November 30, 2021
One of the main reasons for the spread of rotaviruses is non-compliance with personal hygiene rules, when transmission of infection occurs through hands, which in turn contaminate dishes, toys, and linen
The pathogen is transmitted through dirty hands, that is, the transmission mechanism is fecal-oral, although airborne droplets are also possible. It can affect people at any age, and the causative agent of rotavirus gastroenteritis is a virus from the order Rotavirus, family Reoviridae. Routes of transmission: contact and household (through dirty hands and household items); aqueous (when drinking water infected with viruses, including bottled water); nutritional (most often when consuming milk and dairy products).
The possibility of airborne transmission of rotavirus infection cannot be ruled out. But one of the main reasons for the spread of rotaviruses is non-compliance with personal hygiene rules, when transmission of the infection occurs through hands, which in turn contaminate dishes, toys, and linen.
The carrier of the infection is a sick person or a healthy virus carrier. The virus multiplies in the cells of the mucous membrane of the gastrointestinal tract and is excreted in the feces for up to 3 weeks (usually 7-8 days from the first symptoms of the disease). Damage to the mucous membrane of the digestive tract disrupts the digestion of food and leads to the development of severe diarrhea and dehydration. The main mechanism of transmission of rotavirus infection is through food. Infection occurs through the fecal-oral route.
Symptoms of rotovirus
Rotavirus or intestinal flu is highly contagious and spreads quickly in confined spaces. If one family member becomes ill, then with a high degree of probability the infection will be transmitted to everyone. Most often, patients complain of dizziness, nausea, weakness, chills, vomiting and diarrhea.
One of the leading symptoms of rotavirus infection is sudden onset of diarrhea.
During the course of the disease, there is an incubation period lasting up to 5 days, an acute period lasting 3–7 days, and a recovery period (4–5 days).
The onset of the disease is always sudden and is characterized by a sharp increase in temperature, as well as repeated increasing vomiting, cramping pain and rumbling in the abdomen, and the development of diarrhea is possible. The nature of the stool helps diagnose rotavirus infection. On the first day of illness, the stool is liquid yellow in color; in subsequent days, the stool becomes gray-yellow with a clay-like consistency. In addition to intestinal manifestations of the disease, patients are bothered by a runny nose, sore and sore throat, and cough.
The frequency of bowel movements often corresponds to the severity of the disease. If you have large, loose stools, dehydration may develop. From the very beginning of the disease, abdominal pain may be observed. More often they are moderate, constant, localized in the upper half of the abdomen; in some cases - cramping, strong. Signs of damage to the digestive organs persist for 3–6 days.
Rotavirus infection
Rotavirus infection is often also called rotavirus gastroenteritis or intestinal flu, although rotavirus does not belong to the influenza virus family. The route of transmission of the pathogen is fecal-oral, i.e. through dirty hands, although airborne droplets are also possible. Can affect people at any age.
The danger of self-medication for rotavirus infections
Not everyone infected with rotavirus develops the same disease. Its severity and duration depend not only on age, but also on the general condition of the person. What to do if you get sick? It must be remembered that sometimes very serious diseases can be hidden under the mask of ARVI, so it is necessary to exercise caution and immediately consult a doctor at the first signs of illness (vomiting, loose stools, rise in temperature). And if you have severe abdominal pain, do not take painkillers under any circumstances and call an ambulance immediately.
Treatment of rotavirus infection requires an integrated approach, so you should not self-medicate. The doctor will be able to assess the patient’s condition and, taking into account the severity of the disease, will select the necessary medications, including antiviral ones (for example, ARBIDOL®).
Signs of rotavirus infection
This is a disease with a short incubation period (1–5 days) and an acute onset with symptoms of gastroenteritis (on average 3–7 days, and in severe cases more than 7 days). Often, respiratory syndrome can also accompany the symptoms of gastroenteritis. The recovery period takes 4-5 days.
In children, this disease often manifests itself more acutely than in adults: a sharp rise in temperature, up to 39 degrees, vomiting and copious loose, watery stools. Vomit usually contains mucus, and nausea begins even from small portions of food and drink. With excessive vomiting and diarrhea, dehydration can occur, which poses a real danger to the child (8% fluid loss is life-threatening), and the ability to replenish fluid loss with drinking is complicated by an increased gag reflex.
In adults, nausea and vomiting are rare; manifestations of rotavirus infection are usually limited to moderate diarrhea, general weakness and a slight increase in temperature.
