention of the gynecologist to this, because her state of health at the time of the birth of the child plays a big role in shaping the health of the baby. In particular, how complete the composition of his intestinal microflora will be. After all, the colonization of normal microbes in the baby’s intestines occurs in the womb, starting at 26-28 weeks. — What foods are not recommended for children to eat? — There are five main unhealthy foods: carbonated drinks, mayonnaise, ketchup, chips and chewing gum. These are all products of genetic engineering. For example, long-term use of chewing gum leads to dementia (the presence of phenols in it). Moreover, it is coated with a harmful taste-forming substance. And its frequent use leads to disruption of the food reflex. And the next time you swallow food, your stomach will not be ready to digest it. — What foods are best not given until the age of three? — All products up to three years old must be natural, not canned! They can be used raw or cooked. Fried and smoked, pickled, chocolate, of course, are not allowed. Although recently we have to talk about bad habits in young children, when mothers start giving their babies a teaspoon of vodka at night so that they sleep better. And for the sake of appetite, children began to be given beer. This has been happening quite often lately. We receive young children with cirrhosis of the liver because the mother, while breastfeeding the child, drank alcoholic beverages and smoked. — How do you feel about the use of milk in children’s diets? “Given the fact that there are no ideally healthy children, drinking milk may not be beneficial for many of them. Milk can contribute to excessive growth of microflora, and sometimes the child’s body is not able to digest it (lactase deficiency). Therefore, we, gastroenterologists, are more in favor of consuming fermented milk products and cheeses. — If a child is forced to take antibiotics, what should be done as a preventive measure to prevent dysbiosis from developing? — It is best to combine antibiotics with a decoction of herbs, such as yarrow, plantain, chamomile or oregano. They reduce the negative effects of antibiotics on the intestinal mucosa and its microflora by 80%. — How common are diseases of the digestive system? — Diseases of the gastrointestinal tract in children are in second place after respiratory infections. And this is considering that a child suffers from ARVI 2-3 times a year, and the diagnosis of gastrointestinal disease is made once. — Do you treat children only from the region or from Chelyabinsk too? — CHODKB serves residents of the Chelyabinsk region, regardless of its territories, that is, Chelyabinsk is also included here. But given the fact that in Chelyabinsk there are a sufficient number of gastroenterological beds and specialists, diagnostics are also at a high level, we try to take only the most severe and complex cases from Chelyabinsk. And the last stage, if we are no longer able to provide assistance, the Institute of Pediatrics in Moscow takes care of patients. — How do children get to you? “They come on the referral of doctors from the region for a consultation at the regional children’s clinic with a gastroenterologist. After examining the child and conducting the necessary research, the doctor decides whether he needs to be hospitalized or treated on an outpatient basis. The second option for a patient to arrive at a regional children’s clinic or for hospitalization in a department is to be examined by a gastroenterologist at a “travel clinic.” This is when our specialists advise children at their place of residence.
Olga Melchakova, Uralpress news agency
Analysis for dysbiosis in children
To compile a general clinical picture of the child’s health, additional studies may be prescribed. For example, a coprogram (a procedure for determining the degree of digestion of food), ultrasound of the digestive organs (to identify congenital anomalies and chronic diseases), as well as a bacteriological study of the composition of feces (an analysis to determine the number of different types of bacteria in the intestines).
Rules for conducting analysis for dysbacteriosis:
- feces must be sent for examination within three hours after collection;
- At least one day before the test, you should not give your child antibiotics or other drugs;
- if the child has been prescribed an x-ray examination, then feces obtained after two or three acts of bowel movement are suitable for analysis;
- stool should be collected in a sterile container.
Dysbacteriosis develops when the beneficial microflora of the gastrointestinal tract is replaced by harmful bacteria (pathogenic).
Which doctor should I contact?
If dysbiosis is suspected, you should contact a pediatrician and pediatric gastroenterologist. If there are difficulties in making a diagnosis or it is necessary to determine the presence of chronic diseases in a child, then specialists can prescribe an additional examination from specialized doctors (for example, an immunologist, endocrinologist, etc.).
