When a patient complains of pain in the abdominal cavity or dysfunction of the gastrointestinal tract, the doctor may prescribe an x-ray. Considering the structural features of the abdominal organs, this method cannot be called the most informative. To obtain a clear image, a special contrast agent is injected.
Barium sulfate is used as a contrast agent, which fills all cavities. This powder is poorly soluble in water and is resistant to acids and alkalis, while also having the ability to reflect X-rays. Since barium is not absorbed through the intestinal walls, the possibility of it entering the bloodstream arises only in the presence of open ulcers and other damage to the integrity of the walls. The substance is excreted from the body in feces.
Operating principle
The essence of this diagnostic method is based on exposure of the abdominal cavity to a permissible dose of radiation. When X-rays pass through a cavity filled with contrast, a fairly clear picture is obtained, on the basis of which a radiologist can identify many pathological changes and establish the correct diagnosis.
Despite the fact that the patient is exposed to radiation during the study, barium radiography of the abdominal cavity is actively used in modern medicine. Firstly, the radiation dose is insignificant and does not exceed the established daily norm. Secondly, the procedure does not take much time and does not cause discomfort to the patient. And thirdly, x-rays with a contrast agent are an inexpensive and fairly informative diagnostic method.
Content:
- Operating principle
- What will a barium x-ray of the abdomen show?
- Indications for radiography
- Preparing for the study
- Features of the procedure
- Contraindications and restrictions
Modern equipment used for radiography procedures makes it possible to strictly regulate radiation activity. Thanks to this, neighboring organs are practically not exposed to radiation.
What should you take with you to the examination?
Contrast radiography is a rather complex procedure that requires extensive preparation. It is not enough to just cleanse the intestines. It is advisable to take into account other points so as not to get into trouble during irrigography.
When going for irrigography, you need to take with you:
- Direction.
- Passport, medical insurance and results of past examinations, if any.
- A diaper or sheet (optional).
- Women's robe and slippers.
- Wet wipes or toilet paper.
- Spare underwear and clothing below the waist (preferably), since barium leaves white stains on things.
- Light snack.
After receiving the results, it is good to eat something nutritious, since enemas are very draining on the body.
What will a barium x-ray of the abdomen show?
An abdominal x-ray using a contrast agent provides a clear image of the gastrointestinal tract. After examining the image, the radiologist can see pathological changes in the mucous membranes, the presence of tumors, the formation of perforations, changes in the width of the lumen in the intestine, the elasticity of the intestinal walls, motor function, the presence of foreign bodies in the intestine, and fluid accumulation.
Radiography may be routine - to establish a diagnosis for a patient who has consulted a doctor with complaints of pain in the abdominal area. It can also be emergency - when a patient is admitted with abdominal injuries or acute pain, or suspected internal bleeding.
A radiologist interprets the resulting image. He issues a conclusion on the basis of which the attending physician can determine the cause of pain and discomfort.
Possible complications of irrigography
If irrigography is performed by an experienced specialist, then no consequences for the patient are usually noted. The patient recovers literally within a few hours after the examination.
However, if a person undergoing diagnosis has gastrointestinal pathologies, in particular, thinning of the walls, colon rupture may occur. The situation requires urgent surgical intervention. This happens extremely rarely and this is not a reason to refuse an examination if the results of other studies are available.
Procedures such as MRI, ultrasound, CT and irrigography do not replace, but only complement each other and help to create an accurate picture of the disease.
Attention. The article is not a guide to action; be sure to consult your doctor.
You can learn more about preparations for the event from the video:
One of the most common methods for diagnosing the condition of the digestive tract is an X-ray of the intestines. Modern X-ray equipment makes it possible to quickly and painlessly identify the presence of many pathologies, carry out differential diagnostics in controversial situations, and evaluate the quality of the therapy provided. Barium is often used to take x-rays of the intestines. This contrast agent helps to obtain a clearer picture of the presence/absence of changes in the organ.
Indications for radiography
X-ray of the abdominal cavity with barium allows you to study in detail the condition of the stomach and intestines, in particular to see the sections of the small and large intestines, the appendix, and the gall bladder. In the vast majority of cases, x-rays are used for diagnostic purposes or to monitor the effectiveness of therapy.
Phenomena and symptoms in which a patient is advised to undergo an abdominal x-ray with a contrast agent are as follows:
- chronic diarrhea or persistent constipation;
- the presence of blood in the stool;
- suspected internal bleeding;
- sudden weight loss;
- pathological change in the color and consistency of stool;
- chronic or acute pain in the abdominal cavity and lower back;
- suspected internal organ damage;
- abdominal injuries;
- retroperitoneal abscess;
- intestinal obstruction.
In most cases, X-rays using contrast media are preceded by a plain plain X-ray. This is done to ensure that there are no internal damages through which barium can enter the blood.
Contraindications
X-ray of the stomach with barium is contraindicated in the following cases: disturbances in the functioning of the hematopoietic system, a pathological condition associated with clouding of the lens of the eye, affecting visual acuity, oncopathology of the bronchopulmonary system, carrying a child at any stage, endocrine pathologies of the thyroid gland. There are available for X-ray examination of the intestine the following contraindications:
- intestinal perforation;
- unconsciousness of the patient;
- general serious condition of the patient;
- nonspecific ulcerative colitis;
- a combination of segmental or total dilatation of the colon against the background of signs of systemic toxicity;
- severe diseases of the cardiovascular system;
- complete disruption of the passage of contents through the intestines;
- internal bleeding;
- severe pain in the epigastric region;
- pregnancy.
