Diseases of the gastrointestinal tract occupy a leading position in the list of diseases for children and often lead to unpleasant consequences. Their number increases the younger the child is. The largest category of diseases of the digestive system is dyspepsia in infants - functional nutritional disorders.
Acute disorders of the stomach or intestines are a common pathology of infants, in which, against the background of the clinical picture of the digestive system, signs of deterioration in the general condition, metabolism, and coordinated functioning of all organs and systems appear. Such disorders can provoke serious disruptions in the body's metabolism.
Types of dyspepsia in infants
Dyspepsia in newborns is a preliminary diagnosis, the root cause of which needs to be clarified. Depending on the factors that led to the violation, the following types are distinguished:
- Functional or simple dyspepsia, as a rule, appears as a result of eating food of a certain composition and has the following subtypes:
- Fermentative dyspepsia and its symptoms in infants appear due to the penetration of fermentative microorganisms into the intestines, which was preceded by the excessive presence of carbohydrates in the diet menu. Fermentation processes are provided by such products as honey, flour, beans, cabbage, kefir;
- putrefactive dyspepsia in infants, which is characterized by the prevalence of putrefactive bacteria in the intestines as a result of a disrupted process of digestion of proteins and their rotting (eggs, meat, dairy products);
- the fatty form of the disease manifests itself after consuming excessive amounts of fat;
- The toxic form often develops as a result of improper treatment of the functional form. Escherichia coli, salmonella, staphylococcal, viral infections and other pathogens play an important role in its origin.
- The parenteral type progresses as a “background” disease with another disease. It can appear both in diseases of the gastrointestinal tract and in other pathologies of an infectious nature.
- Also, infants experience so-called “borderline conditions” that do not require treatment. One of these conditions is physiological dyspepsia of newborns, characterized by stool disorder in newborns in the first week of life. The following conditions are characteristic of it: Original feces is a thick, viscous mass of a dark green hue, which is released in the first days of a child’s life.
- After which defecation begins to occur more often, the stool becomes liquid, lumpy with mucus.
- And after a few days it turns into a mushy form that is uniform in color.
Nutritional dyspepsia
The main treatment for nutritional dyspepsia is diet. Its goal is to eliminate the abnormal colonization of the upper intestine with bacteria and eliminate increased fermentation, which negatively affects the intestines of the baby. The easiest way is to deprive the baby of food for 6-12 hours, and then administer easily digestible food.
Treatment regimen
First day
Deprive the baby of breast milk for 6-12 hours, give him only lightly sugared tea with a volume of 200-300 ml during this period. After this, breastfeed 2-3 times so that the baby takes 75-100 ml of mother's milk at a time.
Second day
Prescribe breast milk 4-5 times a day, at a time - a volume of 100 ml. Additionally, give sweetened tea.
From the third to the fifth day
Gradually put the baby to the breast for more and more time until the milk intake at a time reaches 150-175 ml. Be sure to carry out control weighings.
If no improvement in stool is observed, you can temporarily replace part of the breast milk with buttermilk or protein milk (75-100 ml per dose). The addition of plasmon to breast milk is effective - a dose of 5 to 10 grams per 24 hours.
The same principles apply to the treatment of babies who are artificially fed . A child is given only tea for 6-12 hours. Mixtures containing a lot of fats and carbohydrates are excluded from the diet. The baby is fed with concentrated (10%) rice broth in the amount of 100-150 ml per dose.
Starting from the second day, part of the rice broth is gradually replaced with half and half milk and broth. If the effect does not occur, churning is prescribed: first 3 times a day, then 5-6 times, the amount per day is from 600 to 800 ml. It is not profitable to keep a child on churning for a long time, and you need to gradually transfer him to mixtures that are more complete in terms of fat content.
give the same effect as churning . Nutritional dyspepsia is also treated with protein milk. It is taken at the beginning 2-3 times a day, and then the total volume is adjusted to 800 ml per day with the addition of sugar from 2 to 8-10%. Protein milk is given to the baby for a maximum of 3-4 weeks.
Doctors may also prescribe kefir or acidophilus milk for treatment. Treatment regimen:
First day
Tea diet for 6-12 hours, the volume of tea is 200-300 ml. Then give concentrated rice broth, 3-4 times 100-150 ml.
Second day
Give the baby concentrated rice broth 125-150 ml 3-4 times a day and churning or kefir 2 times.
Third day
The child is fed a concentrated decoction 2 times a day and 3 times with buttermilk, kefir or protein milk with 2% sugar, 125 ml per dose
Fourth day
The baby is fed buttermilk, kefir or protein milk 4-5 times a day, 125-150 ml, and concentrated rice water 1-2 times in 24 hours.
Fifth day
Give the baby kefir, buttermilk or protein milk with 3% sugar 5 times a day, 150 ml. As stool returns to normal, fat is introduced into the diet. It is best to add it to buttermilk. Mixtures No. 2 and 3 acidified with hydrochloric or lactic acid, as well as kefir and acidophilic milk, act similarly to buttermilk, because they also lead to the same goal - they stop bacterial fermentation and improve the enzymatic functioning of the baby’s stomach. A mixture of milk with decoction and lime water is sometimes used as a remedy - all parts are mixed in equal proportions. Agar-agar perfectly binds water and regulates intestinal motility. Therefore, it is recommended to enrich milk formulas with agar-agar in an amount of 1%.
