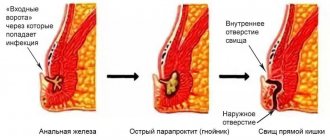
Paraproctitis is a purulent inflammation of the tissue surrounding the rectum.
The infection can get there either hematogenously (through the bloodstream), but most often it is a direct entry from the rectum through natural passages - crypts. Crypts are pockets in the wall of the rectum into which the ducts of the anal glands open. The outer end of the crypt has access to the peri-rectal tissue. Therefore, under some circumstances (decreased immunity, microtrauma, constipation), infection from the rectum directly enters this fiber.
types of paraproctitis
There are several cellular spaces surrounding the rectum. Therefore, paraproctitis is different:
- Subcutaneous (the infiltrate is located directly under the skin in the anal area).
- Submucosal (located under the mucous membrane in the intestinal wall).
- Ischio-rectal.
- Pelvic-rectal.
Paraproctitis is also divided into acute and chronic.
Treatment tactics for developed paraproctitis
Paraproctitis (especially acute) is an absolute indication for surgery.
Acute paraproctitis is a purulent inflammation of tissues. Any purulent focus in the body can resolve with several outcomes:
- The most favorable: the pus finds its way out on its own, the lesion is emptied, the wound heals, and self-healing occurs.
- The pus does not come out, but inside, spreads through the tissues, melting all surrounding tissues and organs, entering the blood and spreading throughout the body. The prognosis is unfavorable.
- The purulent focus is not completely emptied, part of it is encapsulated, creating a chronic focus with constant recurrence.
- The pus can come out completely, but the passage through which it came out does not heal; infection from the environment also constantly gets inside through it. The result is also a chronic inflammatory process.
So, the first most favorable outcome for untreated paraproctitis is possible only in 10-15% of cases. This information is for those who refuse surgery in the hope that “everything will work out.”
Therefore, when a diagnosis of acute paraproctitis is made, one cannot delay the operation.
Why doesn't the wound heal?
The recovery process has certain variations and can be delayed for various reasons that are not considered pathological.
So why doesn't it drag on:
- Attachment of a secondary infection, infection of a wound provided there is a source of infection in the body.
- Daily surface damage due to over-processing of fabrics.
- Non-compliance, repeated violation of hygiene rules and inadequate wound treatment and dressing.
- Incorrect selection of antibacterial drugs, failure to bring the course of treatment to its logical conclusion.
- Failure to comply with diet and other doctor’s recommendations by the patient.
- The chronic course of the inflammatory process in tissues, in which surgery may not bring the desired result.
When the wound does not close for a month, its edges are inflamed, the person is bothered by severe pain, secretory discharge - it is worth contacting a doctor for help.
The wound does not heal even in the presence of autoimmune, inflammatory and metabolic disorders in the body. A similar phenomenon is observed in the case of a patient with syphilis, HIV infection, diabetes mellitus and oncology.
What could be the consequences if paraproctitis is not operated on in time?
The consequences of refusing intervention and independent attempts to treat paraproctitis without surgery are as follows:
- Penetration of inflammation into deeper areas of tissue with the development of phlegmon.
- Pelvic pelvioperitonitis.
- Penetration of infection into the abdominal cavity with the development of peritonitis.
- Sepsis.
- Purulent melting of the pelvic organs - the walls of the rectum, bladder, urethra, genitals.
- Thrombosis and thrombophlebitis of the pelvic veins.
- Outcome into chronic paraproctitis.
Diagnostics
The diagnosis is made by experienced proctologists at the Yusupov Hospital at the first consultation, using basic diagnostic methods: visual or digital examination with a rectal speculum, which is carried out to assess the condition of the skin and subcutaneous tissue around and inside the anus, identifying swelling, hyperemia, and painful lumps.
To confirm the diagnosis, instrumental research methods are prescribed using modern clinic equipment:
- Anoscopy;
- X-ray with the introduction of a contrast agent into the fistula;
- Ultrasound examination with a rectal sensor;
- Sigmoidoscopy (examination of the rectum with an endoscope).
