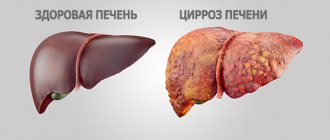
In particular, macropreparations and micropreparations allow us to obtain maximum information about the course of the disease. The macropreparation makes it possible to visually assess the condition of the liver - they study the color, shape, size of the organ, the condition of the blood vessels, changes in the liver mucosa. However, the macropreparation can only be studied after the patient’s death.
To study a micropreparation, an element of tissue is taken from an organ, and after certain manipulations and special preparation it is studied under a microscope.
In case of liver cirrhosis, a microslide allows you to obtain information about the state of the organ cells. The structure, color, uncharacteristic neoplasms, and the number of fibrous and functional tissue cells are assessed. Normally, the ratio of liver and fibrous cells is 90% to 10%, respectively; with this disease, the number of cells is equal or there is a predominance of connective tissue.
Therapeutic measures for cirrhosis depend on the etiological factors of the pathology, the degree of compensation, activity, existing complications and associated disorders. However, today there are no drugs for the treatment of liver cirrhosis that can completely eliminate this disease.
Medicines for liver cirrhosis help correct the consequences of this disorder, prevent further destruction of the organ, and normalize the well-being of the sick person. It is possible to completely get rid of this disease only through organ transplantation.
Content:
- How does alcoholic cirrhosis of the liver develop?
- Classification
- Symptoms of the disease
- Diagnostic features
- How to treat alcoholic cirrhosis of the liver
- How long do people live with cirrhosis of the liver?
The human liver is the main organ that protects the body from the effects of poisons. It takes the brunt of alcohol and neutralizes toxins. In this difficult and sometimes unequal struggle, it itself is gradually being destroyed. As a result, inflammation develops - hepatitis, which, with continued alcoholization and the destructive influence of alcohol, turns into alcoholic cirrhosis of the liver. This complication is life-threatening and, in the absence of sobriety and adequate treatment, leads to disastrous consequences. Therefore, the sooner the patient begins to get rid of this disease, the greater his chances of regaining health. Healing pathology is included in the tasks of the main course of anti-alcohol treatment. Hepatologists deal with advanced stages.
Unconventional treatment
To treat this disorder, not only medications are used, but also alternative medicine. One of the most effective plants is celandine; for liver cirrhosis, it is used as follows:
- Take celandine juice in a small amount before each meal. In order to avoid possible complications, start taking this drug with a drop, gradually increasing the volume to 1 teaspoon. The course of treatment lasts until a lasting therapeutic effect is obtained.
- Prepare a tincture of celandine, take the medicine for 3 months, 15 drops per day.
Another effective folk remedy, which is also used in official medicine, is milk thistle extract. The plant has a hepatoprotective, stabilizing, choleretic effect, and reduces the concentration of liver enzymes.
Milk thistle extract also has an antioxidant effect, supports liver function, and relieves spasms.
Use the product three times a day, 1 tablet before meals. The duration of the treatment course is about 2 months.
In addition to the use of medications and folk remedies, for successful treatment of liver cirrhosis, it is necessary to completely abstain from alcoholic beverages and adhere to a strict diet.
How does alcoholic cirrhosis of the liver develop?
This painful process leads to the death of cells - hepatocytes. In their place, fibrous connective tissue appears, which forms the essence of cirrhotic changes. In the classification of all existing cirrhosis, alcoholic diseases occupy from 30 to 50%. Ethanol entering the blood is neutralized by hepatocytes. Free radicals released during detoxification destroy the cell membranes of the organ. Vessels also suffer from destruction. Their subsequent spasm and hypoxia lead to worsening destruction. The dead zones are replaced by fibrous formations. The main functions of the liver are gradually and progressively lost. In advanced stages they are irreversible. Only transplantation can help the patient. As a result of observing people who drink, it was revealed that the cirrhotic process develops in 35% of alcoholics. The disease occurs more often in men, and is more severe in women.
