Pain in the left hypochondrium when inhaling is a symptom, the cause of which is determined depending on the nature of the pain, intensity and time of appearance. Discomfort can be caused by spasm of smooth muscles, injuries, gastrointestinal diseases, bronchopulmonary diseases and much more. The severity of pain becomes more pronounced when coughing, sneezing and even inhaling.
The first step is to contact a therapist, who, if necessary, will refer you to a specialist. A qualified doctor first collects anamnesis - all the data about the medical history, conducts an examination and then sends you for tests. All this helps him in making an accurate diagnosis.
Any pain is a signal from the body about an existing disorder and should not be ignored under any circumstances. Early diagnosis allows you to prevent the problem from worsening and the process becoming chronic. Let's take a closer look at the causes of pain in the left hypochondrium in front.
Osteochondrosis of the thoracic spine
This disease is very common today.
People who have sedentary jobs are especially susceptible to it. With this pathology, the nerve endings extending from the spine are compressed, which causes pain under the left rib. It often radiates to the back, buttock, and even thigh; it can be encircling in nature, accompanied by numbness and tingling. The fact that the cause of pain is osteochondrosis may also be indicated by a decrease in the mobility of the thoracic region. “Shots” occur not only when inhaling, but also during movements and sudden turns of the body. In most cases, they overtake a person after being in an uncomfortable position for a long time. They often happen during sleep.
Treatment of pain on the left side of the shoulder blade
All therapeutic measures are aimed at eliminating the root cause and relieving pain. The doctor selects medications based on why the pain in the shoulder blade area occurs.
If the cause is a disease of the musculoskeletal system or its complications, then drug therapy looks like this:
- anti-inflammatory non-steroidal drugs;
- muscle relaxants;
- analgesics;
- local anesthetic agents.
Drug therapy must be supplemented with physiotherapeutic treatment, massage, and therapeutic exercises. A neurologist from the SmartMed clinic draws up a comprehensive therapy program, taking into account the individual characteristics of the patient.
If conservative therapy does not provide the desired therapeutic effect, the patient is indicated for surgery
Intercostal neuralgia
Intercostal neuralgia is another very common factor that causes pain under the ribs on the left. The latter is very similar to the heart, which can cause real panic. The reasons may be:
- osteochondrosis;
- unsuccessful rotation of the body;
- hypothermia;
- draft;
- cold;
- enlarged uterus (during pregnancy).
An attack of intercostal neuralgia is often accompanied by numbness of the upper extremities, muscle twitching, increased sweating, and pallor of the skin. The pain intensifies not only when breathing, but also when coughing, sneezing, yawning, turning the body, and can last from several hours to a couple of days. Often a person is forced to remain immobilized all this time, since every movement brings him pain.
When do you experience acute pain in the right hypochondrium when inhaling?
Sharp pain in the right hypochondrium with intensification during inspiration is characteristic of the clinical picture of an acute inflammatory process with local peritonitis. Acute cholecystitis is accompanied by severe right-sided pain with irradiation to the scapula, lower back, shoulder, and collarbone.
At the same time, patients complain of nausea, vomiting, bitter belching, a significant increase in temperature, and chills. When palpating the abdomen, severe pain is detected at the point of the gallbladder, sometimes an enlarged and tense bladder. When asked to breathe deeply, patients, on the contrary, hold their breath until it becomes shallow. In this way it is possible to reduce irritation of the peritoneum.
Gallstone disease is characterized by cutting pain as the stone moves through the ducts. Irradiation is very pronounced to the right side of the chest, lower abdomen, and back. At the height of the attack, vomiting of bile is observed. During the interictal period, the pain remains, but takes on a dull character.
The infection spreads from the gallbladder to the pancreas
In atypical localization, appendicitis reaches the surface of the liver and diaphragm. A high location of pain is characteristic of inflammation of the appendix during a long pregnancy.
The pain is localized not in the iliac region, as in the classic picture, but in the right hypochondrium, in the back, accompanied by vomiting, high fever, and intensifies with inspiration. It is almost impossible to distinguish from cholecystitis. Recognized only during surgery.
