Indications
- Treatment of protozoal infections: intestinal and extraintestinal amebiasis, trichomoniasis.
- Infections caused by gram-negative anaerobes of the Bacteroidaceae family: brain and lung abscesses, necrotizing pneumonia, infections of the osteoarticular system, bacterial endocarditis and sepsis.
- The drug is effective against clostridial flora, which causes infections of the genitourinary system and infections of the abdominal organs.
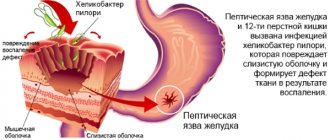
- Metronidazole is used in gastroenterology for the treatment of gastritis, gastric and duodenal ulcers associated with H. pylori.
- Prophylactic use during operations on the colon and gynecological interventions.
Instructions for use of the drug metronidazole
Inside, with a glass of water.
The daily dose is divided into 3 doses for adults, and 2 doses for children 6-15 years old. For trichomoniasis infection, 2 treatment regimens are used: 2 g of the drug once or 0.250 g twice a day, course 10 days.
When Helicobacter pylori is irradiated, metronidazole is combined with penicillin antibacterial drugs to suppress drug resistance. The daily dose of metronidazole is 1.5 g.
Metronidazole in the treatment of intestinal amebiasis is used in a daily dose of 1.5 g.
For acute amoebiasis, the daily dose is 2.250 g. The daily dose for children is 0.5 g.
Treatment of extraintestinal forms of amebiasis requires combination with tetracycline antibacterial drugs. The daily dose of metronidazole is 2.5 g in adults and 0.5 g in children.
Prevention of complications after surgical interventions involves taking 0.750 - 1.5 g of the drug per day for 4 days before surgery and 0.750 in the postoperative period for a week.
Prescription of Metronidazole, contraindications and side effects
The instructions for the drug indicate the following indications for use:
- For suppositories - for urethritis, trichomonas vaginitis, amoebic dysentery, giardiasis. Metronidazole is used to prevent infection during surgery, exacerbation of ulcers, chronic gastroduodenitis associated with Helicobacter pylori infection. Prescribed for chronic alcohol dependence.
- For ointment - for bacterial vaginosis, vulgar or rosacea acne, wounds, trophic ulcers that do not heal for a long time. The medication is prescribed to patients with demodicosis, amoebiasis, trichomoniasis, limbliasis, cystitis, and urethritis. Shows sufficient effectiveness in the treatment of infections of the central nervous system, bacterial damage to the bone tissue of the joints, pelvic organs or abdominal cavity.
Metronidazole tablets and other forms are used for the development of pseudomembranous colitis, ulcers, gastroduodenitis, and for the prevention of complications in the postoperative period.
The medication is contraindicated in patients:
- with individual intolerance to the component composition;
- organic lesions of the central nervous system, including epilepsy;
- leukopenia, liver failure;
- when breastfeeding.
Particular care is taken when treating pregnant women or people with renal failure. In these cases, the treatment regimen and dosage are calculated by the doctor.
The main adverse reactions to Metronidazole are:
- attacks of nausea, vomiting, refusal to eat, diarrhea, constipation, intestinal colic, stomatitis, pancreatitis, dry oral mucosa;
- impaired coordination of movements, ataxia, attacks of dizziness, confusion, depression, hallucinations, unreasonable irritability, excitability, convulsive syndrome, headache, sleep disturbances;
- nettle fever, rashes, redness, arthralgia;
- candidiasis, urinary incontinence, polyuria, cystitis, reddish-brown coloration of urine;
- thrombophlebitis.
Laboratory tests show a decrease in the number of neutrophils and leukocytes.
Side effects and features of administration
The most common violations:
- Gastrointestinal tract: abdominal discomfort, nausea, vomiting, impaired taste perception (“metallic” taste in the mouth), diarrhea;
- immunity: anaphylactic shock, angioedema;
- skin: rash, itching, urticaria;
- genitourinary system: change in the color of urine up to a reddish-brown color, candidiasis.
The drug crosses the placental barrier, which completely limits its use in the first trimester of pregnancy. In the second and third trimester, metronidazole is used if the estimated risk to the fetus is lower than the possible benefit to the pregnant woman. Treatment of a lactating woman requires cessation of breastfeeding.
When treating trichomoniasis, it is necessary to carry out therapy simultaneously in both partners and to exclude sexual contact for the period of therapy.
Metronidazole
Metronidazole
(lat.
metronidazole
) - antibacterial antiprotozoal drug.
Metronidazole is a chemical
Chemical Compound: 2-Methyl-5-nitro-1H-imidazole-1-ethanol. 5-nitroimidazole derivative. White or slightly greenish crystalline powder. Metronidazole is slightly soluble in water and sparingly soluble in alcohol. Empirical formula: C6H9N3O3.
