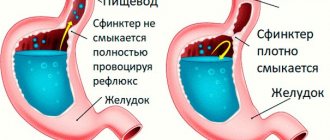
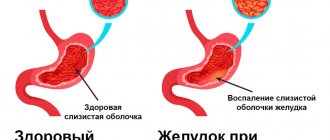
A mandatory test for many examinations is stool microscopy: it reveals the presence of yeast fungi. This indicates intestinal candidiasis, a disease associated with the manifestation of dysbiosis. It is accompanied by unpleasant symptoms, and treatment is prescribed by a doctor after identifying the causes and characteristics of the patient’s problem.
What is yeast fungus
The mold variety of Candida fungi is called yeast. The presence of these cells in the microflora of a healthy person is the norm, but under unfavorable factors they grow greatly, leading to candidiasis. Fungi multiply and accumulate toxins in the body, which affects the patient’s health. Yeasts are detected in stool with the following symptoms:
- pain in the abdomen and intestines;
- feces have an unpleasant odor;
- diarrhea, constipation;
- digestive tract dysfunction;
- decreased or increased appetite;
- skin allergies;
- weight loss;
- itching of the anus;
- flatulence;
- feces of unusual shape and color.
Why do yeast-like fungi appear in stool?
The reasons why yeast molds appear in feces are:
- impaired immunity - congenital or acquired, this can be facilitated by HIV, taking certain drugs, hormones, antidepressants, and many serious diseases leading to exhaustion;
- death of beneficial microorganisms due to antibiotics;
- reduced acidity in the stomach, which increases the proliferation of bacteria;
- dysfunction of intestinal valves;
- decreased digestive function due to acute microbial or viral diseases;
- tendency to constipation, intestinal obstruction;
- diabetes mellitus, intestinal and liver infections;
- influence of industrial poisons, radiation;
- allergic reactions;
- oncology;
- eating disorders;
- unfavorable ecology, sudden climate change.
Causes
Various factors, both internal and external, can provoke intestinal dysfunction. Here are the main ones:
- severe stress, overwork;
- a decrease in the immune system caused by the development of other pathologies;
- alcohol abuse;
- excessive coffee consumption;
- unbalanced diet, frequent consumption of junk food (sweet, fatty, salty and smoked);
- overeating, snacking on the go;
- development of the inflammatory process;
- consequences of long-term use of potent antibacterial drugs;
- development of sexually transmitted diseases;
- diseases of the gastrointestinal tract;
- negative environmental impact;
- menstrual irregularities;
- bearing a child;
- hormonal imbalance, consequences of taking anti-inflammatory, antibacterial or hormonal medications;
- presence of cancer;
- development of hypervitaminosis or vitamin deficiency;
- high blood pressure;
- chemical poisoning.
Often the causative factor is weak immunity, which is unable to restrain the proliferation of pathogenic microorganisms in the human digestive system. This leads to the development of dysbiosis and other intestinal problems.
How does the fungus manifest itself?
If Candida fungi actively multiply in the intestines of an adult or child, the patient will experience the following symptoms:
- pain in the lower abdomen or around the navel: the symptom intensifies after eating fatty foods;
- loss or decreased appetite;
- disruption of the gastrointestinal tract: belching, heartburn, rumbling, bloating, increased gas formation, nausea, vomiting;
- diarrhea or constipation;
- unpleasant and pungent odor of feces;
- changes in the color and shape of stool;
- feces “do not sink”: they are poorly flushed down the toilet and remain on the surface of the water for a long time;
- the presence of whitish, cheesy pieces in the stool;
- itching of the anus;
- whitish-yellow coating on the tongue, unpleasant taste in the mouth;
- yellowness of the skin;
- allergic skin rash, acne, brittle nails and hair.
The more a fungal infection spreads, the more pronounced and aggressive the symptoms become. In advanced cases, difficulty swallowing and weight loss, blood and mucus in the stool, fever, general weakness, daytime drowsiness, insomnia, irritability, headaches, and pallor may occur.
Associated symptoms
In most cases, detection of fungi in stool is not a sign of disease and does not require drug treatment. However, there is candidal colitis - a severe fungal infection of the colon in a child. This form of the disease usually occurs in children with immunodeficiency, severe diabetes mellitus or ulcerative colitis, during chemotherapy, hemodialysis.
Be sure to read:
Pylorospasm: symptoms, diagnosis and treatment (nutrition, medications and physiotherapy)
Symptoms of colitis caused by yeast:
- frequent regurgitation, vomiting;
- “rumbling” along the intestines, bloating;
- child's anxiety, loss of appetite or refusal to eat;
- diarrhea (mucous, frequent, loose stools mixed with whitish lumps).
