Who is this diet suitable for?
We swallow pills and tubes, take tests - everything in order to leave this feeling behind, and it works. But if in all this “entertainment” you forget about the diet, you can’t count on a quick recovery of the body; it will harbor a serious, weighty grudge against you.
This is exactly the diet we will talk about today.
Most often, a diet is prescribed in these cases:
- Acute intestinal diseases during the period of recovery and restoration of the body.
- As a soft transition from a strict therapeutic diet to a general one.
- Chronic intestinal diseases (in remission).
- The combination of the above diseases with lesions of other organs: stomach, pancreas, liver and bile ducts.
Advantages and disadvantages
| pros | Minuses |
|
|
Composition and value of the diet
What is important in the process of diet therapy? Of course, the chemical composition - after all, it must be complete to support the body during a difficult period.
Our diet undoubtedly meets these requirements:
- the daily protein intake is 85-90 g,
- fat – 70-80 g,
- carbohydrates – 350 g.
Calorie content: the daily energy value of your menu will now be 2200-2500 kcal.
Diets for the gastrointestinal tract require limiting the amount of table salt in the diet to 10 g of salt per day, and here the rule “The less is better” works in full force.
On a note
An important point: do not forget about water - drinking balance is extremely important for the recovery of the body, but it is better to find out your personal dose from your doctor.
Fully or partially limited products
All dietary tables exclude:
- Stringy and fatty meat (only lean and rare pork is allowed), fried meat and fish, fried potatoes, pancakes, pancakes, fried donuts, smoked meats, lard, goose, duck and lamb, smoked meats.
- Salted, fried, smoked fish, canned fish.
- Fast food and semi-finished products.
- Soups with fried dressing, onion soup, bean, pea, first courses with the addition of kidneys, millet and cabbage (this also applies to Savoy cabbage), cabbage soup, okroshka, solyanka, rassolnik, any soups with meat/fish/mushroom broths.
- Onion, meat, mushroom, fish, garlic, any mayonnaise-based sauces.
- Vegetables with coarse fiber (radish, radish), difficult to digest (mushrooms), irritating the mucous membrane (garlic, green onions, ginger, pickled vegetables), spinach and sorrel.
- Wheat, pearl barley, barley, millet and corn porridge, legume dishes.
- Ice cream, full-fat puddings, nut and raisin casseroles, nut muffins, chocolate.
- Fatty and sour cottage cheese, fatty fermented milk drinks, fatty cheese.
- Strong coffee and cocoa, fruit sparkling waters, alcoholic drinks.
- Black and other types of pepper, mustard, vinegar, horseradish.
- Pears, lingonberries, raspberries, blueberries, grapes, figs, nuts, currant compotes.
Table of prohibited products
| Proteins, g | Fats, g | Carbohydrates, g | Calories, kcal | |
Vegetables and greens | ||||
| vegetables legumes | 9,1 | 1,6 | 27,0 | 168 |
| swede | 1,2 | 0,1 | 7,7 | 37 |
| cabbage | 1,8 | 0,1 | 4,7 | 27 |
| cucumbers | 0,8 | 0,1 | 2,8 | 15 |
| parsnip | 1,4 | 0,5 | 9,2 | 47 |
| parsley (root) | 1,5 | 0,6 | 10,1 | 49 |
| white radish | 1,4 | 0,0 | 4,1 | 21 |
| turnip | 1,5 | 0,1 | 6,2 | 30 |
| celery | 0,9 | 0,1 | 2,1 | 12 |
| green beans | 2,8 | 0,4 | 8,4 | 47 |
