Mild, moderate or severe pain in the lower abdomen in women, the causes of which can be different, is a very common complaint received from numerous patients - both very young and elderly. In some cases, although these are unpleasant, they are normal variants that do not indicate any pathologies. But, often they are one of the symptoms of a large list of diseases. First of all, gynecological health is under suspicion, although pain can also arise for other reasons. In any case, you need the help of specialists who will identify the source of the painful condition.
Types of lower abdominal pain
The nature of the pain may vary:
- pulling;
- pricking;
- aching;
- cramping;
- bursting;
- blunt;
- cutting;
- encircling;
- burning, as if burning from the inside.
Unpleasant sensations can begin abruptly and intensely, increase gradually, disturb the right, left or middle, radiate to the lower back and other areas. It can last for several minutes or days, stop intermittently or be constant.
The causes of lower abdominal pain in women can be divided into several main categories:
- physiological, caused by changes in the body;
- gynecological diseases;
- problems in the urinary system;
- disorders of the functioning of the intestines and diseases of the digestive system;
- other pathologies and conditions.
In choosing specific research methods and making the correct diagnosis, clarifying the nature, duration, and intensity of pain is of great importance. By studying the symptoms, doctors can assume a certain disease and outline the necessary direction in examining the patient.
First aid before the doctor arrives
The main activities that should be carried out by others or parents before the ambulance arrives include:
- Avoid taking medications, in particular those with an analgesic effect. This will make it difficult to make a diagnosis in the future.
- Constant monitoring of body temperature. When the temperature rises to 38 degrees, measurements must be taken every 15-20 minutes and the resulting values recorded.
- Provide plenty of fluids. If vomiting, loose stools and abdominal pain occur, it is allowed to take pure still water, as well as solutions that can replenish the loss of fluid from the bloodstream, preventing dehydration. It is forbidden to give your child juices, lemonades, coffee or tea.
- Providing peace. The child must be put to bed so that he can take a position that is comfortable for him and relieves pain. Avoid eating.
Lower abdominal pain in women: physiological causes
In this case, pain is associated with physiological changes occurring in the body. They can occur at different stages of the menstrual cycle, early pregnancy, and be observed during hormonal changes (including during menopause).
Soon after fertilization, a woman may feel a nagging pain. This is due to the introduction of the egg into the endometrium of the uterus, the integrity of which is disrupted. As the fetus grows, the internal organs shift, which sometimes provokes severe discomfort.
Many girls experience severe pain during ovulation in the lower abdomen, the causes of which are hidden in changes in hormonal levels resulting from the rupture of the follicle and the release of the egg. They are often accompanied by other symptoms:
Before menstruation, pain is also a frequent companion for many women. If the patient has been examined, no pathologies have been identified, and unpleasant sensations do not interfere with her normal lifestyle, then such manifestations fit within the boundaries of the norm. When the pain is intense and provokes a serious deterioration in the general condition, dysmenorrhea (algomenorrhea) is usually diagnosed.
What does the treatment of salpingopharitis in a child include?
As a rule, treatment is carried out at home with subsequent visits to the doctor for monitoring.
The doctor may prescribe:
- conservative complex therapy: antibacterial, painkillers and anti-inflammatory drugs;
- nutritional correction and bed rest.
In rare cases, surgery may be prescribed to treat inflammation of the appendages in teenage girls, but only based on diagnostic results.
Repeated appointment
On a strictly individual basis, the doctor prescribes treatment and draws up a visit plan, which necessarily includes a second visit for monitoring.
If a patient undergoes treatment with a simple form of inflammation and without complications, then, as a rule, one or two subsequent appointments are required. If a child is diagnosed with a complex form of the disease, this means that visits to the doctor will occur more often than with a simple form.
If the scheme is chosen correctly, the young body will immediately improve. If necessary, the doctor can adjust the regimen, for example, by reducing the duration of taking any medications or the duration of treatment.
If the chosen regimen does not bring the desired results, the doctor may send the child for further examination and prescribe a new treatment regimen.
Control reception
When the full course has been completed, the doctor will schedule a follow-up appointment to assess the child’s condition and prescribe a course (if necessary) of recovery (immunomodulators, restoration of vaginal microflora, proper nutrition and a healthy lifestyle).
A control appointment is scheduled approximately 21–30 days after the course of treatment for ovarian inflammation in teenage girls. It is also necessary to regularly visit a gynecologist once a year for prevention.
Treatment result
This disease can be easily cured with timely consultation with a doctor and the correct treatment method, as well as with constant monitoring by a specialist in pediatric gynecological problems.
