Causes
Unpleasant sensations in the throat and difficulty swallowing can arise both directly from problems with the functioning of the digestive system, and from pathology of organs topographically located close to the esophagus.
If there is a constant desire to cough, hoarseness during a conversation, pain when eating, a feeling of lack of air, experts recommend examining:
- esophagus and gastrointestinal tract as a whole;
- thyroid gland;
- ENT organs;
- cardiovascular system;
- spinal condition.
Ingestion of a foreign body, chest trauma, and intercostal neuralgia can also cause characteristic symptoms.
Treatment
Patients are recommended to eat more frequently in small quantities; their last meal should be no later than three hours before bedtime. If pain is severe, before meals you can give 2-3 tablespoons of a 0.5% solution of novocaine. The rapid healing of ulcers and erosions of the mucous membrane and the subsidence of the inflammatory process are promoted by rosehip oil, sea buckthorn, sunflower oil (they are taken 10-15 ml 3-4 times a day after meals). For esophagitis, all carbonated drinks are prohibited. While eating, you should not rush; chewing food slowly promotes the separation of saliva, which has an alkaline reaction. To neutralize the acidic contents of the esophagus, antacids (magnesium oxide, magnesium trisilicate, aluminum hydroxide, sodium bicarbonate) are used; they are given in combination with astringents that help calm inflammation and restore the mucous membrane (vicalin, vikair, gastrofarm, vinylin). If vomiting is present, cerucal is prescribed. During the period of exacerbation of chronic esophagitis and acute esophagitis, drugs that suppress Helicobacter pylori infection are used - antibiotics, as well as metronidazole.
Diseases of the esophagus
The sensation of a lump in the esophagus can be observed with esophagospasm. This disease is characterized by the development of uncoordinated contractions; the function of the lower esophageal sphincter is not impaired.
Among the main forms of the disease, doctors identify:
- Idiopathic esophagospasm. Due to damage to the nerve plexuses located in the intermuscular layer, a disruption of nervous regulation occurs.
- Esophagospasm of a secondary nature. Develops as a concomitant symptom of peptic ulcer, esophagitis, hiatal hernia, diabetic neuropathy.
Manifestations of esophageal spasm are pain in the chest area. They can occur both when eating food and spontaneously at rest. It is important to note: emotional stress increases the severity of pain. Patients often complain of a feeling of a lump in the esophagus lasting from seconds to 20-30 minutes.
Dysphagia
The main signs of the disease are pain when swallowing (inability to swallow), a constant feeling of a lump in the throat. Dysphagia occurs due to inflammatory processes of the esophagus, pharynx, and larynx. Cicatricial narrowings, foreign bodies, and tumors can also cause characteristic manifestations. Among the causes of swallowing disorders, doctors also identify mechanical compression of the esophagus, which can be observed with an aortic aneurysm or nodular goiter.
But in addition to symptomatic or secondary dysphagia, the true form also occurs. It develops in disorders of nervous regulation and is episodic in nature.
Associated signs of the disease are also:
- Pain in the upper abdomen.
- Heartburn.
- Belching.
- Due to the reflux of stomach contents into the pharynx, patients complain of an unpleasant taste in the mouth.
If the disease occurs against the background of esophagitis, hoarseness of the voice, increased salivation, and a feeling of lack of air are often observed.
What is the danger of discomfort
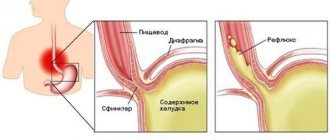
As you can see, discomfort is a fairly common sign of a number of diseases. Most of them concern the organ itself: esophagitis , GERD (a disease associated with incompetence of the esophageal sphincter, which leads to the reflux of acidic stomach contents into the esophagus), gastritis .
Some of the problems are related to neurology, cardiology, spine, thyroid gland, inflammatory diseases of the ENT organs, and oncology. Therefore, it is so important to contact a specialist at the first sign of an unpleasant sensation of a lump in the throat and conduct a diagnostic study.
Thyroid diseases
Iodine deficiency in the body and hormonal imbalances cause hyper- or, conversely, dysfunction of thyroid cells. In this case, hyperplasia of the thyroid tissue occurs, which can be both diffuse and focal in nature.
The increased size of the gland leads to compression of the esophagus and a feeling of a coma.
Thyrotoxic goiter is characterized by an increase in heart rate, bulging eyes, a sharp decrease in body weight, and nervous system disorders (nervousness, tearfulness). As a rule, the impetus for the development of the disease is given by a severe stressful situation, a nervous shock.
