According to the World Health Organization, almost every child living on our planet in preschool age experiences viral gastroenteritis (VG) at least once, and most children under the age of 5-6 years experience this disease several times.
Statistics show that this disease occurs in all countries of the world and in a wide variety of families, regardless of the race and socioeconomic status of the parents. Parents themselves also get sick when a child becomes infected in kindergarten and brings the infection to the family, from where the disease can spread to others. Every year, CH, popularly called intestinal flu, causes about 140 million cases of infectious diarrhea in the world. This disease is not at all as harmless as it seems. About half a million cases of viral gastroenteritis are fatal. Therefore, each of us needs to know what this disease is and how to deal with it.
- Stomach flu and methods of infection
- Symptoms of intestinal flu
- Why is intestinal flu dangerous?
- Disease prevention
- Diagnosis and treatment
What is intestinal flu and methods of infection
Viruses that cause intestinal flu began to be studied not so long ago - in 1973. Then, Australian scientists from the Royal Children's Hospital in Melbourne for the first time discovered special pathogenic microorganisms in the duodenal mucosa in children who suffered from serious gastrointestinal disorders.
Viruses that cause disruption of the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract are part of a large group of acute intestinal infections, which are second only to ARVI in frequency. There are many viruses that cause intestinal flu, but a vaccine so far exists only against rotaviruses. Given the widespread prevalence of this disease, in some countries rotavirus gastroenteritis is included in the National Vaccination Calendar. In the Russian Federation, vaccination against this disease is included in the Calendar of preventive vaccinations for epidemic indications. But at present, there are no criteria for determining an unfavorable epidemic situation for this infection in a certain territory.i
Gastroenteritis in children and adults can also be caused by the following types of viruses:
- noroviruses;
- caliciviruses;
- astroviruses;
- adenoviruses;
- coronaviruses;
- enteroviruses;
- rotaviruses.
The source of infection in all cases is the virus carrier, who himself may not be sick. In approximately 30% of cases, several pathogens are involved in the infectious process, which can complicate treatment.
There are fecal-oral routes of infection, and outbreaks of infection caused by contamination of water and food are also common. The sporadic nature of the incidence is characterized mainly by contact and household transmission of the virus. Often, viruses that can cause gastroenteritis have an excellent ability to survive in environmental conditions and be transmitted from person to person.
Contrary to the belief of many parents, intestinal flu is active not only in the summer, at resorts. According to statistics, in Russia a significant number of cases of CH disease occur during the cold season, from November to April. Infection occurs inside kindergartens, schools, children's clubs, and even intrahospital, where there is overcrowding and a long stay of children in one place.
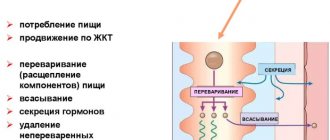
Having penetrated the body, viruses begin their vigorous life activity in the mucous membrane of the gastrointestinal tract, preventing the synthesis of digestive enzymes. This leads to increased osmotic pressure and the appearance of a large volume of fluid and electrolytes in the intestinal lumen. This is how diarrhea begins and other symptoms characteristic of intestinal flu develop, which must be treated with the help of a doctor.
Diagnosis of fungal infection
To diagnose a fungus in the body, it is necessary to identify the clinical signs characteristic of a given disease, and then conduct a series of laboratory tests to identify the type of fungal infection (this is extremely important for further treatment).
Laboratory tests necessary to diagnose a fungal infection:
- Aspergillus fumigatus, DNA [PCR];
- Candida albicans, IgG, titer and DNA [real-time PCR];
- Analysis of vaginal microbiocenosis, including 8 indicators and quantitative DNA [real-time PCR];
- Sowing Candida spp, yeast-like fungi.
Other tests needed to diagnose a fungal infection:
- Ultrasound, which allows you to identify space-occupying formations of a pathological nature that may occur due to a fungal infection affecting internal organs.
The most common symptoms of stomach flu
The incubation period for intestinal flu can last only 12 hours – i.e. infection can occur, for example, in the morning, and by the evening you will feel symptoms of the disease. But in some cases, it may take up to five days for clinical signs to appear. According to the severity of the disease, CH is divided into mild, moderate and severe forms. There are atypical forms of the disease, when it manifests itself differently from the majority of those infected with this infection.
As a rule, the onset of the disease is acute, and the symptoms at first may resemble the clinical signs of ARVI - there is an increase in body temperature, runny nose, redness in the throat, pain during swallowing, conjunctivitis and a dry cough. Nausea also appears, the patient is bothered by frequently recurring vomiting, diarrhea, flatulence, discomfort and pain in the upper abdomen and umbilical region. A loud, audible rumbling in the stomach may be disturbing. In this case, the stool may have a strong unpleasant odor, mixed with mucus and foam. Depending on the severity of the disease, diarrhea with intestinal flu can occur from three to twenty or more times a day.
In addition, common symptoms of CH include lethargy and weakness, decreased appetite, pale skin, headaches, dizziness and even fainting. Children may experience limb cramps and a sharp drop in body weight.
In adults, CH may also be asymptomatic or present with minor intestinal upset. At the same time, such a person can actively infect relatives and colleagues. As a result, within three to five days, almost everyone around can become infected and with rapid manifestation of symptoms, when treatment will need to be treated for a fairly long period of time.
