Share information with your Facebook friends
VK
The foods we consume are directly related to health. If we eat properly and the body receives a sufficient amount of proteins, fats and carbohydrates, and at the same time the products are of high quality and properly prepared, then the risk of stomach disease is significantly reduced. But, unfortunately, the modern rhythm of life involves a lot of snacking and eating on the go. That is why there are so many people suffering from diseases of the gastrointestinal tract (GIT).
The role of nutrition in the treatment of gastrointestinal diseases
Proper nutrition is the basis for the treatment of diseases of the gastrointestinal tract. All kinds of modern medicines, of course, help, but their effect will be nullified if you do not change your unhealthy lifestyle and continue to eat harmful foods.
The diet may have the following clinical effects:
- using the right products you can regulate acidity;
- activate and normalize gastric motility;
- improve digestive function;
- cleansing;
- mucosal regeneration;
The importance of restoring microflora
Normal intestinal microflora is a balance of beneficial and harmful bacteria that inhabit the human intestine. If harmful ones predominate, and beneficial ones are in the minority, this condition is called microflora imbalance and requires correction. This is what gastroenterologists do.
They recommend taking a stool test for dysbacteriosis and bacterial culture in case of noticeable disturbances in the intestines (bloating, diarrhea, nausea, constipation, pain, etc.).
Based on the test results, appropriate treatment is prescribed, after which the microflora is normalized and the person’s well-being improves. Normal intestinal microflora is important for the production of essential vitamins, strengthening the immune system and protecting against various diseases.
Various factors can worsen the condition of the intestinal microflora, these are:
- taking antibiotics and NSAIDs;
- passion for the Western diet (with the presence of fast foods);
- lack of fiber in the diet;
- taking painkillers;
- treatment with proton pump inhibitors;
- use of H2-histamine receptor blockers.
Some doctors believe that the intestinal environment does not need to be sterile. But harmful bacteria should make up no more than 15 percent of the total microflora. Only then will the imbalance persist.
Microflora can change depending on a person’s age, mood, well-being, climate, and season.
Microflora disturbances can cause the following diseases:
- oncology;
- asthma;
- colitis;
- autism;
- eczema;
- diabetes;
- obesity;
- multiple sclerosis;
- heart diseases.
That is why we must take care of the state of the intestinal microflora. Let's look at some useful tips on this matter.
What foods should you eat?
Some of the healthiest foods for the stomach are those that contain fiber. For example, vegetables, fruits, bran, grains. Such products take a long time to digest and at the same time have a beneficial effect on the digestive system and activate gastric motility.
The richest fruit in terms of fiber content is banana. In other fruits and vegetables, the bulk of this beneficial component is contained in the peel. Therefore, it is better to eat them fresh or in the form of vegetable salads dressed with vegetable oil. It’s good to add greens to this dish. Only if you have no contraindications, stomach pain, ulcers, gastritis.
It is better to eat whole grain bread, it has a lot of fiber.
Dairy products such as kefir, fermented baked milk, cottage cheese, cheese, and sour cream are especially useful. They normalize acidity and contain calcium, vitamins A, B1, B2, B12.
For people suffering from gastritis and ulcers, a diet containing cereals, such as semolina, rolled oats, rice, buckwheat, is recommended; it is better to eat them mashed or well boiled, so as not to disturb the mucous membrane with coarse particles. These cereals are rich in potassium and magnesium. At the same time, they have a beneficial effect on the mucous membrane of the digestive organs and promote healing of the irritated surface.
Establishing diagnosis
Only a doctor can make an accurate diagnosis, and only after conducting appropriate tests and studies, the results of which will make the whole picture clear. The specialist will prescribe a series of studies that will help narrow the range of problems and exclude more serious diseases. The main methods for diagnosing irritable stomach syndrome include:
- X-ray. It is during the X-ray that the amount of gastric juice that is currently present in the stomach will be visible.
- Study of the acidity of the environment. To do this, a special probe is inserted through the person's mouth, with which the acidity in the stomach is measured. To do this, several areas are selected, which is necessary for a more accurate result. In addition, the probe measures basal temperature, as well as how quickly or slowly acid is produced. Today, thanks to the latest technologies, it is possible to accurately determine where the cells are located that produce either less or more acid.