An abscess and hydatid cyst of the liver, with pronounced suppuration and growth, stretch the organ, put pressure on the capsule, and therefore cause constant pain of a pulsating nature (with abscess formation). Movement and breathing stimulate pain.
Malignant neoplasms in the liver tissue or metastases into it are accompanied at the initial stage by a feeling of heaviness, then turn into intense constant pain in the hypochondrium on the right, intensifying with breathing.
The patient may experience pain in the right hypochondrium due to irradiation from neighboring organs during an exacerbation of chronic pancreatitis or peptic ulcer. Appears:
- dagger or cutting pain with the main localization in the epigastrium, just above the navel;
- nausea and vomiting;
- diarrhea, bloody or covered with fatty film;
- tachycardia;
- dizziness;
- decrease in blood pressure.
In addition to irradiation, pain during breathing can accompany organ rupture and the initial symptoms of peritonitis. With perforation of an ulcerative perihepatic intestinal area caused by Crohn's disease, peritoneal manifestations should also be expected.
Heart diseases
Pain in the left hypochondrium may well be caused by heart diseases, such as ischemia, angina, cardiomyopathy and others. The most serious of them is myocardial infarction. Pain in this case is accompanied by both the development of the pathology and the condition preceding it.
Associated signs indicating a heart attack:
- dyspnea;
- chills;
- cold clammy sweat;
- nausea;
- vomit;
- diarrhea;
- sharp pallor of the face (even to the point of cyanosis) and puffiness;
- numbness of hands.
Pain on the left side can radiate to the shoulder blade, shoulder, or neck. It is sharp, burning (and not aching, as, for example, with colitis), accompanied by heaviness behind the sternum. If you have such symptoms, you should immediately call an ambulance, as this is a life-threatening condition.
Pain under the left rib behind
Such localization of pain may lead the doctor to think about the presence of kidney disease. To confirm the diagnosis, a general blood test and ultrasound examination are prescribed. Sometimes pain under the ribs at the back indicates the presence of lumbar or thoracic osteochondrosis. X-rays, CT scans, and blood tests may be needed to make a diagnosis.
Pain in the left intestine
Other reasons can cause such pain, namely:
- pericarditis;
- pneumothorax;
- pleurisy;
- renal colic;
- acute pancreatitis;
- myocardial infarction.
Lung cancer
With cancer of the left lung, when the tumor grows into the pleura, pain appears in the chest. They usually appear at a late stage. The pain radiates to the neck, arm and stomach. It can be sharp and stabbing. Often has a girdling character.
This symptom is accompanied by others characteristic of lung cancer:
- This is primarily a cough.
- The patient suffers from lack of appetite and rapidly loses weight.
The signs of this pathology are in many ways similar to dry pleurisy. And pain in the left side when inhaling is one of the common symptoms. Pleurisy is often the first and only manifestation of tuberculosis, occurring at its initial stage. It is diagnosed when there are foci of disease in the lungs or lymph nodes.
Tuberculous pleurisy can be purulent. Accompanied by fever, increased sweating, shortness of breath, chills. A person suddenly loses weight.
How to relieve pain under the left shoulder blade
Pain sensations below the shoulder blade on the left, especially if they are quite intense, interfere with movement and breathing freely, require qualified help, since they pose a threat to human health and life. You cannot ignore them and self-medicate. Taking analgesics, antispasmodics and other painkillers can relieve pain, but will not eliminate the cause, which must be discovered by a doctor.
Important! Emergency care will be required in case of severe pain with increasing intensity and rapid deterioration in well-being.
Stomach ulcer
With a perforated stomach ulcer, pain may also occur under the left rib in front. This symptom is preceded by signs characteristic of colitis (flatulence, bloating). Then the person is overtaken by pain, it is dagger-like and strong. Sometimes tolerable, and sometimes capable of causing loss of consciousness, it can shift slightly to the right.
Often pain occurs after eating. Accompanied by other symptoms: nausea, loss of appetite, vomiting, belching with an unpleasant aftertaste. If cutting, stabbing pain occurs and there is a history of a stomach ulcer, urgent hospitalization is necessary.
