pharmachologic effect
The product has an antiprotease and antifibrinolytic effect on the body. Due to the influence of the active substance aprotinin , the activity of a number of proteolytic enzymes is suppressed. Aprotinin is a kallikrein . Under its influence, inflammatory cytokines are released, and the substance also helps maintain glycoprotein homeostasis.
When using aprotinin in surgical practice using AIK, a decrease in inflammatory processes is observed, which, in turn, helps reduce blood loss and also reduces the need for blood transfusion.
Pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics
After the drug is administered to the patient intravenously, aprotinin is actively distributed in the intercellular space, as a result of which its concentration in the blood decreases very quickly. The terminal half-life is 5 to 10 hours.
On average, 80% of aprotinin binds to plasma proteins. The drug, which is in free form, determines about 20% of antifibrinolytic activity.
The total clearance is about 40 ml per minute.
The accumulation of aprotinin is mainly observed in the kidneys; less of the substance accumulates in cartilage tissue. A very low concentration of the active substance is observed in the human brain; aprotinin almost does not penetrate into the cerebrospinal fluid. A small amount of the active substance Gordox penetrates the placental barrier.
The active substance is metabolized by lysosomal enzymes in the kidneys; within 48 hours, from 25 to 40% of aprotinin in the urine remains in the form of inactive metabolites.
How Gordox works
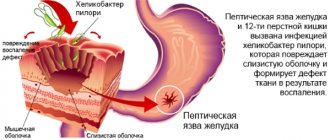
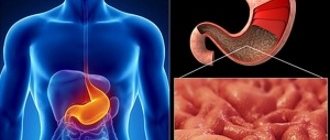
Gordox for pancreatitis prevents the activation of proteolytic enzymes and is effective in reducing fibrinolytic activity in the blood and preventing bleeding. The drug is prescribed if the level of trypsin and lipase in the blood serum is elevated, which is accompanied by severe pain in the left hypochondrium.
The active ingredient of the drug is aprotinin; alcohol, water, and sodium chloride are used as auxiliary ingredients. Aprotinit is a polypeptide obtained from the lungs of livestock.
Gordox has antiprotease, hemostatic, antifibrinolytic properties. The main component of the product does not allow proteases to activate and acts as a kallikrein inhibitor. The drug releases inflammatory cytokines and a component that maintains constant levels of glycoproteins.
In surgery, aprotinin is used to reduce the inflammatory response, which reduces blood loss and reduces the likelihood of blood transfusion.
Thus, Gordox has the following pharmacological effect:
- reduces the fibrinolytic activity of the blood because it inhibits the action of enzymes (kallikrein, trypsin, chymotrypsin, plasmin kininogenase). Inhibits both the general activity of gland enzymes and the activity of specific proteases;
- stimulates the dissolution of blood clots and blood clots;
- reduces the activity of cytokines, proteins that trigger the inflammatory response;
- prevent the loss of glycoproteins (clotting factors).
The drug is removed from the bloodstream in 10 hours
After administration of the solution, atropine is located in the intercellular space, which is why its level quickly drops. Most of aprotinin accumulates in the kidneys, a much smaller part accumulates in cartilage.
A minimal amount of the drug ends up in the brain, and almost none of it enters the cerebrospinal fluid. A small concentration of aprotinin leaks through the placenta. The active substance Gordox disintegrates under the action of lysosomal enzymes of the kidneys.
Indications for use
Description of indications for use of Gordox is as follows:
- acute manifestations of pancreatitis (the drug is used as part of complex treatment);
- chronic form of pancreatitis (with frequent relapses and severe disease);
- pancreatitis that developed as a result of surgical interventions and injuries;
- primary bleeding due to hyperfibrinolysis (after injuries, operations, before and after childbirth, with polymenorrhea );
- pancreatic necrosis;
- diagnostic operations and examinations on the pancreas;
- prevention of postoperative nonspecific parotitis after surgery;
- angioedema;
- symptoms of shock (traumatic, toxic, hemorrhagic);
- tissue injuries (deep, extensive).
Also, the use of Gordox is indicated as an auxiliary treatment for coagulopathy , in which secondary hyperfibrinolysis and severe bleeding are noted. This remedy is also used as a prophylaxis for pulmonary embolism and bleeding after surgery.
When is Gordox necessary?
Since Gordox has antiprotease activity, it is indicated for diseases of the pancreas and organs that are accompanied by an increased content of kallikrein and other proteases.
Gordox is prescribed for the following diseases:
- acute pancreatitis (used as one of the means of complex therapy);
- chronic pancreatitis (if frequent relapses occur or the disease is severe);
- pancreatitis formed as a result of injury or surgery;
- primary bleeding resulting from hyperfibrinolysis;
- pancreatic necrosis;
- angioedema;
- signs of shock (toxic, traumatic, hemorrhagic, burn);
- deep tissue trauma.
Side effects
As a rule, when using Gordox, patients do not experience any side effects. In rare cases, dyspeptic and allergic effects may occur. in blood pressure occur .
