02/16/2022
287 281
12 minutes
Author, editor and medical expert – Klimovich Elina Valerievna.
Editor and medical expert – Harutyunyan Mariam Harutyunovna.
Sore throat is a common symptom. According to statistics, 5% of patients of ENT doctors and therapists present this particular complaint3. It predominates in acute respiratory viral diseases (ARVI) and tonsillitis3, but its appearance can also be caused by other reasons.
Up to contents
Causes
Pain in the throat when swallowing is due to the presence of a large number of nerve endings in this area. The lymphoid ring is also located here - the same “tonsils”. These are the organs of the immune system that are the first to respond to infection. That’s why so often the throat hurts when swallowing, and then the temperature rises and other symptoms appear.
The causes of pain can be inflammatory or non-inflammatory. Most often these are bacterial and viral infections. But there may also be tumors, as well as vascular pathologies.
Anatomy of the throat
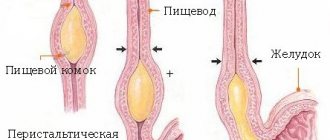
In the pharynx and larynx, as well as at the border of the oral and nasal cavities along the back wall of the pharynx, there are accumulations of lymphoid tissue - the lymphoid-pharyngeal ring. It performs a protective function and is an important organ of our immunity. The largest collections of lymphoid tissue are called tonsils and there are several of them: two palatine, two tubal, one pharyngeal (aka adenoid) and one lingual.
Below is the larynx - this is a complex organ, representing a complex of various tissue structures, consisting of several cartilages, muscles, with a developed network of blood, lymphatic vessels and nerves.
Signs of pathology
It is not always possible to recognize a sore throat right away. It may not be sharp, but resemble a tickling sensation - as if something is stuck and you want to clear your throat. Some describe it as “an itchy throat.” But all this speaks of discomfort localized in a specific area.
In addition to discomfort in the throat, symptoms of bacterial or viral intoxication may appear:
- chills;
- fever;
- increased sweating;
- runny nose;
- myalgia;
- hoarseness of voice;
- fast weight loss.
But even without them, if you experience pain in your throat, it’s worth visiting a therapist. He will prescribe an examination and the necessary treatment or refer you to a more specialized specialist.
Prevention
Throat diseases can be avoided if you follow simple rules of a healthy lifestyle. The list of useful actions includes hardening, proper balanced nutrition, walks in the fresh air, active recreation, sports, and giving up bad habits such as alcohol and smoking.
Any complex throat disease can be prevented in time and eliminated in the initial stages, following the advice and recommendations of the attending physician. Correct therapy guarantees the result in the form of absolute recovery. You should not delay treatment and make unclear diagnoses on your own; treatment of the throat, as well as other organs, should always be trusted to specialists.
Diagnostics
The cause of the sore throat is determined by the doctor. To do this, a comprehensive examination is carried out:
- examination of the oropharynx;
- taking anamnesis;
- general blood analysis;
- scraping from the tonsils followed by microscopy (if necessary).
Most often, such an examination is sufficient to make a diagnosis. If pain when swallowing persists, an ultrasound of the thyroid gland, an ECG, consultation with an endocrinologist and additional blood tests may be prescribed.
Treatment
Of course, the method of treatment and choice of medications is directly related to the identified diagnosis. That is why you should not engage in home research and self-medication, because only an otolaryngologist can make the correct diagnosis. Moreover, it will be very difficult to obtain antibiotics without a prescription, but even if it is possible to purchase such drugs without a prescription, there is a risk of causing great harm to your health instead of treatment, disrupting the body’s microflora. Do not forget about the compatibility of various drugs.
Never self-medicate children and pregnant women!
Accompanying diseases
Throat damage can occur due to diseases of various types. Pathologies accompanied by pain when swallowing:
- pharyngitis;
- ARVI;
- angina;
- measles;
- tuberculosis;
- trauma to the larynx or esophagus;
- gonorrhea of the pharynx;
- rubella;
- abscess of the retropharyngeal space;
- angina;
- candidiasis;
- mononucleosis;
- scarlet fever;
- diphtheria;
- chemical burn of the pharynx;
- acute thyroiditis;
- allergic reactions;
- radiation therapy;
- tumor of the thyroid gland or larynx;
- osteochondrosis;
- varicose veins of the esophagus.
