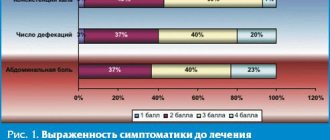
Among all diseases of the gastrointestinal tract (GIT), the incidence of chronic pancreatitis ranges from 5.1 to 9%, and in the last few decades, the incidence of pancreatitis in our country has doubled1.
Chronic pancreatitis is an insidious disease, largely due to its recurrent nature. Patients are often concerned about periods of exacerbation, accompanied by severe pain, nausea, and vomiting.
Where does chronic pancreatitis come from? What causes the disease and is it possible to fight it? Let's try to figure it out.
Symptoms of chronic pancreatitis
Symptoms of chronic pancreatitis may vary depending on the stage (remission or exacerbation), course and physical condition of the patient. The main signs of the disease are as follows:
- acute pain without clear localization. Pain can be felt in the right hypochondrium, upper or middle abdomen and spread to the back. In many patients, pain occurs immediately after eating, especially if the diet contained fatty, smoked or spicy foods;
- frequent loose stools are one of the main signs of indigestion. Digestive problems in chronic pancreatitis are caused by a lack of enzymes;
- heaviness in the abdomen, nausea, which also indicate a lack of digestive enzymes;
- increasing feeling of hunger, muscle tremors, weakness, cold sweat;
- intoxication, manifested in fever, chronic fatigue, and a feeling of general malaise.
Analgesics
Painkillers are used to relieve moderate pain. They work well:
- Analgin;
- Baralgin;
- Acetomifene.
They are usually combined with drugs with a different mechanism of action.
Baralgin is used in the acute period of the disease by injection and is a typical representative of this group.
- analgesic effect;
- antispasmodics;
- hypothermia (reduces elevated body temperature).
It easily penetrates the blood-brain barrier (BBB) and is therefore prohibited for use by pregnant and lactating women.
It is prescribed and monitored by a doctor. Self-medication for pain relief is not recommended.
Causes of chronic pancreatitis
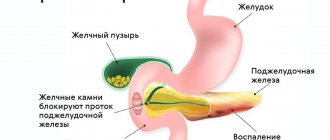
One of the most common causes of chronic pancreatitis is poor diet and unhealthy lifestyle. Constant overeating, abuse of fatty foods and alcohol cause blockage of the excretory ducts of the pancreas.
Narrowed excretory ducts provoke the accumulation and premature activation of digestive enzymes. As a result, the pancreas actually begins to digest itself, and inflammation forms1.
In addition, the following factors can lead to chronic pancreatitis3:
- ulcer of the duodenum, stomach and enteritis. Chronic inflammation of the mucous membrane of the gastrointestinal tract makes it difficult to secrete pancreatic juice, which often causes chronic pancreatitis;
- cholelithiasis. After leaving the gallbladder, the stone causes blockage of the common duct and inflammation of the pancreas develops;
- genetic predisposition;
- toxic effects of drugs.
Pancreatitis: development of the disease
The main function of the pancreas is to produce enzymes that actively process food and break down many substances. This gland produces pancreatic juice, which contains enzymes in an inactive form. They are activated in the duodenum. If their outflow is disrupted for any reason, enzymes are activated in the tissues of the gland itself: the organ begins to self-destruct. Developing inflammation causes:
- replacement of functioning cells with fat or connective tissue;
- In acute cases, massive necrosis (death) of organ cells is observed.
Clinically, acute or chronic pancreatitis is characterized by an acute onset of episodes of rapidly increasing pain accompanying the destruction of pancreatic cells. A similar clinical picture is observed with reactive pancreatitis. This occurs when the gallbladder or other organ of the digestive system narrows. Existing cholecystitis is a disease that most often causes a reactive process in the pancreas. Symptoms resemble an attack of acute pancreatitis.
The pain begins on the left side and is usually called "streaking" and is worsened by lying down and drinking alcohol.
