Home » Rectal prolapse
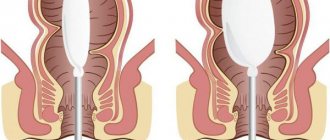
Prolapse of the intestine from the anus is a disease characterized by partial or complete location of the rectum outside the anus. Even in its most severe forms, this disease usually does not threaten the patient's life, but is accompanied by debilitating symptoms. The rectum falls out of the anus, which brings a lot of discomfort to the patient.
Types of rectal prolapse
Bowel prolapse is also called rectal prolapse or pelvic floor prolapse. Patients are diagnosed with two types of pathology:
- internal bowel prolapse;
- external bowel prolapse;
Internal rectal prolapse is a violation of the anatomical position of the rectum
, in which there is a displacement of its distal part beyond the anal sphincter. May be accompanied by pain, incontinence of intestinal contents, mucous and bloody discharge, sensation of a foreign body in the anus, false urge to defecate.
External intestinal prolapse is accompanied by weakness of the anal muscles, fecal disturbances, the appearance of mucus and blood, flatulence and bloating.
Traditional methods
The recommendations of traditional healers are based on the belief in the stimulating effect of herbal decoctions on the rectum and surrounding muscles. For this we offer:
- sitz baths with the addition of a decoction of sage, horse chestnut, knotweed, oak bark, chamomile flowers;
- compresses from quince juice, shepherd's purse decoction;
- calamus root for oral administration.
Continued smoking and constant coughing worsen the prolapse condition.
Causes of rectal prolapse
Why does the rectum prolapse? Prolapse of the intestine from the anus can be caused by a number of reasons. The appearance of pathology is influenced by the following factors:
Gastrointestinal tract disorders. Diarrhea disrupts intra-abdominal pressure, which negatively affects the functioning of internal organs. Constipation also negatively affects the functionality of the intestines. Feces accumulate in the body, which leads to prolapse of the intestine from the anus.
Sedentary lifestyle. Often the intestine falls out of the anus if a person leads a sedentary lifestyle . When sitting, blood flow and pressure in the anus are disrupted. In this regard, the soft tissues become thinner, bleeding begins, and the rectum prolapses. At-risk groups include salespeople, office workers and drivers.
Increased physical activity. Constant physical activity affects internal organs. There is strong pressure on the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract. When the vessels of the anus become thinner, the rectum prolapses.
Genetic predisposition. Those who are genetically predisposed to rectal prolapse have weak blood vessels from birth. In such people, intra-abdominal pressure is disrupted, and the risk of developing hemorrhoids and intestinal prolapse increases.
Alcohol abuse. With excessive alcohol consumption , intra-abdominal pressure increases, microflora and intestinal motility are disrupted.
Poor nutrition. Abuse of baked goods, sweets, and salty foods leads to inflammation of the intestinal mucosa and increased intra-abdominal pressure. The patient is bothered by cramps in the intestines and bloating. The rectum prolapses from the anus.
Long-term use of medications. With long-term use of medications, the functioning of the esophagus deteriorates and the functionality of the intestines is disrupted. Blood flow in the intestines is disrupted, intra-abdominal pressure increases.
Pregnancy and labor. During pregnancy, the fetus exerts strong pressure on the internal organs. The pelvic organs bear a particularly heavy load. During labor, a woman pushes, which provokes an increase in intra-abdominal pressure. Anal fissures form, the rectum begins to prolapse after childbirth.
The presence of benign and malignant neoplasms. If a patient is diagnosed with neoplasms, then pressure is observed on all internal organs. The vessels of the anus are deformed and weakened.
Ulcerative colitis and duodenal ulcer. Gastritis and duodenal ulcer lead to an inflammatory process. The pelvic floor muscles are damaged, which causes rectal prolapse.
Respiratory tract diseases. Chronic cough and other respiratory diseases often lead to rectal prolapse. This is explained by an increase in intra-abdominal pressure.
An infectious process in the body can also provoke intestinal prolapse. The appearance of parasites contributes to the weakening of all internal organs. The vessels of the anus are damaged. Also, the rectum falls out due to problems with the nervous system. These include depression, multiple sclerosis, neurosis and other diagnoses.
Diet
Despite the fact that there is no diet for rectal prolapse as such, dietary correction is a mandatory component of conservative treatment. Since rectal prolapse is very often caused by chronic constipation, a “Constipation Diet” or a “Fiber Diet” may be prescribed. They are based on the inclusion of high-fiber foods (fiber) in the diet and drinking plenty of fluids. Sources of fiber are products of plant origin: bran, cereals (oatmeal, wheat, barley, pearl barley), garden greens, legumes, raw vegetables/fruits, seeds, nuts (almonds, peanuts). That is, in essence, it is necessary to include large amounts of whole, natural food in your diet.