In addition to the symptoms of enteritis, the disease is accompanied by manifestations inherent to ARVI: runny nose, pain and redness in the throat, weakness, lack or loss of appetite.
Children are at high risk for severe and complicated acute respiratory viral infections and influenza. Their immune system is still imperfect and cannot always adequately fight off infection. Therefore, the risk of severe course and complications even with a common cold in children is much higher than in adults, therefore, they more often require treatment with antiviral drugs. Antiviral drugs used in pediatric practice must be well studied in preclinical and clinical studies, and must also have high efficacy and a favorable safety profile.
ARBIDOL® powder for suspension and 50 mg tablets are recommended for the treatment and prevention of influenza A and B, and other acute respiratory viral infections in young patients over 2 years of age, as well as in the complex therapy of rotavirus infection.
Prevention of rotavirus
Nonspecific prevention includes a set of sanitary and hygienic measures (regular hand washing, using only boiled drinking water, room ventilation, wet cleaning). Another important point is the timely isolation of a sick person who exhibits signs of acute respiratory viral infection and intestinal infection.
Gastroenterologists advise taking prebiotics and probiotics as a preventive measure. Probiotics, called “friendly bacteria,” are live microorganisms that aid digestion and improve protection against possible infections. Natural probiotics are found in fermented milk products: organic yogurt and cheeses, miso soup, sourdough bread, and sauerkraut. There are also probiotic supplements that come in capsules or drinks.
Arbidol® (Arbidol®)
Antiviral agent. Specifically inhibits in vitro influenza viruses A and B {Influenzavirus A, B), including highly pathogenic subtypes A(H1N1)pdm09 and A(H5N1), as well as other viruses that cause acute respiratory viral infections (ARVI) (coronavirus {Coronavirus) associated with severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS), rhinovirus (Rhinovirus), adenovirus (Adenovirus), respiratory syncytial virus (Pneumovirus) and parainfluenza virus (Paramyxovirus)). According to the mechanism of antiviral action, it belongs to fusion inhibitors, interacts with the hemagglutinin of the virus and prevents the fusion of the lipid membrane of the virus and cell membranes. It has a moderate immunomodulatory effect and increases the body's resistance to viral infections. It has interferon-inducing activity - in a study on mice, the induction of interferons was noted after 16 hours, and high titers of interferons remained in the blood up to 48 hours after administration. Stimulates cellular and humoral immune responses: increases the number of lymphocytes in the blood, especially T-cells (CD3), increases the number of T-helpers (CD4) without affecting the level of T-suppressors (CD8), normalizes the immunoregulatory index, stimulates the phagocytic function of macrophages and increases the number of natural killer (NK) cells.
Therapeutic effectiveness for viral infections is manifested in a decrease in the duration and severity of the disease and its main symptoms, as well as in a decrease in the incidence of complications associated with viral infection and exacerbations of chronic bacterial diseases.
In the treatment of influenza or ARVI in adult patients, a clinical study showed that the effect of the drug Arbidol® in adult patients is most pronounced in the acute period of the disease and is manifested by a reduction in the time for resolution of symptoms of the disease, a decrease in the severity of manifestations of the disease and a reduction in the time for elimination of the virus.
Therapy with Arbidol® leads to a higher frequency of relief of symptoms of the disease on the third day of therapy compared to placebo: 60 hours after the start of therapy, the resolution of all symptoms of laboratory-confirmed influenza is more than 5 times higher than the same indicator in the placebo group.
A significant effect of the drug Arbidol® on the rate of elimination of the influenza virus was established, which, in particular, was manifested by a decrease in the frequency of detection of viral RNA on the 4th day.
Refers to low-toxic drugs (LD50>4 g/kg). Does not have any negative effects on the human body when administered orally in recommended doses.
Use of Arbidol during pregnancy and children
The use of Arbidol during pregnancy is contraindicated.
It is not known whether the active substance of the drug Arbidol or its metabolites passes into breast milk in women during lactation. If it is necessary to use the drug Arbidol, breastfeeding should be stopped.
Contraindications for children:
- age up to 2 years;
- age up to 6 years (according to indications, nonspecific prevention of SARS);
- age up to 12 years (according to indications for treatment of SARS).
Medical Internet conferences
The effectiveness of using the drug Arbidol for rotavirus infection in children
Levin D.Yu.
Kadura A.A.
Scientific supervisor: doctor of medical sciences, prof. Mikhailova E.V.