Pathogenetic therapy
In a significant proportion of patients, the etiological factors of cirrhosis remain unknown. These patients use therapy aimed at stopping the primary pathogenetic mechanisms of the pathological process: reducing the level of iron in hemochromatosis and copper in Wilson-Konovalov disease; prescription of immunosuppressants for cirrhosis that developed as a result of autoimmune hepatitis, etc. The leading role in the progression of cirrhosis belongs to the persistence of inflammatory-necrotic processes and the associated increased fibrogenesis. Mechanisms that maintain constant CP activity include the action of etiological factors; increased functional load on hepatocytes, accumulation of toxic substrates in them, leading to increased lipid peroxidation (LPO), disruption of the stability of cell membranes; disruption of the blood supply to the liver parenchyma (regeneration nodes) due to capillarization of sinusoids and a decrease in the vascular bed; inclusion of autoimmune mechanisms.
Theoretically, the main goal of pathogenetic therapy for cirrhosis ultimately comes down to interrupting the processes of fibrogenesis and resorption of fibrotic tissue in the liver [10]. It is known that the main producer of connective tissue components in the liver is activated stellate cells. The leading regulatory substances involved in the activation, proliferation and migration of these cells are transforming growth factor 1β, platelet-derived growth factor, fibroblast growth factor, epidermal growth factor, tumor necrosis factor α, thrombin, lipid peroxidation products and necrotic hepatocytes, acetaldehyde, bile components, accumulating during cholestasis, etc.
Due to the fact that drugs regulating the fibrogen-producing function of stellate cells are still at the stage of experimental research, to prevent the progression of fibrosis, drugs conventionally designated as “hepatoprotectors”, which have antioxidant, cytoprotective and antifibrotic effects, have become widespread. The main hepatoprotectors with proven clinical effectiveness used in the treatment of patients with cirrhosis are UDCA (Ursosan, Ursofalk), essential phospholipids (Essentiale forte N, Eslidin), which in addition to phosphodylcholine include meteonine, which stimulates the synthesis of endogenous phospholipids, silymarin (Legalon), ademetionine (Heptral). The mechanisms of action of all of these hepatoprotectors include: 1) increasing the detoxification function of hepatocytes as a result of increasing the reserves of glutathione, taurine, sulfates and activation of enzymes involved in the oxidation of xenobiotics; 2) stabilization and repair of cell membrane structures caused by blockade and binding of lipid peroxidation products; 3) indirect antifibrotic effect, mediated by relieving hepatocyte necrosis and reducing the content of lipid peroxidation substrates in liver cells. At the same time, it has been shown that essential phospholipids and silymarin have a direct antifibrotic effect due to a decrease in the activity of enzymes involved in the synthesis of connective tissue components and/or stimulation of the activity of collagenases in the liver [11, 12]. To resolve intrahepatic cholestasis, two hepatoprotectors are used - UDCA and ademetionine, which restore transport systems for bile components, promote the excretion of xenobiotics from the hepatocyte into the bile and the flow of bile through the intrahepatic bile ducts. In this case, the point of application of ademetionine is predominantly lobular (hepatocellular and canalicular), UDCA - lobular and extralobular (ductular) cholestasis.
The main factors determining the choice of hepatoprotector for chronic liver diseases, including cirrhosis, include the degree of activity of the pathological process, the pathogenesis of hepatocyte necrosis (increased lipid peroxidation, immune or autoimmune reactions), the presence of cholestasis, and the need for long-term antifibrotic therapy [13]. The etiology of the disease is of certain importance, especially if etiotropic therapy is not possible.
In case of a stable compensated course of cirrhosis in the absence of complications of PH and significant deviations in biochemical liver tests, the drugs of choice are hepatoprotectors with a direct antifibrotic effect: essential phospholipids (Essentiale forte N, Eslidin) and standardized silymarin (Legalon). An important role is also played by UDCA, which additionally has anti-inflammatory, immunomodulatory effects and an anti-apototic effect, which is especially important in viral cirrhosis.