In addition to the intensity of the pain, it is accompanied by nausea;
- uncontrollable vomiting, without relief;
- diarrhea (greasy stool with undigested food residue);
- heat.
Diagnosis of chronic pancreatitis
Identifying chronic pancreatitis can be difficult due to the nonspecific clinical picture. Nausea, abdominal pain, digestive problems - these symptoms are characteristic of many diseases, for example, stomach ulcers or chronic cholecystitis. Therefore, identifying the disease may require a whole range of studies. Diagnosis of chronic pancreatitis may include2,3:
- external examination of the patient. Chronic pancreatitis may be indicated by bluish areas of the skin on the front and side walls of the abdomen. In some patients, bright red patches of skin on the chest and back become noticeable. Palpation may reveal pain in the left hypochondrium and the upper third of the abdomen;
- a general and detailed blood test, which shows the presence of an inflammatory process, based on an increase in the concentration of leukocytes;
- laboratory blood test to identify markers of nutritional status;
- fecal elastase test;
- ultrasonography. In some cases, ultrasound examination (ultrasound) can be performed through the walls of the stomach and duodenum, which significantly increases the accuracy of the examination. This method is called endoUS and combines the possibility of endoscopic and ultrasound diagnostics of the gastrointestinal tract (GIT);
- computed tomography: used to determine complications of pancreatitis associated with thickening of the pancreas tissue.
Exacerbation of chronic pancreatitis
Chronic pancreatitis may hardly manifest itself until the period of exacerbation. Relapse of the disease is usually associated with two main reasons3:
- alcohol consumption. Even a small amount of alcohol consumed can provoke the transition of the disease into the acute phase;
- violation of the diet, overeating, a large number of fatty, fried, spicy dishes on the menu.
Other factors can also provoke exacerbation of chronic pancreatitis in adults, for example, chronic stress, physical fatigue, poisoning or the toxic effects of certain medications3.
Exacerbation of the disease is manifested by the following symptoms3:
- attack of acute or dull pain in the hypochondrium. Painful sensations spread to the subscapular region or the entire back;
- progressive diarrhea. In this case, the feces have a characteristic greasy shine. Undigested food remains are often observed in the stool;
- the occurrence of specific bitterness in the oral cavity, nausea and loss of appetite;
- whitish coating on the surface of the tongue;
- weight loss.
Exacerbation of chronic pancreatitis in adults can last for one to two weeks. You cannot fight the disease on your own during this period: the best solution is hospitalization and constant monitoring by specialists.
Action of NSAIDs
The therapeutic properties of the drugs are achieved by reducing the production of prostaglandin and blocking COX-2 (cyclooxygenase enzyme). These remedies fight the symptoms of the disease, but do not affect its causes. Therefore, additional therapy is needed that eliminates the root cause of the pathology.
NSAIDs are often used for pain relief for:
- inflammatory diseases,
- rheumatism,
- degenerative changes in organs and tissues.
They are also used for migraines and other non-rheumatic diseases and injuries.
Treatment of chronic pancreatitis
The answer to the question “how to cure chronic pancreatitis” remains open even for modern doctors. The treatment regimen is determined by the doctor for each individual case. The main thing is that therapy should be comprehensive, affecting the main cause of the disease.
Treatment of chronic pancreatitis includes2,3,4:
- immediate cessation of bad habits. Smoking and abuse of strong alcoholic beverages aggravate the inflammatory process and contribute to the subsequent development of the disease;
- strict adherence to the diet. The daily diet should contain high-calorie foods, without spicy foods, salt and pure sugar. You should eat food often, in small portions. In case of exacerbation of chronic pancreatitis, therapeutic fasting is prescribed, which will help stop pancreatic secretion and relieve pain. After 1-3 “hungry” days, the patient is transferred to a special diet;
- basic therapy. In this case, we are talking about taking the following type of drugs: antispasmodics and analgesics, antisecretory and detoxification drugs. Treatment is carried out under the supervision of a doctor with strict adherence to the instructions;
- taking enzyme preparations, the task of which is to compensate for the impaired functioning of the pancreas. The fact is that the pancreas does not recover (it is not the liver), and therefore will no longer be able to work at full capacity during chronic pancreatitis. That is why the first line of therapy is enzyme preparations, which should be taken for life. An example of an enzyme drug prescribed for chronic pancreatitis is Creon®;
- complex therapy. May include taking antispasmodics or analgesics, antisecretory and detoxification medications. Therapy is carried out under the supervision of a physician with strict adherence to the instructions;
- taking anti-inflammatory and painkillers that improve the patient’s well-being;
- herbal medicine, which can be prescribed during remission only as prescribed by a doctor.