Stages of surgery for acute paraproctitis
- Opening and cleansing of the purulent focus.
- Elimination of the connection of the purulent focus with the rectum.
If both stages are completed, we can talk about radical surgery; complete recovery occurs in 80-85%.
However, it is not always possible to perform a radical operation at once. Opening a purulent focus during paraproctitis should be carried out as early as possible; this is an emergency situation, such intervention is carried out in the nearest surgical hospital.
Excision of the purulent tract and affected crypt requires the skill of a coloproctologist surgeon and should be carried out in a specialized proctology department. Often the second stage of the operation is carried out some time after the first.
Devices and light guides
We use Biolitec and LAMI 1470 laser devices, registered in Russia. They are distinguished by flexibility and accuracy of settings, reliability. What you need for effective, safe and predictable treatment.
For laser obliteration of the purulent cavity with paraproctitis, we use FiLaC radial laser fibers (Germany), as an alternative to reduce the price of the service - Mediola fibers.
General overview of the operation
Autopsy of acute paraproctitis is an emergency operation performed for life-saving reasons. Therefore, preparation for it is minimal, and there is only one contraindication - the patient’s extremely serious condition.
The opening of paraproctitis is usually carried out under general or epidural anesthesia, since it requires maximum muscle relaxation.
The easiest way to open ulcers is with superficial paraproctitis - subcutaneous and submucosal. They are also the most easily diagnosed - a general examination and rectoscopy (examination of the rectum using a rectal speculum) are sufficient.
Incisions used for acute paraproctitis: 1 – perianal abscess; 2 – retrorectal; 3 – ischiorectal
For subcutaneous paraproctitis, a semilunar incision is made around the anus in the place of greatest fluctuation and translucency of pus. The pus is released, all the bridges that divide the purulent cavity into several sections are destroyed. The purulent cavity is cleaned as much as possible, washed with antiseptics and antibiotics, and the wound is drained. Tamponade with antiseptic ointments (Levosin, Levomekol, Vishnevsky ointment) is possible.
With a highly qualified surgeon, the second stage can be carried out simultaneously: excision of the purulent tract that goes into the rectum. To do this, a button-shaped probe is inserted into the wound, with the help of which the passage is found. On the side of the rectum, at the site of the protruding end of the probe, the affected crypt is found. It is excised to healthy tissue. As a rule, sutures are not placed on the intestinal wall.
If the surgeon is unsure, the second stage of the operation can be delayed by 1-2 weeks (this is the period during which the purulent wound will be maximally cleaned and begin to heal, but it will still be possible to find its internal opening in the wall of the rectum. In addition, illiterate one-step excision of the external sphincter can lead to to its insufficiency in the postoperative period.
For submucosal paraproctitis, the incision is made from the side of the rectum. First, a digital examination and examination of the rectum in the speculum are performed. A puncture needle is inserted into the site of the largest protrusion. When pus is obtained, an incision is made in this place. Then, using a forceps, they pass bluntly into the cavity of the abscess; if necessary, the incision is widened. A rubber drainage is inserted into the opened abscess and its end is brought out through the anus.
The greatest difficulties are presented by surgery for ischiorectal, pelvic-rectal and retrorectal paraproctitis. The pus in these forms is localized deeply. Deep forms of paraproctitis are not always quickly diagnosed. To clarify the diagnosis and precise localization, a CT or MRI of the pelvic area is sometimes required.
The choice of access method for such paraproctitis is always difficult for the surgeon. Here, percutaneous access and emptying of the abscess with subsequent excision of the purulent tract or opening of the abscess only from the rectum is possible.
The fistula tract is inspected. If it is located transsphincterically, it is dissected into the rectal cavity using a probe, as with subcutaneous paraproctitis.