Currently, the duration of antifibrotic therapy is not clearly defined. However, it is known that the time frame for proteolysis of fresh accumulations of the extracellular matrix that occurs during hepatocyte necrosis is 6 weeks or more [14]. Consequently, if it is possible to eliminate or block the effect of the etiological factor, antifibrotic therapy is prescribed for an average of 3 months. With the development of cirrhosis, therapy aimed at slowing down the rate of fibrosis should be constant. Taking into account the multifactorial pathogenesis of hepatocyte necrosis in cirrhosis, it is advisable to alternate and even combine drugs with an antifibrotic effect, with each of them taken for at least three months. An approximate scheme of alternating drugs for cirrhosis: Essentiale forte N 2 capsules 2 times a day for 3 months, then Legalon 140 mg 2 times a day for 3 months, then Eslidin 2 capsules 2 times a day for 3 months, then Ursosan 10–15 mg/kg/ day (250–500 mg 2 times a day) 3 months, etc. If patients have biochemical signs of cholestasis (increased serum levels of alkaline phosphatase and γ-glutamyl transpeptidase, regardless of bilirubin content), the drug of choice is UDCA (Ursosan or Ursofalk ) at a dose of 15 mg/kg/day, divided into 2-3 doses, which is taken for a long time - at least until cholestasis resolves.
When signs of decompensation of the process appear or increase due to toxic influences (alcohol, drugs, including herbs) or the presence of autoimmune reactions, which is accompanied by the development of hyperbilirubinemia, hypoalbuminemia, hypergammaglobulinemia, possibly an increase in the level of aminotransferases, as well as complications of PG, the primary goal of therapy is a rapid decrease in activity process. For this purpose, glucocorticosteroids are used, which block the production of proinflammatory cytokines, stabilize cellular and lysosomal membranes, bind free radicals, induce protein production, etc. [15].
For many years, to achieve a quick effect and prevent side effects, we have been using a course of pulse therapy with prednisolone at a dose of 3 mg/kg × 6 (210–360 mg) or methylprednisolone - 500 mg intravenously once a day for 3 days. Pulse therapy with prednisolone is repeated at intervals of 3–5 days, with an average of 2–4 courses. If indicated, oral prednisolone 40–20 mg/day is subsequently continued with a step-by-step dose reduction to 5–10 mg per week. In the presence of biochemical signs of cholestasis, Ursosan 15 mg/kg/day is simultaneously prescribed for 3 or more months in combination with 10–15 days of intravenous administration of ademetionine (Heptral) 800 mg/day; in the absence of cholestasis, essential phospholipids or Ursosan 10 mg/day kg/day, which lasts for at least 3 months. All patients are also shown parenteral (preferably intravenous) administration of B vitamins, primarily vitamin B12 at 1000 mcg/day for 10–14 days, followed by a dose reduction [16]. It should be noted that steroid pulse therapy is a generally accepted method for quickly stopping inflammatory reactions caused by excessive production of proinflammatory cytokines, as well as autoimmune genesis, especially for patients who have contraindications to long-term treatment with glucocorticoids [17].
If it is impossible to carry out etiological therapy for viral cirrhosis, the main role is given to UDCA - Ursosan 10 mg/kg/day for 6 months or more. However, in the presence of liver steatosis, the drug of choice is essential phospholipids: Essentiale forte N or Eslidin 2 capsules 2 times a day until the process resolves. It should be noted that UDCA and other hepatoprotectors are ineffective in decompensated cirrhosis, the main method of treatment for which is liver transplantation.
Classification
The disease is divided according to changes in the organ and severity. The following types of cirrhosis are distinguished:
- Small-knot.
- Large-knot.
- Mixed.
Stages of alcoholic cirrhosis of the liver:
- Compensated – without pronounced symptoms.
- Subcompensated – with initial manifestations, but with preservation of functions.
- Decompensated – accompanied by partial and then complete failure of functioning.