Types of pain under the shoulder blade on the left
Before proceeding with diagnosis and treatment, it is important to understand the nature, localization, intensity of pain, their connection with movement, breathing, and eating. If it hurts below the left shoulder blade after eating, then heart pathologies and diseases of the musculoskeletal system can be ruled out. The cause of pain is diseases of the gallbladder, pancreas, and stomach.
The nature of the pain syndrome can be girdling, acute, burning, increasing, aching, dull, sharp.
Aching pain in the left shoulder blade
It can be constant or periodic, indicating both pathologies of internal organs and diseases of the spine. Without treatment, it can turn into a stabbing, burning sensation. Attacks more often occur when raising an arm, physical activity, or staying in one position for a long time.
Appears with scoliosis, chronic cholecystitis, scapular-costal syndrome, intervertebral disc herniation, initial stages of cervical osteochondrosis, bruises and other mild injuries, intercostal neuralgia.
Acute pain under the left shoulder blade
This is a severe pain syndrome in the back below the shoulder blade, which limits movement and makes breathing difficult. Characteristic for myocardial infarction, bursitis of the shoulder joint, exacerbation of osteochondrosis, spondylosis, hernia, subphrenic abscess, pleurisy, acute cholecystitis, intercostal neuralgia.
In case of myocardial infarction, pain under the scapula from behind is not relieved by analgesics, it decreases after taking nitroglycerin
Sharp pain in the area of the left shoulder blade
It may occur suddenly or be the result of prolonged aching pain. Shooting, sharp pain is a sign of osteochondrosis, hernia, trauma, intercostal neuralgia, tuberculosis of the scapula, aortic aneurysm, perforated gastric ulcer, radiculitis.
Stitching pain behind the left shoulder blade
It manifests itself as lumbago, which is typical for pinched nerve endings in diseases of the musculoskeletal system. If it is accompanied by compression of the chest and lack of air, then myocardial infarction or lung abscess cannot be ruled out.
With a perforated stomach ulcer, pain occurs, as if stabbed with a knife.
Nagging pain in the left side of the back under the shoulder blade
Inherent in most pathologies of the musculoskeletal system, as well as bronchopulmonary diseases.
Constant pain on the left side under the shoulder blade
Such pain does not leave the patient even in a lying position. It interferes with sleeping, breathing, and walking. More often, pain intensifies with physical activity, coughing, and sneezing.
Constant nagging or aching pain occurs with injuries to the spine or scapula, scapular-costal syndrome, bronchopulmonary diseases, pyelonephritis, and oncology. Girdle pain with disorders of the digestive system is characteristic of patients with acute pancreatitis.
Burning pain on the left side of the shoulder blade
It is simply unbearable and occurs with intercostal neuralgia, myocardial infarction, angina pectoris, muscle strain.
Important! If a burning sensation that spreads to the sternum is accompanied by shortness of breath, you should immediately call an ambulance. This is a sign of a heart attack.
Gastritis
When there is periodic pain in the upper left side, gastritis can be suspected. Discomfort is also felt in the stomach. The pain is not acute - aching, radiating under the shoulder blade. It usually occurs after eating and then subsides. It often does not bring much discomfort to a person, so many do not attach importance to it for a long time. Meanwhile, the disease progresses.
Painful sensations with gastritis are accompanied by periodic nausea, heartburn, unpleasant belching, vomiting, problems with stool (constipation or diarrhea), weakness, and pale skin. When moving, turning the body, as well as taking a deep breath, the pain in the stomach area and above may intensify. Many manifestations are similar to signs of colitis, so gastritis is differentiated from this disease first of all.
Osteochondrosis
Currently, this is the most common spinal disease. During its development, degenerative-dystrophic changes in bone and cartilage tissue occur. According to statistics, about 90% of the world's population suffers from osteochondrosis.
