Pain in the throat can occur at any time. They are usually a consequence of colds in the nasopharynx, but can also be independent. And since there are many nerve endings in the throat, pain can occur even with the most minor irritations. This symptom is often an indication of the onset of the inflammatory process. If discomfort occurs, you should immediately consult a therapist to identify the causes and begin treatment of the disease at an early stage.
Clinical picture of pain
Additional manifestations of pain when swallowing foods can indicate the cause of the discomfort. However, signs appear already in the later stages. Therefore, you need to pay attention to the main additional symptoms accompanying pain:
- attacks of nausea;
- vomit;
- regurgitation of undigested food;
- heartburn;
- general malaise.
If there is a foreign body in the esophagus, a person becomes weak. The skin becomes pale due to internal trauma. Other signs of the disease include decreased appetite, weight loss and frequent bloating.
If a patient has a hernia, pain occurs when swallowing saliva. An unpleasant sensation spreads to the ear. To alleviate the condition, the body independently makes a muscle spasm, which causes belching or vomiting.
How is diagnosis carried out?
To determine the exact cause of pain when swallowing, you need to undergo a diagnosis from a gastroenterologist. To begin with, the doctor collects anamnesis, interviews the patient and performs palpation (physiological examination).
To check the wall of the esophagus and stomach, laboratory research methods are used:
- radiography;
- fibrogastroduodenoscopy;
- determination of gastric juice concentration;
- manometry;
- Ultrasound of the chest and stomach.
Patient examination methods are aimed at assessing motor function. If erosions, tumors or ulcers are found during diagnosis, a biopsy is prescribed. The resulting biopsy specimen (biomaterial) is sent for histological examination. This will help determine the nature of the tumors - malignant or benign.
Esophageal injuries
If a patient comes to the doctor asking why there is pain in the middle of the chest when swallowing, then the doctor must determine the cause. This is often associated with trauma to the esophagus, which may be:
- received due to various types of damage: gunshots, stab wounds, incised wounds, etc.;
- associated with internal pathological processes: neoplasms, narrowing, expansion in different areas (neck, thoracic region, etc.);
- associated with various pathologies of body systems, for example, damage to large vessels;
- received due to damage during surgical treatment, for example, during intubation, neck injuries, etc.
The type and duration of treatment depends on the type of injury and the severity of the damage.
Possible causes of pain when swallowing
Pain in the esophagus when swallowing food may not be directly related to the swallowing reflex. Only a gastroenterologist can make a final diagnosis and prescribe treatment, so you should not try to use the information below for self-diagnosis. The causes of pain in the esophagus when swallowing can be associated with both gastrointestinal diseases and mechanical damage.
There are 5 most common triggers:
- Infections.
Bacterial and viral infections that affect the mouth, throat, or entire esophagus can cause pain when swallowing. For example, acute or chronic stomatitis, tonsillopharyngitis make the process of contracting the muscles of the pharynx and upper esophagus very painful.
- Presence of a foreign body.
If pain in the esophagus occurs during the passage of food, and not during swallowing, then the cause is more likely to be a stuck foreign body. Foreign objects or particles of solid food that do not reach the stomach can partially or completely block the passage of food through the esophagus.
The presence of a foreign body may be indicated by an additional symptom such as difficulty breathing. Sharp objects (such as fish bones) can scratch the soft walls of the esophagus, which can also make the passage of food painful.
- Esophageal dysphagia symptoms
- Inflammatory processes.
Inflammation of the epiglottis ( epiglottitis ) and inflammation of the esophageal tube ( esophagitis ) are fairly common causes of pain in the esophagus when swallowing food. Additionally, the patient may notice dysphagia (impaired swallowing) and expectoration of pus. How to eliminate pain in the esophagus when swallowing, the causes of which are already clear, we will consider further.
- Gastroesophageal reflux disease.
But the most common reason why the esophagus hurts when eating is reflux disease. Unpleasant sensations arise due to regular regurgitation of gastric contents, including acid into the distal part of the esophageal tube. In the early stages of the disease, unpleasant symptoms can only be felt in the morning: pain in the esophagus appears even when swallowing saliva.
- Tumors , cancers .
Fortunately, malignant diseases are not a common cause of deviation. However, if you feel like something is pressing in the esophagus when swallowing (perhaps even without acute pain), then you need to contact an oncologist.
It is likely that a benign or malignant tumor on the wall of the esophageal tube is interfering with the normal passage of food. Sudden weight loss may indicate cancer. Smokers, as well as people who have suffered from other types of cancer, are at risk.