Diet therapy in the presence of dystrophy is carried out more carefully, especially with artificial feeding. If a child has severe dystrophy, he is first kept on breast milk for some time, and only then formula is added. In such cases, it is better not to dilute milk with broth and water. Treatment is carried out with buttermilk or protein milk. Make sure that the child is not malnourished. Gradually increase the amount of fats and carbohydrates in the diet. The weight curve improves gradually, do not expect an immediate effect. For parenteral dyspepsia, it is necessary to temporarily reduce the amount of food, exclude fatty mixtures, prescribe acidic mixtures and subsequently carry out treatment as indicated above. Diarrhea will stop when the infectious process is suppressed.
In cases of dyspepsia due to malnutrition, the child's caloric intake increases. Protein milk and larosan are added to the main diet, which affects weight gain.
For acute dyspepsia, which is caused by overfeeding the baby, first give castor oil 1 tsp to remove pathological products from the intestines. If there is severe vomiting, do gastric lavage. To soothe abdominal pain, apply warm compresses to the abdomen. To expel gases, a special gas outlet tube is sometimes used or the baby is given carminative water, chamomile or mint tea, 1 teaspoon each.
To calm the child (after all, one of the symptoms of nutritional dyspepsia is anxiety), warm baths, warm wraps, and taking valerian are recommended. If the stool remains liquid for a long time due to irritation of the colon, the administration of carbolene, aluminum hydroxide, tannalbine is useful.
Causes
In infants, the main root cause of the disease will be a nutritional factor (nutritional dyspepsia), in other words, deficiencies in the child’s diet. Common food causes that cause dyspepsia in newborns may include:
- discrepancy between the volume and composition of food consumed and the capabilities of the digestive system;
- feeding a formula that is not of good quality;
- premature introduction of complementary foods;
- binge eating;
- unformed digestive tract;
- toxic poisoning (in toxic form);
- enzyme deficiency.
Pathology mainly affects children who are carriers of other diseases:
- disorders of the central nervous system,
- rickets,
- protein-energy malnutrition,
- allergic reaction,
- exudative-catarrhal diathesis,
- anemia,
- vitamin deficiency,
- helminthiasis,
- prematurity.
As a rule, dyspepsia manifests itself due to the fact that the enzymatic function of the infant’s digestive system is still imperfect and is unadapted and hypersensitive to any changes in the diet.
Fermentative dyspepsia - slowdown in the absorption of carbohydrates
Fermentative dyspepsia causes pain in the abdominal area.
If carbohydrates are not absorbed in the body, then a state of fermentative dyspepsia develops. At the moment, the clear objective reasons for the appearance of this condition are not clear.
One might think that dyspepsia develops if the diet contains too much fiber.
Another option for the occurrence of this condition is poor-quality chewing of food. In other words, eating on the run, drinking carbonated and energy drinks. The intestinal function is activated in the body, as there is a large amount of acids that irritate the mucous membrane.
Carbonated drinks and foods high in sugar, which are consumed in the summer when the weather is very hot, cause the development of this condition in the body. The intestines absorb harmful substances, thereby poisoning the body, which negatively affects the functioning of the entire digestive system (cyclic process).
When the pancreas does not cope with its task (as a result of functional disorders), the secretion of amylase, as well as other enzymes that contribute to the breakdown of sugar, decreases.
Symptoms of the disease
Excessive amounts of food, frequent feeding, early introduction of complementary foods, and excess flour in a child’s daily menu can cause disruption of the body’s digestive function.
Dyspepsia in newborns is accompanied by the following symptoms:
- weight loss,
- stomach pain,
- indigestion,
- vomit,
- Difficulty in emptying or the stool, on the contrary, becomes liquid, may also bother you.
In many cases, the factors that precede the onset of signs of pathology remain unidentified.
When breastfeeding, the baby loses weight, has frequent vomiting and upset bowel movements. Treatment with medications and other means does not have the desired effect. The child continues to lose weight, gradually becoming skeletal, and the number of bowel movements does not stabilize. Along with this, no characteristic features of rickets in infants were identified.
Manifestations of the disease
Dyspepsia may cause a headache.
Typically, dyspepsia manifests itself in the form of pain that is observed in the upper abdomen, and the person also feels discomfort.
Taking into account how the disease develops, belching, gagging, and other symptoms may also be added. Symptoms usually occur intermittently rather than constantly.
The most important nuance is the wrong diet. Often, normalization of the gastrointestinal tract is carried out independently, without the need to visit a doctor.
The pain subsides after defecation (liquid consistency, light yellow, with signs of fermentation). Typically, this condition is observed throughout the day, and there are no blood spots, since the functioning of only the upper intestines is disrupted. Food may not be completely digested.
A person constantly feels bloated and suffers from flatulence. If toxins constantly enter the body, this contributes to the appearance of headaches. The person becomes irritable, nervous, drowsy.