The main reasons for the development of the disease:
- improper formation of the spine during intrauterine development;
- hereditary predisposition;
- the natural aging process of the body;
- disturbance of phosphorus and calcium metabolism;
- unbalanced diet;
- inactive lifestyle or, on the contrary, high-intensity physical activity;
- vibrations that are long-lasting or regular (for example, when driving);
- excess body weight;
- smoking;
- various types of injuries;
- weakness of muscle tissue in the back;
- scoliosis;
- flat feet;
- infectious diseases;
- constantly being in a state of stress;
- living in unfavorable environmental conditions;
- wearing uncomfortable shoes, including high-heeled models;
- pregnancy.
If, when you inhale, there is a stabbing sensation in the left side under the ribs, this is considered a symptom of thoracic osteochondrosis. In addition, a person may experience a feeling of numbness in the area of the heart and stomach. Often the pain radiates to the left shoulder blade or shoulder. The patient also experiences rapid onset of fatigue even with minimal mental and physical exertion.
In most cases, the treatment regimen for osteochondrosis includes the following points: medication, physical therapy, physiotherapy, massage, traction, kinesiotaping, diet.
Pancreatic diseases
The pancreas is located on the left side, and with pathologies of this organ, pain in the hypochondrium often occurs. This is one of the most typical symptoms of pancreatitis. The pain is girdling in nature. It is unsharp, aching, and often quite strong. The intensity increases as you inhale. A person has to “fold” in half to alleviate the condition.
Pain usually occurs after a feast. Especially abundant and with the use of strong drinks. Inflammation of the pancreas is accompanied by nausea, vomiting with bile, and heartburn. The urine becomes dark, and the stool becomes abnormally light in color. During acute attacks, the temperature may rise significantly.
What changes occur in the hypochondrium during the act of breathing?
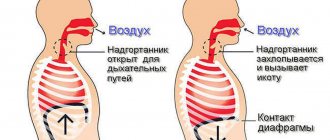
The diaphragm, which serves as the upper border of the hypochondrium, is an active participant in the act of breathing. It, together with the chest, provides respiratory movements. The goal is to create negative pressure in the pleural cavity so that the lung tissue stretches as much as possible and air enters it during inspiration.
The anatomical structures of the “sigh”, in addition to the diaphragm, include the external intercostal muscles. When contracting, the ribs move upward, the chest increases in volume, especially in the lower sections. This is facilitated by additional contraction of the diaphragm. As you inhale, it flattens and descends towards the abdominal cavity.
At rest and during exhalation, the dome moves towards the chest. In people of different build types, it is possible to breathe predominantly through thoracic breathing (more typical for women, depending on the work of the intercostal muscles) or abdominal breathing, when the main participant is the diaphragm.
As it moves, it simultaneously pulls the abdominal organs with it. The liver is “attached” to the inside of the diaphragm by a powerful falciform ligament. Dense connective tissue fibers attach the gallbladder to the lower surface of the right lobe of the liver. Sometimes the cecum with a vermiform appendix and loops of the small intestine are located here.
During exhalation, the internal intercostal muscles and the abdominal wall are actively engaged. They apply pressure from below on the organs located in the upper floor of the peritoneum and the diaphragm in order to reduce the volume of the chest. By contracting simultaneously with the abdominal muscles, the diaphragm increases pressure in the abdominal cavity.
The respiratory center of the medulla oblongata regulates the sequence of these movements, transmitting nerve signals through the spinal canals.
The greater the resistance of the lung tissue (loss of elasticity during sclerosis, inflammation), the more the muscles tense. Their work increases significantly with an increase in breathing frequency and physical activity.
With forced breathing, the muscles of the neck, back and chest are involved in the process
Pathologies of the spleen
Another organ located on the left is the spleen. It is closest to the surface of the body, so any abnormal processes occurring in it immediately make themselves felt. Problems with the spleen often occur after or during infectious diseases, since this organ is responsible for filtering blood from dead red blood cells. It greatly increases in size, fighting the virus, which explains the discomfort.
Sometimes the spleen is damaged by the ribs as a result of injury. It breaks. In such cases, pain appears not only when sighing or moving, but also on its own. It can be very strong, difficult to bear, and it radiates to the back.