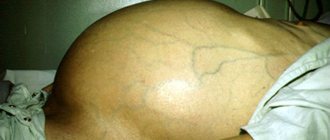
Ascitic syndrome
With the development of ascitic syndrome, in addition to the use of medications, the patient must adhere to a diet with a low sodium content. Every day, diuresis is determined (the daily norm is 0.5-1 l), the patient is regularly weighed and electrolyte parameters are monitored. If the volume of daily diuresis is less than 300 ml, the doctor prescribes diuretics.
For liver cirrhosis and the development of ascites, the most effective diuretics are aldosterone antagonists - veroshpiron and aldactone. The daily dose is up to 200 mg, after 7-10 days it is reduced to 100 mg per day, then diuretics perform a supporting function - up to 75 mg per day, this dosage of the drug is used for several months and even years. If the use of aldosterone antagonists does not bring the expected therapeutic effect, thiazide diuretics (furosemide, Lasix) are prescribed. These drugs are used every other day, 40-80 mg per day.
Symptoms of the disease
As such, there are no symptoms at the early stage of compensation. On this basis, identifying the cirrhotic process is quite difficult. Therefore, the disease is not detected for the first few years. Initial suspicions arise against the background of hepatitis with increased organ size. When receiving compensation, the patient complains about:
- Decreased appetite and nausea.
- Emaciation.
- Weakness.
- Belching, heartburn, flatulence.
- Unpleasant sensations in the right hypochondrium.
When examining the patient, an increase in the size of the liver borders is determined. At the stage of subcompensation, the following is revealed:
- Severe asthenic syndrome: constant weakness and increased fatigue, apathy, depression.
- Great emaciation with aversion to food.
- Low blood pressure.
- Tachycardia.
- Redness of the skin of the face, hands and feet.
- Visible enlargement and palpation of the parotid glands.
- Specific obesity: thin limbs and fat deposits in the abdomen and thighs.
- Gynecomastia in men.
- Testicular atrophy, infertility, impotence.
- Changing fingers in the form of drumsticks.
- Yellowish skin with spider veins.
- Contractures of the muscles of the palms with gradual loss of their functions.
Decompensation is characterized by:
- Signs of portal hypertension with ascites - accumulation of fluid in the abdominal cavity.
- Rectal hemorrhoidal and esophageal (esophageal) bleeding.
- Jaundice with liver failure, enlarged spleen.
- Vomiting, complete lack of appetite, constant diarrhea.
- Coma.
- Hepatic encephalopathy with personality changes and disturbances of consciousness.
Palpation of the abdomen reveals a sharply compacted liver. High numbers of transferases indicate an advanced process. Cirrhosis is often complicated by dysfunction of the lungs, heart, and pancreas. Polyneuropathy appears on the part of the nervous system.
Symptomatic therapy
To reduce and maintain portal pressure at the lowest possible level, as well as to prevent portal crises, a number of drugs are used that reduce the volume of circulating blood (spironolactone, furosemide), the volume of cardiac output (non-selective β-blockers - propranolol or nadolol), the tone of the portal and collateral veins (vasopressin or somatostatin), increasing the tone of the visceral arteries (vasopressin or somatostatin/octreotide). Traditionally, most patients with cirrhosis are prescribed a continuous dose of propranolol 10 mg 3–4 times a day, followed by dose adjustment, which is considered adequate when the heart rate decreases by 30% of the initial one in combination with normal blood pressure (BP). If there are contraindications or the development of side effects when taking propranolol, drugs from other groups are used.
Diagnostic features
When identifying cirrhotic changes, the existing symptoms are taken into account. Additionally, clinical and biochemical blood tests are taken from patients.
They define:
- Anemia.
- Less commonly, leukocytosis.
- Decreased platelets.
- Increase in gamma globulins.
- Increase in AST (more) and ALT.
Ultrasound data plays an important role. They reveal a decrease in the size of the organ and foci of fibrosis. Computed tomography provides an even more accurate picture. With its help, not only the structure is assessed, but also pathological changes in nearby anatomical formations. Informative methods include elastography, and the most accurate is liver biopsy. All obtained data are examined using a special Child-Pugh scale, which allows you to accurately determine the phase of the disease: compensated, subcompensated, decompensated.