Long-term and difficult treatment of salpingopharitis in a teenage girl is possible in complicated cases and in the chronic stage of the disease. The duration of treatment is determined individually, at the initial or secondary visit to the doctor. If necessary, parents are also examined.
Pathologies of the reproductive system
There are many causes of pain associated with gynecological problems. Among the most common:
- Endometritis. It is characterized by inflammation of the endometrium, which can occur acutely or chronically. Often accompanied by menstrual irregularities, spotting, uterine bleeding, and nagging pain.
- Adnexitis. Inflammation of the uterine appendages is one of the most common diseases in gynecological practice. In addition to painful sensations (can be in one side or spread to the entire lower abdomen), patients are faced with signs of intoxication and fever. The disease is caused by bacteria, viruses or fungi.
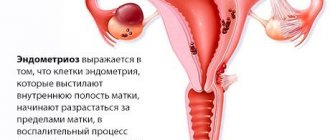
- Endometriosis. In this disease, the cells of the uterus grow and end up outside the uterus. Accompanied by pain during urination, defecation, sexual intercourse and simply with sudden movements, heavy bleeding during menstruation. Regardless of the cycle, brownish discharge is observed.
- Uterine fibroids, which are usually characterized by dull pain in the pelvic area. Cysts and other benign, as well as malignant formations can cause discomfort of varying intensity and spasms.
- Spikes. They may be the result of inflammation in the genital organs, varicose veins and other diseases. Complications during pregnancy. This may include spontaneous abortion, placental abruption and other pathologies. In such cases, the pain is sudden and sharp, accompanied by bleeding from the genitals.
Separately, it is worth focusing on sexually transmitted infections - mycoplasmosis, gonorrhea, chlamydia, trichomoniasis and other diseases. They affect the reproductive organs, causing pain, profuse vaginal discharge of a pathogenic nature, burning, itching and are fraught with complications if left untreated.
Treatment
Help before diagnosis
For abdominal pain associated with menstruation, non-drug methods are sufficient. Herbal teas with chamomile and mint are effective. You can put a warm (not hot!) heating pad on your lower abdomen and lie with it in the “fetal position”, pulling your knees towards your body. To reduce menstrual cramps, it is advisable to give up strong tea and coffee, spicy and smoked foods. A woman’s psychological mood, the ability to calm down and relax are very important.
For minor pain that occurs in pregnant women, doctors recommend avoiding physical activity and heavy lifting and getting plenty of rest. It is necessary to exclude from the diet foods that increase gas formation, since flatulence is one of the main causes of abdominal pain during gestation. If pain intensifies, protective tension in the abdominal muscles appears, and bloody discharge from the vagina occurs, you should seek medical help as soon as possible.
Conservative therapy
Treatment of women experiencing pain in the lower abdomen should be etiopathogenetic, so drugs are prescribed only after identifying the root causes of the pain syndrome. Drug therapy is supplemented with a gentle regimen, if indicated - bed or half-bed, a fortified diet with an adequate amount of fluid. Treatment regimens may include the following groups of medications:
- Painkillers
. Taking antispasmodics and analgesics is effective for all types of inflammatory diseases of the genitourinary system and algomenorrhea, accompanied by severe pain. Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are also used for inflammation. - Antibacterial drugs
. Antibiotics are indicated for adnexitis, endometritis, cystitis, intestinal infections, etc. More often drugs from the group of cephalosporins, fluoroquinolones, and macrolides are used. For uncomplicated urinary tract infections, uroseptics are appropriate. - Hormones
. For the treatment of severe algomenorrhea, combined oral contraceptives or natural progestins are recommended. A similar treatment regimen is selected for women suffering from endometriosis. - Sedatives
. Medicines are effective for chronic pelvic pain, algomenorrhea, especially if they are combined with severe neuropsychic symptoms.
Surgery
A number of obstetric pathologies require urgent surgical intervention. In case of an ectopic pregnancy, an operation is performed to remove the fallopian tube along with the fertilized egg (tubectomy), and in case of an uncomplicated pregnancy, an organ-preserving operation - tubotomy - is possible. Complete premature placental abruption is an indication for cesarean section, regardless of gestational age.
Gynecological diseases (ovarian apoplexy and torsion of the tumor stalk) are treated surgically by oophorectomy, adnexectomy, wedge resection of the ovary. In severe forms of endometriosis, endometrioid lesions are excised. Surgical treatment is also required for abdominal pathologies: appendicitis (appendectomy), hernias (hernioplasty).