If the fistula tract is located extrasphincterically, it is usually excised with partial sphincterotomy (sphincter dissection) or the fistula tract is eliminated using the ligature method.
The essence of the ligature method is that a strong thread is inserted into the fistula tract. The incision is extended so that the thread is placed along the anterior or posterior midline of the sphincter. The thread is tied. Subsequently, every 2-3 days during ligation, the thread is tightened more and more tightly, which leads to a gradual crossing of the sphincter and elimination of the fistula tract. Such a gradual, rather than sudden, dissection of the sphincter allows one to avoid the formation of its insufficiency after surgery.
Reasons for formation
Fistula after paraproctitis is a common proctological problem. An acute inflammatory process leads to the formation of an abscess that spontaneously opens. Paraproctitis, a fistula of the rectum in which is accompanied by specific symptoms, can be operated on without eliminating the entrance gate of the pathogens, while the pathological process continues to develop. Other reasons for the development of fistula tracts in the subcutaneous tissue of the rectum are:
- Injuries received during childbirth;
- Resection of the rectum;
- Complications after gynecological interventions;
- Other inflammatory diseases, which include: tuberculosis, colorectal cancer, AIDS and Crohn's disease.
When examined by a proctologist at the Yusupov Hospital, a rectal fistula is diagnosed. In the presence of this pathology, one hole is often observed, localized near the anus. To assess the length and other features of the fistula tract, studies are prescribed using high-precision equipment.
Chronic paraproctitis
Chronic paraproctitis occurs after spontaneously opened or inadequately treated paraproctitis. In 10-15% of cases, it can occur after proper adequate drainage of acute paraproctitis.
Actually, chronic paraproctitis is a fistula that occurs in the soft tissues of the peri-rectal region. It can be complete (with two outlet openings - in the skin of the perineum and in the wall of the rectum) and incomplete (one opening is external or internal). It can also have multiple branches and multiple holes.
The presence of a fistula implies constant infection from the environment and constant recurrence of inflammation in the peri-rectal tissue.
Treatment of chronic paraproctitis is surgical. The operation can be either emergency (during exacerbation of the disease) or planned.
The most favorable prognosis is to perform a planned operation in subacute cases after some preparation (anti-inflammatory and antibacterial therapy). It is not recommended to perform the operation during a period of stable remission, since the internal opening of the fistula may not be found at this time.
Postoperative period
After surgery, it is recommended for wound healing:
- careful hygiene of the operation area - that is, washing this area at least 6-7 times a day with a stream of warm water. The use of constant compresses, ointments and lotions is not required;
- monitoring the effectiveness of pain relief. Our clinic specialists select the optimal regimen and methods of using various drugs to control pain.
In some cases (after plastic surgery or in the presence of severe inflammation), antibiotics are necessary.
In addition, a diet correction is necessary, including foods high in fiber and various liquids, excluding spicy, spicy and sour foods, and alcohol, so that the stool is soft and does not injure the surgical site. Upon discharge from the clinic, the doctor gives detailed recommendations on nutrition and lifestyle.
It is necessary to remember about specific therapy in the presence of inflammatory bowel diseases (Crohn's disease, Ulcerative colitis, etc.), as well as the high risk of re-formation of fistulas in the presence of post-radiation fistulas (in patients who have undergone radiation therapy courses) and in patients with Crohn's disease, which requires careful monitoring in the postoperative period.
Cost of treatment
Free treatment under compulsory medical insurance policy
A type of social insurance for citizens of the Russian Federation, which provides guarantees of free medical care in the detection of surgical diseases.
Quota treatment (VMP)
Providing medical care for the most severe diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, requiring the mandatory use of expensive instruments and/or the use of complex surgical techniques.
Treatment on a paid basis
It assumes the possibility of receiving medical care for any surgical disease, regardless of the presence of a compulsory medical insurance policy, without the need to complete additional documents and obtain a quota, for citizens of all countries of the world.