GBOU VPO Saratov State Medical University named after. IN AND. Razumovsky Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation
Department of Children's Infectious Diseases
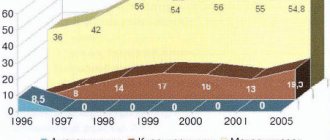
In Russia, the frequency of rotavirus gastroenteritis among acute intestinal infections is 7-35%, and among children under 3 years of age it exceeds 60%. The issues of treatment of rotavirus diarrhea still remain relevant. Considering the accumulated data on the persistence of rotavirus after rotavirus infection in follow-up, it is necessary to search for drugs that can increase the efficiency of rotavirus elimination.
The purpose of our study was to evaluate the effectiveness of the drug Arbidol against rotavirus infection in children aged 3-7 years.
A comprehensive clinical and laboratory observation was carried out on 70 children aged 3-7 years who were hospitalized at the Regional Children's Infectious Diseases Clinical Hospital in Saratov with a diagnosis of intestinal infection of rotavirus etiology. 40 children (group 1) received Arbidol in combination with basic treatment as part of therapy. The comparison group (30 children) received only basic therapy. The antiviral drug was prescribed orally at a dosage of 50 mg 4 times a day for 5 days. Laboratory diagnosis of rotavirus intestinal infection, as well as assessment of the elimination of rotaviruses during therapy, was performed by detecting rotavirus antigens using enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay in the acute period and during treatment.
It was found that in moderate to severe forms of the disease, the clinical effect of the drug is associated with a decrease in the duration of diarrhea syndrome (1.1 days less than in the comparison group) (p<0.05). The drug affected the duration of the intoxication syndrome (significantly less by 1.2 days than in the comparison group) (p<0.05). In the case of a moderate-severe form of rotavirus infection, during the use of an antiviral drug, the percentage of positive results in the detection of rotavirus antigens at the end of therapy decreased by 3 times (p<0.05); in the case of a severe form, positive dynamics of rotavirus elimination were also noted.
Thus, the inclusion of the drug Arbidol in complex therapy contributes to the intensification of the treatment of intestinal infections of rotavirus etiology in children: a more rapid regression of intoxication symptoms, a significant decrease in the duration of diarrhea syndrome, a decrease in the duration of rotavirus persistence (in the case of a moderate-severe form by 3 times, in the case of a severe form by 1 ,3 times).
Arbidol dosage
Inside, before meals.
Add 30 ml (or approximately 2/3 of the bottle volume) of boiled water and cooled to room temperature to the bottle containing the powder. Close the bottle with a lid, turn it upside down and shake thoroughly until a homogeneous suspension is obtained. Add boiled and cooled water to a volume of 100 ml (up to the mark on the bottle) and shake again. Before each dose, shake the contents of the bottle thoroughly until a homogeneous suspension is obtained. Measure a single dose using the included measuring spoon.
For nonspecific prevention of SARS (in contact with a patient) in children over 6 years of age and adults:
- children from 6 to 12 years old - 20 ml (100 mg).
- children over 12 years of age and adults - 40 ml (200 mg) 1 time / day for 12-14 days.
For the treatment of SARS in children over 12 years of age and adults:
- children over 12 years of age and adults - 40 ml (200 mg) 2 times a day for 8-10 days.
Arbidol Maximum
Registration number: LP-002690 dated 10/31/2014
Trade name of the drug: Arbidol® Maximum
International nonproprietary name: Umifenovir
Dosage form: capsules
Composition per capsule:
Active ingredient: umifenovir hydrochloride monohydrate (in terms of umifenovir hydrochloride) – 207 mg (in terms of umifenovir hydrochloride) – 200 mg.
Excipients: potato starch - 45.67 mg, microcrystalline cellulose - 11.20 mg, colloidal silicon dioxide (Aerosil) - 2.80 mg, povidone (kollidon 25) - 7.73 mg, calcium stearate - 2.80 mg, croscarmellose sodium – 2.80 mg, weight of capsule contents – 280 mg.
Hard gelatin capsules No. 0:
Composition of the capsule shell (body and cap): titanium dioxide (E 171) – 1.92 mg, gelatin – 94.08 mg. The total weight of the capsule is 376 mg.
Description
Hard gelatin capsules No. 0, white. The contents of the capsule are a mixture containing granules and powder from white or white with a greenish-yellow or cream tint to light yellow or light yellow with a greenish tint.
Pharmacotherapeutic group: antiviral agent.