| horseradish | 3,2 | 0,4 | 10,5 | 56 |
| garlic | 6,5 | 0,5 | 29,9 | 143 |
| spinach | 2,9 | 0,3 | 2,0 | 22 |
| sorrel | 1,5 | 0,3 | 2,9 | 19 |
Fruits | ||||
| bananas | 1,5 | 0,2 | 21,8 | 95 |
| melon | 0,6 | 0,3 | 7,4 | 33 |
Berries | ||||
| grape | 0,6 | 0,2 | 16,8 | 65 |
Cereals and porridges | ||||
| corn grits | 8,3 | 1,2 | 75,0 | 337 |
| pearl barley | 9,3 | 1,1 | 73,7 | 320 |
| Wheat groats | 11,5 | 1,3 | 62,0 | 316 |
| millet cereal | 11,5 | 3,3 | 69,3 | 348 |
| barley grits | 10,4 | 1,3 | 66,3 | 324 |
Bakery products | ||||
| vysivkovy bread | 9,0 | 2,2 | 36,0 | 217 |
| Old Russian grain bread | 9,6 | 2,7 | 47,1 | 252 |
| Rye bread | 6,6 | 1,2 | 34,2 | 165 |
Confectionery | ||||
| candies | 4,3 | 19,8 | 67,5 | 453 |
| cookie | 7,5 | 11,8 | 74,9 | 417 |
| butter cookies | 10,4 | 5,2 | 76,8 | 458 |
Ice cream | ||||
| ice cream | 3,7 | 6,9 | 22,1 | 189 |
Cakes | ||||
| cake | 4,4 | 23,4 | 45,2 | 407 |
Raw materials and seasonings | ||||
| seasonings | 7,0 | 1,9 | 26,0 | 149 |
| mustard | 5,7 | 6,4 | 22,0 | 162 |
Meat products | ||||
| pork | 16,0 | 21,6 | 0,0 | 259 |
Sausages | ||||
| dry-cured sausage | 24,1 | 38,3 | 1,0 | 455 |
Bird | ||||
| duck | 16,5 | 61,2 | 0,0 | 346 |
| goose | 16,1 | 33,3 | 0,0 | 364 |
Fish and seafood | ||||
| dried fish | 17,5 | 4,6 | 0,0 | 139 |
| smoked fish | 26,8 | 9,9 | 0,0 | 196 |
| canned fish | 17,5 | 2,0 | 0,0 | 88 |
Oils and fats | ||||
| animal fat | 0,0 | 99,7 | 0,0 | 897 |
| cooking fat | 0,0 | 99,7 | 0,0 | 897 |
Non-alcoholic drinks | ||||
| bread kvass | 0,2 | 0,0 | 5,2 | 27 |
Juices and compotes | ||||
| Orange juice | 0,9 | 0,2 | 8,1 | 36 |
| grape juice | 0,3 | 0,0 | 14,0 | 54 |
| Cherry juice | 0,7 | 0,0 | 10,2 | 47 |
| Strawberry juice | 0,6 | 0,4 | 7,0 | 31 |
| tangerine juice | 0,8 | 0,3 | 8,1 | 36 |
| tomato juice | 1,1 | 0,2 | 3,8 | 21 |
| * data is per 100 g of product | ||||
The importance of protein in gastrointestinal diseases
A weak body copes worse with “collecting” proteins from the diet, so it may lack this essential element.
Patients with gastrointestinal diseases are advised to pay attention to getting enough protein. In this case, dry protein mixtures help.
Diso Nutrimun is an easily digestible protein that can easily fit into the menu, will help damaged tissues and organs recover and will not force you to “get” the required amount of protein from foods that are not part of the diet.
General rules
The causes of dysfunction of the digestive organs are: poor nutrition, imbalances in the diet (its imbalance), lack of a meal plan.
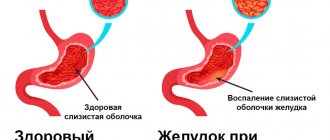
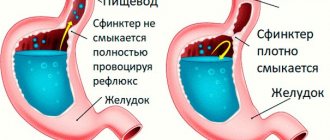
All diseases of the gastrointestinal tract have a chronic course, and this forces the patient to give up their usual diet for a long time, and sometimes for life. Diet therapy is an important treatment method, since proper nutrition can improve the patient’s quality of life and reduce the risk of exacerbation. There are many diseases of the digestive system, which occur in acute and chronic forms and are manifested by various symptoms. Pain in the left hypochondrium does not always indicate a disease of the pancreas. Only through examination can a correct diagnosis be established, possible concomitant pathologies identified and adequate treatment carried out. Accordingly, therapeutic nutrition will be somewhat different.
