Magnetic resonance imaging is an examination method that is used in gastroenterology if there are suspicions of serious pathologies in the gastrointestinal tract. It is based on the influence of a strong magnetic field and radio waves. MRI makes it possible to detect a tumor at an early stage, plan and predict the course of the operation, and also keep the patient’s condition under control after the operation.
Non-invasiveness and the absence of radiation harmful to the human body are the main advantages of this method over other diagnostic methods. MRI allows you to obtain the most accurate and reliable information about structural changes in any organ of the gastrointestinal tract.
Advantages and disadvantages of the method
There are several diagnostic procedures that can be used to assess the condition of the intestines. Compared to them, magnetic resonance imaging has several significant advantages:
- The diagnostic procedure is non-invasive and does not cause pain or discomfort in the patient;
- It has been repeatedly proven that MRI does not harm the body;
- After the procedure, you can immediately receive the results of the study;
- The list of restrictions to the procedure is minimal;
- The procedure does not require preparation, it has no rehabilitation period and complications;
- Possibility of obtaining three-dimensional images and video recordings.
An MRI of the colon is an excellent alternative to a more painful and unpleasant colonoscopy. Diagnostics using a tomograph is no less informative, but the difference in sensations is significant.
The only disadvantages that can be noted are the high cost of the study and the presence of some contraindications: for example, this type of diagnosis is not available for people with metal structures in the body (plates, rods, pacemaker, etc.). Such patients are prescribed a different type of diagnosis.
General characteristics of the examination
The intestine is the longest organ and the most labor-intensive to examine. Various methods are used to diagnose intestinal diseases. It depends on the part of the intestine and the alleged illness. The most common method is colonoscopy. With its help, you can study the intestines literally centimeters at a time. However, this procedure is quite unpleasant, requires careful preparation and is not always possible. It is not able to cover areas of the small intestine and is contraindicated in a number of diseases. Due to its pain, many patients are looking for alternative methods of examination and ask the question: “Do they do MRI of the intestine and rectum?” Knowing about the safety and effectiveness of the study, it is often preferred. Intestinal MRI is also actively used as an additional diagnostic method.
In what cases is intestinal diagnostics indicated?
The doctor may prescribe an MRI in the following cases:
- The appearance of acute abdominal pain some time after eating;
- Detection of blood in the stool;
- Chronic constipation, or, conversely, constant diarrhea;
- Congenital intestinal anomalies;
- Suspicion of the presence of metastases in the gastrointestinal tract;
- Nausea and vomiting;
- Sudden weight loss;
- Increased gas formation.
Magnetic resonance imaging is also carried out to monitor the dynamics during the treatment of the following pathological processes:
- The presence of neoplasms in the intestines;
- Polyps, diverticula;
- Duodenal ulcer;
- Chronic diseases of the gastrointestinal tract.
Diagnosis using MRI can be carried out before the upcoming surgical intervention in order to determine the exact localization of the pathological process, its characteristics and severity. MRI is also prescribed if the patient has contraindications to other types of intestinal examination.
As a preventive measure, magnetic resonance imaging is recommended for people predisposed to cancer. For example, if close relatives have experienced colon cancer. In this case, a preventive examination is recommended to be carried out at least once a year.
When is an MRI performed and when is a colonoscopy performed?
When choosing a technique, the doctor is guided by the symptoms of the disease.
Intestinal colonoscopy is prescribed in the following cases:
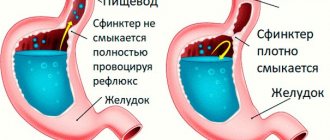
- If you have symptoms: cramps and pain in the abdomen, bloating, belching, nausea for no obvious reason; constipation, diarrhea; no appetite. These symptoms are characteristic of diseases in which there is damage to the mucous membrane
- If it is necessary to conduct screening for intestinal diseases in order to clarify or establish an accurate diagnosis, as well as in persons at high risk of certain gastrointestinal diseases.
- If necessary, determine disease activity.
.
MRI of the intestine is prescribed in the following cases:
- gastrointestinal bleeding;
- uncontrollable vomiting;
- feeling of distension of the anus;
- gas retention;
- traumatic injuries;
- monitoring the effectiveness of treatment;
- preparation for surgery.
The effectiveness of the techniques depends on the characteristics of the disease and the location of the pathology. The first method is more effective in identifying inflammation and tumors, and the second - in the presence of foreign bodies, in case of problems with patency.
Rules for preparing for research
To get the most reliable results, you need to properly prepare for the upcoming intestinal diagnostics. Let's consider the basic rules of preparation:
- The most important rule is to follow a special diet that prevents increased gas formation. First of all, you should avoid all foods that cause fermentation at least one week before the MRI. These include dairy products, legumes, various sweets, fast food, fresh vegetables and fruits, alcoholic drinks, etc.
- If the patient often experiences flatulence, increased gas formation and bloating, this problem must be solved in advance. You need to start taking sorbents or carminatives for at least 4-5 days.
- If you have constipation, you should do a cleansing enema in advance (at home). You can also start taking mild laxatives a week before the test.
- To avoid spasms, the doctor may recommend taking appropriate medications the day before the proposed test.
- MRI is recommended to be done on an empty stomach (at least 8 hours after the last meal).
- Immediately before the MRI, you must remove all jewelry and metal objects (earrings, chains, bracelets, piercings, hair clips, etc.).
- If an examination is to be performed in a closed tomograph, and the patient has a fear of confined spaces, the doctor may recommend taking sedatives.
The above preparation measures are mandatory for everyone who wants to obtain reliable examination results.
What foods should you avoid before the procedure?