The diagnosis is made based on objective examination data. Depending on the disease, treatment is prescribed.
When your throat hurts...
And this is how infectious and non-infectious causes of pain in the throat are distinguished:
- Infectious causes:
— Viral 70% (rhinoviruses, coronoviruses, adenovirus, influenza and parainfluenza viruses…) — Bacterial 15%. The most common cause is Group A B-hemolytic streptococcus (GABHS) - Fungal. The main causative agent is representatives of the genus Candida. The most pathogenic Candida albicans is 50% of all cases!
- Non-infectious causes:
— Allergic — Traumatic: cold drinks, ice cream, hot food, tobacco smoke from active and passive smoking, excessive consumption of spices, mustard, horseradish — Burns and injuries of the larynx
— Neuralgic conditions
— Benign and malignant neoplasms;
— Diseases of other human organs and systems
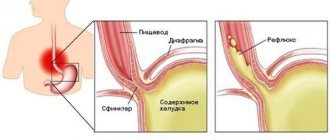
— Exposure to an irritating factor: gastroesophageal reflux, postnasal drip
Infectious causes of pain
Viral causes include primarily acute respiratory diseases, infectious mononucleosis, influenza, measles, and rubella. In addition to pain in the throat, the patient complains of the following symptoms: headaches, runny nose, nasal congestion, cough, fever, weakness, loss of appetite. Etiological diagnosis is difficult, especially in routine practice. In this situation, doctors are forced to rely on literature data. In most cases (20-30%), it is not possible to accurately identify the virus that caused the disease in a given person. Data from successful verification of the diagnosis place rhinoviruses in 1st place in the etiology of ARVI of the upper respiratory tract (30-50%). It should be noted that the influenza virus causes only 5 to 15% of cases of all acute respiratory viral infections.
Lesions of bacterial etiology are the cause of a sore throat in 50% of cases. Bacterial infections are most often localized in the tonsil area (acute tonsillitis). Their characteristic symptoms are: severe pain in the throat; weakness and decreased performance; increased body temperature; redness of the palate, white plaque on the tonsils; enlarged lymph nodes.
Pharyngomycosis in the vast majority of cases is caused by yeast-like fungi of the genus Candida (oral thrush). Sometimes the causative agents are mold fungi (aspergillus, penicillin, geotrichum). To trigger the pathological growth of fungi, which leads to an inflammatory process, it is necessary to reduce the body's defenses. Therefore, pharyngomycosis accompanies the following diseases and conditions:
- long-term antibiotic therapy;
- diabetes;
- tuberculosis;
- metabolic diseases (obesity, thyroid pathology);
- oncological diseases (during chemotherapy);
- HIV.
The disease begins in the same way as all pharyngitis - with discomfort in the throat. The fungal nature of the process can be suspected based on the characteristic itching and burning. Patients complain of constant soreness and dry mouth. Pain for pharyngomycosis is very characteristic; it intensifies with swallowing and is more intense than with a bacterial infection.
Non-infectious causes of sore throat
Pain in the throat can be a result of exposure to various allergens: food, pollen, house dust, fur and secretions of pets, etc. In addition to discomfort and pain in the throat, patients are concerned about congestion and clear discharge from the nose, sneezing, itchy eyes .
Various external factors can cause pain: mechanical injuries to the larynx, chemical or thermal burns. Hard pieces of food and bones can injure the larynx. Chemical burns can be caused by inhaling vapors of harmful substances at work or by ingesting harmful substances while eating. Thermal burns most often occur when eating hot foods or drinks.
Pain in the throat may be a manifestation of neurological disorders. Usually this condition is accompanied by a feeling of a lump in the throat, difficulty swallowing, and headaches. This feeling can manifest itself constantly, or maybe with a certain frequency.