Metronidazole - medicine
Metronidazole is the international nonproprietary name (INN) of the drug. According to the pharmacological index, metronidazole belongs to the groups “Other synthetic antibacterial agents” and “Medicines for the correction of disorders in alcoholism, toxic and drug addiction”; according to ATC, metronidazole is included in the groups:
- “A02 Drugs for the treatment of diseases associated with acidity disorders” as part of combinations intended for the eradication of Helicobacter pylori
: - "omeprazole, amoxicillin and metronidazole", code A02BD01,
- "lansoprazole, tetracycline and metronidazole", code A02BD02,
- "lansoprazole, amoxicillin and metronidazole", code A02BD03,
- "rabeprazole, amoxicillin and metronidazole", code A02BD13,
- “vonoprazan, amoxicillin and metronidazole”, code A02BD15;
Metronidazole is also a trade name for the drug.
Metronidazole is an antibiotic agent
Metronidazole is active against the following microorganisms:
- protozoa (protists): Trichomonas vaginalis, Entamoeba histolytica, Giardia intestinalis , Lamblia spp.
- bacteria:
- anaerobic:
- Gram-negative Bacteroides spp.
(including
Bacteroides fragilis, Bacteroides ovatus, Bacteroides thetaiotaomicron, Bacteroides vulgatus
),
Parabacteroides distasonis
,
Fusobacterium spp.
,
Veillonella spp.,
Prevotella
bivia, Prevotella buccae
and
Prevotella disiens - gram-positive Clostridium spp., Eubacterium spp., Peptococcus spp., Peptostreptococcus spp.
The following bacteria are resistant to metronidazole: Mobiluncus spp
.
Indications for use of metronidazole
- Intestinal amebiasis, trichomoniasis, balantidiasis, giardiasis, cutaneous leishmaniasis.
- Trichomonas vaginitis and urethritis.
- Infections of bones and joints, central nervous system (including meningitis and brain abscess), bacterial endocarditis, pneumonia, empyema and pulmonary abscess caused by Bacteroides spp
. - Infections of the abdominal cavity (peritonitis, liver abscess), infections of the pelvic organs (endometritis, endomyometritis, abscess of the fallopian tubes and ovaries, infections of the vaginal vault after surgery), infections of the skin and soft tissues caused by Bacteroides spp ., Clostridium spp., Peptococcus spp. ., Peptostreptococcus spp.
- Sepsis caused by Bacteroides spp., Clostridium spp.
- Pseudomembranous colitis caused by antibiotics.
- Prevention of postoperative complications, including operations on the colon, rectal area, female genital organs, removal of the appendix.
- Radiation therapy for patients with tumors - as a radiosensitizing agent, in cases where tumor resistance is due to hypoxia in tumor cells.
- For intravaginal use: urogenital trichomoniasis (including urethritis and vaginitis), nonspecific vaginitis of various etiologies, confirmed by clinical and microbiological data.
- For external and local use: rosacea and vulgar acne, bacterial vaginosis, long-term non-healing wounds, trophic ulcers, infectious skin diseases, oily seborrhea, seborrheic dermatitis, bedsores, hemorrhoids, anal fissures.
- Mixed (aerobic and anaerobic) infections of various localizations, periodontal diseases, purulent-inflammatory processes of the maxillofacial area.
- Chronic alcoholism.
- Gastrointestinal diseases associated with Helicobacter pylori
: gastric and duodenal ulcers, atrophic gastritis, MALToma, condition after gastric resection for cancer.
Metronidazole in Helicobacter pylori eradication regimens
Metronidazole is classified by WHO as a drug active against Helicobacter pylori
(Podgorbunskikh E.I., Maev I.V., Isakov V.A.).
However, in Russia the level of resistance to metronidazole is almost twice as high as the European average: 55.5% in Russia and 25.5% in Europe, data from 2001 (Maev I.V., Vyuchnova E.S., Shchekina M.I. .). The figure on the right (taken from the article by Belousova Yu.B., Karpov O.I., Belousov D.Yu. and Beketov A.S.) shows the dynamics of resistance to metronidazole, clarithromycin and amoxicillin in Helicobacter pylori
isolated from adults (top) and from children (bottom).
Its very widespread and inappropriate use has led to increased resistance to metronidazole. Currently, in treatment regimens it is recommended to use nifuratel instead of metronidazole (Shcherbakov P.L.). As a result, modern Russian Standards for the diagnosis and treatment of acid-dependent and Helicobacter pylori-associated diseases recommend metronidazole in only one of the “second-line” regimens (applied only if the patient had an unsuccessful attempt to eradicate Helicobacter pylori
using one of the “first-line” regimens). : metronidazole 500 mg 3 times a day, tripotassium bismuth dicitrate 120 mg 4 times a day, tetracycline 500 mg 4 times a day and one of the proton pump inhibitors in a standard dosage (omeprazole 20 mg, lansoprazole 30 mg, pantoprazole 40 mg, esomeprazole 20 mg, rabeprazole 20 mg 2 times a day) for 10–14 days.