The following dietary tables are used in gastroenterology:
- No. 1 - indicated for diseases of the stomach and duodenum;
- No. 2 - prescribed for acute gastritis , chronic gastritis with secretory insufficiency, colitis and enteritis during the recovery period;
- No. 3 - recommended for intestinal diseases (colitis) accompanied by constipation ;
- No. 4 - for colitis occurring with diarrhea ;
- No. 5 - indicated for hepatitis , pancreatitis , conditions after gastrectomy and liver surgery, cholecystitis and after surgical removal of the gallbladder, with stagnation of bile.
These are the main tables, but there are also varieties that are prescribed differentially depending on the stage of the disease and the severity of functional disorders of a particular organ.
For example, Table No. 4 has four varieties, taking into account the presence of fermentation processes in the intestines, concomitant pathology of the pancreas, gluten intolerance in patients and the acute process of the disease. Dietary Table No. 5 is distinguished by the presence of five varieties. During the period of exacerbation, options with the greatest mechanical and chemical sparing are recommended, and subsequently the patient is transferred to the main table.
This approach allows you to individualize nutrition and adjust it by the type of culinary processing and the consistency of the dishes. Despite the variety of dietary tables and some differences in the range of products, they adhere to the most important and important principle of nutrition for diseases of the digestive system - sparing.
A gentle diet for gastrointestinal diseases implies:
- Elimination of the negative effects of food - mechanical, physical and chemical.
- Compliance with the regime and the principle of fractional nutrition, since large volumes of food have a negative effect on the functions of the stomach (secretory and motor).
- Eating food at the optimal temperature is 400 s.
- Chew thoroughly. This helps to prepare food well: chop it and moisten it with saliva, which is also involved in the digestion process. With leisurely and good chewing of food, digestion and assimilation of its components occur more fully.
Mechanical sparing is achieved by excluding products that contain a lot of fiber, coarse fibers and connective tissue (this applies to rough meat, poultry skin and fish). This also includes culinary processing of foodstuffs—cooking, short-term baking, and mashing of foodstuffs. Among gastroenterological diets, the main part includes pureed dishes.
Unfavorable mechanical effects are caused by:
- Fruits with peel and berries (gooseberries, currants, grapes).
- Cabbage, legumes, mushrooms, bran bread, whole grain cereals, nuts.
- Solid foods, tough meats, large pieces of food, cartilage and tendons.
- Any fried or baked food with a distinct crust.
In this regard, the most suitable cooking methods for patients with gastroenterological diseases are boiling, steaming, stewing or short-term baking. In addition, food that is quickly digested and leaves the stomach will also have minimal mechanical impact. Patients are recommended to eat liquid, mushy, mashed and pureed foods. The degree of mechanical sparing depends on the form of the disease - exacerbation, unstable remission or remission.
Food with a temperature of 37-400 °C has the least impact on the mucous membrane. Hot dishes with a temperature of 60 °C or more irritate the mucous membrane and delay the evacuation of food.
Chemical sparing is achieved by including products that minimally stimulate gastric secretion. The diet for the gastrointestinal tract (GIT) should contain soups (low-fat and not fried), liquid porridges with water or milk, boiled meat and fish, eggs (in the form of an omelet), milk and non-acidic dairy products, weak tea, stale white bread , alkaline still waters.