Types of operations for chronic paraproctitis
The main goal of surgical intervention for chronic paraproctitis is the elimination of the fistula tract. The extent of the operation depends on the location of the fistula.
To accurately localize the openings of the fistula tracts, dyes (methylene blue) are injected into the wound. Sometimes radiopaque contrast is used with radiography.
Types of operations for chronic paraproctitis:
- Dissection of the fistula.
- Fistula excision.
- Ligature method.
- Plastic surgery.
- Laser obliteration of fistula.
- Obliteration of the fistula with a collagen thread.
With a transsphincteric location of the fistula, it is possible to dissect the fistula tract from the rectal lumen or excise it (Gabriel's operation) along its entire length, followed by complete or partial suturing of the wound.
In case of extrasphincteric location of the fistula (after pelvic-rectal or ischiorectal paraproctitis), excision of the fistula is performed with dosed sphincterotomy or the ligature method.
Plastic surgery involves excision of the fistula and closing its internal opening with a flap of the intestinal mucosa.
New methods - laser coagulation of the fistula tract or filling it with collagen thread - are possible if the fistula tract has a simple linear shape.
Paraproctitis: insidious fistula and false shame
This disease is one of those that people are embarrassed to discuss with friends and acquaintances. Moreover, the visit to the doctor is delayed from day to day. What can I say - it’s a shameful place, and that’s all... The disease is insidious with both severe physical pain and moral suffering. But this, unfortunately, is not all - without timely treatment, paraproctitis can poison a person’s life for many years, ultimately resulting in very dire consequences. And all because it was once awkward to cross the threshold of a proctologist’s office.
Anatoly Ivanovich Vanin, the head of the proctology department of the polyclinic of the Medical Center of the Administration of the President of the Russian Federation, Candidate of Medical Sciences, tells us why paraproctitis is dangerous and how to cure this disease - successfully and without false shame.
“Let me remind you that “para” in Greek means near, around, and proctitis is inflammation of the mucous membrane of the rectum,” said A.I. Vanin. — Thus, paraproctitis is an inflammatory disease of the tissue surrounding the rectal area, the lower part of the rectum.
The main reasons are stress, a decrease in the body's immune defense, a sedentary lifestyle, excessive use of antibiotics, severe hypothermia, nutritional errors, most often dry food, on the go, and as a result - constipation or, conversely, loose stools. Paraproctitis occurs regardless of age, but more often in men, because they smoke a lot and drink often. However, recently more and more women and girls are becoming ill: the desire to wear tight-fitting trousers, especially jeans made of thick, coarse fabric, as well as underwear, which, cutting into the crotch, injures the skin, is affected. Such abrasions become susceptible to infection, including viral infections. When hypothermia occurs - this is when girls flaunt in short skirts and thin tights in cold weather - herpes appears, which also provokes paraproctitis. Elderly people usually suffer from chronic paraproctitis if they suffered an acute form of the disease in their youth.
How does the disease occur? In the lower part of the rectum (in the anus) there are mucous glands that moisten the surface of the intestine with their secretions, facilitating the exit of feces if it is dry. With constipation, the mucous membrane is damaged, abrasions and cracks form, which become infected. Let me note that one gram of feces contains millions of units of different flora. This is where all the trouble begins.
The same thing happens when the stool is liquid - the acidic mass causes loosening of this area, also with possible infection. And even with normal bowel movements, something similar is possible - there seem to be no special complaints, but the body is weakened, and then the person just ate hot sauce, mustard, horseradish. The mucous membrane instantly becomes irritated and burns occur. The disease then develops according to a well-known scenario: the infection, along with inflammatory manifestations, spreads to the perirectal tissue - the connective tissue surrounding the rectum.