ATX code: J05AX13
Pharmacological properties
Pharmacodynamics
Antiviral agent. Specifically suppresses in vitro influenza viruses A and B (Influenza virus A, B), including highly pathogenic subtypes A(H1N1)pdm09 and A(H5N1), as well as other viruses that cause acute respiratory viral infections (ARVI) (coronavirus, associated with severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS), rhinovirus (Rhinovirus), adenovirus (Adenovirus), respiratory syncytial virus (Pneumovirus) and parainfluenza virus (Paramyxovirus)). In in vitro studies, it specifically inhibits the SARS-CoV-2 virus, which causes novel coronavirus infection (COVID-19). The EC50 (half maximal effective concentration) in Vero E6 cells is 4.11 µM, which corresponds to 2.11 µg/ml. The clinical significance of this requires further study.
According to the mechanism of antiviral action, it belongs to fusion inhibitors, interacts with the hemagglutinin of the virus and prevents the fusion of the lipid membrane of the virus and cell membranes. It has a moderate immunomodulatory effect and increases the body's resistance to viral infections. It has interferon-inducing activity - in a study on mice, the induction of interferons was noted after 16 hours, and high titers of interferons remained in the blood up to 48 hours after administration. Stimulates cellular and humoral immune responses: increases the number of lymphocytes in the blood, especially T-cells (CD3), increases the number of T-helpers (CD4) without affecting the level of T-suppressors (CD8), normalizes the immunoregulatory index, stimulates the phagocytic function of macrophages and increases the number of natural killer (NK) cells.
Therapeutic effectiveness for viral infections is manifested in a decrease in the duration and severity of the disease and its main symptoms, as well as in a decrease in the incidence of complications associated with viral infection and exacerbations of chronic bacterial diseases.
When treating influenza or ARVI in adult patients, a clinical study showed that the effect of the drug in adult patients is most pronounced in the acute period of the disease and is manifested by a reduction in the time for resolution of symptoms of the disease, a decrease in the severity of the manifestations of the disease and a reduction in the time for elimination of the virus.
Therapy with the drug leads to a higher frequency of relief of symptoms of the disease on the third day of therapy compared to placebo - 60 hours after the start of therapy, the resolution of all symptoms of laboratory-confirmed influenza is more than 5 times higher than the same indicator in the placebo group.
A significant effect of the drug on the rate of elimination of the influenza virus was established, which, in particular, was manifested by a decrease in the frequency of detection of viral RNA on the 4th day.
Refers to low-toxic drugs (LD50 > 4 g/kg). Does not have any negative effects on the human body when administered orally in recommended doses.
Pharmacokinetics
Quickly absorbed and distributed throughout organs and tissues. The maximum concentration in blood plasma when taken at a dose of 50 mg is achieved after 1.2 hours, at a dose of 100 mg - after 1.5 hours. Metabolized in the liver. The half-life is on average 17-21 hours. About 40% is excreted unchanged, mainly with bile (38.9%) and in small amounts by the kidneys (0.12%). During the first day, 90% of the administered dose is eliminated.
Indications for use
Prevention and treatment in adults and children over 12 years of age: influenza A and B, other acute respiratory viral infections.
Complex therapy of recurrent herpes infection.
Prevention of postoperative infectious complications.
Complex therapy of acute intestinal infections of rotavirus etiology in children over 12 years of age.
Contraindications
Hypersensitivity to umifenovir or any component of the drug; children up to 12 years of age. First trimester of pregnancy. Breastfeeding period.
Carefully
Second and third trimesters of pregnancy.
Use during pregnancy and breastfeeding
In animal studies, no harmful effects on pregnancy, embryonic and fetal development, labor or postnatal development were identified.
The use of Arbidol® Maximum in the first trimester of pregnancy is contraindicated.
In the second and third trimester of pregnancy, Arbidol® Maximum can be used only for the treatment and prevention of influenza and if the expected benefit to the mother outweighs the potential risk to the fetus. The benefit/risk ratio is determined by the attending physician.
It is not known whether Arbidol® Maximum passes into breast milk in women during lactation. If you need to use Arbidol® Maximum, you should stop breastfeeding.
Directions for use and doses
Inside, before meals.