Epidemiology of hepatitis B
According to the World Health Organization (WHO), up to two billion people (30% of the population) worldwide are infected with the hepatitis B virus. Of these, 300 to 500 million are carriers of the virus, that is, a source of infection.
HBV infection is the biggest problem in developing and poor countries in sub-Saharan Africa, China and Southeast Asia. In underdeveloped countries, most infections occur in the perinatal period or early childhood. In developed countries, sexual transmission is most common. An estimated 500,000 to 700,000 people die each year from HBV infection, and the condition is associated with acute and chronic liver disease.
Hepatitis B is the ninth leading cause of death in the world.
Recently, the incidence rate (the number of new cases) has begun to fall. The largest decrease was reported among adolescents and young adults, which may be attributed to vaccination in this age group.
How to treat alcoholic cirrhosis of the liver
Therapy implies that the drinker must completely stop drinking alcohol. Only in this case is it possible to achieve a positive result. The second important condition for healing is the selection of a special diet. The food should be dominated by products containing a complete complex of proteins and vitamins. Fried, smoked, salted and preserved foods are excluded. These goals are best met by the fifth liver table. Drug therapy includes:
- Long-term use of hepatoprotectors.
- Ursodeoxycholic acid.
- Multivitamins. After the injection course, they continue to be given in tablets.
- Hormone therapy.
- Ademetionine is the best way to restore and stimulate hepatocytes, protecting them from destruction. It can improve the flow of bile, has detoxifying properties and protects the brain from the effects of poisons. It has an antidepressant effect.
- Protease inhibitors. With their help, inflammatory phenomena are reduced and fibrosis processes are prevented.
Treatment of complications includes eliminating the cause of portal hypertension (increased pressure in the hepatic vein system) by restricting blood flow in the veins of the esophagus. For this purpose they prescribe:
- Pituitary hormones.
- Nitrates.
- Beta blockers.
- Diuretics.
Lactulose is prescribed for intestinal detoxification and improvement of digestive processes. When ascites appears, large doses of diuretics and albumin are administered. Excess fluid from the abdominal cavity under the influence of drugs is actively excreted by the kidneys. When hepatic encephalopathy develops, the following is carried out:
- Active detoxification.
- Antibacterial therapy.
- Prescribing a special diet to minimize protein.
In case of complete liver failure, it is recommended to treat the patient in a surgical hospital for the purpose of organ transplantation.
Route of transmission and risk groups
The source of infection is people. In infected people, the virus is found in quantities sufficient to infect sensitive contacts in:
- blood;
- saliva;
- cerebrospinal fluid; sperm;
- vaginal discharge
- other body fluids.
Transmission of the virus from person to person occurs through parenteral contact with blood and other infected body fluids:
- sexual contact;
- close family contact (through skin and mucous membranes);
- intravenous drug injection;
- during perinatal transmission from an infected mother to her child;
- transfusion of blood and blood derivatives (no longer such a significant source of infection, since blood is tested for the presence of hepatitis B virus) and tissue and organ transplantation;
- in medical and other institutions in contact with infectious material (infected needles, surgical instruments, during tattooing, piercing, acupuncture, etc.).
The key source of infection is people who carry the virus but do not have symptoms - asymptomatic carriers. It's important to note that about 30% of people have no symptoms!
How long do people live with alcoholic cirrhosis of the liver?
Prognostic expectations depend on the stage of the disease, complete abstinence from alcohol, the age of the patients, compliance with dietary recommendations and existing complications. The more advanced the form of the disease, the worse the survival rate. The answer to the question of clients of drug clinics: does alcohol cause cirrhosis of the liver is always an unequivocal yes.
The text was checked by medical experts: Head of the socio-psychological service of the Alkoklinik MC, psychiatrist-narcologist L.A. Serova.
CAN'T FIND THE ANSWER?
Consult a specialist
Or call: +7 (495) 798-30-80
Call! We work around the clock!