When assessing the level of resistance to metronidazole, the following results were obtained: in the mid-1990s, there was a steady increase in the average European level of resistance.
Initial data typical for Russia, where the number of Helicobacter pylori
resistant to nitroimidazole derivatives continues to grow, reached 56.6% by 1998 (see figure on the left).
The reason for such a high level of resistance is the widespread use of the drug for the treatment of urogenital and other infections, as well as their irrational use in eradication therapy regimens in previous years. However, attention is drawn to data on the possibility of restoring sensitivity to metronidazole in a previously resistant strain of H. pylori under anaerobic conditions. Researchers explain this phenomenon by the fact that, while in the stomach cavity, Helicobacter pylori
periodically enters anaerobic conditions, and therefore, in a number of patients with resistant strains, radiation therapy with the inclusion of metronidazole achieves success (Kazyulin A.N. et al.).
Order of use of metronidazole and dose
When taking metronidazole orally:
- adults and children over 12 years old - 7.5 mg of metronidazole per kg of body weight every 6 hours or 250-750 mg 3-4 times a day
- children under 12 years of age - 5–16.7 mg of metronidazole per kg of body weight 3 times a day
When administered intravenously
to adults and children over 12 years of age, the initial dose is 15 mg of metronidazole per kg of body weight, then 7.5 mg of metronidazole per kg of body weight every 6 hours or 500–750 mg every 8 hours. The duration of taking metronidazole is determined by your doctor.
With intravaginal administration
500 mg of metronidazole 1 time at night.
For external and local use
The dose of metronidazole is determined by the doctor, the frequency of treatment is twice a day.
Daily dose
metronidazole for adults when taken orally and intravenously should not exceed 4 g
.
This order of use of metronizadol and dose do not apply to the treatment of Helicobacter pylori-associated gastrointestinal diseases, for the treatment of which see Standards for the diagnosis and treatment of acid-dependent and Helicobacter pylori-associated diseases, 2010.
Use of metronidazole during pregnancy and breastfeeding
Metronidazole is contraindicated in the first trimester of pregnancy; in the second and third trimesters it should be taken with caution only if the benefit to the pregnant woman outweighs the risk to the unborn child, given that metronidazole crosses the placenta.
FDA Category of Effect on the Fetus is B. Metronidazole is excreted into human milk, creating concentrations similar to those in blood plasma. May impart a bitter taste to breast milk. To exclude the effect of metronidazole on the child, breastfeeding during metronidazole therapy and for another 2 days after stopping its use is not recommended.
Professional medical publications addressing the use of metronidazole in the eradication of Helicobacter pylori
- Ivashkin V.T., Sheptulin A.A., Baranskaya E.K. and others. Recommendations for the diagnosis and treatment of peptic ulcer disease (a manual for doctors). - M. - 2004.
- Belousova Yu.B., Karpov O.I., Belousov D.Yu., Beketov A.S. Pharmacoeconomics of the use of bismuth tripotassium dicitrate for peptic ulcer disease // Therapeutic archive. – 2007. – T. 79. – No. 2. – P. 58–66.
On the website gastroscan.ru in the literature catalog there is a section “Antibiotics used in the treatment of gastrointestinal diseases”, containing articles on the use of antimicrobial agents in the treatment of diseases of the digestive tract.
Medicines containing the active ingredient metronidazole
Bacimex, Deflamon, Klion, Metrovagin, Metrogyl, Metroxan, Metrolacare, Metron, Metronidazole, Metronidazole IV Brown, Metronidazole Nycomed, Metronidazole-AKOS, Metronidazole-UBF, Metronidazole tablets 0.25 g, Metronidal, Metroseptol, Orvagil, Rosamet, Rozeks, Siptrogil, Tricho-PIN, Trichobrol, Trichopol, Trichosept, Flagyl, Eflora.
Instructions for use of metronidazole
Some official instructions from manufacturers of drugs with the active substance metronidazole (pdf):
- Nycomed (Denmark):
- “Instructions for medical use of the drug Metronidazole Nycomed”, tablets of 250 and 500 mg, dated July 31, 2001.
- “Instructions for medical use of the drug Metronidazole Nycomed”, infusion solution, 500 mg of metronidazole in 100 ml of solution, dated November 23, 2000.
- “Information for medical professionals and specialists regarding the drug Klion”, tablets containing 250 mg of metronidazole, solution for infusion
Back to section
Interaction with other medications
Sulfonamides potentiate the main effect of metronidazole.
Simultaneous use with disulfiram increases the risk of developing psychosis. The medications should be taken two to three weeks apart.
During therapy with metronidazole, it is necessary to stop drinking alcohol, including drugs made from ethanol. Neglect will lead to disulfiram-like reactions.
Metranidazole potentiates the activity of indirect anticoagulants, which increases the risk of bleeding. While taking metronidazole, it is necessary to strengthen monitoring of prothrombin time and adjust the dose of anticoagulants.