What to do if an exacerbation of pancreatitis occurs suddenly, and the ambulance has not yet arrived? Before the doctors arrive, you need to lie down, try to relax your abdominal muscles as much as possible and apply a heating pad with cold water to the sore spot. You should not take painkillers or any other medications - this will interfere with correct diagnosis. And, of course, any food and drinks, even plain water, are strictly prohibited, because any food or liquid can cause increased pain3.
Features of therapy
If you have pancreatitis, you need to follow a diet.
During the treatment period, you must strictly adhere to the rules. Patients are strictly prohibited from self-medicating.
Also, doctors do not recommend placing hot water bottles on the stomach, inducing vomiting, etc. Such actions in acute pancreatitis can lead to aggravation of the situation.
If the patient has purulent pancreatitis or an inflammatory process in the peritoneum, then treatment is carried out using medications.
In acute pancreatitis, the patient must completely abstain from liquids and food. That is why for the first 3-5 days of therapy, patients adhere to a starvation diet. Treatment of the patient should be carried out with strict adherence to bed rest.
In order to periodically cool the upper abdomen, it is necessary to use ice compresses. Traditional medications are also taken, the action of which is aimed at relieving vascular spasms.
Despite the fact that acute pancreatitis brings excruciating pain, the administration of morphine to the patient is strictly contraindicated. This is explained by the fact that the pharmaceutical medicine increases sphincter spasm and increases the disease.
During the treatment of acute pancreatitis, it is necessary to strictly adhere to the general rules. Pharmacy medications for the treatment of the disease are prescribed only by a doctor, taking into account the individual characteristics of the patient.
The drug Creon® 25000 for chronic pancreatitis
Find out more
Decreased pancreatic function inevitably leads to a lack of digestive enzymes in the body, so-called enzyme deficiency. As a result, the quality of digestion suffers, and the body does not receive the necessary energy and nutrients for full functioning. Creon® is designed specifically to compensate for the lack of its own enzymes through their delivery from the outside and belongs to the group of enzyme preparations. The drug contains enzymes identical to those produced by the pancreas. The key feature is that the active ingredient Creon® is small particles - minimicrospheres, which are collected in a capsule. The fact is that science has been studying enzyme preparations for more than 100 years in order to increase their effectiveness. To date, scientific advances indicate that preparations with particles whose size does not exceed 2 mm4.5 can most accurately recreate the natural process of digestion. Moreover, it has been scientifically proven that the smaller the particles of the drug, the more effective it can be4,6.
Creon® is the only drug whose capsule contains hundreds of small particles - minimicrospheres7. Their size does not exceed 2 mm, which is recorded as recommended in world and Russian scientific works4,5,6.
What tablets can be used for pancreatitis
In case of pancreatitis, tablets are selected taking into account the existing symptoms, and the main purpose of taking them is to unload the pancreas and reduce its activity. Medicines from the following groups help stop the synthesis of digestive enzymes in organs:
- proton pump blockers and H2-histamine receptor inhibitors;
- enzyme preparations with pancreatin;
- myotropic antispasmodics;
- analgesics.
Rice. 2
This set of tools is enough to eliminate the inflammatory process and restore the functions of the pancreas. Drugs of other groups (enterosorbents, heartburn relievers, antibiotics, etc.) are prescribed if necessary or if there are complications.