In a significant number of newborns, gastrointestinal lesions are combined with candidiasis of the skin of the perianal area (itching and white plaque around the anus).
Conducting laboratory analysis
After you visit your doctor's office with suspected dysbiosis or other intestinal pathologies, he will most likely order a comprehensive laboratory test. This procedure is needed to identify yeast spores in the patient's stool. After submitting the material, laboratory staff place it in a special habitat. Over time, the activity of the fungi increases and they begin to multiply. This leads to the fact that associations of microorganisms can be seen even without the use of a microscope.
There are other tests that can determine the presence of pathogens, such as a laboratory blood test for candida antibodies and immunoglobulin levels. The vital activity of fungi can also be detected in urine, so doctors often prescribe a general urine test to their patients.
If feces are poorly flushed in the toilet, constantly floating on the surface of the water, this may indicate the presence of fungus in the intestines. In this case, you also need to see a doctor for a diagnostic examination.
Diagnostics
Intestinal candidiasis in adults and children is detected using the following methods:
- Microscopy of feces and smears from the intestinal mucosa. The biomaterial is examined under a microscope. As a result, the number of fungi in the stool is determined, and the exact type of candidiasis pathogen is determined.
- Bacterioscopy, bacterial culture on nutrient media. Fungal colonies are grown in a nutrient medium. Through analysis, it is possible to determine the sensitivity of the microorganism to various antifungal drugs. The method allows you to prescribe an effective course of treatment.
- Additional tests. Blood test for the content of immunoglobulins and antibodies to Candida fungi, urine test for dysbacteriosis.
- Colonoscopy. Examination of the intestines using an endoscope - a device with a camera. The method allows you to assess the condition of the mucous membranes and the degree of their damage by the fungus. During the procedure, scrapings and biopsies are often taken to further analyze tissue and cells.
Signs of the presence of fungi in the intestines. Alexander Ogulov
Treatment options
The essence of treating dysbiosis is to eliminate all negative factors that affect the condition of the body. Therapy should be comprehensive and include a special diet, medications and traditional medicine. Let's consider each treatment method separately.
Pharmacy drugs
If test results confirm the presence of fungi in the body, then treatment must be started immediately. When prescribing a particular drug, the doctor must take into account the condition of the patient’s body, his age and the degree of development of the disease. Below are the most common medications prescribed for the presence of yeast in the body.
Table. Effective drugs for the treatment of yeast fungi.
| Name of the drug, photo | Description |
| A potent synthetic drug with antifungal and anti-inflammatory properties. Belongs to the group of triazoles and is used in the treatment of various fungal diseases. The dosage and duration of the treatment course are prescribed by the doctor. | |
| An effective broad-spectrum drug. It has fungistatic, fungicidal and antifungal properties against various types of dermatophytes. | |
| Another antifungal drug used when yeast appears in the patient’s body. Slows down the proliferation of pathogenic microorganisms and leads to their complete destruction. It begins to act almost immediately after use. It is completely eliminated from the body in about a week, mainly through the kidneys. | |
| A fungicidal drug with antifungal and antibacterial properties. It is a broad-spectrum medicine, therefore it is often used in the treatment of gastroenterological diseases. | |
| An antibacterial drug with antifungal and bactericidal properties. Its action is to block the synthesis of pathogenic fungi. It has virtually no contraindications, so it is often prescribed to children. |
If pathogenic microorganisms were found not in feces, but in urine, a laboratory urine test must be done to make an accurate diagnosis. Only after the doctor detects pathogen spores in the urinary and reproductive system can treatment begin.
How will diet help?
The main point of a speedy recovery is diet. Food should be light, healthy, rich in vitamins. Since in the process of dysbacteriosis the nutritional components are poorly absorbed, the body weakens. You should refuse:
- sweets;
- bakery products;
- coffee;
- alcohol;
- carbonated drinks;
- legumes;
- cabbage;
- grapes;
- fried foods;
- seasonings, mayonnaise, ketchup;
- canned goods;
- raw milk;
- plums, cherries, sour apples.
The main task is to restore the intestinal microflora and improve intestinal function. For this purpose, professional preparations and folk remedies are used. Vitamin complexes are used.
Treatment of fungi in feces is a long process that lasts from one month to six months. As your condition improves, you can gradually introduce foods from the list of prohibited foods, but within reason. Try not to use medications unless absolutely necessary, especially non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, antibiotics, and hormonal drugs.