Pathologies of the spleen are often accompanied by increased body temperature, inflammation of regional lymph nodes, headaches, and enlarged liver. When an organ ruptures, the skin in the navel area turns blue. If such symptoms are present, you should immediately seek medical help.
Which doctor should I consult for pain on the left under the scapula?
At the first painful sensation in the area of the shoulder blade, you should consult a specialist and undergo diagnostics. Since the nature of back pain is often neurological, you should make an appointment with a neurologist.
The doctor will conduct a visual examination, study the patient’s complaints, draw up a clinical picture: the nature and conditions of the pain syndrome (in a lying position, during movement), its intensity, accompanying symptoms.
With glenohumeral arthritis, pain worsens at night, when lying down
To understand exactly why your back hurts, your doctor will prescribe an additional examination:
- laboratory - clinical analysis of blood and urine, which will show the inflammatory process;
- instrumental, necessarily including MRI, since this diagnostic method provides the most accurate information about the condition of the spine, muscle tissue, nerve endings and blood vessels.
You can undergo magnetic resonance imaging on the new Siemens Symphony 1.5 Tesla device manufactured in 2022 at the SmartMed clinic. Immediately after the examination, the doctor will interpret the results obtained, make a final diagnosis and prescribe effective treatment.
If instrumental diagnostics reveals a pathology that is not within the competence of a neurologist, the doctor will refer the patient to a therapist, pulmonologist, cardiologist, gastroenterologist, traumatologist or other specialists.
What to do if such pain occurs
When a person experiences pain in the left hypochondrium when inhaling, it is recommended not to waste time and contact a medical facility to determine its correct cause. The following doctors diagnose this condition:
- endocrinologist;
- cardiologist;
- gastroenterologist;
- gynecologist;
- surgeon.
Self-medication is strictly prohibited, because it will worsen the general condition and provoke the emergence of various complications. You need to know when to go to a medical facility. There are situations when pain cannot be ignored. An ambulance should be called in the following cases:
- aching pain that lasts for an hour;
- dull pain accompanied by coughing and vomiting (often with blood);
- stabbing pain that does not go away for more than half an hour and gets worse;
- sudden sharp pain.
So, we have looked at the most common situations in which pain occurs in the left hypochondrium when taking a deep breath. It can also occur with movement, coughing, sneezing, and even at rest. In most cases, the cause of pain is serious dysfunction of vital organs: heart, stomach, lungs, pancreas, spleen.
And sometimes we are talking about critical conditions when a person needs help urgently. Therefore, if there is pain in the left chest, you cannot endure it and wait for it to go away on its own. You need to contact a doctor as quickly as possible, establish the cause and eliminate it before unwanted complications and consequences appear.
Pathological causes
There is no medicine that would treat pain in the left side. The fight against an unpleasant symptom is, first of all, a search for the root causes. Let's look at diseases that can cause pain on the left side.
Acute appendicitis
The appendix is a vermiform appendix that is an organ of the immune system. The process is not always located on the right side, as is observed in most people. The inflammatory process can be triggered by blockage of the appendix with feces, food fragments, an infectious process, an allergic reaction, bad habits, and stress. Poor nutrition and strict diets can also cause appendicitis.
Almost everyone knows that when the appendix is inflamed, it hurts in the lower right side. But in fact, at the very beginning the pain is localized in the upper abdominal cavity and only then moves to the right side. In addition to pain in the hypochondrium, bloating and colic appear.
After defecation, the pain subsides, and then an attack of acute pain appears again. Deep breathing and physical activity lead to increased discomfort. Lying on the right side reduces discomfort. The pain typically occurs in the evening and at night.
With appendicitis, there is a sharp pain that intensifies with inhalation and physical activity.
Acute appendicitis is a surgical pathology that requires emergency medical care. First aid for appendicitis is extremely important; if it is provided incorrectly, it can blur the clinical picture and cause difficulty in making a diagnosis.
Gastritis
Gastritis can be acute or chronic. Inflammation of the gastric mucosa occurs for a number of reasons: stress, bacterial infection, dietary errors, neuroses, and more. Exacerbation of the disease causes pain in the epigastric region and left hypochondrium. It has an aching or sharp burning character.
