Magnetic resonance imaging is an examination method that is used in gastroenterology if there are suspicions of serious pathologies in the gastrointestinal tract. It is based on the influence of a strong magnetic field and radio waves. MRI makes it possible to detect a tumor at an early stage, plan and predict the course of the operation, and also keep the patient’s condition under control after the operation.
Non-invasiveness and the absence of radiation harmful to the human body are the main advantages of this method over other diagnostic methods. MRI allows you to obtain the most accurate and reliable information about structural changes in any organ of the gastrointestinal tract.
Indications for MRI of the gastrointestinal tract
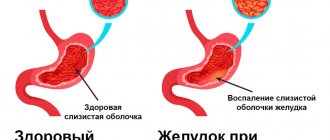
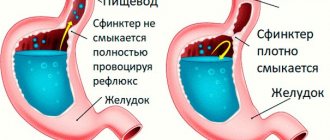
MRI is prescribed for gastritis and stomach ulcers.
Under the influence of a whole complex of unfavorable factors, the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract is disrupted, and diseases arise that interfere with the normal functioning of the body and can even pose a threat to human life. Such unfavorable factors include:
- irregular and unbalanced diet, causing gastritis or stomach ulcers;
- unsatisfactory psychological state of a person, frequent stress;
- poor environmental situation, poisoning of the body with food containing toxins;
- addiction to cigarettes or alcohol.
These factors, individually or in combination, can provoke the occurrence of very serious gastroenterological diseases, the diagnosis of which is carried out using MRI. These include:
- internal bleeding;
- acute and chronic gastritis;
- stomach and duodenal ulcers, polyps;
- inflammatory processes in the pancreas (pancreatitis);
- intestinal obstruction;
- malignant neoplasms in the stomach, pancreas or intestines;
- gallstones.
Magnetic resonance imaging is also performed if there is a suspicion of the presence of foreign objects in the intestines.
In gastroenterology, MRI is rarely prescribed, since the stomach is a hollow organ and is difficult to diagnose using tomography. As a rule, an MRI is required to clarify the results of a previously performed ultrasound or x-ray.
This type of diagnosis makes it possible to identify the initial stage of the tumor, which is especially important for its timely removal and preservation of the normal functioning of the organ.
MRI is absolutely harmless, so it can be repeated to check the operated organ. Pregnant women are also allowed to undergo MRI (except for the first trimester of pregnancy and MRI with contrast).
CT scan of the gastrointestinal tract shows:
- foreign bodies in the digestive tract;
— the condition of the surrounding and adjacent organs of the mediastinum;
— detailed adjacent bone structures;
- condition of the walls of hollow organs - esophagus, stomach, intestines;
— wall defects;
— vascular network of neoplasms;
— three-dimensional models of vessels, bones and dense formations in the bile ducts.
CT diagnostics provides a layer-by-layer image with a slice thickness of 5 mm. This method is considered the final stage of examination of the abdominal organs after X-ray and ultrasound examination, through which the location of the pathology and the exact diagnosis are clarified. The advantage of computed tomography of the gastrointestinal tract is associated with the high speed of the study - the procedure lasts 3-5 minutes.
MRI preparation measures
Before the MRI, you need to cleanse the intestines with an enema.
In order to get the most reliable result, preparing for an MRI involves a special diet the day before it.
The day before the procedure, the subject should eat foods rich in coarse fiber - apples, cabbage and other vegetables and fruits. The last meal should take place no later than 6-8 hours before the procedure.
Immediately before the MRI, you should cleanse the intestines with an enema. To absorb gases in the intestines after an enema, you need to take activated charcoal and drink an antispasmodic to relax the muscles and reduce the peristalsis of the organs being examined.
When performing MRI, there are general requirements that must be met to obtain an accurate picture of the organ being examined.
During magnetic resonance imaging, the patient must lie still. It is better to wear loose clothing that does not cause discomfort. In some cases, it is advisable to take a sedative or undergo a light anesthesia.
It is prohibited to take electronic cards and mobile devices with you. Not only can they affect the reliability of the result, but they can also be spoiled during the MRI process.
It is also not allowed to come to the procedure wearing metal jewelry or cosmetics. Metal particles contained in cosmetics can heat up when exposed to an electromagnetic field and cause discomfort in the patient. For the same reason, any other metal objects (belt, keys) should be left outside the office door.
During the procedure, it may be necessary to administer medications, so the likelihood of allergic reactions to them should be clarified before the examination.
Carrying out the procedure
Before starting the procedure, the doctor explains the entire examination process to the patient, talks about the rules and contraindications. Next, the patient lies down on a special table, which then smoothly moves into the tomograph. To obtain the most accurate results, you should remain calm and still. Often, during the examination, the stomach walls are straightened by slightly stretching with the help of an iron-containing solution, which is prescribed to the patient and relieves pain. Sometimes a specialist administers intravenous contrast, shows the most clearly needed areas, and this does not cause any discomfort.
When is MRI contraindicated?
It is strictly forbidden to do an MRI for people who have metal particles in their bodies (metal plates after fractures, etc.), hearing aids, devices for regulating the heart (pacemakers), neurostimulators and other medical devices. MRI is also contraindicated for patients suffering from claustrophobia.
Children under 7 years of age are examined only in exceptional cases.