- Research using stimulants. The stimulant activates the production of secretion. Using this study, the acidity of the stomach is measured, which a person will have on an empty stomach, as well as after eating
- FGDS, during which the doctor will completely examine the internal state of the mucous membrane of not only the stomach, but also the duodenum, which is closely connected to it
- Ultrasound examination, during which it is determined whether there are any abnormalities in the pancreas, as well as the absence of enlargement of other important organs
Before making a diagnosis, the doctor will fully study the results and, guided by them, prescribe treatment, if required.
Heavy foods for the stomach
Below is a list of foods that are not good for the stomach. They can irritate the walls and lead to painful conditions of the digestive organs and the formation of ulcers, bloating, pain, difficult digestion, and heartburn. These products include:
- fast food;
- fatty food;
- fried foods;
- very spicy food;
- high consumption of herbs and spices;
- low-quality products (spoiled);
- alcohol and soda;
Vitamin D
Another fat-soluble vitamin that has a significant effect on the functioning of the immune system is vitamin D. It is known that it [4]:
- stimulates the activity of macrophages;
- induces differentiation [maturation] of immune cells;
- increases monocyte proliferation;
- increases the activity of T-regulatory cells, which regulate the strength and duration of the immune response;
- reduces the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines;
- increases the synthesis of antimicrobial peptides.
It has been proven that with a vitamin D content of more than 50 ng/ml in the blood plasma, the likelihood of developing respiratory infections is 27% lower than with severe deficiency [vitamin D level less than 20 ng/ml] [5]. At higher concentrations of the vitamin in the blood, the risk of developing influenza, respiratory syncytial virus infection, and pneumonia is reduced [6]. The decrease in the likelihood of developing the latter is associated with the beneficial effect of vitamin D on the respiratory tract: it reduces the production of cytokines in epithelial cells, reducing the severity of inflammation, and blocks the proliferation of smooth muscles of the respiratory tract [7].
The daily dose of vitamin D is 600-800 IU. For pregnant and lactating women it reaches 800-1200 IU, and for people over 50 years old 800-1000 IU.
Light foods for the stomach
Products that are good for the stomach should be consumed by patients with gastrointestinal diseases in the acute stage and in remission.
Those with a sweet tooth are allowed to eat savory cookies, yeast-free buns, and pies. The baked goods must not be fresh, but yesterday’s or dried. You can eat marshmallows and marshmallows in small quantities.
It is better to choose lean varieties of meat, such as chicken, turkey, beef, and rabbit. The same applies to fish. These products are more easily absorbed in the intestines. The meat can be eaten simply boiled or baked, or you can prepare various dishes without using oil, for example, steamed cutlets, zrazy, and meatballs.
It is useful to consume dairy products, especially cottage cheese. You can use it to make cheesecakes and casseroles. You are allowed to eat a little hard low-fat cheese.
Among the drinks, it is useful to drink rosehip decoction, weak tea with milk, fruit and vegetable juices.
It is better for patients with diseases of the gastrointestinal tract to consume vegetables and fruits after heat treatment, boiled, baked, steamed. Vegetables are especially beneficial for the stomach. For example, beets, cauliflower, pumpkin, carrots and potatoes.
Vitamins that protect the body in general and mucous membranes in particular
Severe deficiency of any vitamin negatively affects the immune response, since each of the essential micronutrients is included in several biochemical cascades at once. For example, deficiency of vitamin C causes scurvy, B12 – corresponding anemia, which is accompanied by a significant decrease in protective functions. In this context, the optimal means of increasing the body's defenses are multivitamin complexes. However, some nutrients play a special role in the formation of the immune response, let's talk about them in more detail.
Foods that are good for the stomach and stimulate the gastrointestinal tract
In some patients, most often the elderly, intestinal motility deteriorates and the person begins to suffer from constant constipation. But there are foods whose consumption stimulates gastric and intestinal motility, which improves digestion and reduces the likelihood of constipation. These foods that are good for the stomach include:
- Fermented milk products (kefir, fermented baked milk, cottage cheese).