A single dose for adults and children over 12 years of age is 200 mg (1 capsule).
| Indication | Dosage regimen |
| In adults and children over 12 years of age: | |
| Nonspecific prevention during an epidemic of influenza and other acute respiratory viral infections | in a single dose 2 times a week for 3 weeks. |
| Nonspecific prophylaxis in direct contact with patients with influenza and other acute respiratory viral infections | in a single dose 1 time per day for 10-14 days. |
| Treatment of influenza and other acute respiratory viral infections | in a single dose 4 times a day (every 6 hours) for 5 days. |
| Complex therapy for recurrent herpes infection | in a single dose 4 times a day (every 6 hours) for 5-7 days, then in a single dose 2 times a week for 4 weeks. |
| Prevention of postoperative infectious complications | in a single dose 2 days before surgery, then on days 2 and 5 after surgery. |
| For children over 12 years of age: | |
| Complex therapy of acute intestinal infections of rotavirus etiology | in a single dose 4 times a day (every 6 hours) for 5 days. |
The drug should be taken from the moment the first symptoms of influenza and other acute respiratory viral infections appear, preferably no later than 3 days from the onset of the disease.
If, after using the drug Arbidol® Maximum for three days in the treatment of influenza and other acute respiratory viral infections, the severity of the symptoms of the disease, including high temperature (38 ° C or more), then you must consult a doctor to assess the validity of taking the drug.
Use the drug only according to the indications, method of administration and in the doses indicated in the instructions.
When treating influenza and ARVI, concomitant symptomatic therapy is possible, including taking antipyretic drugs, mucolytics and local vasoconstrictors.
Side effect
The drug Arbidol® Maximum is a low-toxic drug and is usually well tolerated.
Side effects are rare, usually mild or moderate and transient.
The frequency of adverse drug reactions is determined in accordance with the WHO classification: very often (with a frequency of more than 1/10), often (with a frequency of at least 1/100, but less than 1/10), infrequently (with a frequency of at least 1/1000, but less than 1/100), rare (with a frequency of at least 1/10,000, but less than 1/1000), very rare (with a frequency of less than 1/10,000), frequency unknown (cannot be determined from the available data).
Immune system disorders : rarely - allergic reactions.
If any of the side effects indicated in the instructions get worse, or you notice any other side effects not listed in the instructions, tell your doctor.
Overdose
Not marked.
Interaction with other drugs
When prescribed with other drugs, no negative effects were noted.
No special clinical studies have been conducted to study the interactions of the drug Arbidol® Maximum with other drugs.
There was no evidence of undesirable interactions with antipyretic, mucolytic and local vasoconstrictor drugs in a clinical study.
special instructions
It is necessary to follow the regimen and duration of taking the drug recommended in the instructions. If you miss one dose of the drug, the missed dose should be taken as early as possible and continue taking the drug according to the started regimen.
If, after using the drug Arbidol® Maximum for three days in the treatment of influenza and other acute respiratory viral infections, the severity of the symptoms of the disease, including high temperature (38 ° C or more), then you must consult a doctor to assess the validity of taking the drug.
Impact on the ability to drive vehicles and machinery
It does not exhibit central neurotropic activity and can be used in medical practice by people of various professions, incl. requiring increased attention and coordination of movements (transport drivers, operators, etc.).
Release form
Capsules 200 mg.
10 capsules per blister pack made of polyvinyl chloride film and printed varnished aluminum foil.
1 or 2 contour packages with instructions for use are placed in a cardboard pack.
Storage conditions
Store at a temperature not exceeding 25°C. Keep out of the reach of children.
Best before date
2 years. Do not use after the expiration date stated on the packaging.
Vacation conditions
Available without a prescription.
Marketing authorization holder/organization receiving consumer complaints
OTCPharm JSC, Russia 123112, Moscow, st. Testovskaya, 10 fl. 12, room II, room 29 Tel. Fax www.otcpharm.ru www.arbidol.ru
305022, Russia, Kursk, st. 2nd Aggregatnaya, 1a/18, tel./fax, www.pharmstd.ru
Composition and release form
Powder for the preparation of a suspension for oral administration, granular, white or almost white, with a characteristic fruity odor;
the prepared suspension is homogeneous, white or white with a yellowish or creamy tint, with a characteristic fruity odor. Composition 5 ml:
- umifenovir hydrochloride monohydrate - 25.88 mg,
- which corresponds to the content of umifenovir hydrochloride - 25 mg
Excipients: sodium chloride - 26.85 mg, maltodextrin (kleptose linecaps) - 750 mg, sucrose (sugar) - 840.42 mg, colloidal silicon dioxide (Aerosil) - 24.6 mg, titanium dioxide - 25 mg, pregelatinized starch (type PA5PH) - 129.5 mg, sodium benzoate - 9.25 mg, banana flavor - 12.4 mg, raspberry flavor - 6.1 mg.
37 g - dark glass bottles with a capacity of 125 ml (1) complete with a measuring spoon - cardboard packs.