Receptor and proton pump blockers
This group of drugs does not directly affect the gland, but partially or completely stops the release of hydrochloric acid in the stomach. As a result of a decrease in its synthesis, the pancreas receives a signal that the body does not need digestive secretions. Slowing down the functioning of the organ leads to a faster restoration of its functionality, and the risk of complications is reduced.
Rice. 3
When choosing drugs to reduce the secretion of hydrochloric acid, you can choose drugs that block H2-histamine receptors or inhibit the proton pump.
H2-histamine receptor blockers (“Roxatidine”, “Ranitidine”, “Famotidine” and Lafutidine) stop only one mechanism of hydrochloric acid production in the stomach (such drugs do not affect gastrin and acetylcholine receptors), act for a short time, have side effects and addictive.
Rice. 4
Proton pump inhibitors (“Omeprazole”, “Pantoprazole”, “Rabeprazole” and others) are more effective and safe, do not cause side effects or addiction, act for a long time and stop the formation and release of hydrochloric acid, acting on the lining cells of the stomach walls. Reviews of the effectiveness of these drugs are in most cases positive.
Enzyme preparations
Enzymes are indispensable medicines for pancreatitis, which allow you to restore the digestion process and relieve the pancreas. Medicines for pancreatitis in this group are represented by tablets with pancreatin, including herbal origin (Pancreatin, Mezim Forte, Peppaza, Wobenzym) and acid-resistant capsules with programmed release microgranules (Creon, Ermital, Mikrazim ").
Rice. 5
When choosing enzyme preparations, not only the dosage of active substances plays a role. Experts pay attention to the course of the disease, the causes of its occurrence, the presence of concomitant diseases or intolerance to individual components.
Important! Tablets containing bile, turmeric extract and simethicone are contraindicated for pancreatitis, as they not only compensate for the lack of enzymes, but also enhance their synthesis in the pancreas, provoking increased inflammation.
Gastroenterologists call the most effective and safe drugs suitable for the treatment of pancreatitis:
Rice. 6
- Capsules “Creon”;
- “Ermital” capsules;
- Micrazim capsules.
The listed drugs are used for chronic pancreatitis, as well as for errors in nutrition to prevent exacerbations. Reviews about them are in most cases positive, but the possibility of side effects while taking them cannot be ruled out.
Analgesics and antispasmodics
In case of acute inflammation of the pancreas or exacerbation of a chronic process, it is important to eliminate the pain syndrome. For this purpose, analgesics and antispasmodics are used. The former cope well with the discomfort that arises during primary inflammation. Antispasmodics are recommended for use in pain caused by pressure from cysts, pseudocysts and stones on the gland ducts.
Rice. 7
Recommended analgesics for use in pancreatitis:
- Paracetamol is an effective and safe drug that does not irritate the gastric mucosa and helps reduce inflammation.
- Analgin is a potent drug that is used alone or in combination with antispasmodics.
- Baralgin is a remedy similar in composition and action to Analgin.
Drugs with an analgesic effect are not without drawbacks. They can irritate mucous membranes, cause allergies and affect the functioning of the cardiovascular system, liver and kidneys. Therefore, they are prescribed taking into account the individual characteristics of the patient. However, reviews of these painkillers are more often positive than negative.
If acute pain occurs due to increased pressure in the pancreatic ducts, analgesics will be ineffective. To eliminate symptoms, it is better to use antispasmodics:
- Papaverine is a remedy based on the compound of the same name, which effectively relaxes the smooth muscles that make up the pancreatic ducts.
- Drotaverine is a myotropic antispasmodic that helps restore the patency of the pancreatic ducts during spasm. Has a weak anti-inflammatory effect.
- Mebeverine (Duspatalin) is a drug with a pronounced and long-lasting effect, but it acts primarily on the smooth muscles of the stomach, intestines and bile ducts. Its use is especially useful for secondary pancreatitis that occurs against the background of gallbladder pathologies.