Before an abdominal MRI, certain preparations are made. Its goal is to prevent active gas formation inside the intestines and suppress peristalsis in hollow internal organs. All these phenomena negatively affect the information content of the resulting images.
In preparation for an abdominal MRI, it is necessary to minimize the consumption of gas-forming, hard-to-digest foods, or better yet, completely eliminate them from the diet. This applies to:
- Confectionery products containing cocoa;
- Fresh fruits, vegetables (especially cabbage, legumes), berries;
- Milk, cream, fatty cheese and cottage cheese;
- Brown bread, baked goods;
- Dates, raisins, dried apricots and other dried fruits;
- Alcoholic and carbonated drinks, jelly, kvass, strong coffee;
- Gribov;
- Nuts and seeds;
- Smoked meats, marinades and spices.
In other words, the pre-MRI diet includes low-carbohydrate foods. It must be observed 2-3 days before the examination. It is imperative to have a bowel movement naturally. Sometimes the doctor prescribes laxatives or a cleansing enema.
Immediately before an MRI of the abdominal organs, it is important to abstain from eating for 4-6 hours. You should not smoke or chew gum, as this can cause the release of bile into the intestines. In this case, the information content of the study is reduced.
How is an MRI of the intestine performed?
Magnetic resonance imaging is carried out using a special device - a tomograph. To begin, the patient needs to lie on his stomach on a special retractable couch. For a high-quality, reliable and informative diagnosis, the patient must be motionless, so the body is fixed using special straps. Then the couch is brought into the machine itself - a tomograph; the lower part of the abdomen should be located under the annular part of the equipment.
During the procedure, you need to lie silently; you are allowed to speak only if the doctor asks you something (the tomograph has a microphone). There is also a panic button that you can press if you feel unwell. This happens especially often in people with claustrophobia.
If a detailed examination of the intestinal structures is necessary, an MRI with a contrast agent may be prescribed. In this case, before diagnosis, patients need to drink a liquid with a contrast agent; intravenous administration of the solution is also acceptable. As a rule, diagnosis takes 30-60 minutes. At the end of the manipulation, the patient can receive the diagnostic results in his hands.
How is ultrasound diagnostics and colonoscopy performed?
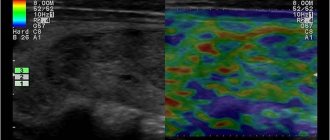
Many patients believe that undergoing an ultrasound of the intestine is a study during which a specialist will perform exclusively external manipulations, as is done when examining many organs. An intestinal ultrasound is performed a little differently.
First of all, a special catheter is inserted into the patient through the rectum to a depth of 5 cm. Its diameter is very small and does not exceed 8 mm. With its help, a special liquid is introduced into the intestine - a contrast agent, the purpose of which is to better visualize the walls of the organ.
During the examination, the patient does not experience pain. This diagnostic procedure is not very different from other types of ultrasound examinations.
As for colonoscopy, this is a much more unpleasant and sometimes even quite painful procedure. During the examination, a special device is inserted into the patient's intestines through the anus - an endoscope, which is a flexible tourniquet with a camera at the end.
For a complete examination of the intestines, the specialist will need to insert the endoscope deep enough, which causes pain to the patient. Another significant disadvantage of endoscopy is that it takes much longer to perform than ultrasound diagnostics.
What pathologies can be identified
Using this method of intestinal diagnostics, the following ailments can be identified:
- Intestinal obstruction;
- Malignant neoplasms and their metastases;
- Benign neoplasms (polyps, lipomas, hemangiomas);
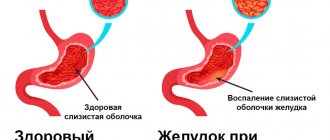
- Inflammatory processes;
- Foreign body in the intestinal cavity;
- Aneurysms and other problems with intestinal vessels;
- Bleeding in the intestines;
- Congenital structural anomalies.
After magnetic resonance imaging, you can determine not only the diagnosis, but also the degree of its severity. After receiving the results, the specialist will prescribe the necessary treatment.
Is it permissible to perform an ultrasound examination of the abdominal cavity after a colonoscopy?
It is not advisable to perform an ultrasound examination after a colonoscopy. In exceptional cases, specialists can still resort to ultrasound examination, for example, if there is a question about performing a biopsy, removing polyps, or stopping intestinal bleeding. In such cases, ultrasound will help monitor the dynamics of the treatment. In all of the above cases, ultrasound diagnostics are carried out exclusively through the peritoneal cavity.
As a rule, the patient is initially prescribed an ultrasound examination, and only then a colonoscopy. The choice of a specific method depends on the medical history, the patient’s condition and existing complaints.
Research results
If the intestines are in satisfactory condition and no pathological changes are detected, the study protocol indicates the following:
- The shape, size and diameter, localization of the intestine correspond to the norm.
- Intestinal patency is normal.
- There are no foreign bodies.
- No foci of inflammation or bleeding were found.
- Metastases and various neoplasms are absent.
But even if pathologies are found during the examination, do not panic. Today, almost any pathological process can be treated. Some pathologies can be treated conservatively; only in extreme cases, surgical care is required. Be healthy!
Contraindications to MRI of the gastrointestinal tract
Absolute:
- 1st trimester of pregnancy;
- wearing a pacemaker, middle ear implants;
- foreign metal objects (shards, bullets, shavings);
- metal clips/clamps on cerebral vessels.
Relative:
- allergy to iodine, breastfeeding, severe renal or liver failure (with contrast administration);
- inability to remain still during the study (children, mental illness, claustrophobia, panic attacks);
- decompensated cardiovascular pathology;
- joint prostheses; insulin pump; vena cava filters; neurostimulators.