For more information about MRI, watch the video:
Contraindications
Many medical diagnostic methods have contraindications, and MRI of the stomach is no exception.
Pregnancy, lactation period
MRI during pregnancy must be agreed upon with your doctor. Pregnancy is not a strict contraindication, but it is not advisable to carry out this diagnosis before 12 weeks, since during this period the organs of the unborn baby begin to form. The lactation period is also not a contraindication for MRI of the stomach. You should not be afraid of the effect of contrast on breast milk, since the time it takes to be removed from the body is no more than 2-3 days.
Presence of foreign metal objects in the body
Patients should definitely inform the specialist about the presence of foreign metal or electronic objects in the body, such as pins, prostheses, implants, etc. They may distort the results or fail. It is possible that such objects may cause injury to the patient during the examination.
What can be seen on a tomogram?
As in the case, complex computer processing of images obtained on MRI is performed. The result is a very clear picture of pathologies affecting the abdominal wall, intraperitoneal space and further body structures.
The doctor immediately sees which organs are affected and can clearly show it to the patient or relatives. The image from MRI is much clearer to non-specialists than CT, or, moreover, obtained from ultrasound.
Visualization helps to better justify the need for surgical intervention and obtain consent for surgical treatment. MRI images are transferred to the patient in digital form, say, as files recorded on a flash drive. Subsequently, they can be printed on a home printer and viewed on a computer screen.
In our clinic, MRIs are performed in strict accordance with standards, obtaining high-quality results that are easy to interpret for any specialist.
If there are contraindications, you can undergo a CT or ultrasound. An experienced doctor will examine you, identify indications and refer you to tests that will give the best results. Rate this article: (1 rated 5 out of 5)
How does the process of magnetic resonance examination of the stomach and duodenum proceed?
Best materials of the month
- Coronaviruses: SARS-CoV-2 (COVID-19)
- Antibiotics for the prevention and treatment of COVID-19: how effective are they?
- The most common "office" diseases
- Does vodka kill coronavirus?
- How to stay alive on our roads?
The patient changes into loose clothing without metal elements, removes all metal accessories and jewelry, after which he is asked to sit on the tomograph table. If an MRI with contrast is prescribed, the patient must drink a contrast agent 30-40 minutes before the start of the tomography. In some cases, it may be necessary to administer a substance intravenously to stretch the intestinal walls.
The subject is fixed in the most relaxed and comfortable position using special bolsters and belts to ensure complete immobility for the entire duration of the scan. For those who are disturbed by the noise of the tomograph, earplugs are provided. Next, the table together with the patient is sent into the cavity of the tomograph cylinder, and the doctor in the next room starts the tomograph and begins the procedure. To communicate with the patient, the device has a two-way communication system, so if the subject feels discomfort, unpleasant or painful sensations, he can immediately inform the doctor about it.
The duration of the scan is on average 30-60 minutes.
What is diagnosed by magnetic resonance?
Since the abdominal cavity is vast and consists of several sections, the tomograph reveals diseases of many systems: digestive, genitourinary, endocrine. Also, MRI can be useful in cases of damage to large vessels, although CT in this case is informative (with contrast).
A separate category of research is the use of a magnetic field to diagnose tumors. MRI effectively detects cancer of the stomach, liver, kidneys, and metastases of tumors with a primary source outside the abdominal cavity. Many tumor processes are extremely difficult or practically impossible to detect on CT, so it is obvious which diagnostic method should be used.
Tomography with contrast
Many medical centers offer contrast-enhanced tomography. The use of this method is often associated with suspicions of the development of a tumor process. At the same time, we are not always talking about malignant formations. Thus, the introduction of contrast makes it possible to distinguish a cyst from a hemangioma and helps determine the specifics of the neoplasm.
During the procedure, the patient is given a gadolinium-based substance intravenously. It has a cumulative function and the ability to dye fabrics. In this case, areas affected by the pathological process are colored differently from healthy tissue. As a result, it becomes possible to see tumors smaller than 1 mm and metastases. The amount of substance administered depends on the patient’s body weight.
When is a CT scan indicated?
On X-ray tomograms made using a computer, hollow organs are clearly visualized. Especially with the use of contrast agents. This is an excellent alternative to endoscopic examination of the stomach, intestines, and especially the gallbladder, which is unattainable with an endoscope.
CT scans clearly visualize the bones, which provides surgeons with guidance when surgery is to be performed. CT makes it possible to prepare based on the individual characteristics of the body, for example, to find out at what level the appendix of the cecum is located.
Results and their interpretation
The examination result looks like an image of layer-by-layer sections with a thickness of 2 to 4 mm. The doctor compares the obtained indicators with the norm and analyzes pathologies. The conclusion issued by the doctor after the examination states:
- What organs were examined;
- Have neoplasms been identified, what is their nature, location, prevalence;
- Are there metastases in tissues located near the lesion;
- Has the preliminary diagnosis been confirmed?
The document describes not only all identified pathologies and disturbances in the functioning of systems, but also healthy organs. Additionally, the patient is given printed photographs, as well as video materials recorded on a disk or memory card.
Depending on the identified pathologies, it is necessary to contact a specialized specialist. Based on the MRI results, the doctor will make a diagnosis and prescribe conservative or surgical treatment.