Rice. 8
Each of the listed drugs is positively assessed by patients. In rare cases, reviews contain negative reviews, and often this is caused not by the quality of the drugs, but by their high cost.
Experts note that antispasmodics require strict dosage, as they affect smooth muscles throughout the body, including the myocardium, vascular walls, and bladder. They are not prescribed to patients with low blood pressure, certain types of arrhythmia, or intestinal atony.
Additional funds
In addition to enzyme preparations and painkillers, it is recommended to use prebiotics based on soluble dietary fiber for pancreatitis. They are necessary to restore intestinal microflora and protect the pancreas from excessive stress.
When they enter the digestive tract, fibers absorb fats and glucose, which stimulate the pancreas to intensively produce digestive secretions and insulin. Thanks to this, the gland functions within its capabilities, which allows it to recover faster. In addition, soluble fiber is a good nutrient medium for beneficial microflora, resulting in improved absorption of essential nutrients in the large intestine.
All types of cabbage, citrus fruits, apples, beans and pumpkin, zucchini and carrots, oatmeal, prunes and whole grain bread can be a source of soluble fiber. Unfortunately, most of the listed products are prohibited during an exacerbation, as they cause bloating and stool disturbances. You can replace them with rye bran or psyllium husk. A more convenient and safer option is the Smart Fiber additive. The fiber in it has the structure of a powder that dissolves without a trace in any food and drink, without changing the taste, color or consistency of the dish. It is enough to consume one spoon of the product per day to cover the daily requirement for dietary fiber and get rid of discomfort in the stomach.
What else is important to know about enzyme preparations?
The minimum starting dosage is Creon® 25,000 units, which is stated in Russian recommendations for the treatment of chronic pancreatitis and exocrine pancreatic insufficiency2,5. The number indicates the amount of the enzyme lipase, which helps digest fats. If necessary, the doctor can increase the dosage; in European practice, the required dose per single dose can reach up to 80,000 units8. By comparison, the pancreas of a healthy person produces up to 720,000 of these units during each meal9.
Therapy should be taken seriously, since high-quality “nutrition” of the body is the key to its functioning. How long can a person live without energy from food? With chronic pancreatitis, the body must be supplied with enzymes at every meal, even with a snack. Thus, in accordance with the instructions for the drug Creon®, a full dose is required for a meal (for example, 25,000 units), and half for a snack. Creon® capsules are convenient to use: you can open them and add minimicrospheres to food, thereby selecting the desired dose10. More information about the admission rules can be found here.
Antispasmodic spectrum injections
If the condition normalizes without surgical intervention, further treatment is carried out in the gastroenterological or therapeutic department. To restore pancreatic function, several groups of drugs with different mechanisms of action are used. Among them are antispasmodics, which can be injected intramuscularly into the arm or buttock:
- papaverine;
- drotaverine (No-shpa);
- atropine.
They have a myotropic effect (expand the lumen of blood vessels, improve blood circulation) and relieve spasm of smooth muscles.
Papaverine is a drug named after its main active ingredient. This is one of the strong antispasmodics. It is available in various pharmacological forms, one of which is a 2% injection solution. It is administered intramuscularly, but can also be administered intravenously as part of a complex lytic mixture. To ensure an effective analgesic effect, a drip method of administering such solutions is used. The mechanism of action is based on:
- about normalization of the outflow of bile and pancreatic juice;
- About a decrease in pressure inside a diseased organ.
- glaucoma;
- atrioventricular block (a type of heart rhythm disorder)
- arterial hypotension;
- liver pathology;
- individual intolerance.
- Pregnant women;
- Women during breastfeeding;
- children's age up to 1 year.
Due to side effects, the drug can be prescribed individually only according to special doctor’s indications:
- allergic reactions;
- rhythm disturbances;
- low blood pressure;
- heart rhythm disturbance;
- increased sweating;
- eosinophilia in the blood picture (usually with a pronounced allergic component).
When prescribing the drug, carefully study the instructions. It is used individually, taking into account all existing concomitant diseases.