At any stage of the disease, strong pathogens of secretion are excluded, which include:
- spices (all types of peppers, ginger, mustard, spicy vegetables, seasonings, horseradish);
- smoked and spicy prepared gastronomic products, snack foods, canned meat and fish, dishes with tomato sauce, meat sauces and strong broths;
- meat and fish broths rich in extractive substances, mushroom decoctions;
- vegetables rich in essential oils (garlic, onion);
- all fried foods;
- stewed meat and fish;
- rye bread, butter pastries;
- black coffee;
- pickled and pickled vegetables, sour fruits;
- hard boiled eggs;
- overheated edible fats;
- high acidity fermented milk products, whey;
- carbonated drinks and kvass;
- alcohol.
If diseases of the stomach and duodenum are accompanied by constipation , adjustments are made to the basic diet for this disease - the amount of boiled vegetables prepared in the form of puree (most often zucchini, pumpkin, carrots, beets), well-boiled and mashed dried fruits, infusion from dried fruits and vegetable oil.
For liver diseases, dietary Table No. 5 , and the presence of constipation requires an increase in dietary fiber and magnesium in the diet - salads from boiled carrots and beets, puree from plums, apricots and peaches, vegetable/fruit juices, vegetables and fruits in any form, grain bread , cereals - buckwheat, oatmeal, pearl barley.
They often resort to treatment with folk remedies. Indeed, herbal medicine is one of the auxiliary methods of treating diseases of the gastrointestinal tract. It is effective in seasonal prevention of relapses or at the first signs of exacerbation. At home, to relieve pain, you can use decoctions of marshmallow, anise, chamomile, centaury, mint, fireweed, and coriander. Decoctions of calamus, elecampane, marshmallow, licorice, burdock, flax seed, alder and sage have an enveloping and mucus-forming effect. Potato juice has the same effect. In this case, it is necessary to take into account the effects of herbs on the secretory function of the stomach.
The purpose of the diet for diseases of the gastrointestinal tract
Adequate nutrition is what this diet primarily brings “to the world.” It helps the body to be in good shape and fight off the weakening attacks of the disease.
Since the diet is often called “transitional”, it should not be as soft and gentle as others. Therefore, it only moderately, but limits irritants of the mucous membrane and receptor apparatus. At the same time, she stands guard and excludes everything that can cause fermentation, or even rotting (and this happens!) in the intestines; does not allow the appearance in the diet of foods that activate bile secretion and the secretory function of the stomach, pancreas and bladder.
On a note
Diets designed to spare vulnerable parts of the gastrointestinal tract resist the presence of hard connective tissue in dishes, which is inherent in products of animal origin.
It is these indigestible parts that linger in the intestines as unwanted guests - and cause rotting processes in the large intestine. You won’t get out of the disease with such introductory notes, no matter how hard you try. And such diets insist on introducing the required amount of protein into the diet - and here we have no exceptions either. Let us explain: proteins are absorbed in our body a little earlier, still in the small intestine, and do not reach the “center” of the disease. But they help the body “climb out” faster.
This is why dry mixtures such as Nutrimun become literally irreplaceable - because they are really easy to digest in the stomach - unlike meat dishes that are difficult to digest. But we are not only “on a diet,” but we also protect the digestive organs from unnecessary stress.
About cooking
Once again, the chopped and pureed form of food is everything to us, but only when it is boiled, steamed or baked without a crust . But if you are desperately hungry for a piece of tasty meat (or even a piece of something that is not pureed), consult your doctor. Sometimes, if the specialist is confident that you can digest these innovations, he will allow you to prepare a small piece of food with a delicate consistency. But, of course, it will also need to be thoroughly boiled or stewed.
Diet and serving of dishes for gastrointestinal diseases
The diet obliges you to eat often, but little by little, so as not to force your stomach to do too much work and digest impressive portions of something tasty.
You need to eat 5-6 times a day—yes, that often—and the gastrointestinal tract will be sincerely grateful to you.
- Serve hot food very carefully: the temperature of such a dish should not exceed 60°C.
- The situation with cold dishes is similar: no lower than 15°C.