Treatment
Self-treatment in the event of pain in the esophagus is unacceptable, since very serious complications can develop, including narrowing of the organ and perforation. In most cases, surgical intervention is required (for neoplasms, detection of a foreign body, hernia).
If the cause of pain is a burn to the mucous membrane, then gastric lavage is necessary, and in severe cases, bougienage (insertion of a special instrument to dilate the esophagus). For severe pain, anesthetic drugs will help: Novocaine, Anestezin, Lidocaine. Heartburn will go away after taking medications that protect the mucous membrane from irritation (Almagel, Simethicone).
Before consulting a doctor, you can resort to symptomatic treatment
Relieves spasms No-Shpa, Nitroglycerin. When taking antacids, proton pump inhibitors, H2 blockers, the production of hydrochloric acid decreases. If peristalsis and spasms are reduced, prokinetics, antispasmodics or calcium channel blockers are prescribed.
Tissue regeneration will happen faster if you follow a diet that excludes any rough, spicy, sour foods, and also give up alcohol and smoking. It is necessary to eat in small portions and preferably pureed food, steamed or boiled. At the first opportunity, you should visit a doctor to find out the cause of pain in the esophagus and receive adequate medical care.
Causes
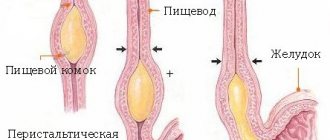
The human esophagus consists of mucous, submucosal, muscular and adventitial membranes. Injury or dysfunction of one of these structures can cause severe pain, nausea and other unpleasant symptoms. Gastroenterologists identify 7 main factors that can lead to pain.
Reflux esophagitis
Pain may occur due to the patient having reflux esophagitis. This is an inflammatory process that is caused by the action of gastric juice on the mucous membrane of the esophageal tube. This problem arises in patients suffering from gastroesophageal reflux and functional disorders of the digestive system. In this case, the esophagus can hurt even at rest.
Important: Patients may also experience additional symptoms, which should definitely be taken into account. A person may suffer from heartburn, dysphagia and other signs of inflammation.
Peptic esophagitis
This disease causes pain even when swallowing liquids, soft foods and saliva. The nature of the pain syndrome and its intensification can be affected by the food taken and the position of the patient’s body. The pain is very persistent and is localized in the retrosternal region or in the area of the xiphoid process. Pain can radiate to other parts of the body:
- back;
- neck;
- upper part of the esophageal tube;
- rib cage;
- interscapular region;
- collarbone;
- jaw and more.
Important: The sensations are often confused with coronary pain. The difference is that pain in the esophagus with peptic esophagitis does not depend on physical activity and tension. Checking for heart pain is very simple. If after using nitroglycerin the pain in the esophagus does not subside, then the cause is another disorder.
Foreign bodies in the esophagus
In some cases, cartilage and bones of poultry and fish get stuck inside the esophagus. Also, quite often, surgeons have to remove coins, needles, nails, pins, buttons, paper clips and other small objects that have gotten inside from the esophagus.
- Pain when swallowing deeply, on the side of the neck, whoever had this, please come in!!!
If there is a foreign body inside, the patient experiences increased salivation, and pain in the chest area intensifies when swallowing saliva or liquid. The patient may feel a lump that creates discomfort in a certain part of the esophagus. Over time, symptoms such as fever, dysphagia, deterioration of the patient’s health and condition, and even purulent mediastinitis may occur.
Important: Over time, a foreign body can lead to complications, regardless of how long ago the object entered the esophagus and how long it remains motionless in it.
Burns
Burns of the esophagus occur in two cases. In the first, the cause is the accidental ingestion of caustic chemicals, alkalis and acids into the esophagus. In the second case, the reason is that the patient tried to commit suicide and committed suicide using caustic substances.
With burns of the esophagus, the patient experiences pain not only when swallowing, but also immediately after toxic substances enter the body. The pain is localized not only in the esophagus, but also in the larynx, oral cavity and stomach. The most dangerous thing is what complications a burn of the esophagus has.
Hernia
If the hernia is extensive, the pain may radiate to the spine. A clear sign of pain in the esophagus due to hernias is a weakening of the symptom in the upright position of the patient's torso and the absence of a reaction when taking nitroglycerin.