Paraproctitis begins with itching and slight discomfort in the anal area, then the disease gains momentum, purulent streaks form, which can turn into various fistulous forms and break out to the surface of the skin. If there is no breakthrough, the purulent mass comes out along with mucus and other unpleasant putrefactive discharges through the anus. Acute paraproctitis develops suddenly: the temperature rises, sharp pain appears in the rectal area, giving no rest, and after a sleepless night the person consults a doctor. True, there are erased forms of the disease - the patient does not seem to complain of severe pain, but the inflammatory infiltrate is palpable. In this case, to make an accurate diagnosis, you need to do an ultrasound, computed tomography or magnetic resonance imaging. A blood test alone is not enough, since the picture may be normal, although leukocytosis is sometimes observed.
In the chronic form of paraproctitis, fistulas do not heal for a long time. And then smears are taken from the patient to determine the cause of this protracted process, since the fistulous form of chronic paraproctitis can be caused by tuberculosis, syphilis, cancer, Crohn's disease, and other diseases. But more often the banal fistulous form is affected - with the release of E. coli and pus.
There are also internal incomplete fistulas, when the infection enters the anal fissure. Inflammation of perifocal tissue leads to abscess formation. The pus cannot come out due to the very dense thick skin. In this case, it is necessary to open and drain the abscess. If pus comes out through the internal opening of the fistula, then the discharge comes from the anus. Fistulas are located differently in all patients. In some - 2-3 cm from the anus - they can be felt with your fingers, seen in the mirror, in others - in the upper parts of the rectum.
The most common treatment for paraproctitis is ichthyol ointment and suppositories. They reduce tissue tension, relieve pain, help patients adapt to their condition; some even refuse surgery.
Initially, we try to puncture the abscess - release the pus, and then relieve the inflammation. The fistula is washed with a 1% dioxidine solution, and at the same time the patient is prescribed an anti-inflammatory drug - sumamed (0.5 g once a day for 3 days in a row). Fistula lavage is performed on an outpatient basis. Typically, after three procedures, the fistula closes in most patients. This is followed by taking medications that support the immune system.
But it happens that the fistula remains, however, without obvious purulent discharge. Treatment continues at home. Sitz baths are recommended: 1 tbsp. spoon of sea salt and baking soda per 5 liters of warm water. The duration of the bath is 10 minutes. Such procedures help the discharge of pus and clean the fistula well. After the bath, suppositories or ultraproct ointment are introduced. You can make microenemas from mumiyo: dissolve 1 tablet in 0.5 cups of hot water, administer warm.
I’ll tell you about one amazing case of recovery, which was helped by... a honey fair organized by Moscow Mayor Yuri Luzhkov in Manege. The patient came to us for procedures for a whole month, and to no avail: there was no pus, but the fistula remained. Here we just received information from this fair about the healing properties of sweet clover honey. They began to give the patient microenemas - 1 tbsp. a spoonful of honey in 0.5 cups of water. And everything healed in two days. Just a miracle!
I must note that such enemas - both with honey and with propolis oil solution - are very effective. The intestine even begins to squelch with pleasure: she likes warm, sweet things so much! Microclysters (1 tablespoon per 0.4-0.5 glasses of water) are done at night, and in the morning after stool, UltraProct suppositories are administered.
Sometimes you have to wait a long time for the abscess to break through. Then we recommend using the same ichthyol ointment, cakes made from baked onions, potatoes, and carrots. They help the fistula break through and pus drain. The patient chooses which flatbread is better, as they say, “at random” - whichever works more effectively, he “cooks” from it.
When all methods of conservative treatment have been exhausted, but the disease does not go away, we refer the patient for surgery, of course, if there are no contraindications. It is called Gabriel's operation, named after the surgeon who first performed it: a speculum is inserted into the anus, the mucous gland and fistula are excised. The treatment is very radical. True, scars appear after it, and even with hard stool, the lack of mucus causes certain inconvenience. Therefore, we try to injure this area as little as possible and, if possible, operate in extreme cases. It is better to use folk remedies and be observed at the clinic for a year. If the fistula heals, you can forget about the operation for decades.