Other causes of sore throat accompanied by sore throat and cough: drainage of discharge from the nasopharynx due to adenoiditis or sinusitis, space-occupying formations of the nasopharynx (cyst/bursa of Thornwald); irritation of the respiratory tract by dry air, smoke, including active and passive smoking. In adults, a common cause of such complaints, often with a feeling of a lump in the throat, a “foreign body,” is an exacerbation of chronic pharyngitis associated with pathology of the gastrointestinal tract: gastritis, esophagitis, gastroesophageal reflux, cholecystitis, gastric ulcer. Severe dysphagia, regurgitation and pain when swallowing can be caused by varicose veins of the esophagus. Chronic pathology of the kidneys, endocrine system, blood, previous radiation and chemotherapy can lead to the formation of a chronic inflammatory and atrophic process in the pharynx. The first manifestation of hyperglycemia (increased blood sugar) may be thirst and dry mouth, accompanied by catarrhal changes in the pharynx. Similar complaints occur with Itsenko-Cushing syndrome. In patients with hypothyroidism, swallowing is often impaired, speech becomes slurred due to swelling and dryness of the tongue and lips, and it is difficult to perform pharyngoscopy.
Hypovitaminosis can also cause discomfort and pain in the throat. Vitamin A deficiency causes dryness and erosion of the mucous membranes. Vitamin B2 deficiency produces a triad of symptoms: dermatitis, cheilitis and glossitis (bright red, smooth and shiny dry tongue), accompanied by burning and pain in the mouth when talking and eating. Vitamin C hypovitaminosis occurs with dietary deficiency of ascorbic acid, inflammatory processes in the intestines and is manifested by pain, hemorrhagic and ulcerative-necrotic manifestations in the oral cavity and in the area of the palatine tonsils, mobility and tooth loss.
Diseases of the spine (cervical osteochondrosis, tuberculous spondylitis, radiculitis) can cause pain in the throat. Neuralgia of the glossopharyngeal nerve manifests itself as intense pain in the pharynx, especially against the background of chronic stress in anxious and suspicious patients. Metabolic disorders, intoxication, and trauma contribute to its occurrence. Characterized by unilateral pain in the root of the tongue, tonsil, lasting several minutes, accompanied by dry throat and subsequent hypersalivation. Neuralgia of the superior laryngeal nerve gives similar symptoms, but also includes a painful dry cough and spasm of the vocal folds when inhaling.
Diagnosis and treatment
As we can see, there are many reasons why your throat hurts. And to determine the real cause of this condition, an examination by an otolaryngologist is necessary. If during the diagnostic process with an ENT doctor it becomes clear that the problem is not from the ENT organs, you may need to consult related specialists: a neurologist, gastroenterologist, allergist, endocrinologist. In this case, the patient is sent for CT, MRI, ultrasound of the thyroid gland, gastroscopy, etc.
Every person who has a sore throat needs a medical examination and diagnosis. The sooner you make an appointment, the more effective the treatment will be, and the risk of complications will be minimal.
How to help yourself
Drugs for the treatment of sore throat are divided into symptomatic (simply alleviating the condition) and etiological (acting on the cause). The most common methods of therapy:
- lozenges - “Grammidin”, “Faringosept”;
- sprays - “Stopangin”, “Gexoral”, “Ingalipt”;
- soluble powders - “Antigrippin”, “Influnet”, “Fervex”;
- antiseptic solutions - “Chlorophyllipt”, chlorhexidine, “Lugol”, “Miramistin”, “Furacilin”;
- Antibiotics are prescribed individually. This depends on the tolerance and sensitivity of the particular pathogen.
Another type of treatment is inhalation. During the procedure, the medicine is split into tiny drops, so it is absorbed into the blood more easily and quickly, which gives a noticeable effect after several uses.
The effectiveness of treatment directly depends on the correctness of its prescription. Therefore, it is better to entrust this to a professional rather than try to choose a therapy on your own.
Read also: Dry paroxysmal cough
Dear patients! Remember that only a qualified doctor can make an accurate diagnosis, determine the causes and nature of the disease, and prescribe effective treatment. You can make an appointment with our specialists or call a doctor at home by calling 8-(4822)-33-00-33
Be healthy and happy!