Otherwise, there is always a risk of injuring the already weakened organs of the gastrointestinal tract.
Reviews and results
Therapeutic nutrition for stomach diseases is extremely important for patients and, according to numerous reviews, helps to quickly relieve symptoms. Basic diets for gastroenterological patients are physiologically complete and suitable for long-term use.
- “... Chronic gastritis for 15 years. Sometimes it seems that I was born with it. Exacerbation 1-2 times a year. Of course, I immediately switch to diet food for about a month. I cook for myself, mostly in a slow cooker, sometimes I bake it in the oven. When there is no exacerbation, I switch to my usual diet, although I limit alcohol, especially beer, smoked meats, and spicy foods”;
- “...I checked my stomach. Gastroscopy revealed antral gastritis, low acidity, and Heliobacter was detected. She underwent eridification treatment and was prescribed a diet and medication. Now I understand how wrong I was eating, I ate a lot of spicy, fried, smoked foods, and often ate dry food. Now I’ve decided to normalize my diet and bring my stomach back to normal.”
What can you eat if you have acute diseases of the gastrointestinal tract?
List of allowed products for gastrointestinal diseases:
- Bread : protein-wheat
, wheat loaf, dried (yesterday's) - biscuit dry cookies or buns (not buttery), pies with potatoes, apples, or cheesecakes.
- Milk: see if your stomach tolerates it well. The same applies to fermented milk drinks and curd dishes: souffles, puddings or “balls”.
- Eggs: up to 1 pc. in a day.
- Fats: If your doctor approves the introduction of butter into your diet, great! As part of this diet, you can put 10 g of butter in your favorite dish or just eat a sandwich in the morning. Frying food in butter is strictly prohibited.
- “First” courses: puree soup, which can be prepared with water or a very weak and always low-fat broth. Chop the permitted vegetables into smaller pieces, add a little rice, buckwheat, oatmeal or small pasta like “stars” to the saucepan - tasty and nutritious.
- Meat and poultry: lean varieties and cooked in minced form. Cutlets or meatballs, soufflés or quenelles, rolls made from lean parts of beef, veal, rabbit or chicken - all this can become the highlight of even a festive dinner.
- Fish: cook chopped, make juicy meatballs, cutlets or meatballs. But it is not forbidden to cook it in pieces, but you need to choose a low-fat type: hake, pollock, pike, cod, haddock or ice fish.
- vegetable diet with potatoes, pumpkin, zucchini and carrots, pre-boiled and thoroughly pureed.
- Cereals, pasta. Avoid barley and millet, which still remain an unbearable burden for an irritated stomach. Any porridge should be boiled in water, or better yet, boiled to a viscous, tender mass, but not hard.
- Fruits and berries: choose only very sweet and certainly soft ones, without hard skin, make sure that they are ripe without any “buts”. Plums, melons and apricots should be avoided. Tasty tip: baked apple mousse is a great snack during this diet.
- Drinks: prepare fruit jelly or make compote from pureed sweet fruits and berries, you can steam rose hips or drink natural tea, for example, black tea with milk (unless your doctor has forbidden you milk).
- Sauces, spices: aromatic dill and parsley (greens need to be chopped), laurel. You can also prepare the most delicate sauces: sour cream or milk, they will add a new note to even a boring dish.
Menu for the day
If you have stomach pain, you need to eat small, healthy foods.
Dietary nutrition should be complete, varied, and regular. You need to adhere to the following rules of gentle nutrition:
- The body should receive 3000 kcal worth of food.
- Dishes can be boiled, baked, raw.
- Nothing canned, smoked or pickled is allowed.
- Any fried foods are prohibited.
- Food must enter the body warm.
- Reduce the amount of salt, spices, sauces.
During attacks of pain, you should avoid heavy foods that increase gas formation, such as white bread.
A menu for one day is offered.