Pain on the right and left
In some cases, patients complain of pain in a specific location. Pain in the lower abdomen may occur in a woman on the right due to right-sided inflammatory lesions of the uterine appendages (adnexitis, salpingoophoritis), ileal spasm, tumor formations. Also in this place is the cecum, which has a vermiform appendix - the appendix. If it becomes inflamed, appendicitis develops and the patient needs emergency care.
The most common causes of pain in the left lower abdomen in women are secondary inflammation of the appendages, spasm of the sigmoid colon, tumor process, and ulcerative colitis. Sometimes the problem may be associated with disorders in the joints of the spine and their tissues, a herniated disc, or radiculitis.
Diagnostics
A doctor can guess the cause of pain through examination and palpation. The further diagnostic method is selected based on the results:
- general blood test - will indicate an infectious lesion, detect leukemia;
- general urinalysis - will help determine kidney pathology;
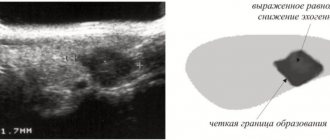
- Ultrasound is the fastest and easiest method for examining the abdominal organs;
- MRI - gives the most reliable results;
- colonoscopy - assessment of intestinal condition;
- radionuclide testing is relevant for some diseases of internal organs, for which other methods are not informative.
Based on the results of diagnostic measures, the patient is diagnosed. Pain treatment is selected according to the detected disease.
Read also: Pulling in the lower abdomen
Disturbances in the functioning of the urinary system
Cystitis is one of the most common causes of aching pain in women. The bladder can become inflamed after simple hypothermia. Pain when urinating, false and frequent urges are characteristic symptoms of this disease. Other frequently diagnosed pathologies of the urinary system include pyelonephritis and urethritis, in which case discomfort occurs not only in the lower abdomen, but also in the back (especially in the lumbar region).
If pain is dull in nature and occurs in the area above the pubis, bladder polyps can be assumed.
What to do in case of acute pain
When the lower abdomen and lower back hurt, we often start looking for reviews from other people who have already encountered such a situation in order to understand the reason and determine the course of action for ourselves. It is worth understanding that it is unlikely that you will be able to make an accurate diagnosis for yourself; here you need to immediately seek qualified help from specialists. If the pain is acute and sharp, it is best not to hesitate and call ambulance workers so that you can be examined and brought to the clinic as soon as possible for diagnosis and diagnosis. After this, you will be prescribed treatment, and you can expect an improvement in your condition.
Digestive problems
Pain in the lower abdomen may also occur due to problems with the intestines or existing diseases of different parts of the digestive system:
- Poisoning from low-quality food contaminated with bacteria. For example, with shigellosis, eschirichiosis and other infections, the pain is paroxysmal and pronounced.
- Hernias of inguinal, Spigelian and white lines. When they are pinched, acute painful sensations occur in the abdominal cavity.
- Pancreatitis. When the pancreas is inflamed, the left side of the lower abdomen and chest hurts, and jaundice may occur.
- Intestinal colic. Characterized by spasm of the large or small intestine. It can be the result of helminthic infestation, food poisoning, or severe stress.
- Cholecystitis. When the flow of bile is disrupted, the risk of developing gallbladder inflammation is high. In this case, the pain spreads to the right side, shoulder or shoulder blade.
If pain occurs accompanied by diarrhea or constipation, changes in the color of stool, the appearance of blood or mucus in the stool, bloating, nausea, vomiting, frequent bowel movements, chills or fever, the cause of such symptoms may be a disorder of the digestive function, organ diseases Gastrointestinal tract.
Why does my lower abdomen hurt?
The content of the article
In most clinical cases, the manifestation of pain in the lower abdomen is a consequence of impaired functioning of the urinary and digestive organs. But there are other serious diseases that manifest themselves with similar symptoms. Regardless of gender, doctors identify the following causes of such pain in women and men:
- Appendicitis. Sharp pain appears in the right iliac region. If the internal organs are abnormally located, the syndrome may also appear on the left side. If the cause of discomfort is appendicitis, a person, in addition to abdominal pain, experiences high fever, nausea and vomiting. If a patient is diagnosed with chronic appendicitis, the pain in the lower abdomen will not be sharp, but weak, often aching.
- Diverticulitis . When a protrusion perforates on the wall of the sigmoid colon, pain appears similar to the sensations of appendicitis. But with diverticulitis, pain spreads to the entire lower abdomen.
- Inflammation of the bladder mucosa . This pathology is characterized by a gradual increase in pain: a person is bothered by a stabbing sensation in the lower abdomen. Against the background of the pathology, high temperature and frequent urination appear.