How to relieve a sore throat on your own
- Avoid smoking and drinking strong alcoholic drinks.
- Avoid hot or too cold food. Preference should be given to moderately warm, non-spicy food with a soft consistency.
- Ventilate and humidify the air in the room more often.
- Talk less so as not to overstrain your vocal cords.
- Drink plenty of fluids - warm water with honey, lemon, herbal teas.
- Dissolve lozenges and throat tablets.
- Gargle with soda solution (1 tsp per glass).
A popular folk remedy for fighting inflammation of the throat and upper respiratory tract is inhalation using boiled potatoes in their jackets or hot infusions of medicinal herbs, currant leaves, mint, lemon balm, raspberries.
Prices for services
- Consultations
- ENT manipulations
| Services | Price | |||||
| Primary appointment (examination, consultation) with an ENT doctor | 1800 rub. | |||||
| Repeated appointment (examination, consultation) with an ENT doctor | 1500 rub. | |||||
| Appointment (consultation) before washing the tonsils | 1000 rub. | |||||
| Type of manipulation | Price | |||||
| Rinsing the lacunae of the tonsils with the introduction of a medicinal substance | 850 | |||||
| Removal of wax plug 1 side | 700 | |||||
| Rinsing the nasopharynx | 600 | |||||
| Navigating Proetsu ("Cuckoo") | 1 000 | |||||
| Aspiration according to Zonderman | 900 | |||||
| Rinsing the lacunae of the tonsils with the introduction of a medicinal substance | 750 | |||||
| Blowing of the Eustachian tubes according to Politzer | 600 | |||||
| Lubrication of the mucous membrane of the ENT organs, turunda with medicinal substances, insufflation of medicinal powder 1 procedure | 500 | |||||
| Opening a nasal boil | 2 500 | |||||
| Introduction of a medicinal substance into the larynx | 650 | |||||
| Pneumomassage of the eardrum | 500 | |||||
| Stopping nosebleeds with medications | 950 | |||||
| Stopping nosebleeds - anterior tamponade | 1 900 | |||||
| Anemization of the nasal mucosa | 250 | |||||
| Toilet external auditory canal | 650 | |||||
| Removing a foreign body from the pharynx/larynx | 2 250 | |||||
| Removal of a foreign body from the ear, nose | 1 250 | |||||
| Opening a boil of the external auditory canal | 1 900 | |||||
| Puncture of one maxillary sinus | 1 900 | |||||
| Opening of one tonsil cyst | 1 400 | |||||
| Paracentesis of one eardrum | 1 750 | |||||
| Taking a smear from ENT organs | 400 | |||||
| Taking a throat swab for BL (diphtheria bacillus) | 400 | |||||
| Application of medicinal substances into the nasal cavity and ear | 500 | |||||
| Intra-ear compress according to Tsytovich | 600 | |||||
| Non-puncture rinsing of the nasal sinus, 1 side (without the cost of the YAMIK catheter) | 1 900 | |||||
| Intranasal blockade | 900 | |||||
| Catheterization of the auditory tube with anemization and anesthesia | 1 000 | |||||
| Taking histology from ENT organs 1 (one) study, without the cost of histology | 900 | |||||
| OTOSCOPE (without consultation) | 400 | |||||
| RHINOSCOPY (without consultation) | 400 | |||||
| PHARINGOSCOPY (without consultation) | 400 | |||||
| Opening a paratonsillar abscess | 4 900 | |||||
| Parameatal block | 500 | |||||
| Closed reduction of the nasal bones (without the cost of anesthesia) | 7 500 | |||||
| Instrumental sanitation of the nasal cavity | 1 000 | |||||
| Cauterization of the pharyngeal mucosa with drugs | 450 | |||||
| Audiometry | 1 400 | |||||
| Washing the abscess cavity after opening (ENT) | 950 | |||||
| Flushing the maxillary sinus through a catheter | 900 | |||||
| Parameatal block (1 procedure) | 900 | |||||
Make an appointment online
Sign up