Sometimes patients feel discomfort in the back of the body, radiating under the scapula. The pain is aggravated by diarrhea, nausea, vomiting, and belching. The disease disrupts the general condition, causing dizziness, weakness, and irritability.
Stomach ulcer
This is a chronic disease that causes trophic disorders. The process is characterized by frequent alternation of periods of remission and relapse. Exacerbation most often occurs in autumn and spring. The emotional state plays a major role in the occurrence of peptic ulcers. Frequent stress causes muscle and blood vessel spasms.
Peptic ulcer disease causes nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, belching, and general malaise. Pain in the left hypochondrium occurs against the background of symptoms of general intoxication of the body. The causes of ulcers are similar to the provoking factors of gastritis. Helicobacter pylori infection plays the main role in the occurrence of ulcers. Pain also occurs in the epigastrium, can radiate to the back and intensifies with inspiration.
Pancreatitis
Pancreatitis can be caused by overeating, poisoning, infections, injuries, gallbladder and stomach diseases. The inflammatory process leads to the fact that the organ ceases to function normally and begins to absorb its own cells.
The acute process causes unbearable pain on the left side under the ribs. The discomfort can be diffuse, occurring over the entire surface of the abdominal cavity and radiating to the back. The person takes a forced position, in which the pain subsides a little - sitting on a chair in a bent position.
An attack may begin after eating and be accompanied by dyspeptic disorders.
The condition is aggravated by the appearance of nausea, hiccups, vomiting, bloating, fever, and weakness. During an attack of pancreatitis, it is forbidden to eat at all. Cold is applied to the upper abdomen. The patient must remain completely at rest.
Splenic rupture
The spleen is the largest organ of the lymphatic system. The organ is located on the left side under the ribs, so if the organ is damaged, painful sensations arise in this area. Essentially, the spleen is a repository of red blood cells, it purifies the blood and is involved in immune processes. The organ is also responsible for neutralizing pathogenic microflora in the blood and accumulating platelet reserves.
Organ rupture causes mechanical damage to the abdominal cavity. The spleen begins to bleed, causing blood to enter the abdominal cavity. Severe shooting pain in the left side under the ribs intensifies not only with physical activity and coughing, but even with inhalation. Over time, discomfort from the left side spreads to the entire abdomen.
Stiffness of breathing is also observed. As the pathological process progresses, the site of the spleen projection becomes bluish, chills, high fever, nausea, vomiting, and arterial hypotension appear.
Rupture of the spleen can also be provoked by acute viral and bacterial infections, excessive motor activity during inflammatory processes in the organ, and a sharp increase in blood volume during pregnancy.
Splenic rupture is a common cause of pain in the left hypochondrium when inhaling.
Diaphragmatic hernia
The diaphragm is the main breathing muscle. Conventionally, the diaphragm separates the abdominal cavity from the thoracic region. The development of a hernia causes an increase in the lumen of the esophagus and movement of the lower lobe of the stomach upward.
The causes of diaphragmatic hernia can be very diverse: heavy lifting, pregnancy, frequent constipation, obesity, diseases of the digestive tract and bronchopulmonary apparatus. The danger of the pathology is due to the fact that the organ that has penetrated into the chest cavity interferes with the normal functioning of the heart and lungs, and even the gastrointestinal tract organs themselves.
This leads to the appearance of aching pain in the left hypochondrium of a constant nature. In addition to pain, there is excessive regurgitation after eating. This is due to the unauthorized reflux of food from the esophagus into the oral cavity. The patient simply cannot take a full breath.
In addition to pain, patients are worried about heartburn, belching of air, bloating, difficulty swallowing, burning behind the sternum, difficulty breathing, persistent cough, tachycardia after eating.
Medications do not eliminate the problem, they only eliminate clinical symptoms and prevent complications. With the help of an operation, the surgeon sets the organ in its place.
Diaphragmatic hernia leads to disruption of the gastrointestinal tract
Acute pyelonephritis
With pyelonephritis, the pyelocaliceal system of the kidneys is affected. The following reasons can cause inflammation: bacterial infection, chronic foci of infection, neoplasms, stones, hypothermia, overwork, etc.