Symptoms of intestinal flu in children that require seeing a doctor:
- infrequent urination, when the diaper remains dry for up to four to six hours, as well as frequent bowel movements;
- child's nervousness;
- increased dryness of the skin, which was not previously observed;
- sunken eyes and crying without secretion of tear fluid;
- the appearance of a rash on the body - small reddish spots;
- cold extremities.
If any of these symptoms appear in newborns, infants, and older children, seek immediate medical attention.
Diet
A child's nutrition should be healthy.
When the disease passes in a simple form, then in order to be cured, you need to take less food, that is, follow a diet.
When the disease is at more serious stages of development, it is necessary to eat 30–50% less than usual, but at the same time you need to eat more often - up to 8 times a day.
If the child is not yet 4 months old, then formula milk must be excluded. In such a situation, a small child must be given mixtures that contain bifidobacteria, lactobacilli, and dietary supplements. If we talk about adults, then if there are intestinal dysfunctions, you should not eat:
- fresh milk;
- black bread;
- various yoghurts;
- fermented baked milk;
- cream;
- boiled beets;
- legumes;
- citrus fruit;
- meat and fish broths.
When a small child has a lack of protein during the course of this disease, it is necessary to add mixtures with it to the diet, starting from the 3rd day of the disease. If the pancreas does not work properly, and malabsorption syndrome has developed, it is necessary to take various medicinal mixtures in food.
Why is intestinal flu dangerous?
One of the most dangerous complications of diarrhea is dehydration, i.e. dehydration, expressed in a critical decrease in the volume of fluid in the tissues. Such a condition can become a threat to the health and even life of the patient. Dehydration in adults and children, which developed during intestinal flu, should be corrected in a timely manner. Most often this happens through oral rehydration - the patient is asked to replenish fluid deficiency by taking special solutions. If a person is in serious condition, fluid infusion may be required using IVs in a hospital setting.
Rotavirus gastroenteritis negatively affects not only the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract, but also all systems and internal organs, including the cardiovascular system. At the height of the disease, doctors often note a change in the functional state of the circulatory system, which is especially dangerous for people suffering from heart and vascular diseases.
Of course, most often intestinal flu leads to functional and morphological disorders of the gastrointestinal tract, which causes exacerbations of diseases such as chronic gastritis, enterocolitis, pancreatitis. Intestinal dysbiosis can also make itself felt, which will require correction after completing the course of treatment for intestinal flu.
Circulatory disorders (diseases that are included in the functional group and manifest themselves as cardiovascular, respiratory and autonomic disorders) and disorders of homeostasis (the ability of the system to maintain its internal state) are most often found in a group of high-risk patients, which includes newborns and preschoolers, the elderly age, as well as adults who suffer from severe concomitant diseases. In the absence of correct and timely treatment of CH, deaths may occur among these patients.
Treatment of candidiasis
Treatment of candidiasis is aimed at eliminating factors that contribute to the occurrence of candidiasis. If the skin is affected, local treatment is carried out using an open method using antifungal ointments.
The attending physician prescribes systemic and local medications for this disease. Local agents are not absorbed into the blood - they act only on the mucous membrane affected by the Candida fungus. They stop the reproduction and growth of fungi, relieve discomfort and restore affected tissue.
Prevention of intestinal flu
Viruses that have a tropism for the intestinal mucous membranes are often characterized by increased resistance to disinfectants, including those containing chlorine. For this reason, they practically do not die when water is chlorinated in water supply facilities. This explains outbreaks of intestinal flu among children and adults during holidays at resorts, when the pools near hotels are crowded with vacationers.
In tap water, viruses can remain viable for up to three months, and on various environmental objects - up to a month. All this indicates that preventing intestinal flu infection requires increased attention and diligence not only on the part of doctors, but also on the part of parents.
How to avoid illness
To avoid infection with VH, the World Health Organization recommends following these rules.
- The main thing is safety. Fruits, vegetables and berries that are consumed raw require careful hygienic processing. It is unacceptable to simply rinse them lightly; a thorough wash is necessary.
- Don't forget about heat treatment. Boiling kills viruses. It is important that the temperature remains uniform for a long time during cooking.
- Fresh food In families with young children, older people and those suffering from chronic illnesses, it is best to eat freshly prepared food, since cold food is an ideal environment for the proliferation of intestinal flu viruses.
- Proper product proximity The rules for storing food are relevant not only for catering establishments; they also need to be remembered in every family. Under no circumstances should cooked or raw foods be stored nearby. All prepared food should be stored in tightly sealed containers.
- Personal hygiene Before eating, be sure to wash your hands under running water and soap. In cafes, restaurants and other public places, regularly use antibacterial agents and sanitizers; they are relevant not only for preventing infection with COVID-19.
How is the disease diagnosed?
Visual methods for diagnosing candidiasis. Upon examination, inflammation of areas of the skin is revealed, limited to a border of exfoliating, macerated epidermis, and a whitish coating on the mucous membranes.
Laboratory diagnostics. Contrary to popular belief, the main method for diagnosing candidiasis is still microscopy of a smear from the affected areas of the mucosa. PCR (DNA diagnostics), which has become popular recently, is usually poorly suited for diagnosing candidiasis.
Laboratory diagnosis of the disease includes:
- microscopy of discharge smear
- cultural diagnostics (seeding)
- enzyme immunoassay (ELISA)
- polymerase chain reaction (PCR).