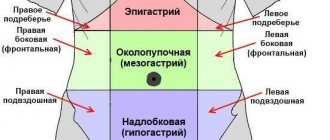
The doctor can detect a swollen abdomen, which, when pressed, rumbles and a splashing sound is heard in the navel area.
Diagnostics
As a rule, the diagnosis of dyspepsia in children includes the following points.
- Analysis of the medical history, complaints and life of the patient.
- Laboratory diagnostics:
- clinical and biochemical blood tests;
- stool tests for occult blood;
- coprogram for putrefactive dyspepsia in an infant - stool analysis.
- Instrumental methods of analysis:
- stomach acid test;
- esophagogastroduodenoscopy (gastroscopy);
- impedance-pH-metry of the esophagus;
- examination of fragments of the gastric mucosa and a breath test for the presence of Helicobacter pylori infection;
- computed tomography (CT);
- Ultrasound of the abdominal organs;
- intestinal colonoscopy;
- electrogastrography;
- radiography;
- esophagomanometry and antroduodenal manometry.
In addition to various studies and tests, it would also be a good idea to consult with a gastroenterologist.
Prevention of dysbacteriosis in babies from the first days of life
Poor sleep and poor appetite are also symptoms of dysbiosis
It is much easier and safer to prevent diseases than to treat them later. An important task for the mother, which she must complete even before the baby is born, is to treat all vaginal diseases and maintain personal hygiene as much as possible.
If during birth the child passes through the birth canal, free from pathogenic and harmful fungal bacteria, then the child will be healthy. The expectant mother must take care of her health.
It is recommended to think about your health while planning pregnancy. In this way, the mother will take care of her unborn child. The main method of preventing dysbiosis is early breastfeeding. Colostrum is an irreplaceable source of essential bacteria, which are essential for the flora of a newborn baby. For the physical development of the baby, early attachment to the breast is necessary.
It is recommended to place the baby on the mother's breast while still on the maternity table.
Physical exercise and regular physical walks for the expectant young mother will bear fruit in the first days of the baby's life. Feeding the baby strictly at a certain time and not overfeeding are factors that have a positive effect on the formation of positive microflora in the body. The diet of a mother who is feeding a child must be properly balanced and include the required amount of proteins and vitamins.
Anti-bloating medications don't always help...
Treatment of dyspepsia in infants
Necessary measures to ensure the weakening and complete elimination of symptoms in a simple form of the disease are regulating the diet, following age-specific and individual rules of behavior, and refusing to take certain medications.
A change in climatic conditions, moving out of town or changing a frosty climate to a warmer southern weather regime can also help.
Taking into account that the main cause of the disease in most cases will be malfunctions of the digestive system, doctors prescribe prokinetics - medications that stabilize gastrointestinal motility.
In case of an ulcer-like type and increased acidity, the child can be given antisecretory antiulcer drugs containing components that lower acidity, h2-histamine receptor blockers (Famotidine, Ranitidine), proton pump inhibitors (Omeprazole).
Home remedies may also help ease the symptoms of the disease. To improve the condition, the patient is recommended to drink decoctions based on medicinal herbs. But the use of traditional methods requires mandatory consultation with a doctor.
Signs of the development of dysbiosis in children
Diathesis as one of the manifestations of dysbiosis
What signs does a young mother encounter when an imbalance develops in her baby? There are several known signs that, if detected in a baby, should promptly contact your treating pediatrician. Signs that appear during dysbacteriosis:
- the baby’s feces become a specific green color and have a sharp sour or putrid odor;
- regular constipation or diarrhea in a baby at a very early age;
- bloating, which is accompanied by colic;
- vomiting or regurgitation immediately after feeding;
- the child sleeps poorly, the baby’s general condition worsens, cries, gains weight poorly, refuses a bottle or breast;
- the child’s immunity is weakened;
- allergies can also be one of the signs of imbalance.
But don’t immediately fall into a state of panic. Such signs can be present in an absolutely healthy child and do not necessarily indicate dysbacteriosis. Such symptoms can also indicate that the digestive system of a newborn child is not fully formed.
The following factors cause a lack of food enzymes at a very early age, which will lead to the fact that food does not have time to be completely digested, rotting of leftover food, and the formation of painful gases that irritate the walls of the child’s still so young intestines:
- sudden overfeeding;
- feeding newborn babies not according to time, but according to the child’s demand;
- switching from one type of baby food to another.
These symptoms are similar to those that occur when there is an imbalance. But in any case, if you detect such signs in your baby, you should definitely consult a doctor and confirm or refute your suspicions.
Prevention
Preventive measures include diet and following the timing of the introduction of complementary foods.
The child should regularly visit the pediatrician, undergo periodic examinations and, in case of any illness (especially if there are infections), undergo a full course of treatment.
After functional dyspepsia, newborn children most often recover within a few days; it does not provoke any exacerbations or complications of the child’s condition. However, if the body's protective function is too weakened, a transition from a functional form to a toxic one may occur. In this case, everything depends on the speed and quality of the first aid provided.
In general, if you arm yourself with patience, you can achieve good results over time when treating dyspepsia syndrome in children.