Inflammation of the left kidney provokes pain in the left hypochondrium and between the ribs with irradiation into the abdominal cavity. The urge to urinate increases, but there is no urine output. Pyelonephritis disrupts the general condition and causes hyperthermia. The clinical picture of acute pyelonephritis is characterized by fever with chills and increased sweating.
Renal colic increases with inhalation and subsides with exhalation. Coughing also worsens colic, and the patient may even experience painful shock. The pain may even cause a person to lose consciousness. Clinical symptoms of an acute process develop at lightning speed. Temperatures rise to critical levels.
Cardiac disorders
The diaphragm is closely connected to the heart, so inhaling can cause severe pain if you have heart disease. Painful sensations in the left hypochondrium can provoke diseases of the muscular lining of the heart - the myocardium.
Cardiomyopathy is fraught with the occurrence of a heart attack, which is characterized by the following symptoms:
- inability to inhale;
- acute shooting pain in the area of the heart and shoulder blades;
- discomfort radiates between the ribs and down to the abdominal cavity;
- in an upright position, the pain in the left side of the abdomen intensifies.
With coronary heart disease, adequate nutrition of the organ is disrupted. Periodic shooting pain occurs in the side and left side of the chest, intensifying with inhalation.
Heart diseases can provoke pain in the left hypochondrium
Respiratory system diseases
The main symptom of the bronchopulmonary system is difficulty breathing. Still, some pathologies can cause pain on the left side when inhaling. One of these diseases is pleurisy. Dry left-sided process causes a suffocating cough without sputum production, which causes an attack of acute pain. Along with this, temperature indicators increase.
Pneumonia also causes left-sided pain. The infectious process affects both the lungs themselves and their membranes. The pain is aggravated by hyperthermia, dry painful cough, shortness of breath, hyperhidrosis, rapid breathing, and inability to take a deep breath.
Musculoskeletal disorders
Nagging pain in the left hypochondrium, which intensifies with inspiration, is caused by bruises and injuries to the sternum with damage to soft tissues. This is due to damage to nerve endings. Fractured ribs also cause pain on the left side when inhaling sharply. Due to improperly fused bones, nerve endings are pinched. As a result, the pain becomes permanent.
Intercostal neuralgia also causes acute shooting pain. Inhalation and twisting of the body increase the intensity of pain. Intercostal neuralgia is compression and irritation of the intercostal nerves.
As a rule, the disease is preceded by an acute muscle spasm due to careless sudden movements, physical overexertion, and prolonged exposure to a draft.
Intercostal neuralgia is characterized by severe burning pain in the chest
The pain can radiate to the heart, shoulder blade, neck, lower back, arm. The attack is accompanied by redness, sweating and even muscle twitching. Therapeutic measures are aimed at relieving pain, inflammation and muscle spasms.
Thoracic osteochondrosis is one of the most common causes of pain when inhaling. Pressure from the nerve endings causes discomfort on the left side. This part of the spine contains a large number of nerve fibers, which can make it seem like there are problems with the heart, stomach or gall bladder.
With thoracic osteochondrosis, patients complain of numbness in the legs, abdomen and chest, as well as reflex muscle tension. In severe cases, disruption of the pelvic floor organs occurs. Treatment for thoracic osteochondrosis is aimed at stopping the destruction of the vertebral discs, restoring their structure, as well as eliminating disturbances in the functioning of the nervous system.
Pathology of the chest organs
The cause of pain in the right side, hypochondrium with a sharp increase in inspiration may be diseases of the chest. These include pathology: respiratory organs, heart and blood vessels, bone skeleton and muscles.
Pneumonia (pneumonia) is a common independent disease or complication of bronchitis and sepsis. Caused by pathogenic bacteria and viruses if the patient’s immunity decreases. Pain during breathing, spreading into the abdominal cavity, is observed with right-sided pleuropneumonia (lobar).
