The human intestine contains a great variety of different bacteria and microorganisms, both beneficial and pathogenic. The largest number are lactobacilli and bifidobacteria. There is a kind of balance in the numerical ratio of all intestinal bacteria, this is called microflora. When this balance is disturbed, dysbiosis occurs. Positive microorganisms simply cannot cope with their work and do not have time to produce a sufficient amount of useful substances. What drugs exist to restore intestinal microflora?
Types of drugs that restore intestinal microflora
To restore the disturbed balance, there are a large number of drugs for intestinal microflora, which can be divided into three groups:
- Probiotics containing live cultures of microorganisms (Linex, Bifidumbacterin, Acepol, etc.)
- Prebiotics are drugs that enhance the growth and reproduction of beneficial bacteria. These include Duphalac, Lactusan and Normaze, which contain lactulose.
- Synbiotics are a complex of living bacteria and substances that enhance their growth. Among the most famous Biovestin are Lacto, Bifido-bak, Maltidophilus.
Probiotics, in turn, can also be divided into several subtypes. Preparations containing only one strain of bacteria include Lactobacterin, Bifidumbacterin and others. If a drug contains several strains of bacteria, it is called multicomponent. The most famous among multicomponent drugs is Linex. Probiotics containing live bacteria are Probifor, Bifidumbacterin forte.
Probiotics are generally safe and do not cause any side effects. They cannot always be replaced with folk remedies; it is better to take them together or use traditional medicine to consolidate the results. However, it is important to remember that not all advertising is true; before purchasing any drug for dysbiosis, you must consult a doctor, and also choose medications only from well-known manufacturers and in trusted pharmacies.
Probiotics
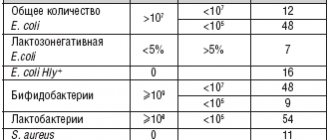
The human intestine contains a huge number of bacteria. They are mainly found in the large intestine. It is estimated that there are more than 40 billion bacteria in the large intestine. The main microorganisms inhabiting the intestines are bifidobacteria and lactobacilli .
Mechanism of action of probiotics
Probiotics act on intestinal microbes by influencing immune mechanisms in the intestinal mucosa, promoting the production of beneficial metabolic products, and interacting with beneficial and harmful bacteria. All this leads to the suppression of pathogenic (harmful) microbiota, increased growth of beneficial bacteria, reduced inflammation in the intestinal wall, and strengthened the gastrointestinal tract barrier. These mechanisms and effects help reduce the frequency and severity of diarrhea, which is the most common reason for prescribing probiotics in children.
Indications for the use of probiotics in children
Probiotics are also used as drugs in the treatment of a number of diseases.
Probiotics are used to treat and prevent many diseases. According to the practical recommendations of the World Gastroenterology Organization (WGO), they can be used in the following cases:
- Prevention of intestinal cancer.
- Treatment and prevention of diarrhea. Probiotics reduce the duration of diarrhea in children by approximately one day.
- Prevention of antibiotic-associated diarrhea (associated with taking antibiotics).
- Prevention of radiation diarrhea.
- Treatment of infection caused by H. pylori. Given the high prevalence of helicobacteriosis, the issue of treating this infection remains relevant. Due to the high frequency of antibiotic use, this bacterium is highly resistant to traditional drugs for its treatment. Probiotics help reduce the severity of undesirable effects of treatment for this infection. It has been suggested that adding certain types of probiotics to a comprehensive treatment may help get rid of this bacterium more quickly.
- Prevention and treatment of hepatic encephalopathy.
- In order to improve the immune response.
- Inflammatory bowel diseases. These diseases include ulcerative colitis and Crohn's disease. The administration of probiotics is justified in ulcerative colitis, while in Crohn's disease no definitive data have been obtained on the effectiveness of their use.
- Irritable bowel syndrome (IBS). IBS is a functional disease that responds well to therapy. This disease is often accompanied by pain and bloating. The use of probiotics has been shown to reduce pain and bloating, which improves the overall well-being of the child.
- Infantile colic. Several types of probiotics have been shown to reduce crying in breastfed newborns and infants. You can find out more about the causes of this disease, its symptoms and treatment methods in our article.
- Impaired absorption of lactose. The use of probiotics can reduce the severity of symptoms associated with lactose intolerance.
- Necrotizing enterocolitis.
- Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease.
These recommendations also paid attention to the effect of probiotics in diseases other than gastroenterological diseases. The effect of their use in bacterial vaginosis was noted, which made it possible to reduce the severity of this disease. They reduce the manifestations of dental caries, reduce the number and duration of respiratory infections. Probiotics also help prevent the development of atopic dermatitis in newborns. The proven effect on allergies in children led to the development of recommendations from the World Allergy Organization for the use of probiotics during pregnancy, breastfeeding and weaning in families with an increased risk of developing allergies.
Probiotics reduce the likelihood of tooth decay.
Anti-dysbacteriosis drugs for children
Dysbacteriosis in a child most often occurs when taking antibiotics that destroy the natural intestinal microflora. Often, after a course of antibiotics, mothers observe in their children poor appetite, diarrhea, constipation, vomiting, decreased immunity, as well as various allergic reactions due to increased intestinal permeability, and rash.