However, frequent recurrences of the fistula are a big risk factor for oncology. Therefore, the patient must undergo an annual medical examination or examination by a surgeon. As a rule, such prevention is justified. During this period, one should not forget about maintenance therapy: make baths, lotions, pads, microenemas, follow a diet, especially for those who suffer from constipation and hemorrhoids. Here are some recommendations.
- As a laxative, drink 1 glass of freshly prepared carrot juice with pulp on an empty stomach. For hemorrhoids, steam and drink carrot tops as tea.
- Juice from ripe rowan berries - 0.5 cups of Zraz a day before meals. Apply the remaining pulp to the hemorrhoids in the form of a compress.
- Drink a mixture of carrot and spinach juices in a ratio of 10:3 3 times a day before meals. The daily dose is 2 glasses.
- Sauerkraut brine - 1 glass 3-5 times a day before meals for hemorrhoids, constipation and heavy bleeding.
- Grate raw potatoes with peel, squeeze out juice, 1 tbsp. Inject a spoonful of juice into the anus with a syringe at night. The course of treatment is 10 days.
- Consume 100-150 g of boiled red beets on an empty stomach for chronic constipation and digestive disorders. For spastic constipation, a salad made from boiled beets and vegetable oil is useful - also on an empty stomach.
- For prolonged constipation, beet broth is used for enemas: pour 20 g of beets with 2 glasses of water, boil for 30 minutes.
- Pour boiling water over washed prunes in the evening. In the morning, eat a few plums on an empty stomach and drink the resulting liquid (without sweetening it) as a laxative.
- Warmed water from pickled lingonberries, taken on an empty stomach, is also a good laxative.
Badger and bear fat are effective in treating the rectum. Turundas or tampons should be soaked in fat and inserted into the anus overnight. If the mucous membrane of the anal canal is erosive, you can make thin sticks from fresh potatoes rich in starch. It envelops well, relieves irritation, heals erosions and cracks in the anal rectum. The sticks are inserted overnight.
Now - about mucous glands and mucus. I am convinced that the removal of any organ, including mucous glands, is an intervention in nature: there is nothing superfluous in the body. However, if the glands are constantly inflamed, their excision is a necessary and necessary measure.
Sometimes patients complain of copious mucus secretion. However, in this way not only inflammatory processes of the mucous glands can manifest themselves, but also concomitant diseases. For example, the growth of mucous membrane in the intestine, like a villous tumor, which produces up to one liter of mucus per day, secreted through the rectum. And although the tumor is benign, the body, in fact, begins to rot. Villous tumors can occur in the rectum and in the overlying intestines. The literature describes a case where the colon was completely affected by it. Therefore, copious mucus discharge should definitely alert you. Often, patients are frightened mainly by the release of blood.
Excessive mucus, when it, as we say, comes out in “buckets”, and with blood, can also occur with ulcerative colitis, most often caused by stress and other reasons. Patients with ulcerative colitis should be observed by a gastroenterologist for at least 10 years: colorectal cancer may develop.
Concluding the conversation, I will say that the specialty of a proctologist is now, alas, gaining power and strength, since many of our diseases depend on the state of medicine and society, and a person’s attitude towards his health. Of course, we are far from Japan, where they thought of, for example, installing special sensors on toilets that detect the presence of blood or mucus in flushed feces. A dispatcher is sitting in some Japanese housing complex and sees on the instruments: in such and such an apartment one of its residents has intestinal problems. He comes and says: someone is sick. And doctors begin to check the whole family.
Many of us are embarrassed to see a doctor in a timely manner - they delay until they press properly. Why be ashamed? If there is slight itching or mucous discharge, you need to go to the clinic. As a last resort, at least tell your loved ones about the unpleasant sensations - this will make it easier to overcome false shame and begin treatment. Paraproctitis and its consequences - fistulas - are completely curable when time is not lost in doubt and torment.