Allergic manifestations are rare during the first administration of the drug; the frequency of their development increases (by approximately 5%) with repeated administration of the drug. The likelihood of severe allergic or anaphylactic manifestations increases if Gordox treatment was carried out twice or more within 6 months.
Contraindications and undesirable effects of the drug
The list of contraindications for the drug is small. Like any drug, Gordox should not be taken if there is intolerance to the main or auxiliary substance of the drug, as well as with hemorrhagic diathesis (DIC syndrome), in the first and third trimester of pregnancy.
Painkillers for pancreatitis
Undesirable effects while taking Gordox occur very rarely. In some patients, the body reacted to the drug with dyspeptic disorder (nausea, vomiting) and allergic manifestations (skin rash, runny nose, urticaria, bronchospasm, conjunctivitis, anaphylactic reaction).
Rarely during treatment, muscle pain appears and blood pressure levels differ from normal (hypotension or tachycardia). Side effects from the central nervous system may also occur, for example, confusion, psychotic disorders, hallucinations.
An allergy to the medication during the first injection occurs very rarely; the risk of its development increases by 5% the next time the solution is administered. Serious allergic or anaphylactic side effects may develop if more than two courses of Gordox therapy are administered within six months.
Gordox, instructions for use for pancreatitis (Method and dosage)
If a patient is prescribed Gordox, the instructions for use when using it must be carefully followed. The drug is administered intravenously, slowly: when administered, a maximum rate of 5 to 10 ml per minute is permissible. When the drug is administered to the patient, he should lie on his back at this time. Gordox is administered through the main veins; they are not used to administer other drugs.
Initially, approximately 10 minutes before the main administration of the drug, each patient is given a test dose of Gordox, which is 1 ml. If there are no allergic reactions, the main dose of the drug is administered.
For an adult, the initial dose of the drug is 0.5–2 million KIU, administered over 15–20 minutes. The maintenance dose is 200 thousand KIU of Gordox every 4 to 6 hours. With the gradual disappearance of symptoms, you can reduce the maintenance dose to 500 thousand KIU daily.
If a doctor prescribes treatment with Gordox for children, the dose is calculated based on body weight: per 1 kg - 20 thousand KIE agents.
Gordox®
When using aprotinin, especially with repeated use of the drug, allergic/anaphylactic reactions may develop. Therefore, before using the drug, it is necessary to carefully evaluate the benefit/risk ratio. 10 minutes before the main dose of Gordox® is administered, a test dose of 1 ml (10 thousand KIU) is administered. 15 minutes before the administration of a therapeutic dose of Gordox®, it is possible to use histamine H1- and H2-receptor blockers. However, allergic/anaphylactic reactions can also develop when a therapeutic dose of the drug is administered, even if no adverse reactions were observed during the administration of the test dose. In case of development of hypersensitivity reactions when using aprotinin, you should immediately stop administering the drug and ensure that standard emergency measures are taken to treat allergic/anaphylactic reactions.
When performing surgery on the thoracic aorta using an artificial cardiopulmonary bypass and using deep cold cardioplegia, Gordox® should be used with extreme caution against the background of adequate heparin therapy.
Determination of activated clotting time is not a standardized test for determining the coagulation capacity of blood, and the use of aprotinin may affect different test procedures. The Coagulation Test (ACT) is subject to various dilution and temperature effects. The ACT test with kaolin does not increase as much in the presence of aprotinin as the ACT test with celite. Due to differences in protocols, it is recommended to take the minimum values of ACT test - 750 sec and ACT test with kaolin - 480 sec in the presence of aprotinin, regardless of the effects of hemodilution and hypothermia. The standard dose of heparin administered before cardiac cannulation and the amount of heparin added to the primary volume in the cardiac bypass should be at least 350 IU/kg. The additional dose of heparin is determined by the patient's body weight and the duration of the extracorporeal circulation period. The protamine titration method is not affected by aprotinin. Additional doses of heparin are determined based on the heparin concentration calculated by this method. Heparin concentrations during bypass should not fall below 2.7 U/ml (0.2 mg/kg) or below the level determined before the use of aprotinin. In patients treated with Gordox®, neutralization of heparin with protamine should be carried out only after interruption of extracorporeal circulation, based on a fixed amount of heparin administered or under the control of a protamine titration method.
Gordox® contains benzyl alcohol. The daily dose of benzyl alcohol should not exceed 90 mg/kg body weight.
Aprotinin is not a substitute for heparin.
Preparations for parenteral administration should be visually inspected immediately before use. Do not use leftover solution for subsequent use.
Use in pediatrics
Contraindicated for use in children and adolescents under 18 years of age
(efficacy and safety have not been established).
Impact on the ability to drive vehicles and operate machinery
There are no data on the effect of Gordox® on the ability to drive vehicles and operate machinery.
Interaction
When aprotinin is added to heparinized blood, an increase in the clotting period of whole blood is observed.
If Gordox is used simultaneously with Reomacrodex , then an increased sensitizing effect is noted.