Diagnosis of dysbacteriosis
“SM-Doctor” is a modern medical center whose specialists quickly identify dysbacteriosis and any of its manifestations. Thanks to our own laboratory and the latest equipment, our doctors accurately determine the cause of the problem and select the best methods to solve it. After collecting anamnesis and a thorough analysis of the patient’s complaints, the pediatrician examines the little patient. During palpation, bloating and tenderness of the anterior abdominal wall may be noted. To confirm the diagnosis, the doctor prescribes additional tests:
- microscopic examination of stool;
- bacteriological examination of stool;
- a set of traditional laboratory tests to assess the general level of health (blood and urine tests, “blood biochemistry”).
If the doctor believes that dysbiosis in a patient is a consequence of an exacerbation of some other disease, the child is additionally referred for consultation to related specialists (cardiologist, gastroenterologist, neurologist, infectious disease specialist, etc.).
The role of nutrition in the development of dysbiosis in children
Correction of diet is the main method of treating dysbiosis. The diet for infants and older children is different. If the baby cannot eat food on his own and is breastfed, then the woman should change the diet. Potential allergens, harmful foods and foods that negatively affect the digestive processes should be excluded from the menu.
For babies who are bottle-fed, it is recommended to switch to adapted formulas (with special marks on the packaging). Frequent changes of baby food are undesirable. Children who eat their own food are prescribed a special diet.
Role of nutrition:
- poor diet is one of the main causes of dysbiosis;
- Dieting is more effective than drug therapy;
- Errors in the menu can reduce the child’s tendency to recover.
Authorized Products
The recommended menu for intestinal dysbiosis depends on the age of the child. It is necessary to prepare dishes for children using the methods of boiling, steaming or baking. All ingredients must be crushed. If a child has a food allergy, this nuance must be taken into account when preparing the diet. For example, a baby may have an intolerance to dairy products, honey, or an allergy to certain berries and fruits.
Authorized products:
The baby should receive all the products required by age as part of a complete and balanced diet. vegetables (potatoes, pumpkin, carrots, zucchini, beets);- cereals (white rice, buckwheat, pearl barley);
- poultry meat (turkey, chicken;
- low-fat fish (hake, cod, perch);
- rabbit meat;
- fermented milk products (kefir, fermented baked milk, cottage cheese);
- sweet varieties of berries (lingonberries, raspberries, blueberries, strawberries);
- butter;
- compotes based on fruits and dried fruits;
- jelly from berries and fruits;
- rosehip decoction.
Products to Avoid
The menu for a child with intestinal dysbiosis should be based on the list of permitted products. Eating certain types of food can reduce the effectiveness of therapy and worsen the condition of the baby's digestive system. Fatty, fried, salty and smoked foods are strictly prohibited. You can't eat fast food. All products from the prohibited list should not be present on the menu, even in minimal quantities.
Prohibited foods: brown rice, millet; raw vegetables; sour varieties of fruit; sweet pastries; confectionery; sausages; whole milk (and cream); lamb and fatty meats; mushrooms; legumes; semi-finished products; waterfowl meat; sauerkraut; turnip; radish; mayonnaise; canned food; carbonated drinks.
Treatment with drugs
Drug therapy for intestinal dysbiosis is carried out in two directions. First of all, pathogenic microorganisms are destroyed. Antibiotics are used to accomplish this task. Antibacterial agents are prescribed to children only if the disease is infectious. In other cases their use is not required. The second direction of therapy is the colonization of the intestinal microflora with beneficial bacteria (special bacterial preparations).
Bacterial preparations:
Self-medication is life-threatening; for advice on the use of any medications, consult a doctor. with microorganisms that have antagonistic activity (Enterol, Bactisubtil);- with Escherichia coli (Colibacterin);
- with bifidobacteria (Bifiform, Bifindumbacterin);
- with beneficial bacteria (probiotics);
- with lactobacilli and kefir fungus (Acipol);
- with bifidobacteria and B vitamins (Bifi-form);
- with lactobacilli (Biovestin Lacto, Lactobacterin);
- with E. coli, lactobacilli and bifidobacteria (Linex, Bifikol).
For symptomatic treatment of pathology, sorbents and enzymes can be prescribed. Such drugs significantly reduce the manifestation of intoxication, remove toxic compounds from the body and improve the process of digestion of food.