- Vegetables: pumpkin, beets, carrots, sauerkraut. You can have vegetable soups, but only without meat.
- Fruits: melon, apple, plum.
- Berries and jam from them.
- Scrambled eggs.
- Honey.
- Various porridges on the water.
Normalization of the nasal mucosa as a medical and social problem
Our body can fully live and develop only if there is a constant exchange of substances between it and its environment. One of the most important forms of communication between the body and the environment, which is not interrupted throughout a person’s life, is communication through the respiratory system. The nose, which is the initial part of the respiratory tract, is a powerful protective barrier that informs the centers about contact with various environmental agents, conditioning the inhaled air, retaining and neutralizing substances that can enter the body with the air [7].
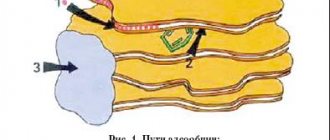
The leading role in the protective function of the nose belongs to the mucous membrane, which is covered with pseudostratified epithelium, consisting of ciliated, goblet, and short and long intercalated epithelial cells. The ciliated cell has numerous cilia at its free end.
| Rice. The structure of the nasal mucosa |
Ciliated cells have 250–300 cilia, 7 microns long and 0.3 microns high. Each cilium consists of 9 pairs of microtubules arranged in a ring and surrounding two unpaired central microtubules. The movement of the cilia of the ciliated epithelium of the nasal mucosa is carried out through the sliding of microtubules. The movement of the cilia is strictly directed - from the vestibule of the nasal cavity towards the nasopharynx. Mucociliary clearance is provided by nasal secretions. The source of the secretion covering the epithelium of the nasal cavity is the mucous glands of the nasal mucosa, goblet cells, extravasation from subepithelial capillaries, lacrimal glands, and the secretion of specialized Bowman glands from the olfactory zone of the nose [7] (Fig.).
The volume of nasal secretion in 24 hours ranges from 100 ml to 1–2 liters. The mucous membrane of the posterior two-thirds of the nasal cavity is renewed every 10–15 minutes. The function of the cilia is optimal at a temperature of 28–33 °C, a sufficient amount of secretion with a pH of 5.5–6.5. Loss of moisture, a decrease in temperature to 7–10 °C, and an increase in secretion pH above 6.5 cause the cilia to stop vibrating [8, 11].
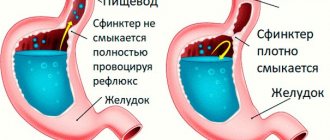
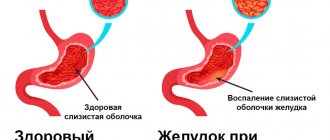
The mucous membrane of the nasal cavity is the first barrier to the protection of the respiratory tract, therefore thousands of microorganisms are deposited on the mucous membrane of the nasal cavity every second. Most of them are representatives of saprophytic microflora and do not cause any harm to humans, while others can provoke the development of an infectious disease. With infectious rhinitis, the proliferation of microbes on the nasal mucosa leads to its damage and peeling of the upper part of the epithelium. This process explains all manifestations of a runny nose: a burning sensation in the nose, discharge of mucus (exudate), nasal congestion, changes in voice (nasality), etc. [9].
Rhinitis is rarely an independent disease. Most often, a runny nose is a symptom of some other nosological form. A runny nose is observed with various acute respiratory viral infections or acute respiratory infections (influenza, parainfluenza, adenoviral infection, measles, etc.). Acute respiratory diseases are the most common in the structure of infectious diseases. In Russia, about 50 million cases of infectious diseases are registered annually, of which up to 90% of cases are acute respiratory viral infections. In the case of pathology of the ENT organs, the mucous membrane with its glandular cells is primarily affected.
In addition to infectious diseases, in industrialized countries currently 10% to 20% of the population suffers from acute allergic diseases. In addition, in the pathogenesis of inflammatory diseases of the upper respiratory tract, along with local and general exposure to the pathogen, sensitization of the body and immunological changes directly in the mucous membrane of the nose and paranasal sinuses play a role [4].