Aprotinin inhibits the effects of urokinase , streptokinase , alteplase .
Aprotinin is a weak inhibitor of serum pseudocholinesterase. of suxamethonium chloride may slow down , muscle relaxation also increases, and apnea .
special instructions
Before starting treatment, it is necessary to conduct skin tests to determine a person's individual sensitivity to aprotinin .
If a history of allergic reactions is indicated, then before starting treatment with aprotinin, one should take histamine H1 receptor blockers and GCS.
If DIC syndrome and hyperfibrinolysis , it is permissible to take Aprotinin only after all manifestations of DIC syndrome have been eliminated, and also if the preventive effect of Heparin .
muscle relaxants for 2-3 days before starting treatment .
When using Gordox during treatment, especially during re-treatment, anaphylactic or allergic manifestations may occur. Therefore, people prone to allergies should clearly determine the degree of benefit and risk.
Gordox contains benzyl alcohol, so the maximum dose of the drug per day should not be more than 90 mg per kg of human body weight.
Gordox is not a substitute for Heparin.
After the ampoule has been opened, its contents should be used; when used again, the solution cannot be administered from an open ampoule.
It is not advisable to mix Gordox with other drugs.
Gordox®
When using aprotinin, especially with repeated use of the drug, allergic/anaphylactic reactions may develop. Therefore, before using the drug, it is necessary to carefully evaluate the benefit/risk ratio. 10 minutes before the main dose of GORDOX® is administered, a test dose of 1 ml (10 thousand KIU) is administered. 15 minutes before the administration of a therapeutic dose of GORDOX®, it is possible to use histamine H1- and H2-receptor blockers. However, allergic/anaphylactic reactions can also develop when a therapeutic dose of the drug is administered, even if no adverse reactions were observed during the administration of the test dose. In case of development of hypersensitivity reactions when using aprotinin, the administration of the drug should be stopped immediately and standard emergency measures aimed at treating allergic/anaphylactic reactions should be carried out.
When performing surgery on the thoracic aorta using an artificial cardiopulmonary bypass and using deep cold cardioplegia, GORDOX® should be used with extreme caution against the background of adequate heparin therapy.
Determination of activated clotting time is not a standardized test for determining the coagulation capacity of blood, and the use of aprotinin may affect different test procedures. The coagulation test (ACT) is subject to various dilution and temperature effects. The ACT test with kaolin does not increase as much in the presence of aprotinin as the ACT test with celite. Due to differences in protocols, it is recommended to use the minimum values of ACT test - 750 seconds and ACT test with kaolin - 480 seconds in the presence of aprotinin, regardless of the effects of hemodilution and hypothermia. The standard dose of heparin administered before cardiac cannulation and the amount of heparin added to the primary volume in the heart-lung machine should be at least 350 IU/kg. The additional dose of heparin is determined by the patient's body weight and the duration of the extracorporeal circulation period. The protamine titration method is not affected by aprotinin. Additional doses of heparin are determined based on the heparin concentration calculated by this method.
Heparin concentrations during bypass should not fall below 2.7 units/ml (0.2 mg/kg) or below the level determined before the use of aprotinin.
In patients treated with GORDOX®, neutralization of heparin with protamine should be carried out only after interruption of extracorporeal circulation, based on a fixed amount of heparin administered or under the control of a protamine titration method.
This medicine contains benzyl alcohol. The daily dosage of benzyl alcohol should not exceed 90 mg per kilogram of body weight.
During the treatment cycle, the maximum dosage of aprotinin cannot exceed 6 million KIU.
Aprotinin is not a substitute for heparin.
Preparations for parenteral administration must undergo visual inspection immediately before use. Do not use leftover solution for subsequent use.
Gordox's analogues
Level 4 ATX code matches:
Aerus
Ingitril
Trasylol
Aprotex
Contrikal
Analogues of Gordox are the following drugs:
- Traxolan
- Aprotex
- Ingitril
- Aerus
These drugs can be used as a substitute for Gordox only after the approval of a doctor.
During pregnancy and lactation
Gordox can be used to treat expectant mothers only after the first trimester of pregnancy. However, even in later stages of pregnancy, the drug is used exclusively as prescribed by a doctor and if there are clear indications for its use. At the same time, constant medical supervision is important when treating with this drug.
clinical data on the safety of using the drug during breastfeeding .
Gordox price, where to buy
The drug is often prescribed for a number of diseases, in particular pancreatitis.
The price of Gordox in pharmacies is on average 4,000 rubles per pack of 25 ampoules. You can buy one ampoule in Moscow at a price from 150 to 250 rubles.
- Online pharmacies in RussiaRussia
- Online pharmacies in UkraineUkraine
- Online pharmacies in KazakhstanKazakhstan
Pharmacy Dialogue
- Gordoks 100000 KIE (amp. 10 ml No. 1) Gedeon-Richter
222 rub. order
show more
PaniPharmacy
- Gordox ampoule Gordox solution for injection 100000 units ampoules 10ml No. 25 Hungary, Gedeon Richter
4663 UAH.order
show more