Diseases of the ENT organs
Due to the topographic proximity of the ENT organs and the esophagus, tonsillitis (acute or chronic), pharyngitis, laryngitis can provoke the appearance of a feeling of a lump in the esophagus. In most cases, these diseases occur as a result of infectious “agents” entering the body. Occurs against a background of elevated body temperature and deterioration of general condition. Depending on the location of the lesion, hoarseness, sore throat, and enlarged regional lymph nodes may be observed.
In addition to inflammatory diseases, the sensation of a lump can also be caused by a neoplasm. An otolaryngologist will be able to identify the true cause after a full examination.
Why does there be a feeling of a foreign body in the throat?
Acute infections
The sensation of a foreign body is provoked by swelling, inflammation, accumulation of sputum, and plaque formation. It is detected in infectious diseases such as:
- ARVI.
The manifestation is insignificant, disturbing at the initial stage of the disease, complemented by weakness, weakness, moderate redness of the throat, general hyperthermia, and muscle pain. - Measles.
The symptom occurs with the onset of the first wave of fever and is more pronounced in children. The pharynx is hyperemic, the posterior wall of the pharynx is granular. The face is swollen. After 3-5 days, the condition improves and characteristic rashes form on the skin. - Diphtheria.
Accompanied by the formation of fibrinous plaque first, then a dense smooth coating. With widespread damage to the oropharynx, involvement of the larynx and trachea, breathing disorders and the development of diphtheria croup are possible. - Scarlet fever.
The throat is bright red, painful, sometimes there is involvement of the tonsils and enlargement of the cervical lymph nodes. A little later, the tongue and lips also become bright red, a pinpoint rash appears on the face and upper body, spreading to the limbs.
Inflammatory diseases of the ENT organs
In acute inflammation, the symptom does not have a clear localization, occurs suddenly, quickly reaches a significant degree of severity, and disappears after a few days. Chronic inflammatory processes are accompanied by periodic moderate or slight sensation of a foreign body, which is more disturbing during periods of exacerbation.
- Tonsillitis.
The tonsils are hyperemic, enlarged in volume, covered with superficial films, multiple small yellowish-white foci or loose plaque. Sore throat, general hyperthermia, and symptoms of intoxication are observed. With chronic tonsillitis in the acute phase, all symptoms are smoothed out. - Pharyngitis.
When examining the pharynx, swelling and diffuse hyperemia are revealed. The general condition remains normal, sometimes there is weakness and an increase in temperature to low-grade levels. In the chronic form, one part of the pharynx is predominantly affected: the oropharynx, nasopharynx or hypopharynx. - Laryngitis.
The patient complains of scratching, soreness, and tickling in the lower parts of the throat. The voice becomes hoarse; in severe cases, the patient speaks in a whisper. There is a paroxysmal dry cough. The symptom is more noticeable in phlegmonous and infiltrative forms. Chronic laryngitis is manifested by coughing, the need to periodically clear the throat, and rapid voice fatigue.
Laryngeal sore throat is accompanied by the same symptoms as acute laryngitis, but is characterized by a more severe course. The pain in the throat is so severe that patients refuse to eat and take a forced position.
Purulent processes
Abscesses in the throat area occur with sore throat, and less often result from rhinitis, pharyngitis, or sinusitis. Sometimes they develop with otitis media, mastoiditis, mumps, and are formed against the background of acute infections or carious teeth. The sensation of a foreign body has a clearer localization than in inflammatory pathologies, appears on the side or in the central part of the throat, and is accompanied by significant hyperthermia and severe intoxication. Detected under the following conditions:
- Peritonsillar abscess.
It manifests itself as sharp, rapidly intensifying pain when swallowing. The pain becomes tearing and radiates to the ear and lower jaw. There is a tilt of the head towards the affected area and a putrid odor from the mouth. Possible trismus. - Retropharyngeal abscess.
It is accompanied by extremely intense pain, forcing patients to refuse food. When the abscess is located in the upper part of the pharynx, nasal breathing disturbances and nasal sounds are observed; in the middle and lower parts - difficulty breathing and hoarseness. - Epiglottitis.
Signs of a purulent process are combined with breathing problems. The patient complains of pain in the lower part of the throat. Hoarseness and muffled voice, wheezing, cyanotic lips and nasolabial triangle, and tachycardia are detected.
Ludwig's angina is one of the most common purulent processes. The sensation of a foreign body appears when the pharynx is involved, accompanied by severe fever, swelling of the neck, breathing problems, loss of voice, and drooling.