The basic principles of creating a diet enriched with fiber include:
- adding bran to soups, cereals, fermented milk products, juices, jelly;
- consumption of raw vegetables/after cooking (beets, zucchini, fresh cabbage of various types, carrots, cucumbers, pumpkin, tomatoes) simultaneously with meat/fish (protein) products;
- using day-old bread made from whole grain flour or with added fiber;
- separate consumption of legumes/cereals (barley, pearl barley, millet) cooked in water with vegetable side dishes;
- if possible, more often consume fruits with the skin as a snack, as well as dried soaked fruits as an additive to kefir or various dishes (figs, dried apricots, apricots);
- eating prunes both whole and in the form of infusion;
- daily consumption of fermented milk products: acidophilus yogurt, fermented baked milk, kefir, matsoni, kumiss;
- daily consumption of free fluid (in the amount of 2.0-2.5 l/day).
The following are subject to exclusion/restriction from the diet:
- bakery products made from premium flour, baked goods made from puff pastry/yeast dough;
- chocolate and cream products;
- products/dishes with a high content of tannins (pears, dogwoods, quince jelly, blueberries, bird cherry, cocoa and coffee, strong black tea;
- dishes with a viscous consistency (mashed potatoes, slimy soups, jelly, pureed porridge), slowing down the passage of food through the esophagus;
- seasonings/spices (mustard sauces, horseradish, garlic, pepper) and spicy foods that strongly irritate the gastrointestinal mucosa, as well as difficult-to-digest foods (hard-boiled eggs, fatty meats/fish, canned food, smoked meats);
- foods that directly cause constipation or take a long time to digest (semolina, rice, noodles, potatoes, vermicelli, legumes).
Symptoms of rectal prolapse
In the early stages there are no symptoms. In advanced stages, the patient is bothered by the sensation of a foreign body in the anus. Painful sensations intensify during defecation and movement. In some cases, pain occurs when coughing and sneezing.
When the situation is not advanced, it is possible to straighten the intestine on your own without the help of a medical specialist. With internal rectal prolapse, the patient feels incomplete bowel movement. Due to intestinal problems, fecal incontinence is observed. Impurities of pus, blood and mucus are found in the stool . This symptom indicates an inflammatory process in the body.
The patient is concerned about flatulence and bloating . Cramping pain appears, which intensifies after eating. Due to impaired functioning of the esophagus, the patient has no appetite, belching and vomiting begin . In most cases, constipation is diagnosed due to excessive accumulation of feces in the rectum. The process of bowel movements becomes more complicated and inconvenient for the patient.
Symptoms include discomfort in the anus. There is itching and burning, cutting pain in the anus during movement and during bowel movements. In the absence of timely treatment, the walls of the anus become thinner, the mucous membrane becomes inflamed and thick. Bleeding develops, which can lead to an infectious process.
In the early stages, intestinal prolapse does not cause discomfort to the patient, but later pain appears.
More information on the topic of genital prolapse:
Genital prolapse, Uterine prolapse, Surgery for prolapse of the uterus and vaginal walls, Laparoscopic facilitated promontofixation with vaginal plastic surgery, Cystocele, Surgery for cystocele, Urinary incontinence, Rectocele, Surgery for rectocele, Prolapse of the uterine walls, Complete prolapse of the uterus, What to do if the uterus prolapses? , Uterine prolapse after childbirth, Consequences of uterine prolapse, Degrees of uterine prolapse, Stage 2 uterine prolapse
Watch a video of operations performed by Professor K.V. Puchkov. You can visit the website “Video of operations of the best surgeons in the world.”
Rectal prolapse and hemorrhoids
Quite often, patients confuse rectal prolapse with hemorrhoids . Prolapse of hemorrhoids has similar symptoms, but treatment for these pathologies is radically different. The diseases are similar in that we are talking about impaired functioning of the gastrointestinal tract. Also, hemorrhoids and rectal prolapse have similar symptoms.
However, when the first symptoms of both diseases appear, you should immediately contact a proctologist . You should not try to cure the disease at home using suppositories and ointments .
Self-medication leads to a worsening of the condition and entails a lot of complications. With hemorrhoids, hemorrhoidal tissue prolapses from the anus, and with prolapse, parts of the rectum fall out.
List of published works on the topic “Rectal and genital prolapse”
“Minimally invasive colon surgery”, K. V. Puchkov, D. A. Khubezov
- Puchkov K.V., Karpov O.E., Filimonov V.B. Laparoscopic rectopexy // Ros. magazine gastroenterology, hepatology, coloproctology.-1997.-T. 7, No. 5 (add. 4). -P.248.