After operation
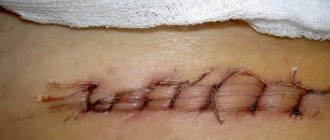
After surgery for acute or chronic paraproctitis, it is important to follow some rules. It is advisable to spend the first few days, even after opening the superficial paraproctitis, in a hospital. Antibiotics and painkillers are prescribed. Dressings are performed daily and can be quite painful.
Immediately after the operation, a slag-free diet is prescribed - semolina or rice porridge with water, steamed meatballs, boiled fish, steamed omelettes. It is necessary to retain stool for 2-3 days after surgery.
After 2-3 days, if there is no independent stool, a cleansing enema is given. It is very important to prevent both constipation and diarrhea. Normal stool has no effect on wound healing. Gradually, baked apples, boiled vegetables, a decoction of dried fruits, and lactic acid products are added to the diet. It is important to drink at least 5 glasses of liquid per day.
Spicy, salty foods and alcohol are absolutely excluded. You should refrain from raw vegetables and fruits, legumes, baked goods, whole milk, and carbonated drinks.
If the postoperative period is normal, the patient can be sent home after a few days. He can carry out further dressings himself. They usually involve treating the wound with hydrogen peroxide, then washing it with an antiseptic (chlorhexidine, miramistin or furatsillin solution) and applying a sterile napkin with antibacterial ointment.
After each stool, a thorough toilet of the perineum is necessary, sitz baths and a new dressing are desirable. In case of stool retention, microenemas can be used.
At first, purulent contents, ichor, will flow out of the wound. Sanitary pads will be required. Over time, the discharge from the wound will become less and less.
The period of incapacity for work after an uncomplicated operation is about 8-10 days. Complete healing of a purulent wound usually occurs after 3-4 weeks.
The patient is also warned that partial insufficiency of the anal sphincter may persist for 1-2 months after surgery. This may manifest itself in periodic incontinence of gas and loose stools. For prevention, special gymnastics for the sphincter are prescribed.
Prevention of complications
If a person recently underwent surgery, the following recommendations will help eliminate the likelihood of complications:
- Do not break your diet, strictly follow your doctor’s recommendations, treat the wound, and if problems arise, consult a doctor as an emergency.
- Monitor the temperature, monitor changes; an increase indicates an inflammatory process in the body. You can keep a diary in which you should record your body temperature. You will have to measure it 3 times per knock.
- Try to avoid problems with stool and digestion; constipation and bouts of diarrhea are unlikely to help you recover faster.
- Follow the drinking regime, consume a sufficient amount of liquid every day. This will help normalize the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract.
- Take a course of antibiotics. If treatment is stopped, even with significant improvement in condition, the risk of complications increases. Because the inflammatory process was not completely stopped.
- Maintaining an active lifestyle is also considered a preventive measure, but do not forget about the doctor’s instructions. If the body is weakened, then additional stress will not bring benefit.
- Taking vitamins and immunostimulants should also be regarded as preventing complications.
- You will have to avoid systematic hypothermia of the body, stressful situations, and inflammatory diseases of the nasopharynx.
- During the off-season, increase immunity and, if it occurs, eliminate imbalance in the intestines.
- After complete recovery, prevent parasitic diseases 2 times a year.
A passive lifestyle, bad habits, frequent stress - all this weakens the body and reduces its protective functions. For this reason, you will have to lead a measured lifestyle, play sports, and give up alcohol and smoking.
Recommended video:
Paraproctitis after surgery can be treated in various ways, but an integrated approach is considered optimal. This way you can achieve better results. Correctly planning therapy helps to avoid relapse of the disease and repeated surgery. It also significantly reduces the risk of complications.
Don't hesitate to see a doctor
Often, when pain occurs in the anus, patients do not rush to see a doctor because they are embarrassed to show the doctor their private parts. They self-medicate, buying ointments and suppositories for hemorrhoids in pharmacies, and use dubious recipes from the Internet. All this only aggravates the situation and can lead to complications.
In addition, all this time I have to endure really very strong and growing pain. According to reviews from patients who have undergone surgery, after opening the abscess, the severe pain goes away almost immediately.