Option #1:
- Breakfast: semolina porridge, rosehip decoction;
- Second breakfast: oven-cooked apple, milk;
- Lunch: vegetable soup, buckwheat, cheese;
- Dinner: milk porridge, chamomile infusion.
Option #2:
- Breakfast: cottage cheese;
- Second breakfast: one glass of warm milk, crackers;
- Lunch: puree soup, steamed meatballs, compote;
- Dinner: porridge, fruit.
Option #3:
- Breakfast: porridge with semolina milk, jelly;
- Second breakfast: oven-cooked pear, warm milk;
- Lunch: oatmeal soup, fish cutlets;
- Dinner: chicken cutlets, tea.
A balanced diet will allow the body to recover easily, taking medications will become more effective, and the condition will not worsen. The habit of eating right will have a positive effect on your appearance and health.
What is not allowed for acute diseases of the gastrointestinal tract?
List of prohibited foods for gastrointestinal diseases:
- Spicy and salty;
- canned food;
- discard spices;
- radish, rutabaga, all types of cabbage, onions and beets, garlic, sorrel, turnips, radishes and some others. (Raw vegetables are not recommended. Vegetables containing coarse fiber are prohibited even when boiled. Therefore, they are excluded);
- whole grain and rye bread;
- mushrooms and any legumes;
- fatty meat, fish and poultry Pork lard and lamb fat;
- fried foods;
- all melons, plums, peaches and apricots, kiwis and pears. Fruits and berries with hard and dense skin.
- carbonated drinks;
Authorized Products
The diet for stomach diseases should consist of:
- Broths/soups prepared in recycled meat/fish/vegetable broth with the addition of mashed/boiled cereals and vegetables (pumpkin, beets, potatoes, cauliflower, zucchini, carrots, young fresh peas), seasoned with egg-milk mixture/butter. During periods of exacerbation of diseases, pureed/creamy pureed soups are recommended, which are less irritating to the coolant.
- Lean varieties of red meat (veal/beef, chicken, turkey, rabbit, boiled/steamed). To reduce the stimulating effect of extractive substances, it is recommended to first boil meat/fish products and then stew/bake them.
- Fresh butter/vegetable oil, sour cream and cream sauces.
- Low-fat boiled/steamed sea and river fish (cod, pike perch, carp, pollock, sea fish fillet, hake) in pieces and minced products.
- Boiled, stewed, thoroughly pureed/chopped vegetables (cauliflower inflorescences, beets, pumpkin, garden herbs, kohlrabi, potatoes, green young peas, tomatoes without skins).
- Cereal well-cooked dishes (outside the period of exacerbation).
- Low-fat milk/dairy products, cottage cheese in its natural form and dishes made from it (baked cheesecakes, casseroles, puddings).
- Non-acidic fruits/berries, in the form of compotes, jellies, jelly. You can eat baked apples in small quantities.
- Dried white bread/flour products.
- Desserts - cottage cheese casserole with prunes, apricot jelly, semolina pudding with apples/pumpkin, mashed potatoes, fruit jelly.
- Spices that do not irritate the mucous membranes: garden herbs, bay leaf, cumin.
- Drinks include rosehip infusion and vegetable/fruit juices, mineral water, herbal teas.