- Puchkov K., Filimonov V., Titov G., Chubezov D. Laparoscopic technology in coloproctology // Proktologia. – 2001. – Suppl. No. 1. – P. 97.
- Puchkov K.V., Khubezov D.A. Laparoscopic rectopexy // Problems of coloproctology. Vol. 18. - M., 2002. - P. 194-195.
- Puchkov K.V., Khubezov D.A., Yudina E.A.. Laparoscopic one-stage recto- and sacrovaginopexy // Current issues of coloproctology: abstract. report 1st Congress of Coloproctologists of Russia with international. participation / edited by G.I. Vorobyova, G.P. Kotelnikova, B.N. Zhukova.- Samara: State Enterprise <Perspective>: SamSMU, 2003. - P. 398-399.
- Puchkov K.V., Khubezov D.A., Politova A.K. Laparoscopic recto- and sacrovaginopexy in patients with a combination of rectal prolapse and uterine prolapse // Current problems of modern surgery: tr. congress, Moscow, February 22-25. 2003 – M., 2003. – P.36.
- Puchkov K.V., Khubezov D.A., Yudina E.A., Khubezov A.T., Podyablonsky A.V. Laparoscopic recto- and vaginosacropexy with one implant // Current problems of pelvic surgery. - M., 2003.- P. 79 –81.
- Puchkov K.V., Ivanov V.V., Bakov V.S., Usachev I.A. Optimization of techniques for surgical treatment of pelvic prolapse // Minimally invasive technologies in surgery: materials from interregion. scientific-practical conf. - Makhachkala: IPC DSMA, 2005. - P.159-160.
- Puchkov K.V., Khubezov D.A. Minimally invasive colon surgery: A guide for doctors. - M.: OJSC "Publishing House "Medicine", 2005. - 280 p.
- Puchkov K.V., Bakov V.S., Ivanov V.V. Simultaneous laparoscopic surgical interventions in surgery and gynecology: Monograph. - M.: ID MEDPRACTIKA - M. - 2005. - 168 p.
- Puchkov K.V., Ivanov V.V., Usachev I.A. The use of polypropylene implants with simultaneous prolapse of pelvic organs // 9th Moscow. international congr. in endoscopic surgery, Moscow, April 6-8. 2005: abstract. report / ed. Yu.I. Galingera. – M., 2005. – P.296-297.
- Puchkov KV, Ivanov VV, Barsukov VA, Filimonov VB Determining of safety of soldering of vessels in tissue mass of various types while using the technique of dosed ligating electrothermal influence of ligasure // Abstracts of The 10th World Congress of Endoscopic Surgery, 13 -16 September, 2006, Berlin. – P.288.
- Puchkov K.V., Chernousova N.M., Filimonov V.B., Vasin R.V., Andreeva Yu.E. Correction of genital prolapse and stress urinary incontinence in women using modern synthetic implants // Journal. obstetrics and women's diseases.-2007.-T. 57 (special issue). — P.204-206.
- Puchkov KV, Filimonov VB, Vasin RV Correction of pelvic floors prolapse and women under tension enuresis // Abstracts book of the 16th EAES Congress 2008 with the help of up-to-date implants, 11-14 July, 2008, Stockholm, Sweden. – P.208-209.
- Puchkov K.V., Filimonov V.B., Vasin R.V., Vasina I.V. Complications of using polypropylene implants for pelvic prolapse // Journal. obstetrics and women's diseases.-2009.-T. 58.(issue 5). — P.66-67.
- Puchkov K.V., Filimonov V.B., Vasin R.V., Vasina I.V. Diagnostic capabilities and value of ultrasonography and magnetic resonance imaging for pelvic prolapse // Journal. obstetrics and women's diseases.-2009.-T. 58. (issue 5). — P.67-68.
- Puchkov KV, Filimonov VB, Vasin RV, Vasin IV Polypropylene implants as the treatment decision for patients with pelvic prolapses, connective tissue displasia and stress incontinence // Abstracts book of the 17th EAES Congress 2009, 17-20 June, 2009, Prague , Czech Republic. – P.96.
- Puchkov KV, Podzolkova NM, Andreeva JE, Dobychina AV, Korennaya VV Polypropylene implants as the treatment decision for patients with pelvic prolapses // 21st ESGE Annual Congress (Paris, 11-14 September 2012) - P.88-89.
Diagnosis of rectal prolapse
To diagnose a proctological disease, you should contact a medical specialist who will conduct an initial examination. It is worth informing the proctologist about the nature of the pain, its frequency and intensity. After obtaining an anamnesis, the attending physician will be able to make a diagnosis and determine the stage of the disease.
Next, a primary examination is carried out , during which the proctologist determines the size of the rectum and detects the presence of bloody discharge. To obtain maximum information about the patient’s condition, a number of diagnostic studies are carried out:
- Anal electromyography is a test that allows you to observe the work of the anal sphincters. Holding function is assessed.