- Acute urinary retention . The pathology is characterized by the appearance of a mechanical obstruction to the outflow of urine: stones in the bladder or neoplasms in the urinary system. Sharp pain is clearly localized 2 fingers below the navel. A person feels a full bladder well, but when going to the toilet, urine does not come out of it. The condition requires immediate medical attention, as there is a possibility of rupture of this organ.
- Cystitis. The clinical picture of this disease is characterized by localization of pain over the pubic region, its nature is usually acute, and the syndrome can radiate to other areas of the abdomen.
- Chronic urethritis. Discomfort in this case is described as increasing, but not severe.
- Inguinal hernia strangulation. The pain syndrome in this case develops quickly, usually after unusual physical activity of a person - lifting an object that is too heavy, performing exercises without prior preparation, etc. The pain syndrome is quite sharp, but at the same time its location is blurred, so the patient cannot always accurately point to the location of the pain. The strangulation is accompanied by diarrhea, which after a few hours turns into vomiting.
- Inflammatory kidney damage . Against the background of severe pain in the lower abdomen, a person develops an elevated temperature, chills, and may develop a fever.
- Acute intestinal obstruction . The pain appears suddenly, the patient suffers from constipation and increased gas formation, in which the gases do not pass away and cause intestinal colic, and weakness develops.
- Irritable bowel syndrome. This is a chronic disease in which a person is often bothered by pain in the lower abdomen, bowel behavior disorders (unreasonable diarrhea or constipation) and flatulence.
- Colon pathologies of inflammatory nature: ulcerative colitis, Crohn's disease. The nature of the pain in this case is pronounced, appears against the background of elevated temperature, and is often accompanied by disruption of the gastrointestinal tract.
- Adhesive disease . This condition develops after operations in the peritoneum or pelvis. Pain in the lower abdomen becomes chronic and difficult to treat.
- Malignant tumors in the urinary system , intestines or abdominal area. Pain is an indicator of the transition of the disease to a severe stage. The syndrome can also spread to those areas where metastases appear - groin, lower back, spine, etc.
The causes of this symptom can be various diseases associated with damage to many organs and systems. In addition to the listed pathologies, metabolic, hormonal, mental and many other disorders in the body can be a provoking factor for pain. Therefore, if such a pain syndrome occurs, it is recommended to consult a specialist and undergo a comprehensive diagnosis.
Other causes of pain
There are many other problems that can cause lower abdominal pain. These include:
- injuries to the abdominal cavity and genital organs;
- prolapse of the vagina and uterus;
- varicose veins of the pelvis;
- torsion of the tumor stalk, etc.
Also, women who tend to overreact to stressful situations, often worry and experience anxiety, suffer from psychogenic pain much more often than others.
The multidisciplinary medical center of the Central Clinical Hospital of the Russian Academy of Sciences has experienced and highly qualified specialists who regularly undergo training in the world's leading clinics, modern diagnostic and treatment resources, and equipment from well-known manufacturers. All this makes it possible to provide comprehensive medical care to patients with problems of varying degrees of complexity.
Inflammatory diseases of the pelvic organs
Pelvic inflammatory processes can be caused by numerous pathogenic microorganisms: bacteria, viruses, protozoa or fungi.
The main symptoms of inflammation of the female genital organs include:
- stomach ache;
- slight bleeding from the uterus and vagina;
- soreness of the uterus upon independent palpation of the abdomen.
When there is inflammation of the appendages on the right side, the pain that appears must be differentiated from acute inflammation of the appendix.
What types of left side pain should you consider?
The nature of the pain serves as a guide to the assumption of the location and type of pathology.
Aching dull pain
Often worries women with a unilateral gynecological problem. Dull pain above the pubis and on the left is possible with cycle disorders, sex, inflammation and endometriosis. Inflammation is indicated by a combination with elevated temperature and weakness.
Nagging pain
In intensity it is significantly inferior to other types, but it exhausts a person with its constancy. In men, it occurs with inflammation of the scrotum, strangulated inguinal hernia, orchitis. Initially, a malignant tumor manifests itself in a similar way.
Sharp pain in the side
The sharp nature of the pain accompanies intestinal spasm, distension with gases, acute expansion of the bladder and pelvis of the left kidney during urinary retention, rupture of the ovary in women, and the passage of stones through the ureter.
Stitching pain
Colic is an acute spasm caused by contraction of the intestines or ureter. Typically subsides after defecation and urination. A type of pain is shooting pain. It is characteristic of inflammation in the lumbar region and joints. Stitching pain can precede the rupture of an ovarian cyst.