Table of permitted products
| Proteins, g | Fats, g | Carbohydrates, g | Calories, kcal | |
Vegetables and greens | ||||
| zucchini | 0,6 | 0,3 | 4,6 | 24 |
| cauliflower | 2,5 | 0,3 | 5,4 | 30 |
| potato | 2,0 | 0,4 | 18,1 | 80 |
| carrot | 1,3 | 0,1 | 6,9 | 32 |
| parsley | 3,7 | 0,4 | 7,6 | 47 |
| beet | 1,5 | 0,1 | 8,8 | 40 |
| dill | 2,5 | 0,5 | 6,3 | 38 |
Fruits | ||||
| quince | 0,6 | 0,5 | 9,8 | 40 |
| pomegranate | 0,9 | 0,0 | 13,9 | 52 |
| pears | 0,4 | 0,3 | 10,9 | 42 |
| dogwood | 1,0 | 0,0 | 10,5 | 44 |
| apples | 0,4 | 0,4 | 9,8 | 47 |
Berries | ||||
| blueberry | 1,1 | 0,4 | 7,6 | 44 |
Nuts and dried fruits | ||||
| dried pears | 2,3 | 0,6 | 62,6 | 249 |
Cereals and porridges | ||||
| buckwheat (kernel) | 12,6 | 3,3 | 62,1 | 313 |
| semolina | 10,3 | 1,0 | 73,3 | 328 |
| oat groats | 12,3 | 6,1 | 59,5 | 342 |
| cereals | 11,9 | 7,2 | 69,3 | 366 |
| white rice | 6,7 | 0,7 | 78,9 | 344 |
Flour and pasta | ||||
| pasta | 10,4 | 1,1 | 69,7 | 337 |
| milk pasta | 11,5 | 2,9 | 67,1 | 345 |
| noodles | 12,0 | 3,7 | 60,1 | 322 |
Bakery products | ||||
| white bread crackers | 11,2 | 1,4 | 72,2 | 331 |
Confectionery | ||||
| jam | 0,3 | 0,2 | 63,0 | 263 |
| jam | 0,3 | 0,1 | 56,0 | 238 |
| marshmallows | 0,8 | 0,0 | 78,5 | 304 |
| fruit and berry marmalade | 0,4 | 0,0 | 76,6 | 293 |
| meringues | 2,6 | 20,8 | 60,5 | 440 |
| paste | 0,5 | 0,0 | 80,8 | 310 |
Raw materials and seasonings | ||||
| milk sauce | 2,0 | 7,1 | 5,2 | 84 |
| dried bird cherry | 8,4 | 0,0 | 16,8 | 101 |
Dairy | ||||
| skim milk | 2,0 | 0,1 | 4,8 | 31 |
| sour cream | 2,8 | 20,0 | 3,2 | 206 |
| acidophilus | 2,8 | 3,2 | 3,8 | 57 |
Cheeses and cottage cheese | ||||
| cheese | 24,1 | 29,5 | 0,3 | 363 |
| cottage cheese 0.6% (low fat) | 18,0 | 0,6 | 1,8 | 88 |
Meat products | ||||
| boiled beef | 25,8 | 16,8 | 0,0 | 254 |
| beef liver | 17,4 | 3,1 | 0,0 | 98 |
| boiled beef tongue | 23,9 | 15,0 | 0,0 | 231 |
| boiled veal | 30,7 | 0,9 | 0,0 | 131 |
| rabbit | 21,0 | 8,0 | 0,0 | 156 |
Bird | ||||
| boiled chicken | 25,2 | 7,4 | 0,0 | 170 |
| turkey | 19,2 | 0,7 | 0,0 | 84 |
Eggs | ||||
| chicken eggs | 12,7 | 10,9 | 0,7 | 157 |
Fish and seafood | ||||
| Red caviar | 32,0 | 15,0 | 0,0 | 263 |
| black caviar | 28,0 | 9,7 | 0,0 | 203 |
Oils and fats | ||||
| butter | 0,5 | 82,5 | 0,8 | 748 |
| ghee | 0,2 | 99,0 | 0,0 | 892 |
Non-alcoholic drinks | ||||
| mineral water | 0,0 | 0,0 | 0,0 | — |
| green tea | 0,0 | 0,0 | 0,0 | — |
| black tea | 20,0 | 5,1 | 6,9 | 152 |
Juices and compotes | ||||
| carrot juice | 1,1 | 0,1 | 6,4 | 28 |
| pumpkin juice | 0,0 | 0,0 | 9,0 | 38 |
| Apple juice | 0,4 | 0,4 | 9,8 | 42 |
| * data is per 100 g of product | ||||