The nasal mucosa is the area that is exposed to a wide variety of foreign particles. Allergen molecules extremely quickly cause an allergic reaction, as a result of which sneezing, itching in the nasal cavity, and rhinorrhea occur within a minute after the penetration of allergens [5, 6].
Other etiological factors for damage to the mucous membrane may include unfavorable ecology, occupational hazards, and bad habits (tobacco smoking, drug addiction). In the city, directly below the surface of the earth, the highest concentration of all types of xenobiotics is found - free radical compounds, carcinogens, heavy metal salts, all types of allergens, and, of course, pathogenic microorganisms. The mucous membrane of the nose, mouth and pharynx is in constant contact with inhaled air and is thus exposed to harmful environmental factors, which leads to its swelling. In any case, conditions arise in which the nasal mucosa becomes easily infected, reacting with the appearance of significant swelling [3].
As a side effect, medications taken for various diseases often cause subatrophy of the nasal mucosa due to systemic action, which is especially important for representatives of holospeech professions due to the upcoming changes in the resonator tract [1, 10].
In some diseases, for example, diabetes, atrophic and subatrophic rhinitis often develop due to disturbances in the microcirculatory system. Taking into account the prevalence of this disease, in particular, due to the decreasing age of those who first become ill (the working population), problems with moistening the nasal mucosa are of a social nature.
As studies show, the planet's population is aging, average life expectancy is increasing and, accordingly, the requirements for quality of life in this population group are increasing. It is known that with a decrease in the level of sex hormones caused by menopause in women and a decrease in the function of the gonads in men, the likelihood of developing subatrophic and atrophic processes on the skin and mucous membranes increases sharply.
Thus, in normalizing the function of the nasal mucosa, the leading directions of therapy are:
1) stimulation of local and general blood circulation, i.e. increased supply of the mucous membrane with nutrients; 2) moisturizing the nasal mucosa and preventing the formation of crusts; 3) fight against local pathological microflora.
Topical preparations containing essential microelements that regulate the rheological properties of mucus meet these principles. It is believed that trace elements contained in an isotonic solution, such as Ca, Fe, K, Mg, Cu, help to increase the motor activity of cilia, activate reparative processes in the cells of the nasal mucosa and normalize the function of its glands [7]. The listed microelements are contained in preparations that are prepared from sea water, sterilizing it and bringing the salt content to isotonic concentration, and from mineral spring water, which has medicinal properties.
It is known that sea water is very beneficial for the human body, as it contains many valuable micro- and macroelements. Sea water activates all vital processes of the body, increases its resistance to various diseases, and has a local antiseptic effect.
Healing properties of sea water:
- Rinsing the nasal cavity with sea water has an antibacterial effect, washing away dust, viruses and bacteria.
- Gargling with warm sea water treats throat diseases and restores the vocal cords.
- Sea baths and air stimulate the endocrine system.
- Sea water accelerates the healing of abrasions and cuts due to the content of large amounts of salts and trace elements.
- Rinsing your mouth with warm sea water strengthens your teeth and gums.
One of the new drugs in this group is Otrivin More [2], which is a purified, decontaminated isotonic solution of ocean water from Brittany, obtained in an ecologically clean area of the Atlantic Ocean, rich in natural microelements. It contains 18 minerals and trace elements.
Thanks to this composition, Otrivin More is ideal for protecting the nasal mucosa from unfavorable city conditions, as well as for facilitating nasal breathing during illness. Otrivin More ensures rapid elimination of pathogens and allergens, that is, it significantly reduces their concentration and promotes mechanical cleansing of the surface of the nasal mucosa. In addition, Otrivin More stimulates ciliated epithelial cells, helps normalize mucus production and dilute it, and also increases local immunity. An important advantage of the drug is the absence of any systemic effect on the patient’s body, which is extremely important for people suffering from various somatic diseases and who are afraid of taking traditional topical vasoconstrictors due to the risk of side effects. In addition, the patient has the opportunity to reduce the dosage of other medications used for complex treatment and speed up recovery.