- Anal manometry is a method that examines the functioning of the anal sphincter muscles.
- Anorectal ultrasound is used to evaluate the structure of the vessels and muscles of the anus. It is possible to determine how well the patient's bowels are being emptied.
- Proctography is also called defecography. The procedure evaluates whether the intestine retains feces normally.
- Colonoscopy is a method that uses a special surgical instrument that allows you to demonstrate the condition of the rectum and colon.
The private proctology center “Proctologist 81” employs doctors of the highest category. To carry out diagnostics, only modern equipment and innovative treatment methods are used. The disease will be detected even at an early stage.
Conservative therapy
At an early stage, conservative treatment is possible. With drug therapy, the sagging portion of the intestine will tighten and assume a physiological position. Medicines reduce discomfort. Normalizing your diet will help get rid of diarrhea and constipation. Another task is to restore the tone of the anal sphincter and the problem area of the intestine.
Doctors usually prescribe drugs to normalize stool - laxative suppositories and oral powders or tablets. If there is pain, the doctor will recommend painkillers. The proctologist will monitor the effectiveness of conservative treatment and positive dynamics. If there is no improvement, the patient will be sent for surgery.
Treatment of rectal prolapse
Each patient is individually selected for a course of treatment depending on his condition. The stage of the disease, the presence of accompanying symptoms and pathologies are of great importance. Rectal prolapse is considered a serious disease for which drug treatment will not make any sense. To relieve the patient of unpleasant symptoms, surgical intervention is performed. The following methods of surgical intervention are distinguished:
- rectosacropexy;
To perform such an abdominal operation, a special surgical instrument is used, namely a mesh allograft. This device allows you to hold the rectum in the required position. During the operation, the rectum is transferred to the area where the muscles are located. The affected area is pulled up and fixed to a place located near the sacrum and rectum.
- Kümmel operation;
With this surgical intervention, the mobilized rectum is fixed to the promontory of the sacrum. Interrupted sutures are applied. A laparotomy is performed, namely incisions or small punctures.
Also, for prolapse, operations are performed through the anus. These include the Delorme operation. The mucous membrane of the affected area of the rectum is removed. A muscle cuff is formed that prevents the intestine from prolapse.
- Altmeyer's operation
Carried out in some cases. We are talking about resection of the rectum or the affected area. A coloanal anastomosis is formed. The intestine joins the anus.
Longo's operation for rectal prolapse is also effective and is performed in most cases.
As a rule, surgical intervention allows the patient to get rid of unpleasant symptoms and pain immediately after the operation. The speed of healing depends on what type of rectal prolapse is diagnosed. The duration of rehabilitation is influenced by the number of concomitant diseases. After surgery, the patient goes home, where he continues treatment conservatively.
Complications after surgery
It is extremely important to adhere to the recommendations of your doctor to avoid complications. If you follow the rules of personal hygiene and pay attention to the symptoms, the risk of relapse is reduced to zero. Recurrence of the disease is diagnosed if the patient takes a hot bath or visits a sauna.
It is necessary to change the diet . It is worth including fermented milk products, cereals and broths, vegetables and fruits in the menu. Drinking plenty of fluids has a positive effect on the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract. It is strictly forbidden to take any medications without the knowledge of your doctor. Self-medication leads to negative consequences and even death.
Complications arise if the patient does not seek medical help on time. Self-medication is fraught with bleeding . Ulcerative colitis and duodenal ulcer develop. The patient is concerned about incontinence and problems with bowel movements. In advanced cases, necrosis of the walls of the rectum or tissue necrosis develops.
If you do not follow the rules of personal hygiene, an infectious process develops that affects all internal organs and leads to an abscess. The wound begins to fester. Seek help from medical specialists at the private proctology center “Proctologist 81”. Make an appointment at a time convenient for you.
Prevention
With congenital weakness of the pelvic muscles and rectovaginal septum, rectocele and prolapse are observed in most cases. To prevent the development of the disease and avoid complications, preventive measures should be followed.
Pay attention to the recommendations of proctologists:
- avoid gastrointestinal disorders, go to the toilet when the urge appears, do not strain when defecating;
- watch your weight - rapid obesity or weight loss contributes to the appearance of prolapse;
- watch your diet and eat foods high in fiber;
- do not self-medicate and diagnose inflammatory and infectious diseases of the gastrointestinal tract in a timely manner;
- avoid lifting heavy objects;
- strengthen the muscles of the pelvic floor and perineum.
Women should visit a gynecologist every six months, even if there are no complaints. During pregnancy, after abortion and after childbirth, it is recommended to attend a preventive examination more often.