Symptoms include:
- sudden onset;
- heat;
- cough with purulent sputum, possibly with blood;
- severe malaise;
- dyspnea;
- pain in the side and hypochondrium when breathing;
- blueness of lips.
Pleurisy - accumulation of inflamed fluid in the right pleural cavity, is a complication of pneumonia, a sign of pulmonary tuberculosis. Irritation of the pleural layers causes severe pain from behind in the area of the lower ribs and in the hypochondrium with irradiation into the abdomen, the inability to deep breathe, shortness of breath, lag of the right side of the chest in the act of breathing.
The x-ray shows fluid in the pleural cavity on the right; in order to accurately find out the cause of pleurisy, it is necessary to take a repeat image after its removal
The patients have a general serious condition, severe intoxication, chills, and high temperature surges. Pleurisy can be caused by a lung abscess, a cancerous tumor, or suppurating bronchiectasis.
An extremely dangerous condition is caused by thromboembolism of the pulmonary artery trunk. If a thrombus enters a lower-order artery, then the changes are limited to the picture of pneumonia with necrosis of part of the tissue (infarction). When a branch of large diameter is blocked, the patient develops:
- sudden suffocation;
- sharp pain in the chest and abdomen;
- blue discoloration of the upper half of the body;
- cough with copious sputum and hemoptysis;
- weakness and loss of consciousness.
The disease is a complication of attacks of atrial fibrillation, thrombophlebitis of the veins of the legs and pelvis, myocardial infarction, and chemotherapy drugs.
The abdominal form of myocardial infarction is often associated with the localization of ischemia in the area of the posterior wall of the left ventricle. Compressive, burning or pressing pain occurs suddenly, is localized in the epigastrium, radiates to the stomach, back, shoulder blade, and makes breathing difficult.
The ECG shows signs of ischemia, blockades, and arrhythmias. The disease is so well known to surgeons that not a single experienced doctor will begin surgery for cholecystitis until an ECG study has been performed.
Congestive heart failure is a complication of severe heart disease affecting the myocardium. Violation of the contractility of the ventricles leads to blood retention in the extremities, abdominal cavity, and lungs. The liver is one of the first to suffer.
Overflow of the portal vein causes the release of the liquid part of the blood into the parenchyma, swelling and stretching of the capsule. The diaphragm has to work under increased load, which causes spastic contractions. Accordingly, the patient feels heaviness in the right hypochondrium and acute colic with pain when breathing.
Right-sided pneumothorax - characterized by rupture of the lung tissue, release of air into the pleural cavity with compression of the right lung. The patient experiences a sudden state of shock; due to sharp pain, he cannot breathe, and his blood pressure drops. The cause is chest trauma, fibrous-cavernous pulmonary tuberculosis, and abscess pneumonia.
The picture of multiple bilateral rib fractures is clinically accompanied by sharp pain during breathing and movement
Diseases of the musculoskeletal skeleton of the chest can cause sharp pain along the lower ribs, especially when breathing and moving. These include:
- bruises and fractures of the right ribs;
- intercostal neuralgia;
- muscle myositis;
- shingles;
- osteochondrosis of the lumbar and thoracic regions;
- strangulation of a herniated disc.
When examining the patient, the doctor detects painful points along the muscles, nerve endings, a sharp increase in pain when compressing the chest and when breathing, neurological signs (impaired sensitivity, changes in tone in the limbs).
Where does pain in the hypochondrium come from?
It is not difficult to understand where pain in the hypochondrium comes from when inhaling if you understand all the anatomical features of a person. It can be caused by any reason, not always related to breathing problems. So, according to this, there are several types of pain based on location:
- pain associated with the digestive organs;
- gynecological pain;
- pain arising from problems with the chest organs;
- pain syndromes associated with other anatomical formations.
Pain can vary
On a note! Even a completely healthy person who does not pay due attention to physical activity can feel pain in the liver area. He may experience pain after a short run. This pain syndrome can be triggered by a spasm of the diaphragm due to a disruption in the respiratory rhythm or an increase in the level of adrenaline in the blood, which causes an increase in the amount of blood in the liver. In this case we are not talking about pathology.