Otrivin Sea can be used both for preventive and therapeutic purposes, and for daily hygiene of the nasal cavity. The new product does not contain preservatives or additional chemical ingredients. The main indications for prescribing the drug are acute rhinitis (including allergic) and nasal congestion. For a runny nose and allergies, Otrivin Sea makes breathing easier, gently cleansing the nasal passages, and also has an antiseptic effect. In addition, the product can be used for nasal hygiene before using other medications. For prevention purposes, it is possible to use the drug Otrivin More during epidemics of various viral diseases, which prevents the development of various forms of infectious process on the nasal mucosa. The drug can also be used for the purpose of hygiene of the nasal cavity, effectively cleansing the nasal mucosa and gently moisturizing it. The natural composition of Otrivin More will not only ensure the high safety of the treatment, but also allows you to use the drug for rinsing the nose for allergies.
Many nasal sprays cause discomfort when taking them, which is associated with irritation of the nasal mucosa. Otrivin More in the form of a nasal douche is free of this side effect. By carefully rinsing the nasal cavity, the drug removes dust, bacteria and secretions and prevents it from drying out, thereby protecting it from the irritating effects of external factors, which is especially important for people working in rooms with excessively dry air (for example, where air conditioners are installed or near heating devices ).
The form of release of the drug is of great importance. When using nasal drops, most of the injected solution flows down the bottom of the nasal cavity into the pharynx. In this case, the required therapeutic effect is not achieved. In this regard, the prescription of metered aerosols looks much more profitable, for example, a feature of the drug Otrivin More is that it is released in the form of a nasal spray.
Otrivin Sea can also be used for daily nasal hygiene. This procedure has been known since ancient times and is no less important for our health than brushing our teeth. In the modern world, in cramped and dusty cities, daily preventive rinsing of the nose with sea water has become especially important.
For the convenience of patients, Otrivin More is available in bottles of optimal volume - 50 and 100 ml, which will be appropriate in both home and travel first aid kits. In addition, the Otrivin More bottle is equipped with a universal nozzle, suitable for the whole family and can be recommended for children from the age of three months. At the same time, the spray tip will ensure accurate and uniform moistening of the nasal cavity, and a special valve that protects the medicine from microorganisms entering it guarantees a long period of use after the first use.
Thus, the drug Otrivin More is a reliable remedy that cleanses the nasal mucosa in adults and children, restoring its physiological function, without causing dryness and having a persistent long-term effect, thereby preventing the development of serious complications and at the same time carefully affecting its structural components . Otrivin More can be used both for the treatment and prevention of a runny nose, as well as to protect the nasal mucosa from irritating environmental influences.
Literature
- Voloshina I. A., Turovsky A. B. Irrigation therapy of atrophic rhinitis. S. 1906.
- State register of medicines. M.: Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation, 2008.
- Gurov A. A. Swelling of the mucous membrane of the upper respiratory tract. How to deal with it? 1254 pp.
- Karpova E. P., Usenya L. I. Topical decongestants for the treatment of inflammatory diseases of the nasal cavity and paranasal sinuses in children. P. 18.
- Markov G.I. Transport function of the ciliated epithelium of the nasal mucosa in inflammatory diseases // Bulletin of Otorhinolaryngology. 1985. No. 4. pp. 36–37.
- Palchun V. T., Magomedov M. M., Luchikhin L. A. Otorhinolaryngology. M.: Medicine. 2002. 576 p.
- Piskunov G.Z., Piskunov S.Z. Clinical rhinology. M., 2002. 390 p.
- Pluzhnikov M. S., Shanturov A. G., Lavrenova G. V., Nosulya E. V. Nasal mucosa. Mechanisms of homeostasis and homokinesis. St. Petersburg 1995. pp. 5–18.
- Ryazantsev S.V. Modern decongestants in the complex therapy of acute and chronic diseases of the ENT organs // Russian Otorhinolaryngology. 2008, No. 6 (19).
- Deitmer T., Scheffler R. The effect of different preparations of nasal decongestans in ciliary beat frequency in vitro // Rhinology. 1993; 31–151–3 (14).
- Satir P. How cillia move // Scientific American. 1974. Vol. 231. P. 45–46.
N. E. Boykova, Candidate of Medical Sciences
Scientific and Clinical Center of Otorhinolaryngology of the Federal Medical and Biological Agency, Moscow
Contact information for authors for correspondence