Infants can do without special medications. Recently, pediatricians have been inclined to believe that mother's breast milk is the best medicine. Therefore, mothers are advised to give up complementary feeding for a while and breastfeed only.
Let's take a closer look at what medications can be given to children and at what age:
- Linux. This is a biologically active food supplement, has a special dosage for children, and is available in the form of bagged powder. It is believed that this drug can be given from birth, observing a certain dosage. You can take it for up to a month, on the recommendation of your doctor.
- Primadophilus. This is a dietary supplement used for the intestines in both children and adults. For children, this supplement is available in powder form. It can be added to breast milk, formula, drinks, and taken with meals. It should only be stored in the refrigerator.
- Hilak forte. This drug is available in drops. It can be used from the first days of life. Infants are given from 15 to 30 drops at a time. However, it should not be given with milk or dairy products.
- Acipol is allowed to be taken by children from 3 months, 1 capsule 2-3 times a day. Of course, infants will not be able to swallow the capsule, so you need to carefully open it and pour the powder into the liquid.
- Normobakt. Available in powder form. Infants are given half a sachet per day, dividing the dose several times. Powder can be added to liquid, but not hot. The course of taking the drug is no more than 15 days.
- Bifidumbacterin. The drug in powder form is dissolved in a small amount of liquid and drunk without waiting for complete dissolution. For newborns, you can add it to milk or formula. It is advisable to take Bifidumbacterin with meals.
Probiotics for newborns
The neonatal period is short and is about 28 days. It is at this time that the baby’s immune system adapts to the new environment. It should be borne in mind that throughout the pregnancy the baby was protected by the walls of the amniotic sac and the fetus existed in an almost sterile environment. The rupture of a bladder and childbirth are a huge shock for the baby, as well as for his immune system, which, like its owner, can do almost nothing at first. Microorganisms that meet a newborn settle on the skin and mucous membranes, multiply and create colonies.
It should be recalled that this is a normal process, that sterile cleanliness is unacceptable even for a child’s room, since it interferes with the formation of protection.
The formation of the correct microflora is facilitated by bacteria that enter the intestines with mother's milk. Mostly it will be useful, but among this “army” there may also be pathogens. In addition, there is a risk of dysbiosis in newborns if the mother took antibiotics during breastfeeding.
Modern children experience health problems almost from the first days of life. As a rule, they are easily corrected by mild means, which include probiotics.
If in the last century, in the 70-80s, the normal microflora of a newborn was formed already on the 8-9th day from the moment of the first breath, then in the 2000s, complete formation is completed only by one and a half to two years. The immune system does not work at full strength, children get sick more often and longer.
The use of probiotics helps with predisposition to:
- allergies;
- dysbacteriosis;
- constipation, diarrhea, and other stool disorders;
- frequent illnesses.
Probiotics, which include Biovestin, can be given to infants in the first year of life. This measure will help the beneficial microflora cope with its task and deliver the required amount of lacto- and bifidobacteria. The drug is effective and safe, easy to use and comes in liquid form, which allows you to add the required dose to breast milk, formula or water.
Lacto- and bifidobacteria, as well as the products of their metabolism, are the main helpers of the newborn’s immunity. It is especially important to receive probiotics for children who, for one reason or another, are bottle-fed. Deprived of breast milk, and therefore of immune protection transmitted from the mother, such babies are prone to more difficult adaptation to foreign flora in the first months.
Indications for use
It is recommended to take children's probiotics after antibiotics to restore intestinal microflora. Such drugs are prescribed to premature babies to populate the digestive tract with beneficial bacteria, and are also used for:
- sensitivity to lactose, which provokes negative reactions from the gastrointestinal tract;
- diagnosing seasonal allergies in order to relieve a number of its symptoms;
- the formation of colic during the development of the digestive system;
- detection of violations associated with the child’s refusal to eat;
- insufficient weight gain.
Probiotics are also prescribed for constipation. They are also necessary when detecting dermatological problems. Often such pathologies are associated with inadequate functioning of the gastrointestinal tract - probiotics can cope with most of them. In this case, the child is prescribed complex treatment prescribed by the doctor.
What should children's probiotics be?
Safety and absence of side effects are one of the requirements for children's probiotics. Preparations for restoring microflora must meet the following conditions:
- resistance to acids – bile and hydrochloric;
- resistance to pancreatic enzymes;
- preservation of the viability of bacteria during the passage of the gastrointestinal tract;
- the ability to colonize the digestive system with beneficial bacteria.
The best probiotics for restoring microflora in children are those that do not injure the intestines. It is also important to exclude the possibility that harmful bacteria will acquire an antibiotic resistance gene. Children's probiotics should remain stable under normal storage conditions, as well as when environmental factors change once they enter the intestine.
What are probiotics?
Probiotics for the intestines of children are a group of living microorganisms that act as a complete microflora of the digestive tract. When they enter the child’s body as part of drugs, they retain their viability. Widely known probiotics include Saccharomycetes yeast, bifidobacteria and lactic acid bacteria. Some types of Escherichia coli and bacilli can also be classified as such.