Application of traditional medicine
Treatment of yeast fungi in the stool of an adult allows the use of folk remedies. However, they should only be used in conjunction with the main therapy. To get rid of intestinal candidiasis, decoctions of antibacterial and anti-inflammatory herbs are actively used: lemon balm, mint, chamomile, calendula, thyme, linden. Also popular are infusions based on aloe, flax seeds, garlic, honey, lemon juice, and Hercules flakes.
Both adults and children can use olive, coconut or sea buckthorn oil. The products have pronounced bactericidal properties, do not irritate the skin and mucous membranes, and do not cause allergies. Oils can be used externally or taken internally. Products with antifungal properties will also help suppress the proliferation of Candida fungi: wild strawberries and strawberries, grapefruits and grapefruit seed extract, Jerusalem artichoke, onions, garlic, ginger, oregano oil, bearberry oil, and colloidal silver.
Table. Traditional medicine recipes for yeast fungi.
| Product name, photo | Application |
| This miraculous vegetable is often used in folk medicine due to its bactericidal properties. If you have yeast in your intestines, garlic and honey will help you cope with this phenomenon. To prepare the product, you need to mix 1 tsp in one bowl. honey and 4 minced garlic cloves. Take the finished product daily on an empty stomach until the symptoms of the disease are completely eliminated. | |
| Pour 400 ml of boiling water over 1 tbsp. l. crushed plant and leave for 2 hours. After infusion, the medicine must be filtered through several layers of gauze to get rid of the remnants of St. John's wort. If desired, the infusion can be sweetened a little by adding a small amount of sugar or honey. Take the infusion orally several times a day. | |
| An excellent remedy against yeast fungi. It is no secret that this oil has restorative, bactericidal and anti-inflammatory properties, thanks to which it can be used not only by adults, but also by children. Drink 2 tsp daily. olive oil before eating. The duration of the treatment course is 10 days. As an alternative, you can use sea buckthorn oil. It has the same properties. | |
| To prepare such a medicinal drink, you need to mix 1 tsp. honey with 50 ml of freshly squeezed lemon juice. Take the finished product throughout the day. It is advisable to divide the prepared mixture into 3 servings. | |
| Take a few aloe leaves, wash them thoroughly and remove the peel. Cut the pulp into pieces and place in a blender. As a result, you should get a green paste, which you need to mix with 1 tsp. honey Store the finished product in the refrigerator. It is recommended to take 2 times a day - 2 tsp in the morning and evening, preferably 20 minutes before meals. |
Before using this or that product, you should definitely consult your doctor. Many drugs have contraindications, just like folk remedies. Otherwise, you may harm your body.
Routes of transmission and growth of microorganisms
In childhood, there are two main routes of transmission of fungal infections:
- intrapartum – during the birth period (during passage through the birth canal infected with fungi, during aspiration of amniotic fluid);
- postnatal – after birth (through the hands of medical personnel, the mother’s skin).
Basically, mushrooms get on the skin and mucous membranes by contact - through hands and household objects. Infants can become “infected” during breastfeeding if the mother has mammary candidiasis and cracked nipples.
Yeasts can actively multiply in the intestines under certain conditions:
- in case of imbalance between beneficial microbiota (lacto- and bifidobacteria) and opportunistic flora;
- at high humidity and temperature (improper child care);
- with hormonal dysfunction (an excess of certain hormones can contribute to the development of the disease);
- as a result of a decrease in the body's defenses against the background of immunodeficiencies, autoimmune pathology, or taking hormonal or cytostatic drugs.
The first factor is very conditional, since the composition of the “normal” intestinal microflora is still unknown and such a diagnosis as “candida dysbiosis” exists only in domestic medicine.
How to protect the body?
There are many different measures that can prevent the occurrence of intestinal problems, including the formation of yeast. It was previously mentioned that the activation of fungal microorganisms occurs against the background of a weak immune system, so the first thing to do as a preventive measure is to improve your health. Normalize your daily routine, make adjustments to your diet. If necessary, exclude harmful foods from it (fast food, sweets, fatty foods). Such food negatively affects not only the digestive system, but also the overall health.
Treatment measures should be carried out at all levels. This includes making adjustments to the usual menu, getting rid of the disease with the help of medications and traditional methods of treatment, and consolidating the results. The main goal in this case: to achieve stable and long-term results in strengthening the immune system. It is he who creates that strong barrier that does not allow Candida fungi to multiply unhindered in the child’s body.