Preparing for the study
The information content of the result depends on the accuracy of compliance with all the rules of preparation for radiography using a contrast agent. During a planned procedure, the patient is prescribed a special diet with a limitation of foods that cause increased gas formation - 3 days before the study. Additionally, the doctor prescribes medications with a laxative effect and describes a regimen for taking them. Two days before an X-ray with barium, you should exclude alcoholic beverages, coffee and tea from your diet, and it is advisable to completely stop smoking. In the last 24 hours before the diagnosis, you should not eat solid food - you can drink broths, herbal teas, and still water.
During the preparation period, taking medications is not recommended. If complete abstinence from medications is not possible, you should drink plenty of water with each dose of medication.
Immediately before the procedure, the patient needs to change into suitable clothes - his own or hospital clothes. It is also worth removing all metal objects, including removable dentures.
Is it harmful to have an X-ray examination of the intestines?
You can often hear the opinion that an X-ray of the intestines is a very dangerous procedure for health. However, if all safety measures are followed, then the likelihood of developing any negative consequences of radiation is negligible. The rays themselves do not “get stuck” in the body, and their intensity is strictly controlled by a specialist and does not exceed acceptable standards.
In this case, the doctor selects the level of radiation in accordance with the individual characteristics of the patient. In addition, the device directs the rays exactly to the place that needs to be studied. The surrounding structures are either not exposed to radiation at all, or it is minimal.
Another concern relates to the effects of using barium on bowel x-rays. This substance rarely leads to allergies, but in most cases it causes difficulties with bowel movements. To be fair, it should be noted that not all patients follow the diet after undergoing diagnosis. Lack of enough water and poor diet in the first days after an x-ray naturally lead to constipation. To avoid this, you need to maintain a smooth transition to your usual food and monitor your water regime.
Intestinal X-ray is, in general, a safe, informative, inexpensive procedure. If you carefully read the reviews of patients, most of them note that the procedure is successful and completely painless only if you follow the doctor’s instructions. It must be remembered that no article from an Internet source can take into account the individual characteristics of the body. Therefore, every moment before and after the x-ray (and during it) must be agreed upon with the attending physician.
An experienced Russian doctor will tell you how to properly prepare for an x-ray procedure in a short video.
Features of the procedure
Best materials of the month
- Coronaviruses: SARS-CoV-2 (COVID-19)
- Antibiotics for the prevention and treatment of COVID-19: how effective are they?
- The most common "office" diseases
- Does vodka kill coronavirus?
- How to stay alive on our roads?
Since the procedure is performed only on an empty stomach, it is usually prescribed in the morning. If interpretation of the image does not reveal reasons for urgent hospitalization, the patient can go home immediately after the examination.
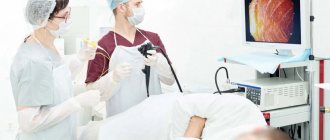
Barium sulfate in powder form is mixed with water and introduced into the gastrointestinal tract through a tube. Another way to introduce a contrast agent into the intestine is through the rectum using a thin tube that is inserted through the anus. The contrast injection procedure itself is painless, although it may be accompanied by some discomfort. If acute pain or other unpleasant sensations occur during the administration of barium, the x-ray technician performing the procedure should be informed about this.
While the images are being taken, the patient must hold his breath and remain motionless. The procedure itself takes 1-5 minutes - during this time a series of images is taken, on the basis of which a conclusion is written.
How is the research conducted?
You will need to stand in front of an X-ray machine.
The radiologist will ask you to drink small sips of barium and take x-rays. Then, at certain intervals, a series of Rg images are taken as the diagnosed parts of the gastrointestinal tract are filled with contrast. In this case, the patient lies on his back, left and right side, turning at certain intervals at the command of the diagnostician.
On average, a contrast study is carried out for 2-3 hours, after which the patient must immediately eat in order to restore the body’s energy balance.
Decoding the results
The doctor who performed the examination deciphers the results. The conclusion is given to the patient immediately or pasted into the medical record. If white flakes are visible on the pictures, it means that intestinal absorption is impaired. The images also show tumors, elongation of certain areas, and diverticula (irregularities, protrusions). If the solution spreads in steps, this indicates intestinal obstruction.
Barium passage is not a painful procedure, but it is unpleasant.
After the study, no side effects occur, but if they do appear, they go away on their own in a short time. To remove barium solution from the body, laxatives are prescribed. Next entry Colon X-ray – how and why it’s done
Indications and contraindications for barium passage
Mandatory indications for barium passage include the appearance of blood streaks in the stool and black stools. Diagnostics is also prescribed for:
- Sudden causeless diarrhea, especially if it is persistent, despite a healthy diet and a healthy lifestyle.
- Chronic abdominal pain, which is accompanied by other negative symptoms. This signals bowel cancer. However, if the pain is severe at the time of the examination, then barium passage is not performed.
- Unexplained weight loss when eating normally.
- Congenital anomalies of the intestinal structure.
- Barium passage is contraindicated during pregnancy (there is a threat to the fetus), severe pain.
- The procedure is not performed for biopsy (this can cause inflammation of the mucous membrane) and intestinal perforation (there is a risk of peritonitis).