Sensation of a foreign body in the throat
Traumatic injuries
The sensation of a foreign body in the throat may indicate the presence of a foreign object or injury caused by the object as it passes through the throat. The cause of the symptom is fish bones, crackers, fruit and berry seeds. Children sometimes swallow inedible objects with sharp edges, such as building blocks. With thermal and chemical burns, discomfort in the throat occurs due to swelling and damage to the mucous membrane.
Tumors
The symptom is included in the typical clinical picture observed with benign neoplasms of the pharynx and is combined with a sore throat, nasal voice, and difficulty in nasal breathing. Slowly builds up over a long period of time. It is detected with papillomas, fibromas, and hairy pharyngeal polyps. It is noted for angiomas, neuromas, and pharyngeal cysts. With benign neoplasia of the larynx, complaints of the sensation of a foreign object are less common, and voice changes prevail.
In patients with pharyngeal cancer, the sensation of a foreign body is the first symptom of the disease. Later, pain, choking, difficulty swallowing, and sensitivity disorders occur. Manifestations quickly progress, complemented by general signs of the oncological process - weight loss, weakness, intoxication. The symptom is also characteristic of laryngeal cancer, affecting the upper parts of the organ.
Allergy
The symptom is observed in allergic reactions accompanied by swelling of the throat. It appears suddenly. The patient is bothered by sneezing, nasal congestion, lacrimation, sore throat, itchy skin. In the spring-summer period, allergies are provoked by contact with plant pollen, throughout the year - with wool, dandruff, feathers of animals and birds, house dust, and food products. The most striking picture is observed with Quincke's edema.
Thyroid pathologies
The thyroid gland is located near the upper part of the trachea, its enlargement causes irritation of the receptors, causing the sensation of a foreign body. The symptom is detected in the following pathologies:
- Iodine deficiency conditions
: diffuse euthyroid goiter, nodular goiter. - Mainly hyperthyroid conditions
: diffuse toxic goiter, thyroiditis (subacute, autoimmune, others). - Benign and malignant tumors
: adenomas, cysts, lymphomas, thyroid cancer.
Digestive system diseases
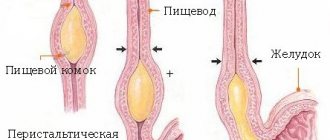
Foreign body sensation is sometimes accompanied by GERD. Patients complain that they want to drink water or cough to get rid of a foreign object. The symptom is provoked by constant irritation of the receptors with acidic contents thrown into the upper parts of the digestive tract during reflux. A distinctive feature is the increase in discomfort when lying down. With dyskinesia of the esophagus, the symptom appears due to a violation of the passage of the food bolus due to a disorder in the motility of the organ.
Dental diseases
Patients with certain tongue pathologies complain of a feeling of a foreign body in the throat: black hairy tongue, papillomatous form of rhomboid glossitis. In the first case, there is a significant increase in taste buds in the posterior and middle thirds of the tongue, coloring the affected area in black and dark brown shades. With rhomboid glossitis, pale pink growths appear on the tongue.
The symptom accompanies benign and exophytic malignant tumors of the oral cavity if they are located on the root of the tongue or in the palate. In addition, the sensation of a foreign body occurs with the stylopharyngeal variant of stylohyoid syndrome.
Neurosis of the pharynx
Initially, the sensation of a coma (foreign body) in the throat was described as a typical symptom of hysteria. Currently, along with hysteria, the causes of pharyngeal neurosis include astheno-neurotic syndrome and severe stress. Pathology can also be observed in cervical osteochondrosis, intervertebral hernia, spondylolisthesis, and certain diseases of the nervous system (neoplastic tumors, stroke, multiple sclerosis).
Throat examination
Osteochondrosis
Lack of physical activity, prolonged stay in a static position, the presence of excess body weight - all these are predisposing factors in the development of a disease such as osteochondrosis. Damage to the cervical area occurs quite often even at a young age.
It would seem, what is the connection between the condition of the spine and the appearance of a feeling of a lump in the esophagus? And everything is explained by the fact that due to the growth of osteophytes on the vertebrae, compression of the nerve endings occurs. Disorders of the innervation of the thoracic region manifest themselves with characteristic symptoms. Also, this disease is accompanied by severe headaches and stiffness of the cervical spine. To clarify the diagnosis, you need to contact a neurologist.
It is important to note: the sensation of a lump in the esophagus is a sign, a consequence of an underlying disease, which may not be directly related to the organs of the digestive system. What exactly is the cause of these symptoms is determined by the doctor. That is why, in order to avoid complications, you should not self-medicate, but seek specialized medical care as soon as possible.