Summarizing all of the above, we must say to those who doubt and feel embarrassed: if pain in the anus appears in combination with fever and general malaise, you should consult a doctor as soon as possible, preferably a coloproctologist.
Paraproctitis is a formidable disease, difficult to treat even in the initial stages. The consequences may be irreversible.
Recommendations for preventing relapse
To avoid relapse of paraproctitis, which threatens the re-development of paraproctitis fistula, it is enough to follow simple rules:
- Drink enough fluids daily (up to two liters per day);
- Stick to a balanced diet: with cereals, fresh vegetables, fruits (preferably enriched with fiber - zucchini, pumpkin, plums, bananas, apricots);
- Eat rye and wheat bran, which facilitates bowel movements and eliminates constipation;
- Use laxatives and cleansing enemas carefully;
- Control body weight to avoid obesity;
- Have sufficient physical activity, avoid excessive exercise and heavy lifting.
The Yusupov Hospital in Moscow is equipped with all the necessary medical equipment, which is used in the diagnosis and treatment of any diseases in the field of proctology, including paraproctitis and its complication - paraproctitis fistula. The clinic's proctologists use advanced techniques and the latest technologies in their practice to ensure high treatment results. For a comfortable stay of patients, the Yusupov Hospital has cozy rooms, round-the-clock medical care is provided, and individual nutrition is organized taking into account the diet recommended by the doctor.
Make an appointment
Advantages of our clinic
- Domestic and German laser. There is an opportunity to save money and choose the Mediola laser as an alternative to Biolitec technology.
- Original consumables. We use only consumables recommended by laser manufacturers. Sterile. After use they are destroyed.
- Doctors' experience. The center's proctologists are at the forefront of the use of laser in the treatment of paraproctitis. They achieve excellent results without relapses and with quick recovery.
- Guaranteed positive results. Proctologists will offer treatment only if they are completely sure of a positive result. In case of advanced cases of the disease or any doubts from the doctor, the patient will be sent to the hospital.
- Local anesthesia. We use only local anesthesia, it dramatically reduces rehabilitation time and the period of disability!
- Legal. We treat according to an understandable contract, and upon payment we give a receipt. We follow the rules of European and national clinical guidelines based on Federal Law No. 489 of 2022.
- Anonymity. Complete anonymity and compliance with the medical confidentiality law.
How is the treatment carried out?
- Local anesthesia. Removes pain, but slight discomfort may be felt at a low pain threshold.
- Opening and drainage of the purulent cavity of paraproctitis. Removing pus, washing the cavity with antiseptics. Preparation for exposure to a laser beam.
- Laser processing. Additional local anesthesia is performed, followed by laser treatment of the purulent focus.
- Completion. Applying a bandage. The patient is sent to the ward for bed rest for 2 hours.
What to do after paraproctitis removal?
- It is important to arrive for dressing changes on time. Their regularity after treatment of a purulent lesion is the key to quick recovery and absence of relapses.
- Compliance with diet. Taking systemic antibiotics, ointments and suppositories. Drugs are prescribed individually according to indications.
- It is not recommended to take a full body shower for 1 week, and avoid physical activity for 4 weeks.
After laser removal of paraproctitis, there is no pain. Relief appears. The temperature will normalize, unpleasant phenomena in the rectum and false urge to defecate will disappear.
The technique is actively developing in European countries. The greatest experience is in Germany and the Baltic countries.
INDICATIONS
Laser treatment of a purulent focus of paraproctitis of the rectum on an outpatient basis is carried out for subcutaneous, submucosal, intrasphincteral forms. In all other cases, it is necessary to open and drain the purulent cavity in a hospital setting under general anesthesia.
Contraindications
- Laser surgery is not recommended for paraproctitis in ischiorectal, pelviorectal or retrorectal forms.
- Laser surgery is not recommended for deep forms of lesions, when the purulent process is generalized and drainage installation is required.