Folk remedies
There are many recipes for folk remedies for the treatment of dysbiosis, but not all of them are suitable for children. For example, children may categorically refuse to use herbal infusions. For children, you can use special folk remedies with a pleasant taste. Some healthy dishes are recommended to be included in the children's menu to prevent abnormalities in the intestinal microflora and reduce immunity.
Kefir drink with dried fruits:
- Prepare several types of dried fruits (dried apricots, prunes, figs).
- Pour hot water over the preparation (the dried fruits should swell within an hour).
- Grind the dried fruits (you can simply cut them with a knife).
- Pour a tablespoon of the preparation into a glass of kefir and mix the drink thoroughly.
- For younger children, dried fruits can be crushed in a blender.
- It is recommended to drink the drink in the morning.
- The product not only improves the condition of the digestive system, but also improves immunity.
Elderberry and rosehip decoction:
- Combine 100 g of rose hips and elderberries.
- Pour the workpiece with hot water (600 ml).
- Boil the broth for twenty minutes over low heat.
- After filtering and cooling, the drink is ready to drink.
- The product can only be used for children over four years of age.
- The decoction should be consumed in small portions before main meals (three times a day).
Honey-banana paste:
- Mash half a banana with a fork.
- Mix the preparation with a teaspoon of honey.
- It is recommended to use the product for breakfast.
- The child must be excluded from an allergic reaction to honey.
Sweet paste made from seeds, figs and dried apricots:
- Combine pumpkin, sunflower, flax seeds, chopped dried apricots and figs in equal quantities.
- Grind the workpiece in a blender.
- The paste can be eaten with cookies or on its own.
- It is recommended to use this remedy before breakfast and dinner (a teaspoon).
Berry paste:
- Crush lingonberries, raspberries and cranberries (you can chop them in a blender).
- It is allowed to add sugar or honey to the preparation (to improve the taste).
- The product should be consumed after breakfast and dinner (a teaspoon).
Video on the topic: Intestinal dysbiosis, symptoms and treatment in children.
Prevention of dysbiosis in children
Some causes of intestinal dysbiosis in children are associated with intrauterine development. The disease can be triggered by infectious diseases of the mother during pregnancy, poor nutrition of the woman and frequent exposure to stressful situations. During the period of gestation, general recommendations should be followed. Elimination of provoking factors will significantly reduce deviations in the state of the microflora of the digestive system in the unborn child.
Measures to prevent dysbacteriosis must be observed at all stages of the baby’s life.
Choose only products recommended for baby food, with a good shelf life, enriched with beneficial bacteria.
Measures to prevent pathology after the birth of a child:
- compliance with sanitary and hygienic standards;
- balanced diet;
- comprehensive treatment of chronic diseases;
- timely treatment of colds;
- prevention of intestinal infections;
- exclusion of stressful situations;
- adherence to sleep and wakefulness;
- taking antibiotics only as prescribed by a doctor;
- After treatment with antibacterial drugs, probiotics should be taken.
Good and bad bacteria
The baby begins to behave restlessly
But in the kingdom of the intestinal microorganism, unfortunately, not only the composition of beneficial bacteria has entered, such as: bifidobacteria, lactobacilli, E. coli, bacteriodes - both neutral and harmful inhabitants have joined here.
The life of neutral bacteria such as peptostreptococci, clostridia, staphylococci, proteus, klebsiel, veillonella, does not give the body either good or bad. And “bad” microorganisms cause significant harm. And the happy time when the baby is just born and he and his mother spend time at home can be overshadowed by his unexpected deterioration in health.
An important problem that always worries parents of a newborn is the state of its digestive organs. When the baby begins to behave restlessly, he develops intestinal colic, constipation, hypovitaminosis, then the parents begin to sound the alarm. And it is right. Because such manifestations are similar to dysbiosis.
Forecast
Compliance with the diet and all the specialist’s instructions allows you to get rid of dysbacteriosis within one month. The duration of therapy can be increased if the child has complications, congenital pathologies of the digestive system or chronic gastrointestinal diseases. In the absence of adequate treatment and violation of nutritional rules, the prognosis will be unfavorable.
Dysbacteriosis can cause serious abnormalities in the digestive tract, which will reduce the baby’s quality of life.