Diseases of the esophagus
Most often, pain in the esophagus is caused by tumor and neuromuscular diseases of the esophageal tube. In addition to the sensation of pain during swallowing, a person is tormented by sudden pain in the form of a “crisis”. The pain is very intense, and is characterized by the fact that it often radiates up the esophagus, into the back and neck. Such a crisis can last from one minute to several hours in a row.
With achalasia cardia, a crisis usually occurs once every 1-3 months. Pain that occurs when swallowing food or saliva occurs in almost every patient with this disease. Pain in the esophagus when swallowing usually has the following characteristics: acute, sharp pain of a cutting nature in the area of the xiphoid process. Characteristic features of such pain are also the feeling that some object is blocking the passage of food and the esophagus is full.
If a person has a tumor of the esophagus, discomfort when swallowing is rare. However, malignant neoplasms in some cases still lead to pain.
Damage to the esophagus
Damage to the esophagus can be internal or external. Internal, closed injuries are factors that affect the mucous membrane of the esophageal tube. External or open injuries occur from penetrating wounds to the chest or throat.
In addition to injury to the esophagus when swallowing foreign bodies, damage often manifests itself in bedsores of the walls. Also, damage that causes pain when swallowing in the esophagus often occurs, such as perforation of the walls of the esophageal tube. It occurs due to the following diseases:
- Why do my knees hurt after running? What to do if pain occurs when running - some effective tips
- tumors;
- chemical burns;
- peptic ulcer.
Important: Pain occurs spontaneously and for a variety of reasons when swallowing in the esophagus. The main thing is to determine what other concomitant symptoms the patient has. It is this factor that can often indicate the cause of the pain syndrome.
Main reasons
Pain behind the sternum when swallowing is associated with damage to the mucous membrane of the organ or its stretching. For each of the esophageal pathologies, additional symptoms can be identified.
Reflux esophagitis
The disease occurs when the gastroesophageal sphincter is insufficient. Under such conditions, gastric juice enters the esophagus, which is not adapted to an acidic environment. Erosion and ulcers form in it. The process is accompanied by pain, burning, and sour belching after eating. In young children, the disease manifests itself with regurgitation and vomiting.
Foreign body
In adults, solid food particles are found in the lumen of the organ - bones, cartilage, nut shells. In childhood, small objects can get there - pins, buttons, coins. Foreign bodies in the esophagus are manifested by increased salivation, a feeling of a lump in the throat, and difficulty swallowing.
Injuries
Damage to the organ wall occurs due to injuries (puncture, cut, blunt). They are open and closed. The cause may be spontaneous rupture, ingestion of sharp objects, or perforation of the wall due to an ulcer. The pain syndrome has characteristic features: it radiates to the back, upper abdomen, and intensifies during esophagoscopy.
Burns
Burns of the mucous membrane are associated with the ingestion of chemicals or too hot food, which destroy the mucous membrane. Subsequently, a scar forms on it, narrowing the lumen of the organ. Symptoms appear immediately after taking the substance: salivation, vomiting blood, decreased blood pressure.
Hernia
A diaphragmatic hernia can be suspected if discomfort during eating is localized on the left. With this pathology, part of the stomach, less often the intestines, rises into the chest cavity. Pain in the esophagus when swallowing occurs when coughing, physical activity, or while eating. Improvement occurs after vomiting.
Neoplasm
Pain when swallowing food occurs with malignant and benign tumors, which most often affect the middle and lower parts of the esophagus. It bothers you at night and is accompanied by a feeling of fullness and regurgitation. The larger the tumor, the more difficult it is for food to pass through. The disease also causes bad breath and vomiting of undigested food. While eating, patients feel discomfort. Symptoms of a malignant tumor of the esophagus include sudden weight loss, weakness, and refusal of meat products.
Aqualor Throat - an effective remedy for sore throat
Sea water is considered one of the best natural ways to combat sore throat. But liquid taken from the coastal zone can be harmful due to the content of large amounts of toxic organic and chemical impurities, as well as pathogenic microorganisms. A solution of sea salt for rinsing, or rather a solution of sea water, Aqualor Throat, is made from clean water collected at a depth of several tens of meters. After collection, the water undergoes additional filtration and sterilization. It also contains extracts of aloe vera and Roman chamomile, which have anti-inflammatory, antiseptic and restorative properties.
The result is a drug that is used for sore throats in adults and children. It has been confirmed that using Aqualor Throat can positively influence the healing process*.
*for pharyngolaryngitis M.R. Bogomilsky, E.Yu. Radzig “Bulletin of Otorhinolaryngology”, No. 2, 2010.